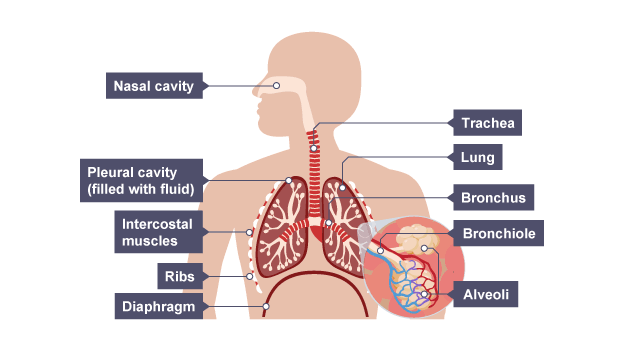
1.5 The Respiratory System 🫁
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Biology Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Cells, Living Processes & Biodiversity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Respiratory system
System of organs to maintain gas exchange
Gaseous exchange
oxygen is taken in for respiration and exchanged for carbon dioxide (waste product)
Trachea
allows air to pass through and supported by rings of cartilage to prevent collapsing
Sites of respiration
respiring cells around body
Nasal cavity
hollow space behind nose to warm and filter air
Lungs
main organs responsible for gas exchange
Bronchus
Two short branches off trachea to carry air into lungs
Bronchioles
Airways made up of multiple branches, leading to alveoli
Thorax
between neck and abdomen
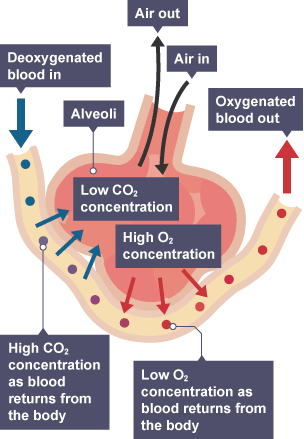
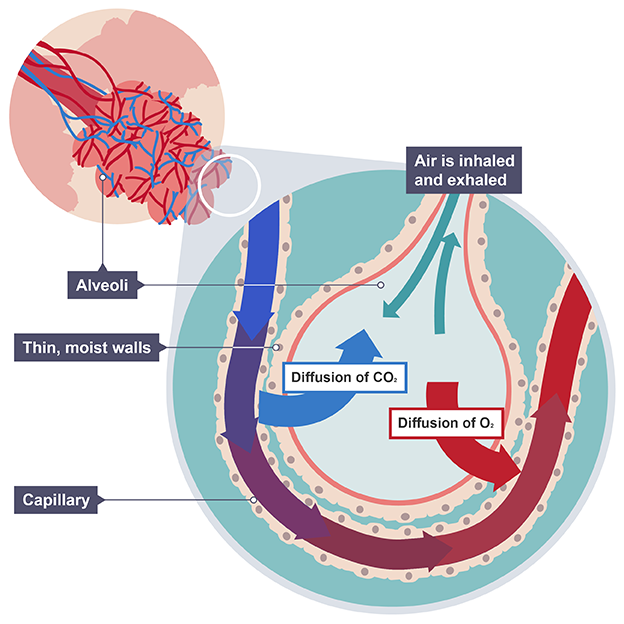
Alveoli
Tiny sacs of lung tissue where gas exchange takes place
Effective exchange surface
Has a large surface area
Good blood supply
Well ventilated for gas exchange
Thin, permeable membrane for diffusion
Capillaries
Small and thin blood vessels where gas exchange occurs, single layer of cells
thin sheet of muscle to help control breathing, pulls down and contracts to become flat so air can easily enter
Intercostal muscles
between ribs, moving rib cage during breathing
Pleural membrane
double layered membrane that encloses and protects each lung to reduce friction
Mucus
particles and bacteria stick and move out towards back of throat
Cilia
ciliated epithelial cells, fine hairs that beat to move mucus
Diffusion
movement of particles from region of high concentration to region of low concentration
Adaptations of the respiratory system
large surface area due to multiple branches of bronchioles and many alveolar sacs
good blood supply for quick diffusion
well ventilated, optimised by effective involuntary muscular action
Need for transport and exchange systems
large organisms have smaller sa:v ratios so are unable to directly obtain substances from environment
Large surface area to volume ratio
faster diffusion rates as more room to diffuse through membrane
Alveoli adaptations
Large surface area as many alveoli are present
Good blood supply
Thin, moist and permeable walls
large diffusion gradient due to lower concentration in capillaries
Moist lining of alveolus
gases dissolve in moisture helping them to pass across
Wall of capillary
one cell thick to optimise diffusion between alveoli and blood
Permeable walls
allows gasses to pass through easily
Many blood vessels surrounding alveoli
maintain a constant diffusion gradient for gas exchange
Site of gas exchange
alveoli in mammals and stomata in plants
Gas exchange in plants
carbon dioxide is taken in and exchanged for oxygen, regulated by guard cells
Leaf adaptations as a respiratory surface
pores called stomata to open/close and regulate gas exchange
surrounded by air spaces to increase surface area
cell membranes are also thin, moist and permeable
occurs in spongy mesophyll
Uses of energy
active uptake/ transport
movement
growth
reproduction
maintain constant body temp
Aerobic respiration
happens in the presence of oxygen
occurs in mitochondria
produces lots of energy
Fermentation (yeast)
can happen in presence or absence of oxygen
occurs in plant and yeast cells
boil and add layer of oil to remove oxygen
Word equation for fermentation (yeast)
Glucose → carbon dioxide + ethanol + little energy
Uses of fermentation (yeast)
making of bread and alcoholic drinks
Enzymes in yeast
work at optimum temperatures and can become denatured
Limewater test
CO2 bubbled in limewater causes change from colourless to milky (cloudy precipitate)
releases energy to its surroundings, usually heat
Word equation for aerobic respiration
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Anaerobic respiration
happens in the absence of oxygen (strenuous exercise)
occurs in cytoplasm
produces little energy
Glucose → lactic acid + little energy
Oxygen debt
extra oxygen body needs after exercise to react with lactic acid
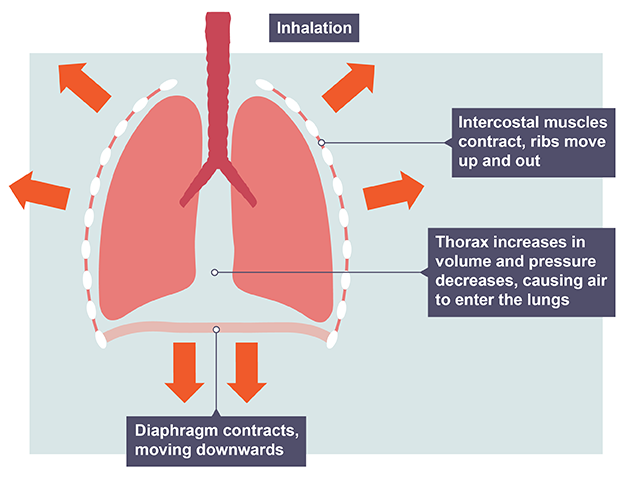
Inhalation
intercostal muscles contract, ribs move up and out
thorax increases in volume and decreases in pressure, causing air to enter lungs
diaphragm contracts, moving downwards
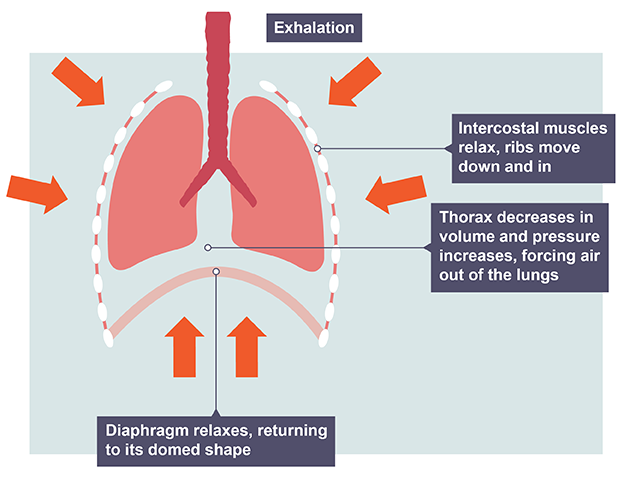
Exhalation
intercostal muscles relax, ribs move down and in
thorax decreases in volume and increases in pressure, forcing air out of lungs
diaphragm relaxes, returning to domed shape
Bell jar model
rubber sheet moves down to increase volume inside glass jar
causes decrease in pressure
balloons inflate as air enters until pressures are equal
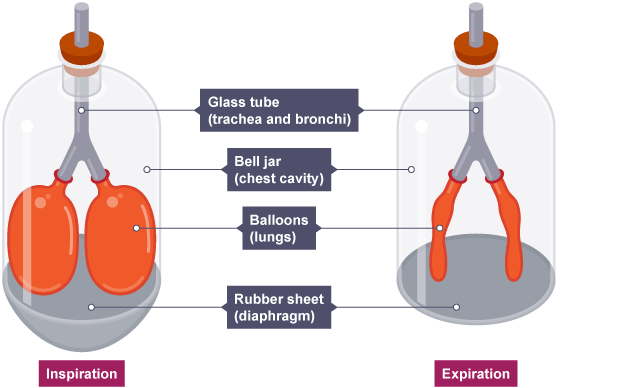
Limitations of the bell jar model
ribs and intercostal muscles are not represented
diaphragm shape is flat and pulled down rather than domed
balloons contain open space instead of many alveoli
Composition of inhaled air
21% Oxygen, 0.04% Carbon Dioxide, 78% Nitrogen, water vapor varies
Composition of exhaled air
Effects of exercising
muscles require more energy (increased respiration)
larger volume of air needed for gas exchange
body increases rate and depth of breathing (+ heart rate)
Recovery time
time taken for breathing rate to return to normal after exercise