1.1 Introduction to biological molecules
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is covalent bonding?
Atoms share a pair of electrons in their outer shells
As a result the outer shells of both atoms is filled and a more stable compound, called a molecule, is formed
What is ionic bonding?
Ions with opposite charges attract one another
This electrostatic attraction is known as an ionic bond
Ionic bonds are weaker than covalent bonds
What is a polar molecule?
A molecule with an uneven distribution of charge is said to be polarised
What is hydrogen bonding?
The electrons within a molecule are not evenly distributed but tend to spend more time at one position
This region is more negatively charged than the rest of the molecule
The negative region of one polarised molecule and the positively charged region of another attract each other
A weak electrostatic bond is formed between the two
Although each bond is individually weak, they can collectively form important forces that alter the physical properties of molecules (especially true for water)
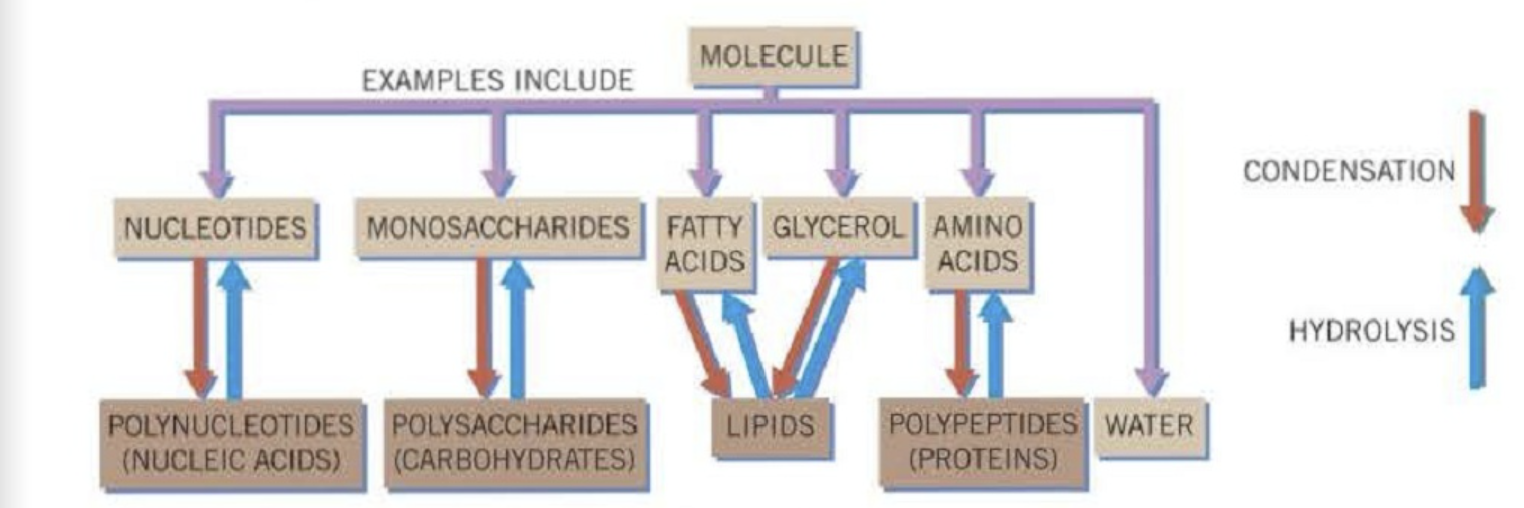
What are polymers and what is polymerisation?
Long chains of monomer sub-units are called polymers and the process by which they are formed is therefore called polymerisation
How are some polymers made?
Polythene and polyesters, are industrially produced
Polysaccharides, polypeptides and polynucleotides are made naturally by living organisms
What is the basic sub-unit of a polysaccharide?
Monosaccharide or single sugar, for example glucose
What are polynucleotides formed from?
Mononucleotide sub-units
What are polypeptides formed from?
By linking together peptides that have amino acids as their basic sub-unit
What is a condensation reaction?
Joins two molecules together with the formation of a chemical bond and involves the elimination of a molecule of water
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
Breaks a chemical bond between two molecules and involves the use of water
Summary of atomic and molecular organisation
What is a metabolism?
All the chemical processes that take place collectively in living organisms
What does one mole contain?
The same number of particles as there are in 12g of carbon-12 atoms
12g of carbon-12 atoms contains 6.022×10²³ carbon atomsW
What is a molar solution (M)?
Solution that contains one mole of solute in each litre of solution
What is a mole?
Molecular mass (molecular weight) expressed as grams (= one gram molecular mass)
E.g. to make a molar solution of sodium chloride we must first find its molecular mass
