vision
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
anatomy of eye
functions of eye
focusing
makes sure light is hitting retina
passively done by cornea
actively done by changing shape of lens
regulating light
pupillary constriction
changing the shape of the iris
recording pattern of light
photoreceptors in retina
photoreception
photoreceptors
responsive to light
retina is made up of specialized cells
cones
high resolution
color
active in bright light
predominately in fovea (central visual field)
rods
low resolution
black/white
night vision
active in dim light
predominately outside of macula
peripheral vision (rods dominant)
the retina
*aim is to produce best image possible
6 layers
peripheral —> higher density of rods
macula (very tiny portion of eye)
central portion of visual field
fovea
highest density of cones
point of greatest visual acuity
easily seen on imaging
pit
blood vessels oriented away —> reduces light absorbed by blood vessels
more direct
optic disc
where ganglion cells converge to exit eye
start of CN II (optic nerve connected directly to eye)
“blind spot” —> where optic nerve exits, no photoreceptors
phototransduction
converting light signals to electrical signals
light doesn’t create AP
changes in membrane potential cause release of transmitter onto postsynaptic neurons
AP isn’t necessary because short distance
photoreceptors contain specialized proteins that are activated by light
rhodopsin
primary visual pathway
conscious visual perception
90% of visual info enters the brain this way
light hits retina —> optic nerve —> crosses in optic chiasm —> optic tract —> lateral geniculate nucleus (of thalamus) —> white matter pathway (optic radiations) —> occipital lobe —> primary visual cortex (V1)
visual field
how much someone can see while looking straight ahead
150 degrees (horizontal)
120 degrees (vertical)
visual fields overlap
blind spot (when both visual fields work together —> don’t notice blind spot)
stereoscopic
3D vision
basis for depth perception (requires both eyes work together)
temporal crescents
monocular
nasal and temporal visual fields diagram
lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
6 layers
retinotopically organized (maintains same organization as retina)
contralateral eye (1, 4, 6)
ipsilateral eye (2, 3, 5)
magnocellular
input from ganglion cells sensitive to movement and contrast
parvocellular
input from ganglion cells sensitive to color and shape
koniocellular
not well known, color sensitivity
superior/inferior optic radiations
superior optic radiations
contain info of LOWER visual fields
inferior optic radiations
contain info of UPPER visual fields
how we get the “upside-down'“
what does the primary visual pathway being retinotopically organized mean?
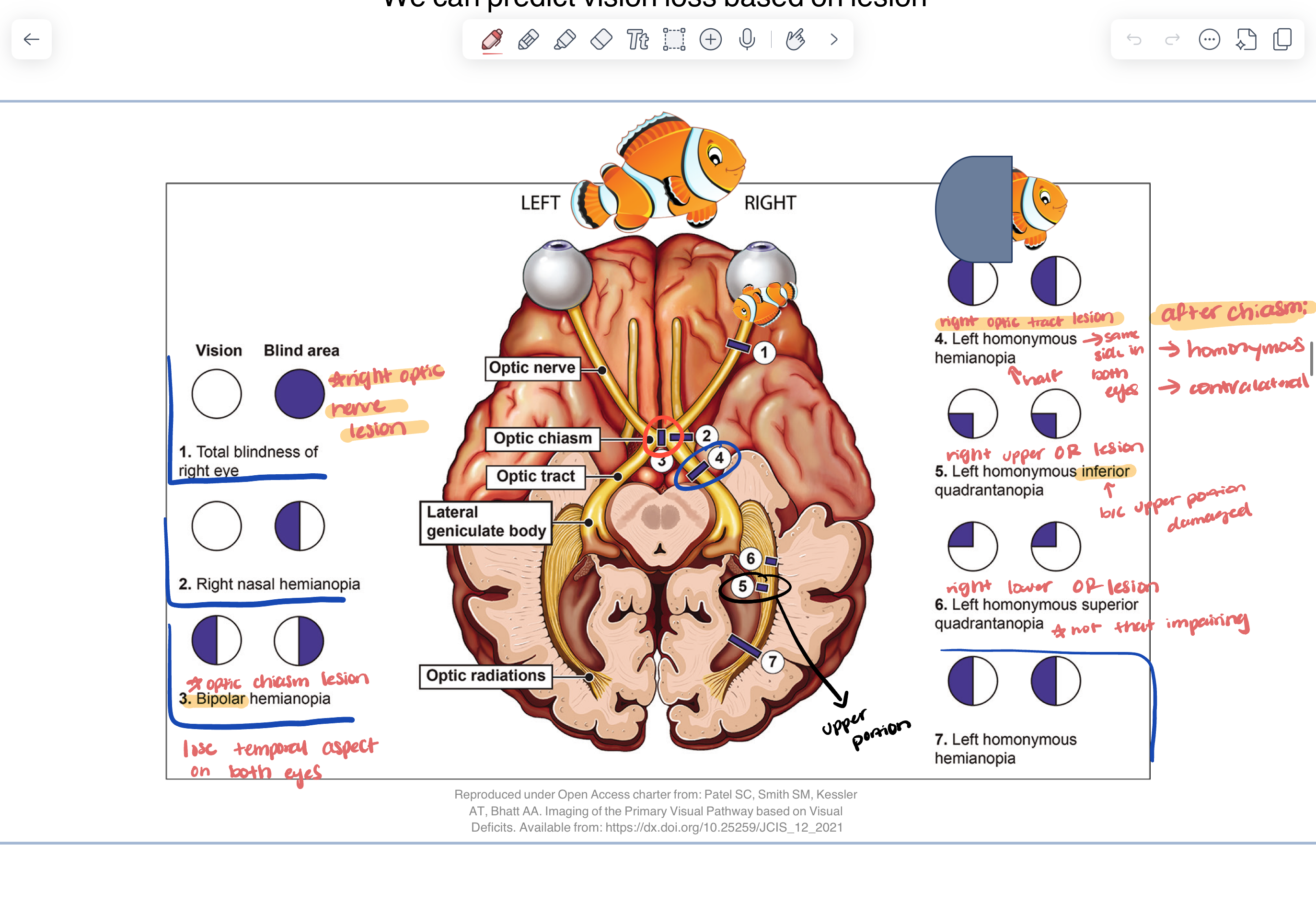
we can predict vision loss based on lesion
visual deficits in primary visual pathway
central (macular) sparing
*central visual field still intact
—> meaning not a straight line down the middle loss of vision
“fill in”
*also referred to as perceptual completion
vision loss does not mean everything is just “black”
blind spot —> makes it so that we participate in “fill in” all the time
occipital lobe
primary visual cortex
V1
striate cortex
visual information is distributed to specialized areas for further processing
motion, color, depth
sent to temporal and parietal lobes for visual processing
higher order visual processing
dorsal stream (parietal lobe)
where and how to
analyzes motion and spatial relationships (where you are in space)
ventral stream (temporal lobe)
what/object processing
analyzes form, color, size, texture
assigns meaning
midbrain visual projection to superior colliculus
function
spatial map for orienting of the head
pathway
reflexive
CN II
optic tract
superior colliculi
auditory info is integrated in superior colliculi
attentional
CN II
optic tract
superior colliculi
dorsal/ventral stream AND thalamus (pulvinar nuclei)
midbrain visual projection to Edinger-Westphal nucleus
function
regulate amount of light that reaches retina
mechanism
all light passes through pupil
size of pupil is regulated by smooth muscles in iris
pupillary sphincter
pupillary dilater
pathway
light
CN II (optic nerve)
pretectal area of midbrain
BILATERAL PROJECTIONS
edinger-westphal nucleus —> stimulate ipsilateral CN III
parasympathetic neurons to CN III (oculomotor nerve) —> determines if too much light
synapse on pupillary sphincter muscles
elicits motor response
pupillary light reflex
*shining light into L eye —> R eye also constricting (consensual response)
light
CN II (optic nerve)
pretectal area of midbrain
BILATERAL PROJECTIONS
edinger-westphal nucleus —> stimulate ipsilateral CN III
parasympathetic neurons to CN III (oculomotor nerve) —> determines if too much light
synapse on pupillary sphincter muscles
elicits motor response
midbrain projection: accommodation reflex
*near focusing
function
prepare for near viewing
change shape of lens
additional coordination
pupillary constriction
convergence of eyes
complex pathway
V1 must be intact
visual association areas
supraoculomotor nuclei in midbrain
edinger-westphal nucleus
iris sphincter
ciliary muscles of lens
CN III motor nuclei
convergence
retinohypothalamic pathway
function
regulate sleep/wake cycles
pathway
specialized cells in retina
optic nerve —> directly to hypothalamus
suprachiasmatic nucleus (damage to chiasm would affect this pathway)
spinal cord
sympathetic ganglia
pineal gland
release melatonin
oculomotor system
CN II, III, IV, and VI
cranial nerves drive the extra ocular muscles
CN VI (abducens) —> pons
abduction
CN IV —> midbrain
down and in
CN III —> midbrain
everything else
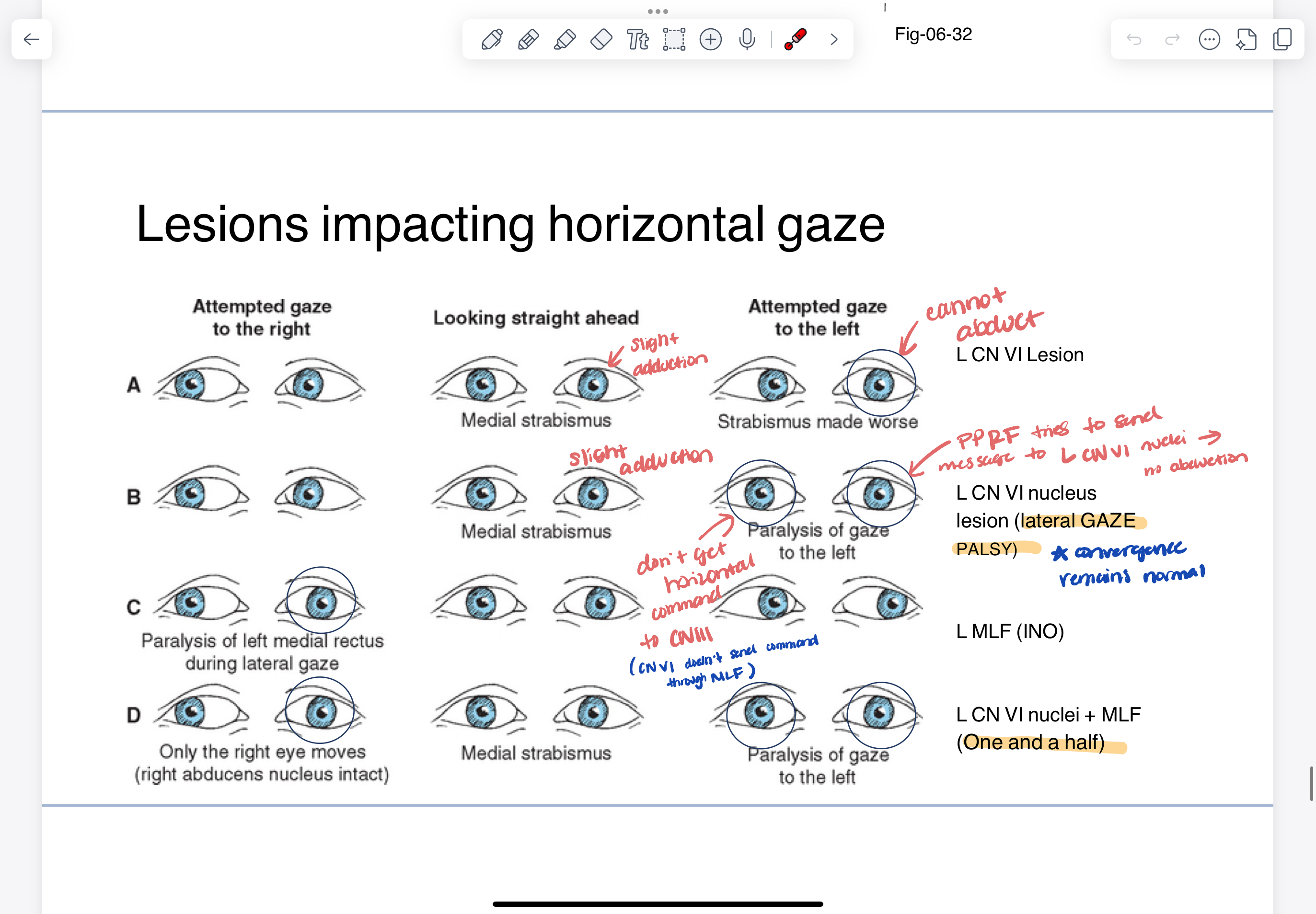
CN III deficits
cranial nerve 3 lesion cont.
CN IV deficits
*does down and in —> likely to notice eye resting in elevation
*head tilt occurs away from side of lesion
CN VI deficits
left eye resting in adduction (CN VI does abduction)
what drives the CN nuclei
coordination of head and eye movements to get the image of the fovea is incredibly complex
coordinate movements between CN III, IV and VI
nerves cannot focus in isolation
inputs from vestibular system (where head is in space)
centers
horizontal gaze
vertical gaze (CN III)
convergence (adduction)
system extremely vulnerable to injury
coordination of eye movements (distribution)
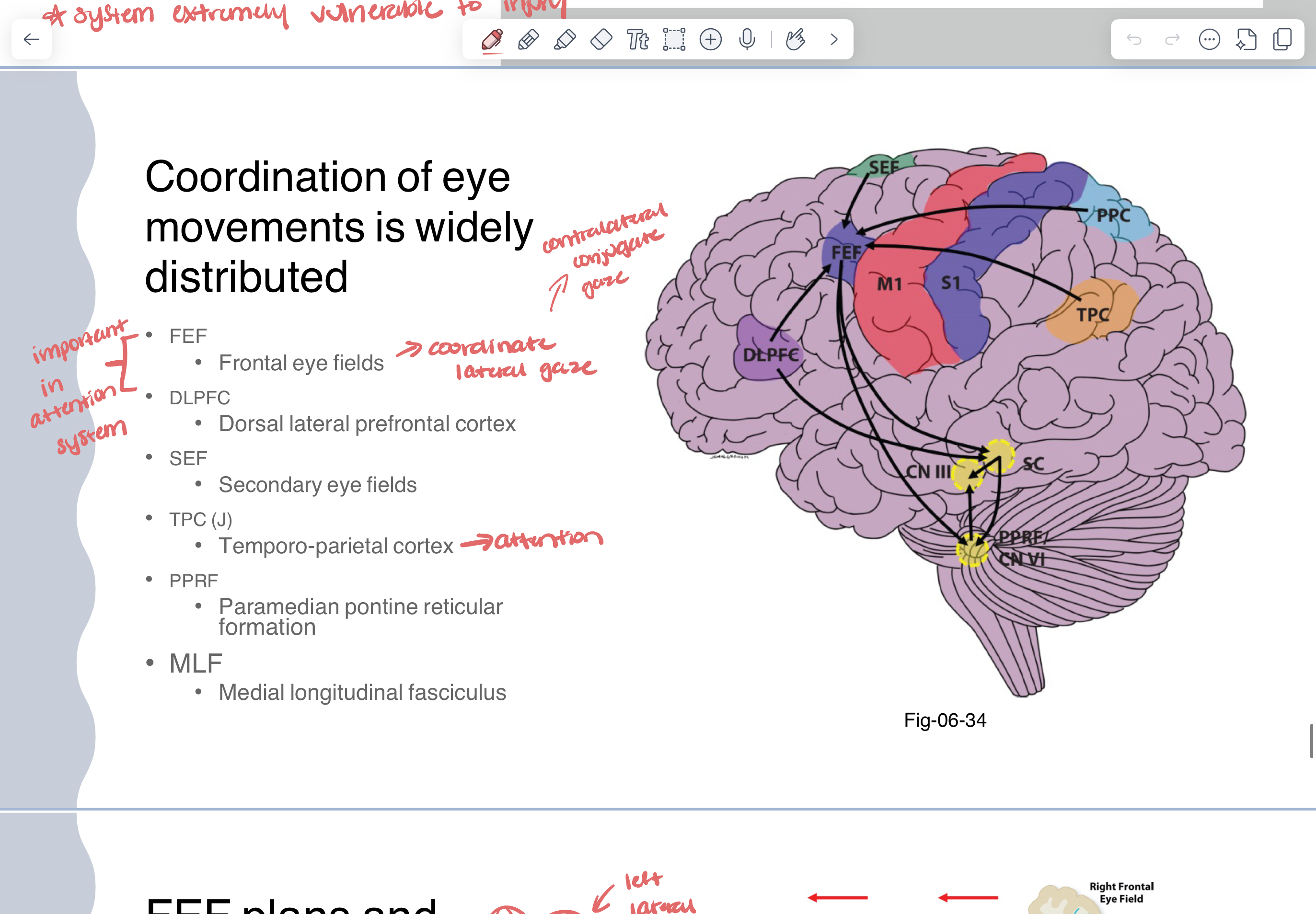
FEF (frontal eye fields) —> plans and initiates lateral gaze
function
plan and initiate lateral eye movements
pathway
initiated through FEF
direct or through the basal nuclei
superior colliculus
contains spatial maps due to retinotopic organization
contralateral horizontal/lateral gazes center
paramedian pontine reticular formation
CN VI —> abduction
white matter pathway MLF connects to other eye
CN III —> adduction
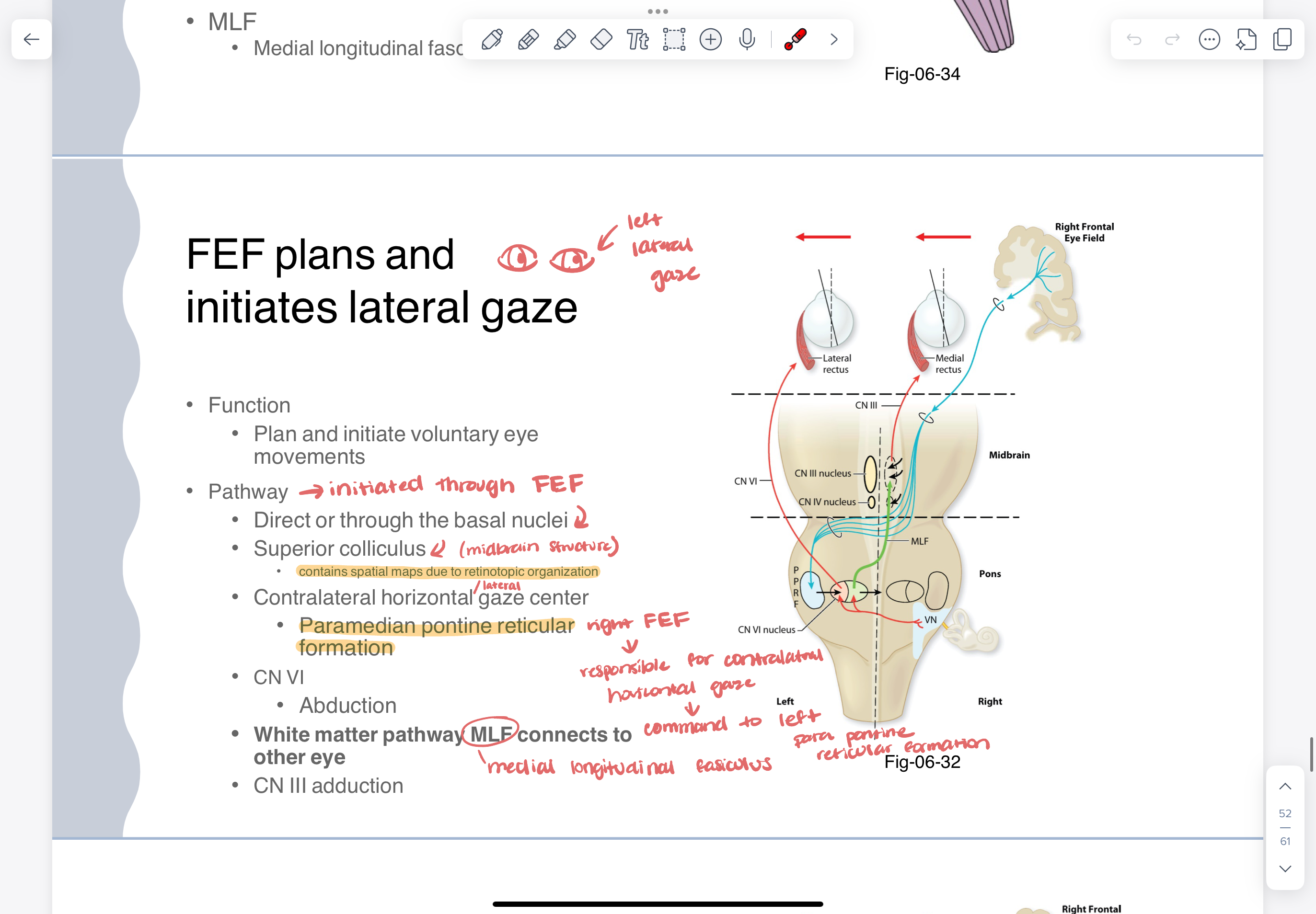
medial longitudinal fasciculus
white matter pathway that connects CN III, IV, AND VI
coordinates lateral gaze
crosses immediately
when looking LEFT
LEFT CN VI activates for abduction
RIGHT CN III activates for adduction
inhibition of right VI and left III to allow for proper motion
lesions impacting horizontal gaze
CN VII
as CN VII exits brainstem it wraps around CN VI —> frequently injured together
nuclei for CN VII AND CN VI damage
lateral gaze palsy with ipsilateral facial paralysis