nuclear weapons
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
uranium 235, plutonium 239, & uranium 233
chemical isotopes used to make bombs
fission
gets power through splitting an atom and initiating a nuclear chain reaction to produce energy
fusion
forging hydrogen atoms together to create a new isotope
nuclear winter
any large-scale use of nuclear weapons will cause firestorms so sizable, that the release of smoke, dust, and fallout will result in drastic climate effects (cold weather and reduced sunlight)
electromagnetic pulse (emp)
instantaneous intense energy field that disrupt at a distance numerous electric systems
image of fission
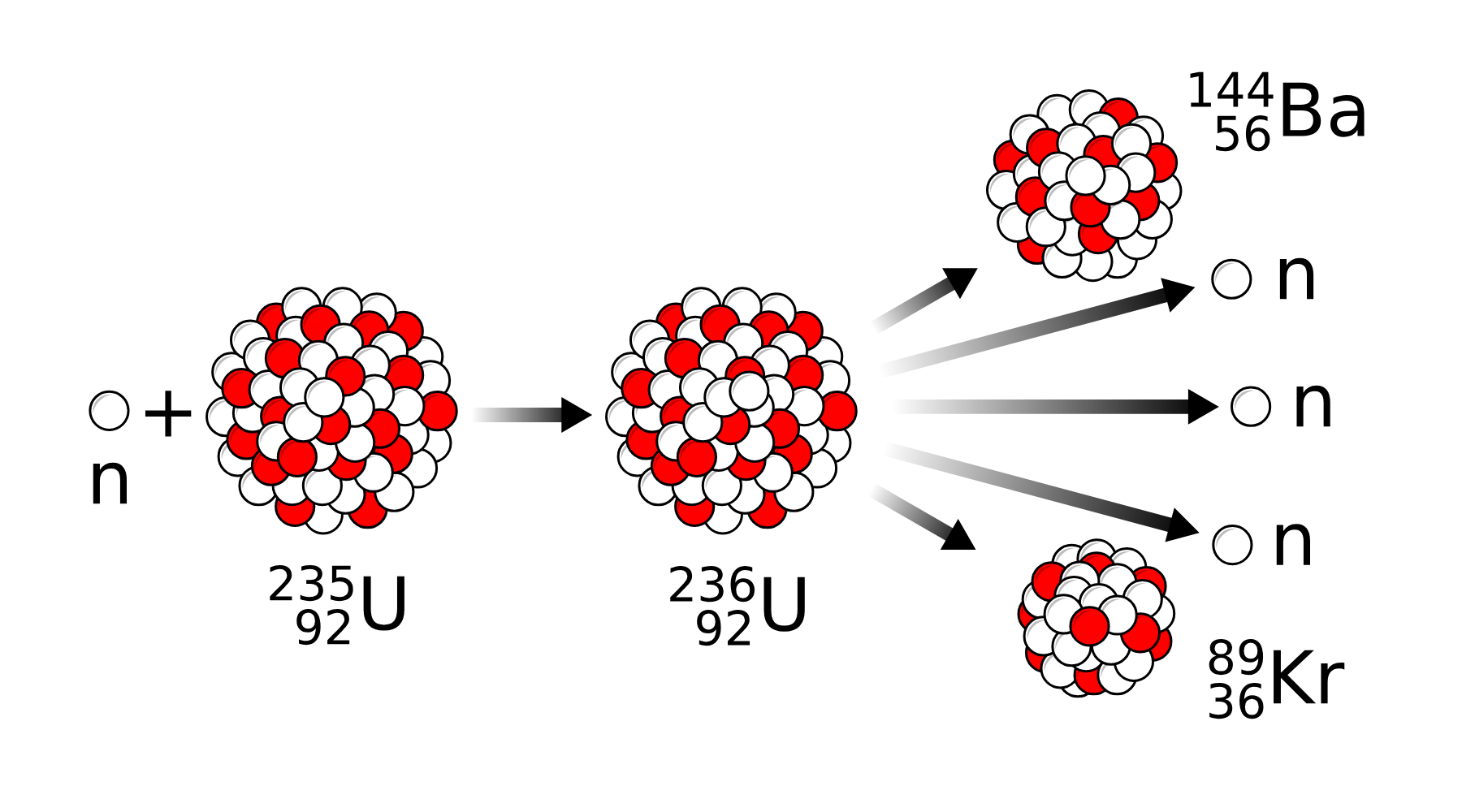
image of fusion
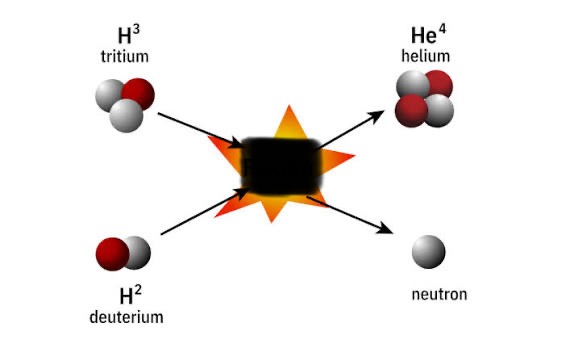
image a shows…
warhead prior to firing
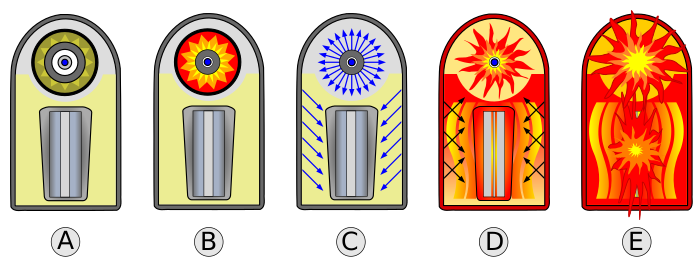
image b shows…
Primary stage fires, starting fission reaction of Pu core
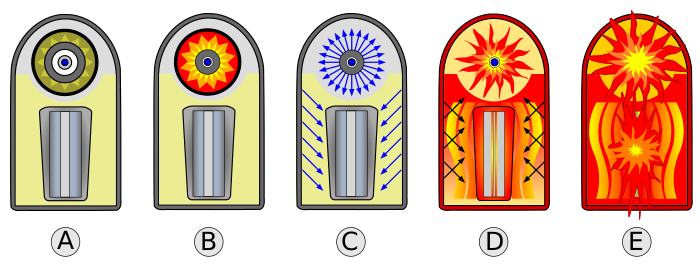
image c shows…
Fission reaction emits x-ray radiation, reflects inside casing, irradiates polystyrene foam
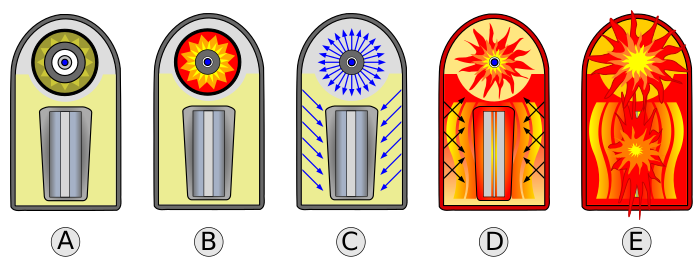
image d shows…
Polystyrene transforms into plasma, compressing plutonium sparkplug, secondary fission begins
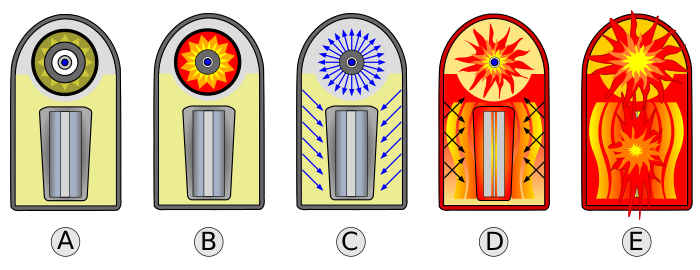
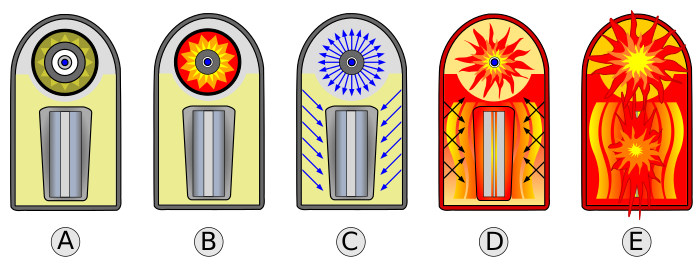
image e shows…
Fusion fuel produces Tritium (3H), starting fusion reaction, U tamper fissions, fireball forms
critical mass
minimum amount of radioactive material needed to sustain a chain reaction
supercritical mass
amount of radioactive material needed for fission to increase
enrichment
procedure for separating u-238 from u-235 and increasing the concentration of fissile material
short range
<1000km
medium range
1000-3000km
intermediate range
3800-5000km
intercontinental range
5000+km
strategic
long-range, high-yield, strategic targets (to win the war)
non-strategic/tactical
short-range, long-yield (to win the battle)
delivery systems
aircraft, land/ground, sea
triads
combines all 3 legs of delivery systems
dyads
combines all 2 legs of delivery systems
transmutation
neutrons discharged by one atom would stimulate the next and so on
einstein-szilard letter
letter drafted by Leo Szilard and Eugene Wigner to Rossevelt delivered by Einstein warning about Nazi atomic bomb, recommending to set up their own atomic weapons programme
the manhattan project
rushed to deploy first atomic bomb before Nazi Germany
4 bombs in the manhattan project
the gadget, little boy, fat man, thin man
the trinity test
july 16, 1945 & first detonation of a nuclear weapon
trinitite
element created in trinity test
policy of containment
policy which seeks to protect all we have
deterrence
to make an adversary not do something
compellence
to make adversary do something
coercion
influencing adversary’s incentive to they behave a certain way
nuclear deterrence
strategy intended to prevent from an attack by threatening retaliation in advance
for deterrence to work…
must have the capability to retaliate & potential attack must belief plan will follow through
mutually assured destruction
full-scale use of one nuclear power on another would be met with such overwhelming retaliatory response that both the attack and defender would be annihilated
extended deterrence
deters attacks not only on oneself but also one’s allies
limitations to deterrence
credible threats are costly, proliferation incentives, arms race dynamic, assumes rational leaders, relies on perception, it goes both ways
nuclear posture
incorporation of some numbers and types of warheads into a state’s overall military structure
capabilities, employment doctrine, & common and control
main nuclear posture details
nuclear doctrine
set of principles which guides a state’s nuclear forces supports its objective
nuclear declaratory policy
statement about the role of weapons for state’s security policy
declaratory policies
security assurance, no first use, & sole purpose
security assurance
pledge to protect allies from attacks and to to not attack non-nuclear states compliant to NPT
nuclear weapons treaty (NPT)
hinders a state from using nuclear warfare
no first use
a commitment by a nuclear-armed state to never be the first to use nuclear weapons in a conflict
sole purpose
defining role of weapons for sole purpose
counterforce
targets adversaries military structure, provides damage limitations, & requires large and diverse forces
countervalue
target population centers move in line with arms control but at the expense of civilians; relies on smaller, less diverse, and less precise arsenal
brinkmanship
the practice of pushing crises to the brink to gain coercive leverage & exploiting the existence of uncertainty by taking steps to intense war
the madman theory
belief that being perceived as mad can help leaders gain coercive leverage
nuclear revolution theory
nuclear weapons revolutionized international politics because they make military victory impossible
mueller’s irrelevance of nuclear weapons
nuclear weapons influence rhetoric, public discourse, defense budget but not the course of history
stability-instability paradox
the likelihood of nuclear war declines while conventional war increase
nuclear taboo
the “normative inhibition” against the (first) use of nuclear weapons, reflected in public opinion, international agreements, a de facto prohibition