Comprehensive Midterm 3 Review: Language, Emotions, Decision Making, Social Cognition & Brain Plasticity
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What is the mental lexicon?
The store of information about words in the brain, including semantic, syntactic, phonological, and orthographic information.
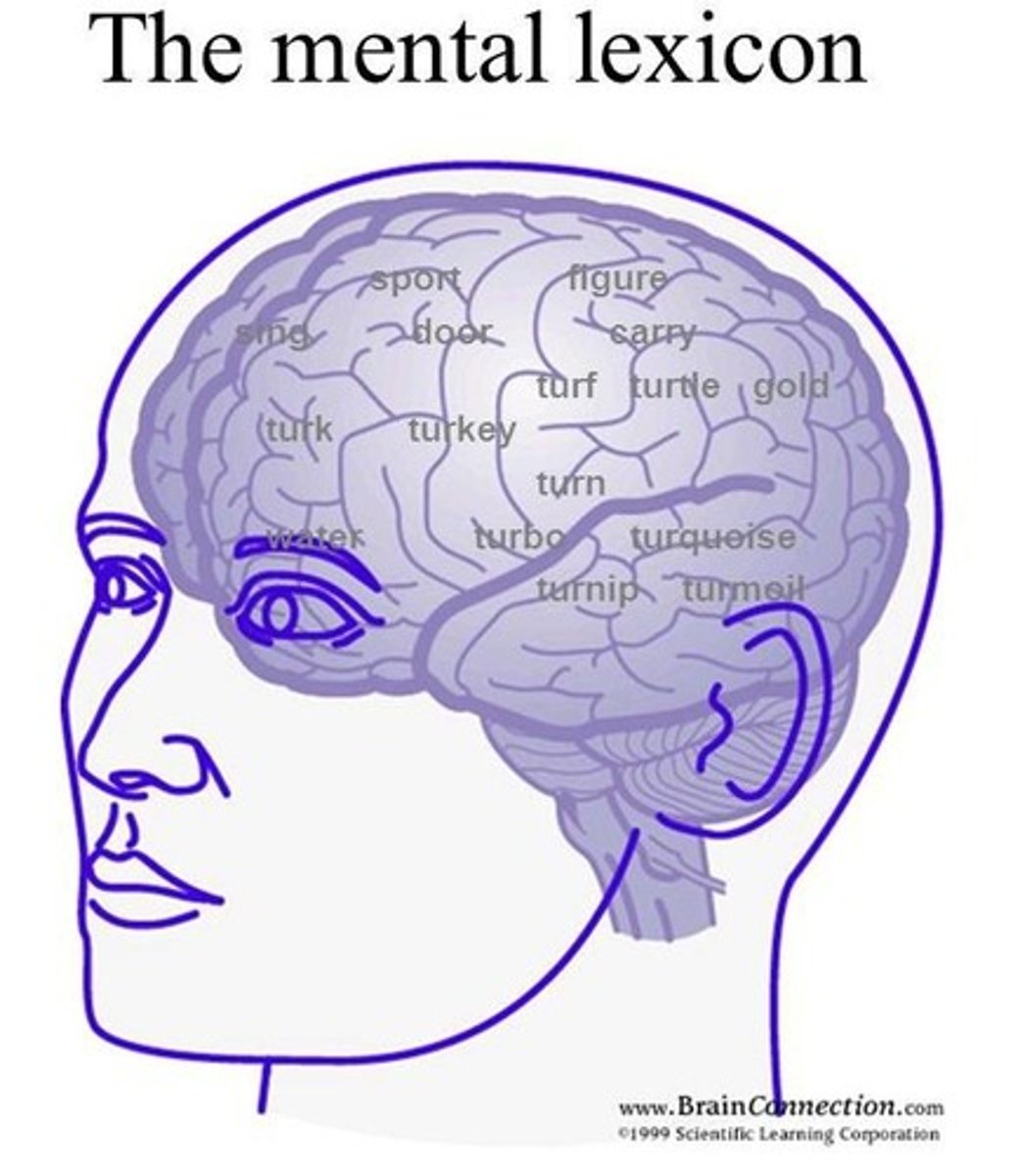
What is a semantic network?
A network where words are represented by 'nodes' and activation spreads to associated nodes based on their connections.
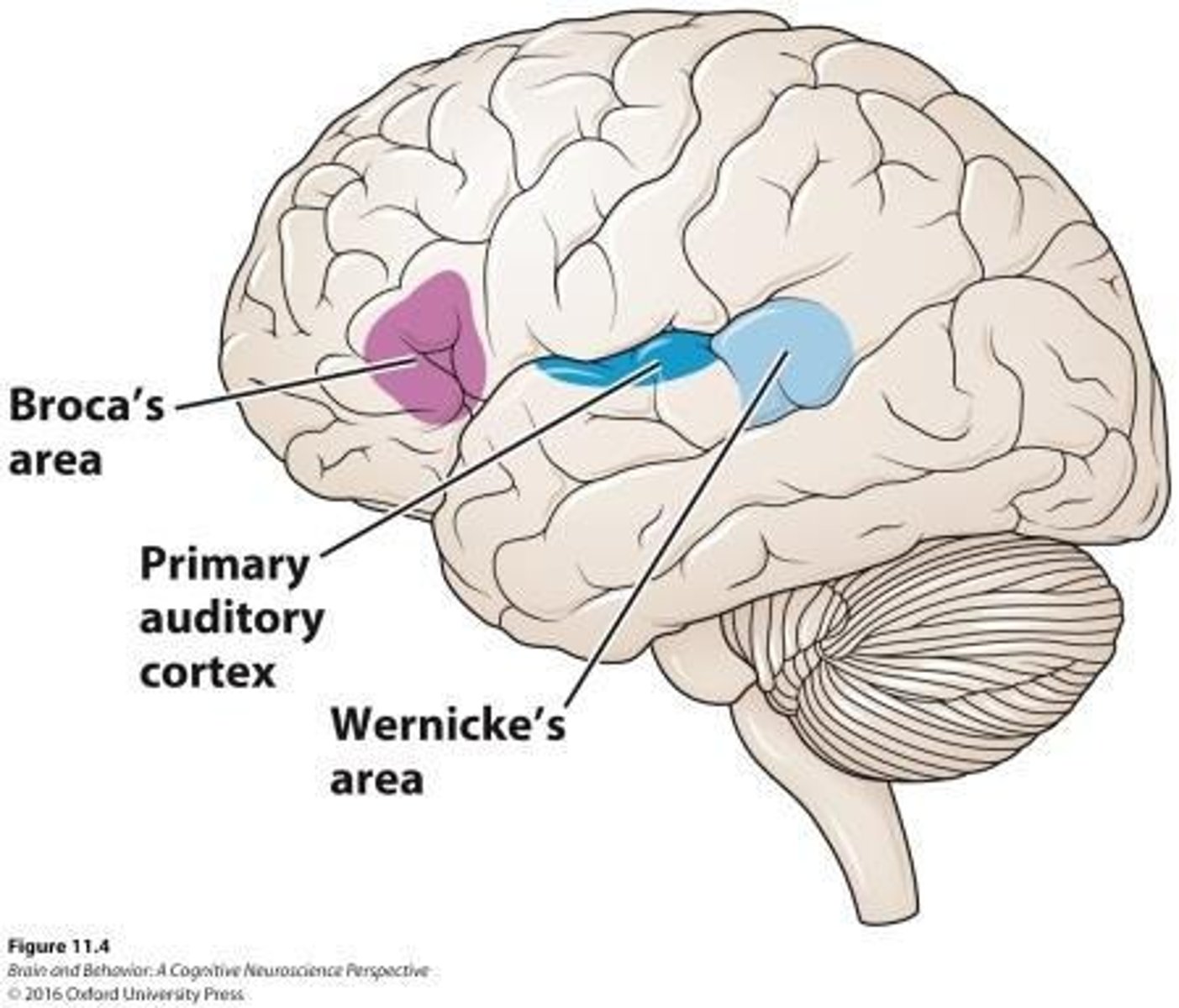
What is the primary auditory cortex responsible for?
It is involved in language comprehension and production, specifically within the left perisylvian language network.
What does the N400 component indicate?
It is associated with semantic processing and peaks 400ms after the onset of a stimulus.
What does the P600 component indicate?
It is associated with syntactic processing and peaks 600ms after the onset of a stimulus.
What is telegraphic speech?
A form of speech that mainly consists of content words and lacks function words.
What is Broca's aphasia?
A type of expressive aphasia related to difficulties in producing language and understanding syntactic relationships.
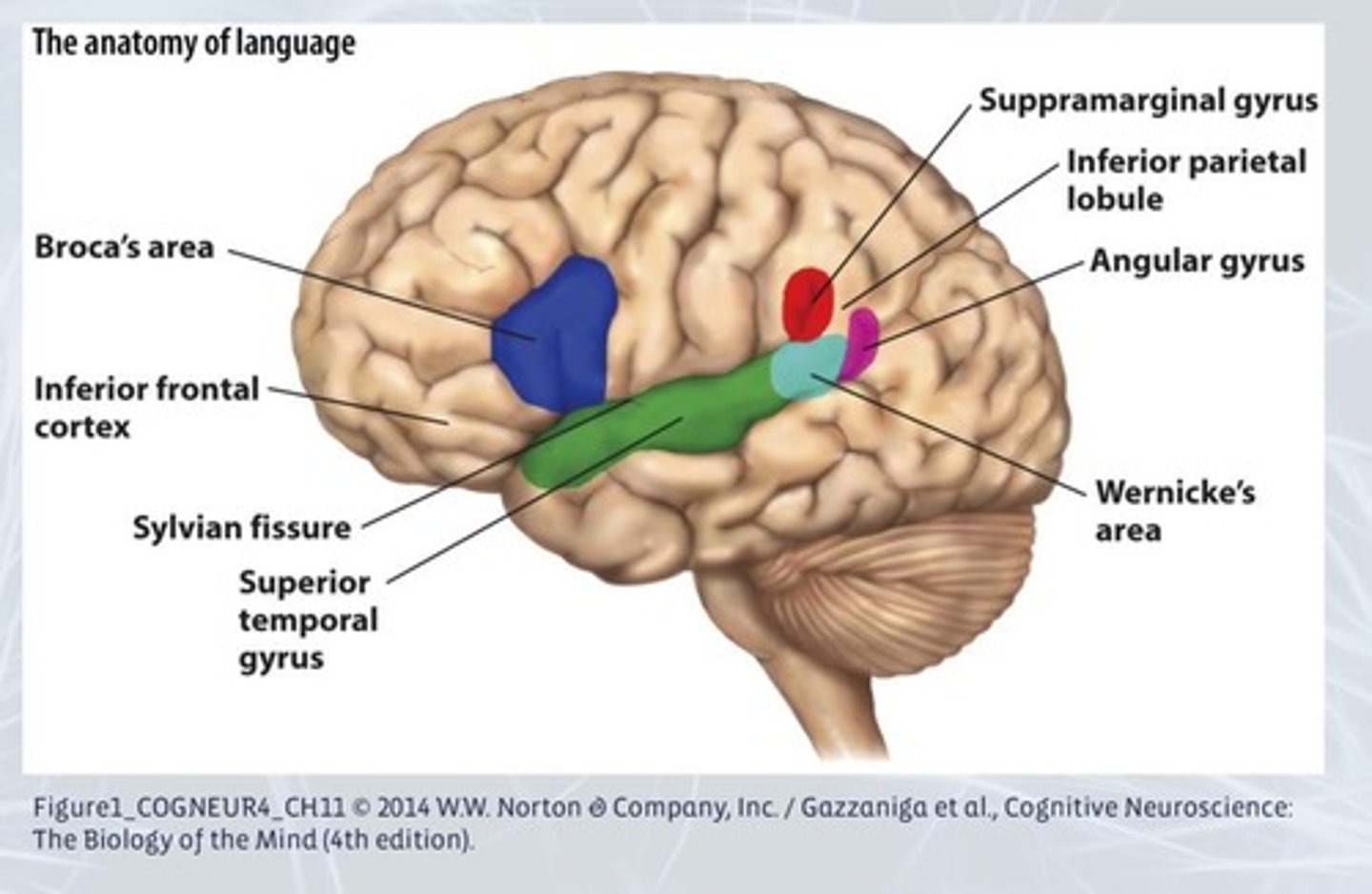
What is Wernicke's aphasia?
A type of receptive aphasia characterized by fluent but meaningless speech and problems with language comprehension.
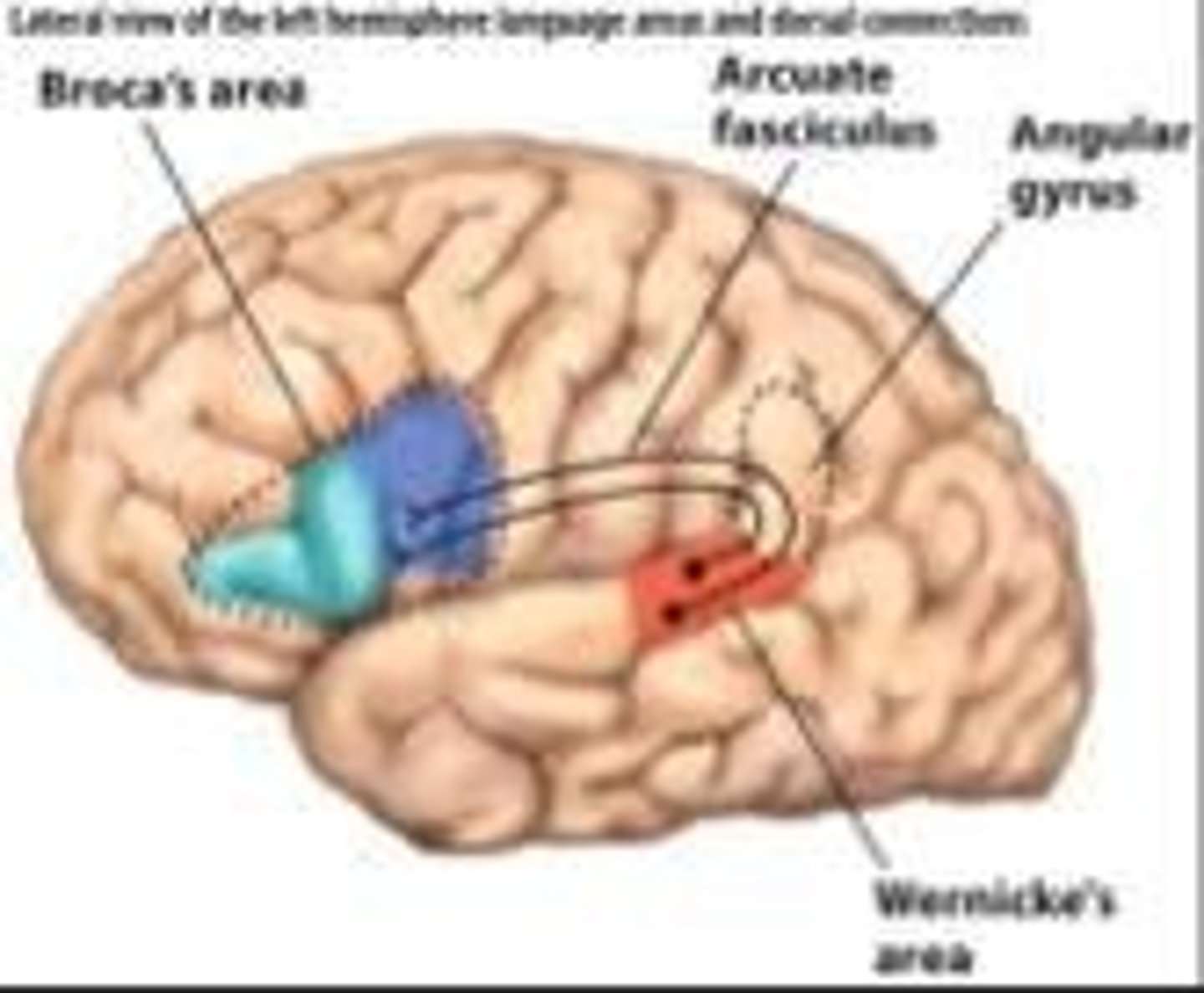
What is conduction aphasia?
A condition where individuals have problems repeating speech but can understand words, caused by damage to the arcuate fasciculus.
What is global aphasia?
A condition characterized by the inability to comprehend or produce speech, usually due to extensive left-hemisphere damage.
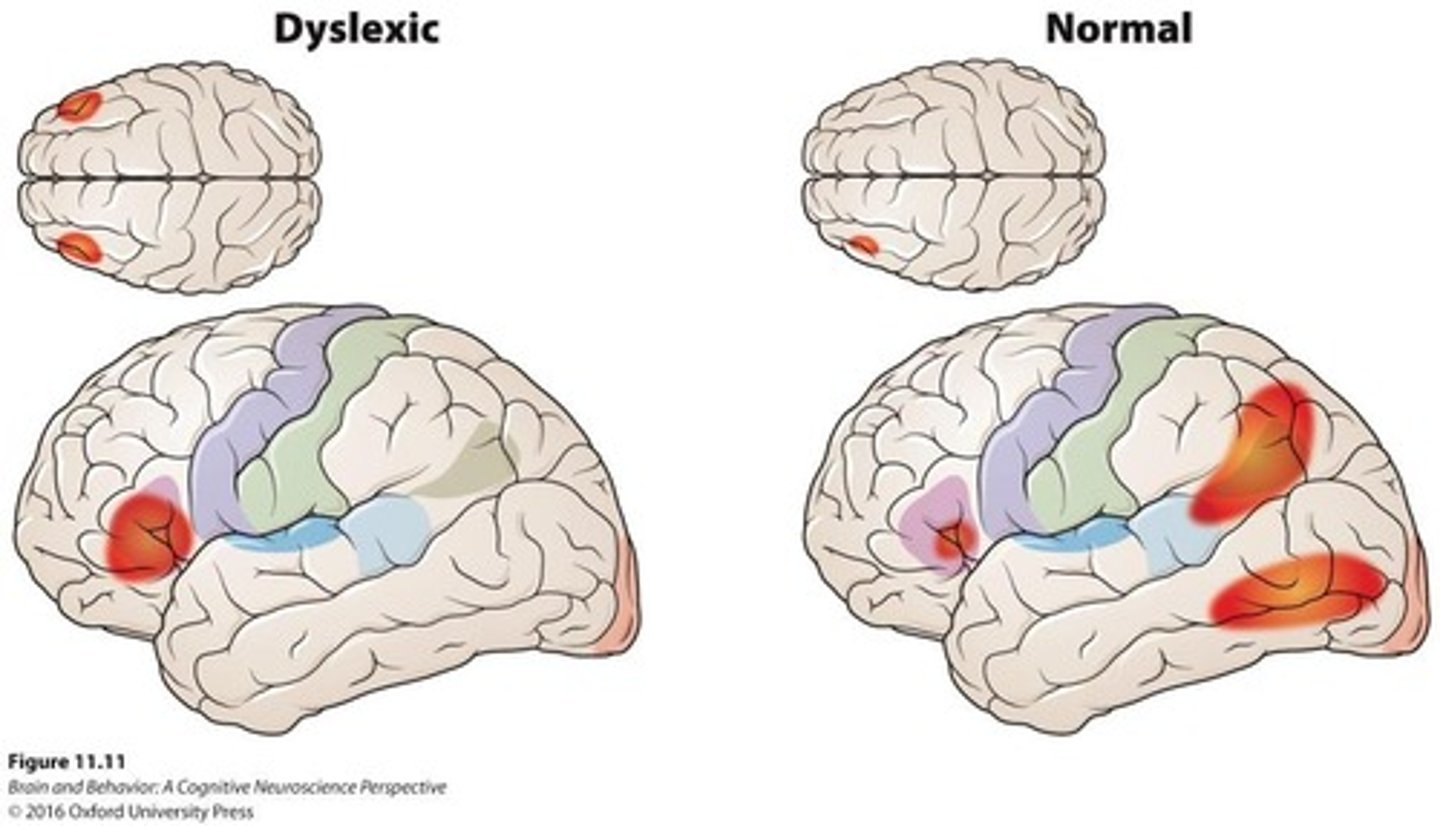
What is dyslexia?
A learning difficulty in reading, associated with less activity in Wernicke's area and compensatory activity in other language areas.
What are the three characteristics of emotions?
Brief responses, specific to events, and socially functional.
What are the three components of emotions?
Physiological reaction, subjective experience/feeling, and behavioral response.
What distinguishes basic emotions from complex emotions?
Basic emotions are innate, universal, and short-lasting, while complex emotions depend on cultural and situational factors.
Who identified the six basic emotions?
Paul Ekman.
Why are Ekman's six basic emotions considered 'basic'?
They have culturally invariant facial expressions, are innate, and occur automatically.
What is the role of the left perisylvian language network?
It is crucial for both language comprehension and production.
What is aggramatism?
A condition often associated with Broca's aphasia, characterized by difficulties in producing grammatical sentences.
What is a word salad?
A confused or unintelligible mixture of seemingly random words and phrases, often seen in Wernicke's aphasia.
What are neologisms?
Newly invented words that may be created by individuals with Wernicke's aphasia.
What is the significance of the arcuate fasciculus?
It connects anterior and posterior language areas and damage to it can lead to conduction aphasia.
What is the impact of damage to Wernicke's area?
It can lead to persistent Wernicke's aphasia, affecting language comprehension and production.
What does arousal refer to in emotional context?
A continuum that varies from calm (very passive) to excitement (very active).
What does valence refer to in emotional context?
A continuum that varies from very pleasant to very unpleasant, with neutral as an intermediate value.
What is the James-Lange Theory of Emotion?
It posits that physiological responses occur first, leading to the experience of emotion.
What is the Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion?
It suggests that emotional states arise in the brain and simultaneously trigger physiological responses.
What does the Two-Factor Theory of Emotion propose?
Emotions involve both physiological arousal and cognitive interpretation of the situation.
What is the role of the amygdala in emotion?
It is involved in basic emotion processing, particularly fear-related processing.
How does the amygdala respond to emotional stimuli?
It is sensitive to high arousal in general, regardless of whether the stimuli are negative or positive.
What is the function of the insula in emotional processing?
It is involved in disgust and interoception, which includes bodily perception and feelings.
What role does the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) play?
It is involved in monitoring, response conflict, and error detection.
What does the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) compute?
It integrates the current reward value and plays a role in emotional decision making.
What is antecedent-focused emotion regulation?
Changing the emotional stimulus or altering the attention paid to it to modify emotional impact.
What is response-focused emotion regulation?
Changing the emotional response itself, such as intensifying or diminishing the emotional experience.
What is reappraisal in the context of emotion regulation?
Altering the meaning of a situation to change its emotional impact.
What is suppression in emotion regulation?
Altering the internal experience and external expression of unwanted emotions.
What is cognitive control?
Mental abilities that involve planning, controlling, and regulating the flow of information processing.
What is the role of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) in cognitive control?
It provides the interface through which goals influence behavior and is essential for goal-directed behavior.
What is the significance of goal maintenance in achieving objectives?
It is crucial for staying focused on tasks and achieving goals.
What is the Tower of London Task used to assess?
It assesses planning and sequencing abilities, with PFC activation during the task.
How does the amygdala enhance memory?
It plays a modulatory role in explicit memory and enhances hippocampal consolidation for arousing events.
What is the 'low road' in emotional processing?
A direct pathway from the thalamus to the amygdala that is fast but crude and not conscious.
What is the 'high road' in emotional processing?
A pathway where the thalamus sends information to the sensory cortex for detailed analysis before reaching the amygdala.
What is the current view of the amygdala's role in vigilance?
It increases the readiness of the cortical response system to salient stimuli, responding to both negative and positive high arousal.
What is the relationship between the amygdala and the hippocampus?
The amygdala interacts with the hippocampus during memory encoding, affecting long-term consolidation.
What is the significance of emotional stimuli detection?
Attention is enhanced for emotional stimuli, making detection more automatic and efficient.
What happens during dysfunctional AMY-PFC interactions?
They play an important role in conditions like depression.
What is the role of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) in goal maintenance?
The PFC helps maintain focus on goals and prevents patients with frontal lobe damage from 'wandering off task.'
Which regions of the PFC are involved in selecting relevant information?
Dorsolateral PFC regions filter out task-irrelevant information and activate task-relevant info.
What is the function of the lateral PFC in working memory?
It maintains information that is no longer present and manipulates that information.
How do the frontal lobes act in terms of information storage?
Frontal lobes do not store information long-term; they act as a temporary buffer.
What does task switching refer to?
The ability to shift from one subgoal to another to achieve an overall goal.
What is the Wisconsin Card Sorting Task used to assess?
It assesses the ability to sort cards according to changing arbitrary rules.
What are the consequences of lateral PFC damage?
It can lead to task switching impairments, perseveration, and a lack of flexibility.
What is inhibitory control?
The ability to override or interrupt processing to prevent inappropriate behaviors.
What does the Go-No Go Task measure?
It measures inhibitory control and how different groups respond to high-energy food images.
What role does the medial PFC/ACC play in goal-oriented behaviors?
It acts as a monitoring system that identifies situations requiring cognitive control.
What is the Error Related Negativity (ERN)?
A brain potential related to the detection of errors.
How does the framing effect influence decision making?
People's choices can be manipulated based on how a question is framed, either in terms of gains or losses.
What is the endowment effect?
People demand a higher price to sell an object they own compared to what they would pay for it.
What is the role of the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) in self-perception?
The OFC ensures that positively biased self-views do not deviate too far from reality.
What is the default mode network?
Brain regions that are active when not engaged in tasks and are deactivated during goal-directed tasks.
What is the significance of the medial PFC in self-knowledge?
It is strongly involved in self-reference processing and knowledge of the self.
What is mentalizing or Theory of Mind (ToM)?
The ability to understand the mental states of others, often assessed through false belief tasks.
What brain region is specifically active during ToM tasks?
The right temporo-parietal junction (rTPJ).
What are mirror neurons and their significance?
Mirror neurons activate when performing or observing an action, playing a role in understanding others' actions.
What are the DSM 5 diagnostic criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
1) Social communication/interaction deficits, 2) Restricted and repetitive behaviors.
What are key deficits associated with Autism?
Impairments in social cognition and understanding mental states.
What is mind blindness?
A deficiency in the ability to understand the mental states of others.
What does the broken mirror theory suggest?
It suggests there is no automatic mimicry and less fMRI activity in mirror areas when imitating facial expressions.
Define stereotype.
Perceiving members of a given category as possessing various common attributes.
What is prejudice?
Negative attitudes, emotions, or behaviors toward members of a group based on their group membership.
What is discrimination?
Unfair treatment of members of a group based on their membership in that group.
What are some forms of prejudice?
Racism, sexism, ageism, homophobia, etc.
What are explicit measures of prejudice?
Questionnaires that may be affected by social desirability bias.
What are implicit measures of prejudice?
Methods like EMG and the IAT test that assess unconscious biases.
What is neurogenesis?
The generation of new nerve cells.
Define synaptogenesis.
The formation of new synapses in the central nervous system.
What is pruning in brain development?
The elimination of synapses, reducing the number of connections between neurons based on experience.
What is myelination?
The process of increasing myelination of the brain during infancy.
What happens to the brain during adolescence?
Early maturation of the limbic regions and late maturation of the prefrontal cortex leads to increased reward-based behavior and less cognitive control.
What is neuroplasticity?
The ability of the brain to change and retain new structures.
How does physical activity affect the brain?
It changes the way the brain processes information and positively affects the structure and function of brain regions.
What is the outcome of meditation (MBSR) on the brain?
It leads to self-regulation of mood and emotion and increases gray matter density in brain regions involved in learning and memory.
What is the significance of becoming aware of implicit bias?
It is the first step in retraining the biased brain to replace biased responses with non-prejudiced ones.
What role does the prefrontal cortex (PFC) play during adolescence?
It is responsible for cognitive control, which is less developed compared to the limbic regions during this stage.
What is the impact of experience on synapse pruning?
Connections that are not used are pruned away, shaping the brain's neural network.
What is the relationship between the ventral striatum and adolescence?
As the ventral striatum matures, it creates stronger incentives for seeking rewards, while the PFC lags in development.
What is the time frame of human brain development?
The brain nearly quadruples in size from birth to adulthood.