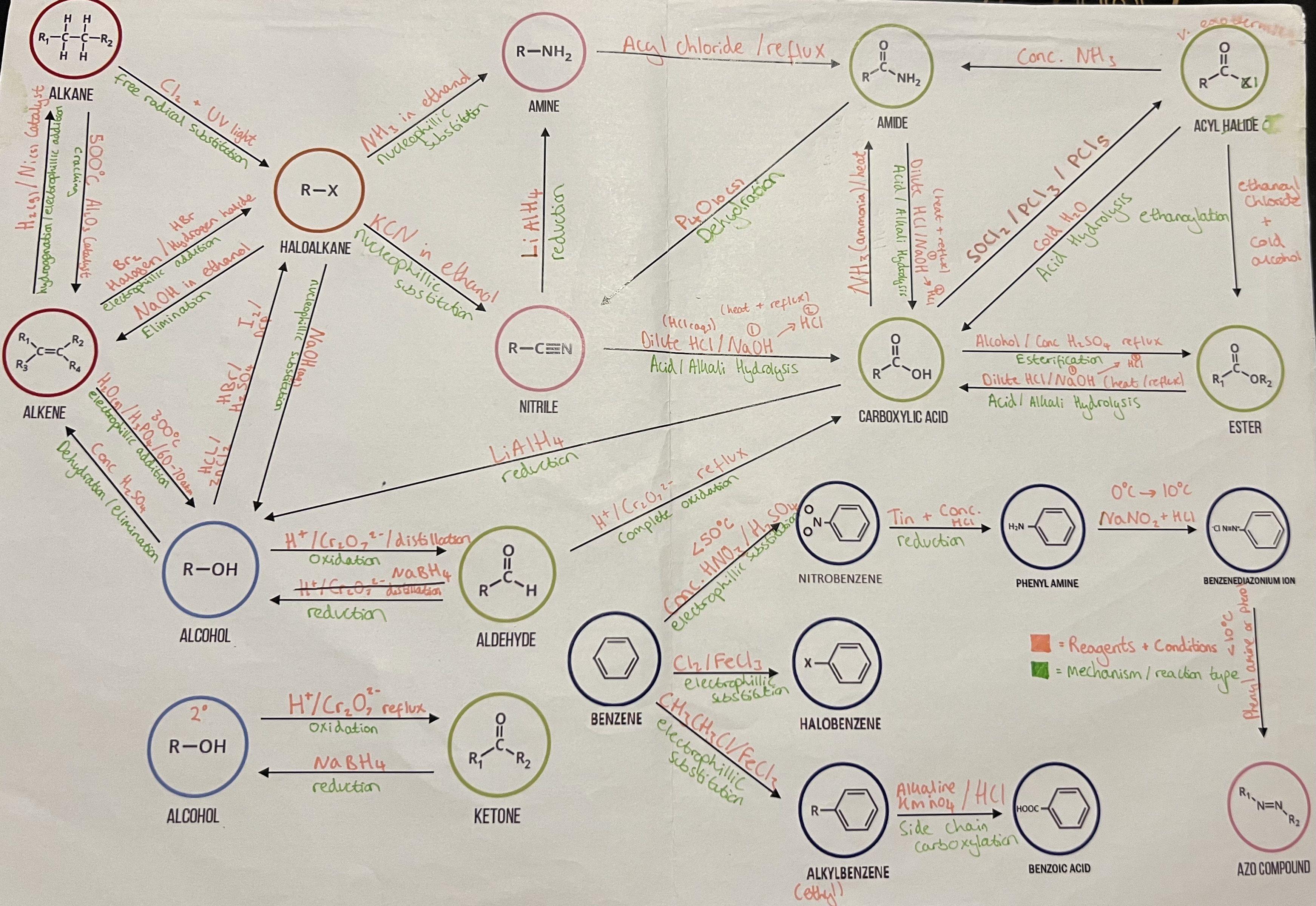
A2 Unit 4.4,4.6 & 4.7 Aldehydes, Ketones, Amines, Amino Acids, Perides and Proteins
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Aldehydes and Ketones

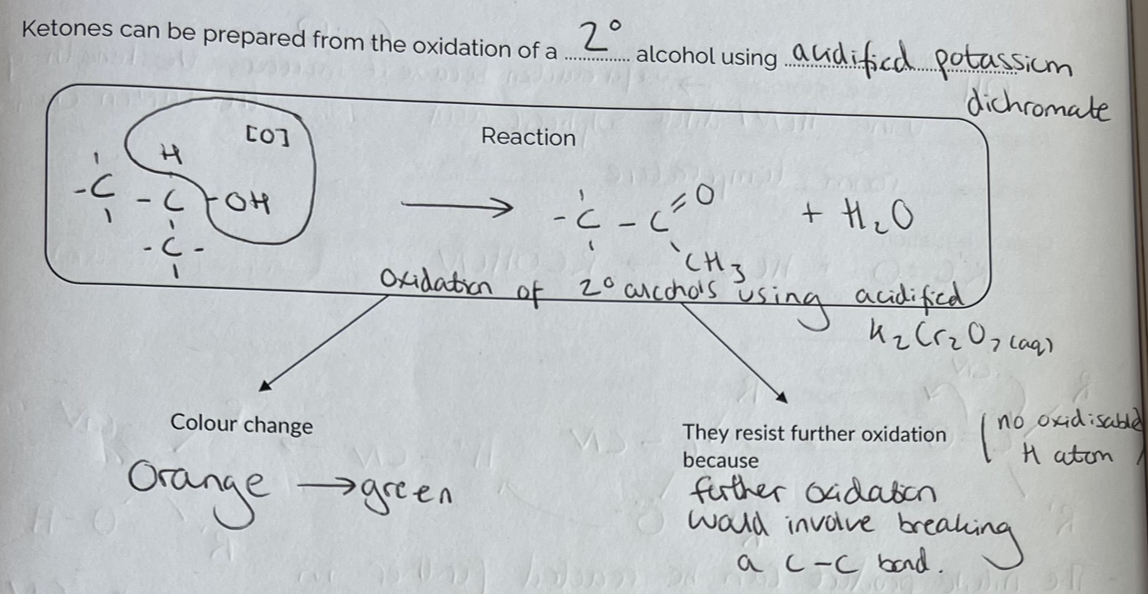
PREPARATION OF ALDEHYDES FROM ALCHOLS

PREPARATION OF KETONES FROM ALCOHOLS
Chemical Reactivity
As the carbonyl functional group has a double bond, it undergoes addition reactions - just like the double bond of the functional group in alkenes.
Alkenes undergo electrophillid addition reactions because the electron cloud of the Tt bond is attacked by electrophiles.
There is a Tt bond in the carbonyl group as well, but it is between two atoms of different electronegativities, C and O. The density of the charge cloud is greater at the more electronegative oxygen end.
Therefore, the bond is Polar Since C=O is polar, the electron deficient carbon atom is susceptible to attack by nucleophiles. Their reactions are nucleophilic addition reactions.
Why don’t substitution reactions occur and are aldehydes more reactive than ketones?

Addition Reaction & Questions
(Practice questions on pg. 6)

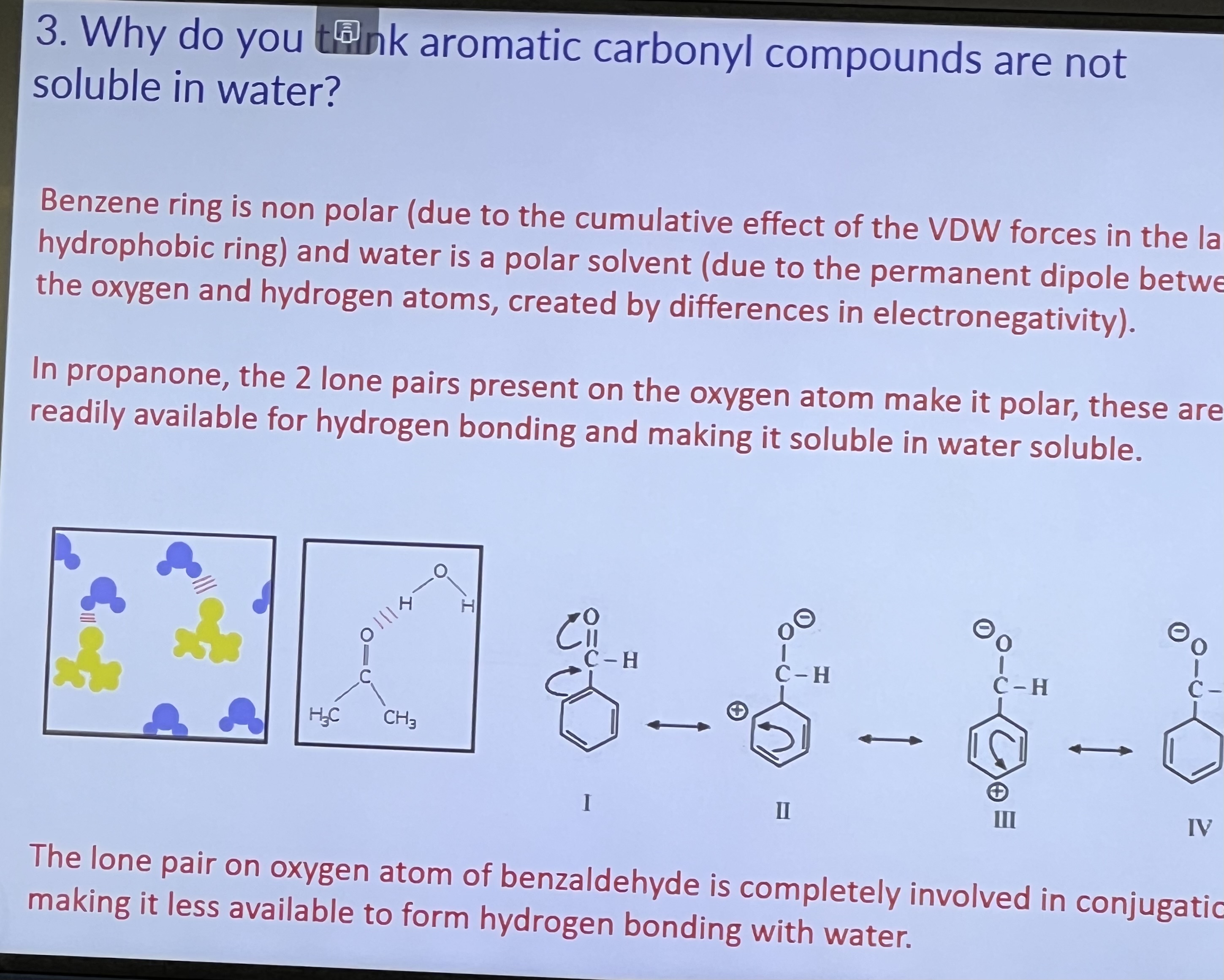
Why aren’t aromatic carbonyl compounds soluble in water?
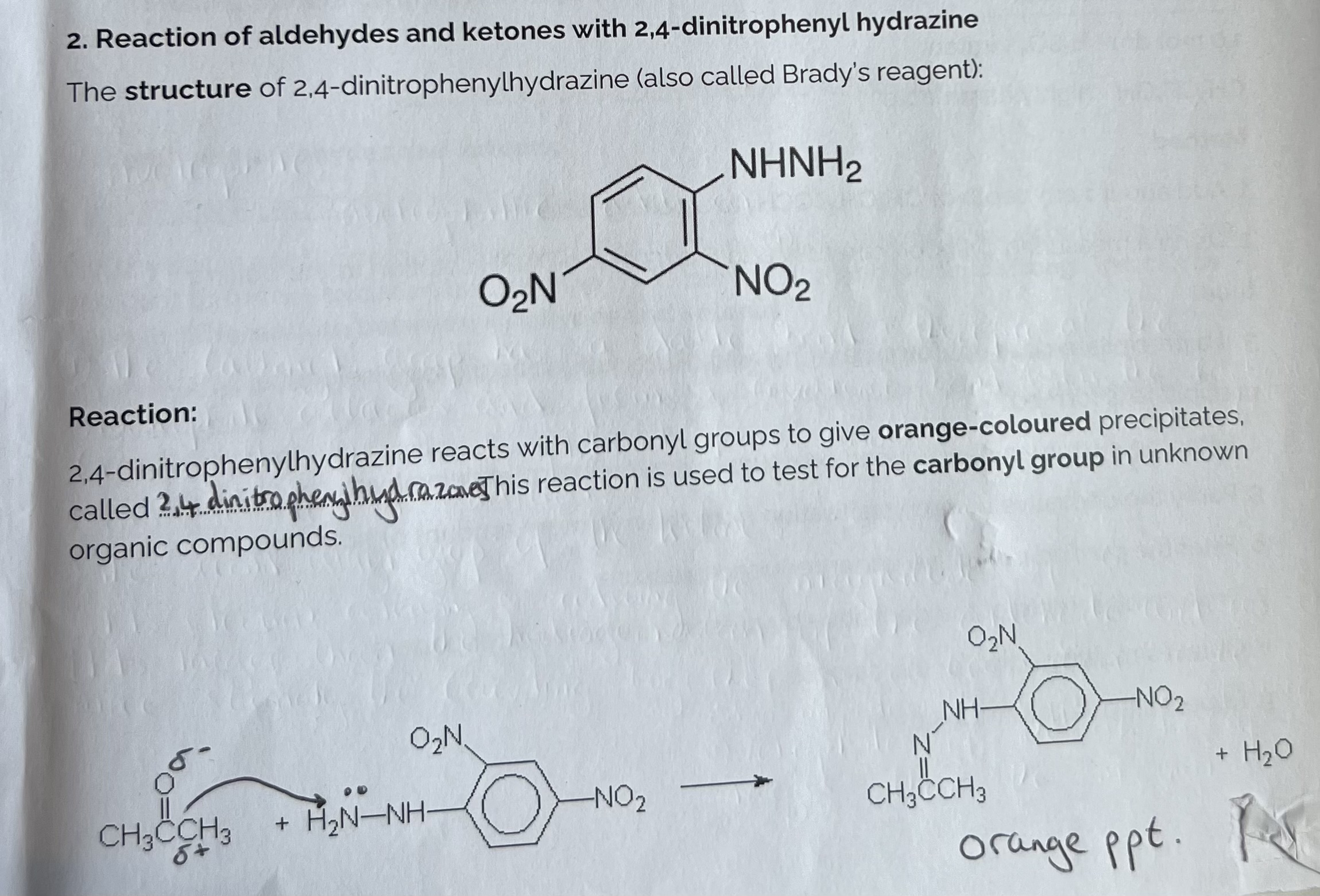
Reaction of Aldehydes and Ketones with 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine (Brady’s Reagent)
Nucleophilic Addition/ Elimination Reaction & Specified Prac.

Risk Assessment & Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones

Chemical Tests
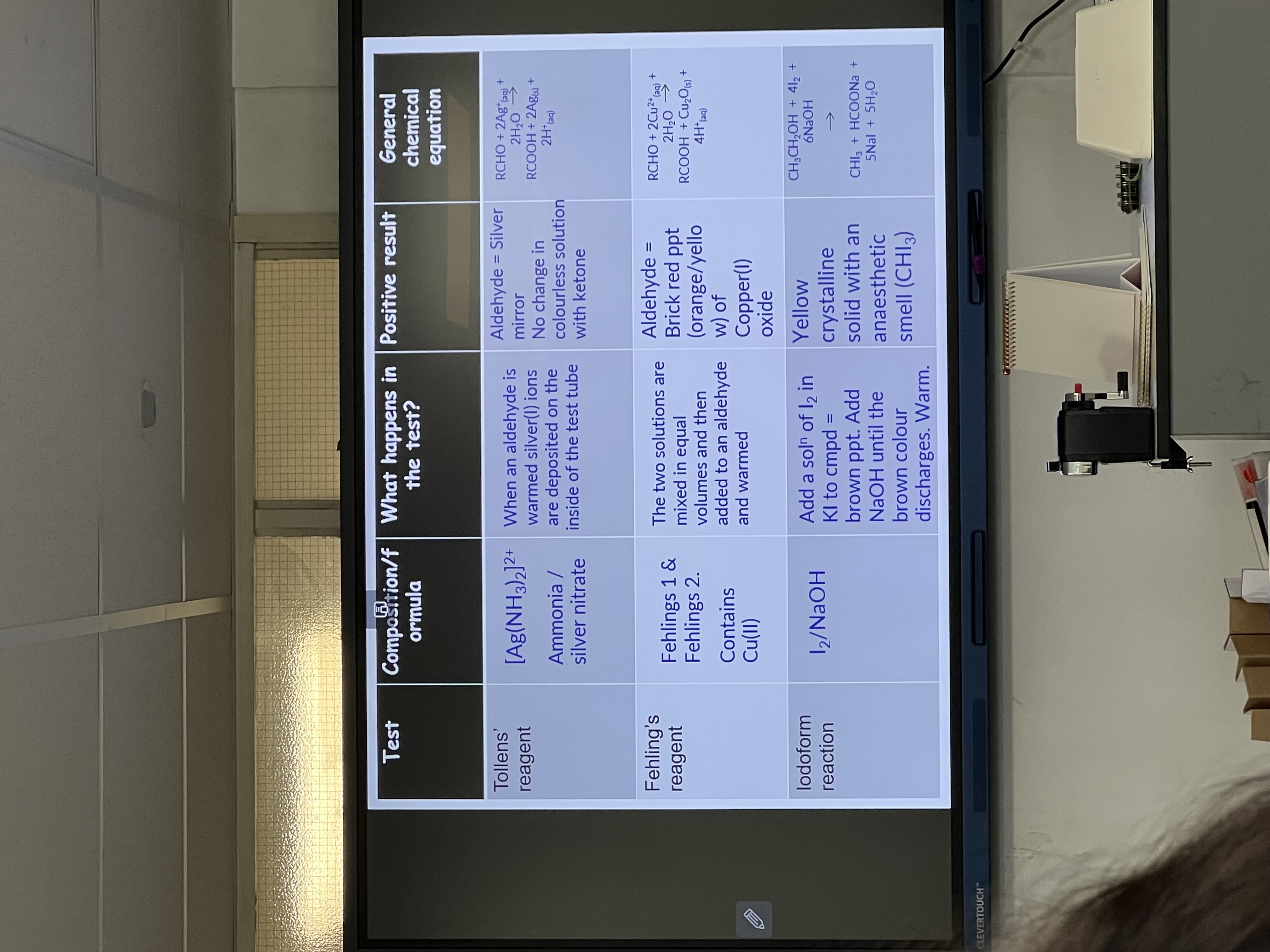
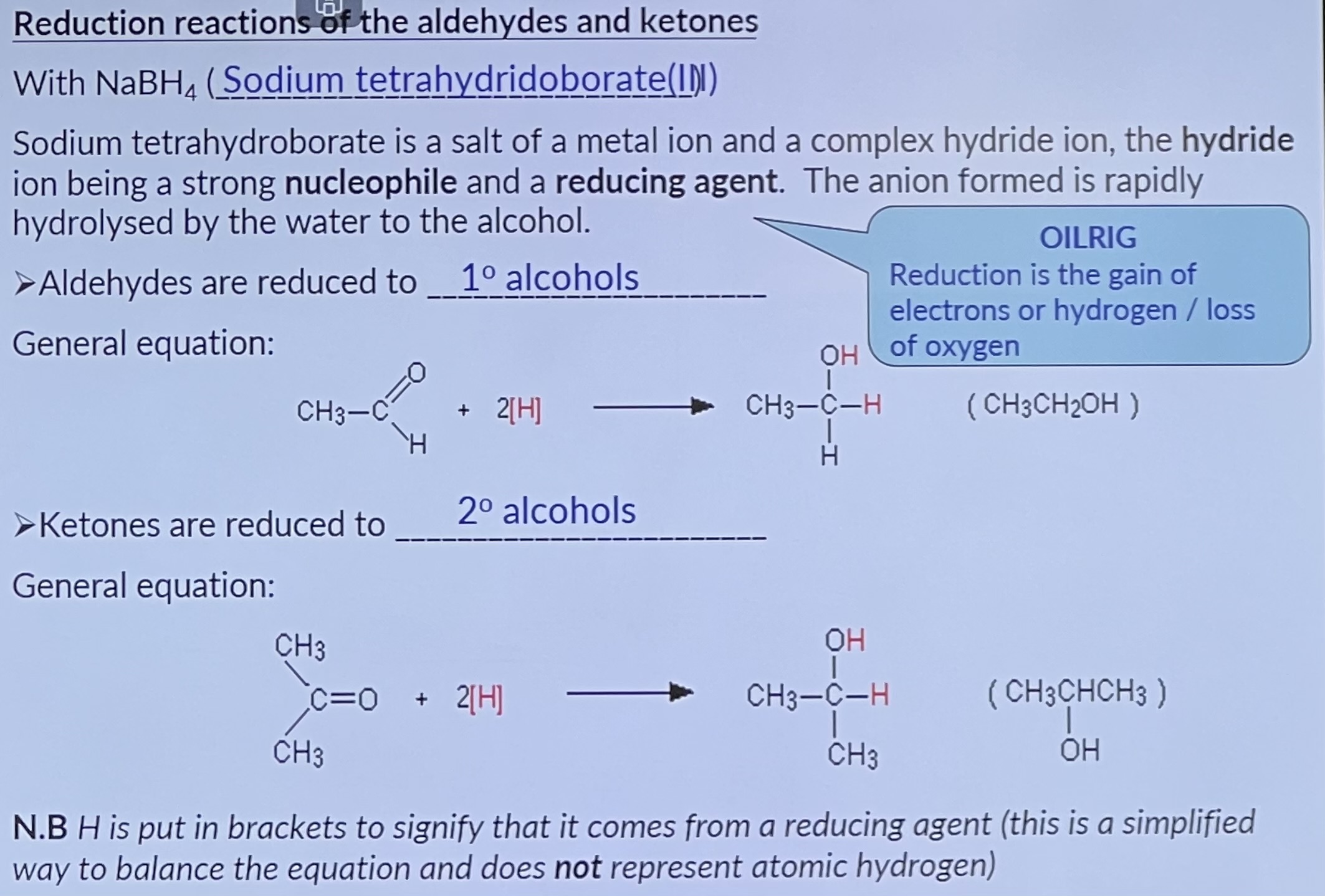
Reduction Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones with NaBH4
The mechanism is similar to that of the addition of hydrogen cyanide, only in this case the nucleophile is ..... once the NaBH4 has reacted with the carbonyl compound, water is added to provide the protons.
Reactions of the Carbonyl Group with Brady’s Reagent & Practical Methods

Primary Amines
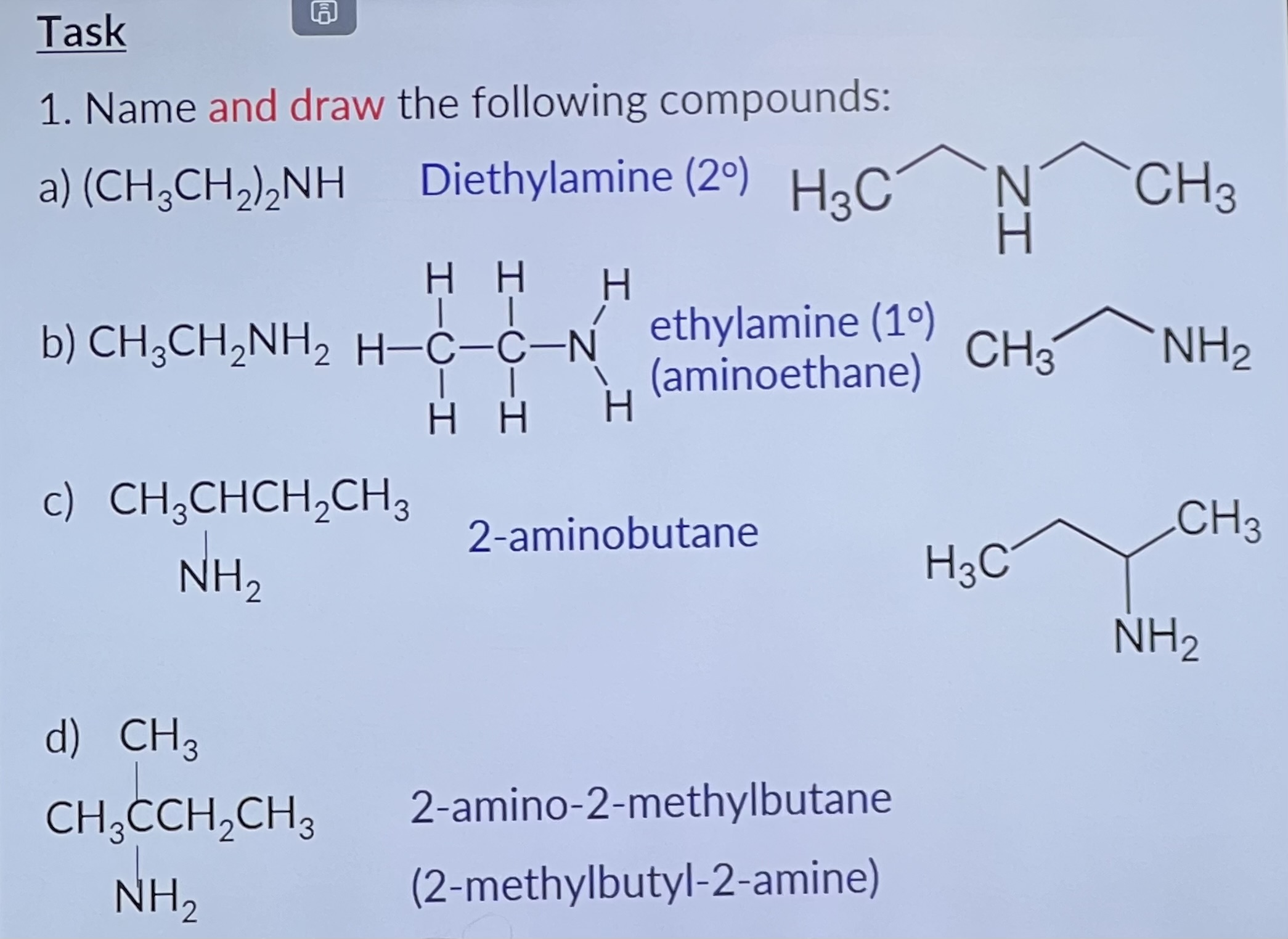
Amines can be considered as compounds formed from ammonia by substituting hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups.
If one of the hydrogen atoms in NH3 is substituted, we get a compound of the form RNH2 called a primary amine.
Such compounds are named using the suffix -ylamine after a stem indicating the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
Thus CH3NH2 is methyl amine.
Substitution of two of the hydrogens of NH3 gives compounds of the form R1R2NH, called secondary amines, named in a similar way to primary amines. Thus, (CH3)2NH is dimethylamine.
The prefix amino- can be used to indicate the presence of an -NH2 group in molecules containing more than one functional group, e.g. aminoethanoic acid.
Naming Compounds
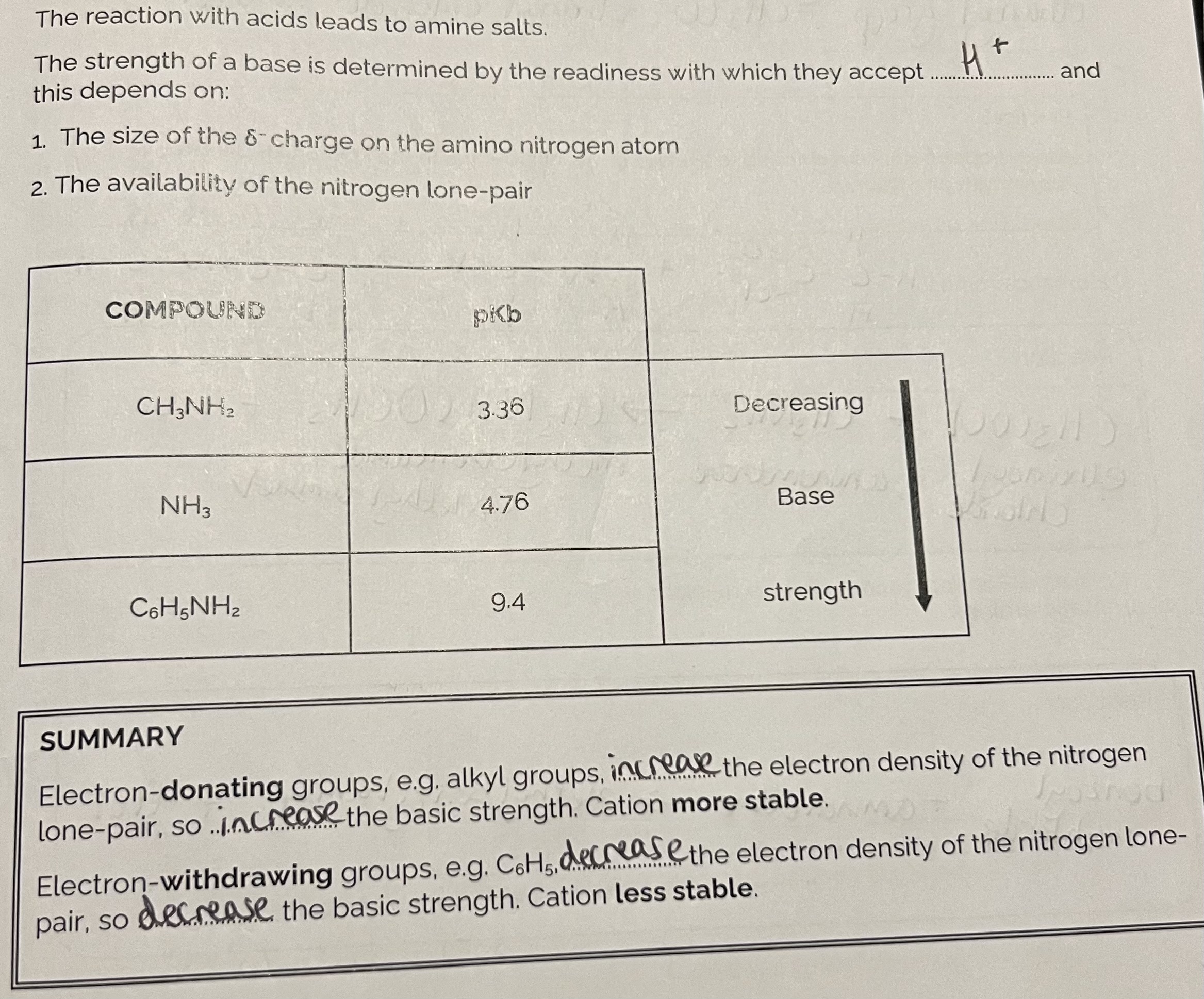
Why is aminomethane (methylamine) a stronger base than ammonia?

Why is aminobenzene (phenylamine) a weaker base than ammonia?

Physical Properties of Aliphatic Amines

Disadvantage of this method

Reduction of a nitrile & nitro-compounds
Use concentrated HCL

Chemical Properties of Amines
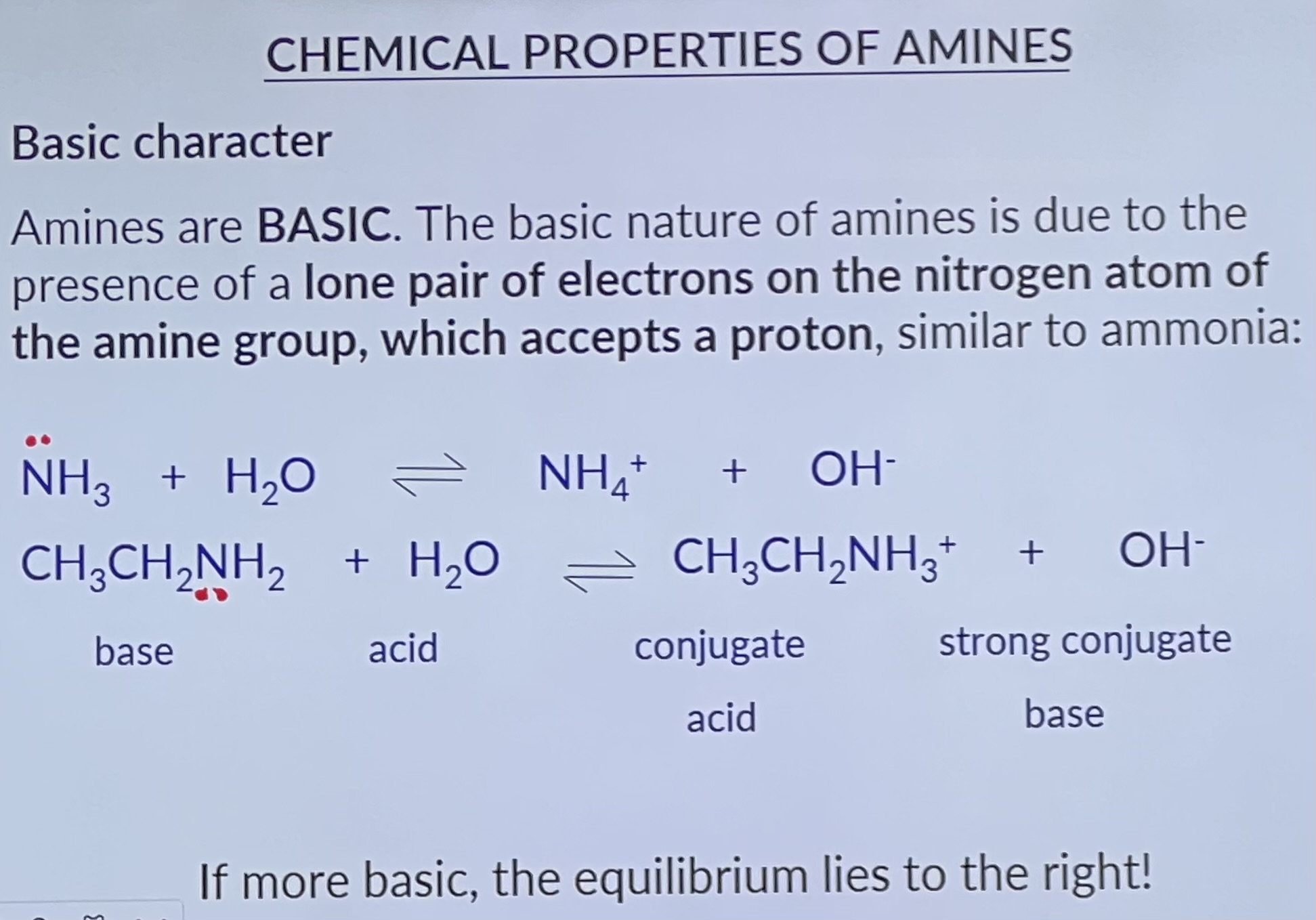
Summary
Reactions of Primary Amines

Example Question

Reactions with nitric acid

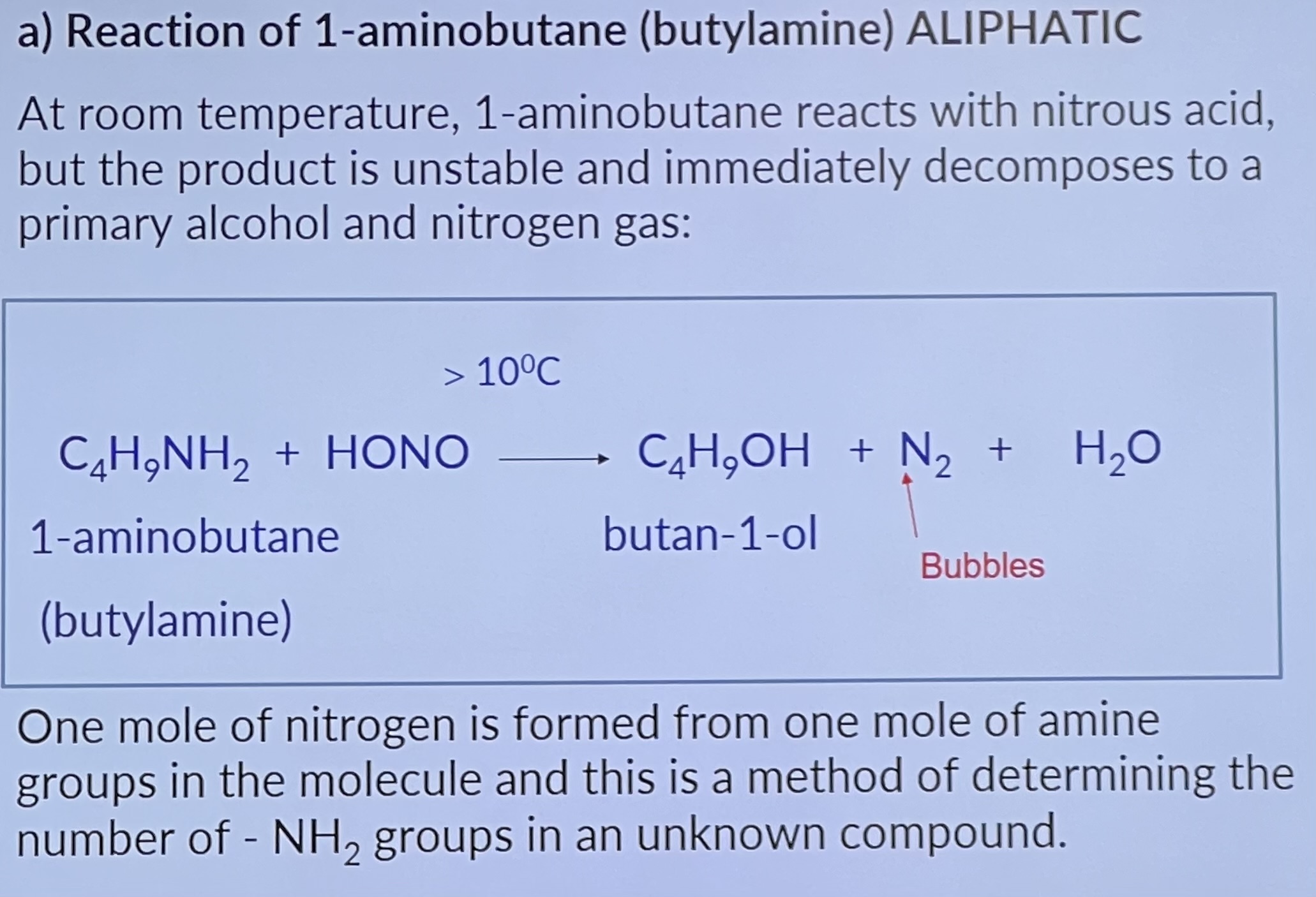
Reaction of 1-aminobutane - Aliphatic
Reaction of aminobenzene - Aromatic
Aliphatic amines do form diazonium salts under the same conditions but they are unstable and decompose rapidly.
The diazonium ion is positively charged and has weak electrophilic properties. In the presence of OH ions it reacts with activated aromatic rings e.g. phenol, 2-naphthol, to form other organic compounds by means of coupling reactions.

Coupling reactions of diazonium salts
Amine is the starting compound

Azo Dyes Questions

The origin of colour
A substance that is white reflects all visible wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation. A substance that appears black absorbs all visible wavelengths.
A substance appears coloured if it absorbs some of the electromagnetic radiation from white light (i.e. with frequencies in the visible spectrum), but not all of it.
When a compound absorbs wavelengths of one particular colour, a complementary colour appears. Pairs of complementary colours are represented on the colour wheel.

Amino acids
These are the building blocks from which proteins are made. Amino acid molecules have two functional groups, an Amine group and a Carboxylic acid.
Although it is possible to have many amino acids, in fact only 20 are commonly found in nature, and these are called the a- amino acids i.e amino acids in which both the amino and the carboxylic acid group are attached to the same carbon called the a-carbon (naming: 2-amino…)

Physical properties or amino acids due to zwitterions
Amino acids are non-volatile, white crystalline solids with high melting points. They are soluble in polar solvents and are good electrolytes, but are insoluble in non polar solvents.
AMPHOTERIC BEHAVIOUR OF AMINO ACIDS - Amino acids have two functional groups. The chemical properties of compounds with two functional groups are often the sum of each individual group. However. with amino acids, the basic amine group and the acidic carboxylic acid group can react with each other.
Amphoteric - A molecule or ion that can both donate and accept a proton (H+) allowing it to act as both an acid and a base.
What is a zwitterion?
A molecule that carries both a positive and negative charge. A proton from COOH can be donated to the NH2 group of the same amino acid molecule to give a zwitterion.

Why does the formation of zwitterions explain the higher than expected melting temperatures of amino acids and the solubility of amino acids in polar solvents?

The formation of dipeptides
When two amino acids (same or different) react together, the compound formed is known as a dipeptide. The reaction is between the COOH of one amino acid and the NH2 of the other.
The two amino acids are linked together by amide bonds, also called a peptide link.
A molecule of water is eliminated and so the reaction is known as a condensation reaction.

Protein Structure
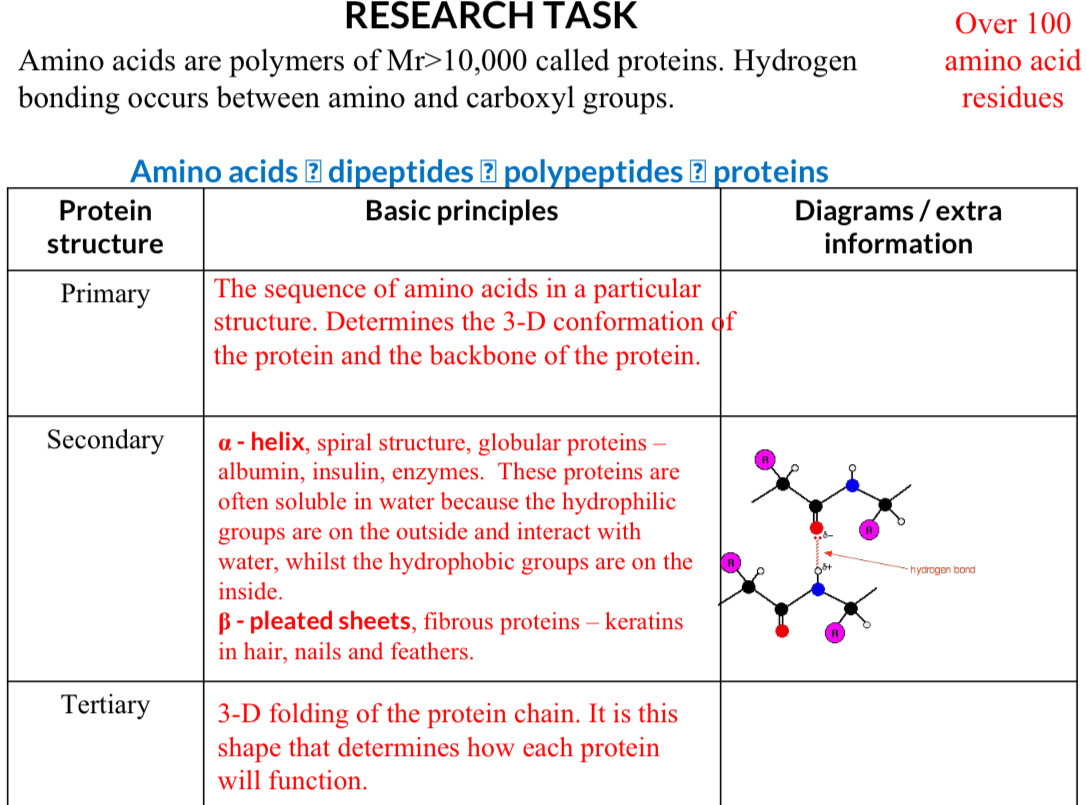
Proteins in living systems

Example Question

Reaction Summary Sheet