A&Pll: Chap. 25 & 26 The Endocrine System
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
*Everything highlighted in yellow is part of quiz review. Know the features of hormones and what they do for quiz #1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
The Endocrine System
Control system of the human body.
Produces chemical messages in the form of HORMONES
Made up of specialized glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
Nervous System vs. Endocrine System
Differences:
hormones can stimulate more blood cells than neurotransmitters
however, the nervous system functions a lot faster (electrical impulses)
Similarities:
Both endocrine + nervous systems exhibit control via a feedback system
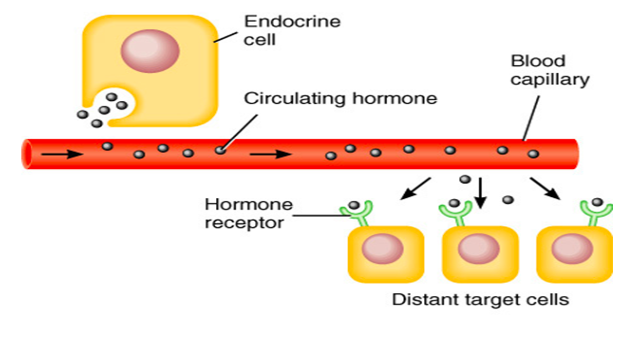
Hormones
Chemical messages that are released from glands
Only act on a target tissue or organ with specific receptors for specific hormone.
ALL hormones have ONE common feature – all travel through bloodstream *Ductless System
Chemical Classification of Hormones
Non Steroidal (proteins) Amino Acid based - usually long chains
organic compounds that make protein
nitrogen, oxygen, carbon+hydrogen
synthesize from tryptophan and tyrosine
Steroids – derived from Cholesterol
Lipid soluble, easily passes through the plasma membrane
Works for the effective functioning of the body
Ex. testestoraone, aldosterone, cortisol
Hormones Stimulus - Cellular
Change permeability or potential of plasma membrane by opening ion channels
Synthesis of protein including enzymes within cell
Activates inactive enzymes or inhibits active enzymes
Induces secretion by cells
Stimulates mitosis
Dual Functioning Endocrine Glands
Hypothalamus
Nerve cells in hypothalamus make chemicals that control release of hormones from pituitary gland
gathers info sensed by brain (light, temp, feelings) to influence hormone release from pituitary
Pancreas
Part of Endocrine (insulin & glucagon) and digestive system (digestive enzyme)
Gonads
Testes in males (Sperm) and Ovaries (eggs) in females
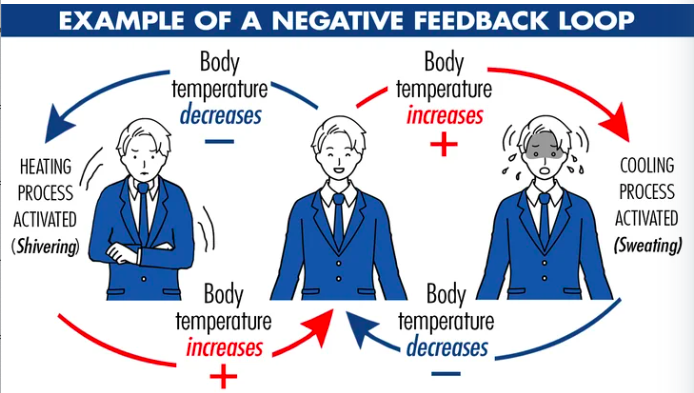
Negative Feedback Loop
Usual regulatory mechanism for hormone production in the endocrine System
Causes a decrease in function
Keeps concentration of hormones in a narrow range
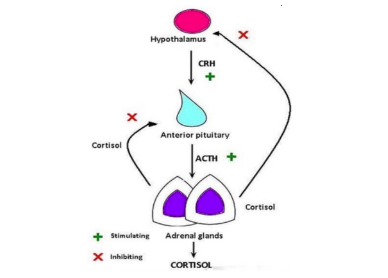
Negative Feedback Loop - Stress
CRH = corticotropin releasing hormone
ACTH = adrenocorticotropic hormone
Adrenal Glands = fight or flight
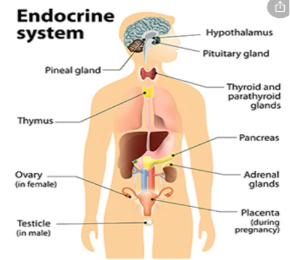
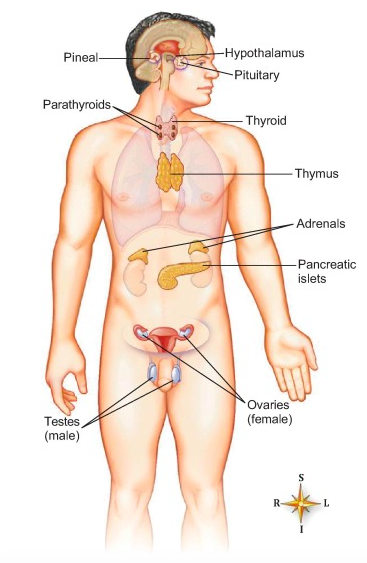
Major Endocrine Glands in the body
Hypothalamus - brain
Thyroid - neck
Pituitary - brain
Pancreas - abdomen
Parathyroid - neck
Thymus - chest
Adrenals - on top of kidneys
Pineal - brain
Reproductive glands - gonads
Endocrine Glands in the Body - Infundibulum
stemlike stalk that connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland
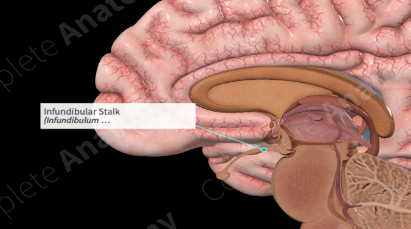
Endocrine Glands in the Body - Hypothalamus
Connects endocrine system with nervous system
Main function to tell pituitary gland to start/stop making hormones
Nerve cells make chemicals that control release of hormones from pituitary
Gathers sensory information from sensed by the brain, then sent to pituitary gland
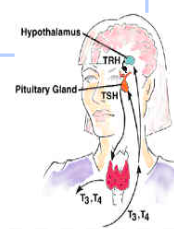
Endocrine Glands in the Body: Thyroid Gland
Located in the anterior neck, the surface of the trachea
Hormone:
Thyroid Hormone (T3-T4)
Stimulated by thyroid Stimulating hormone (TSH) from Anterior Pituitary
Calcitonin Function:
Elevates metabolic rate
increases heart rate and respiration rate
stimulates appetite
Reduce blood Ca+
Thyroid Gland
Hormone: calcitonin
Function:
Acts to reduce blood Calcium levels
Inhibits the activity of osteoclast (bone breakdown)
Thyroid Gland Diseases
Hypothyroidism - decrease in T3/T4
Hyperthyroidism - increase in T3/T4
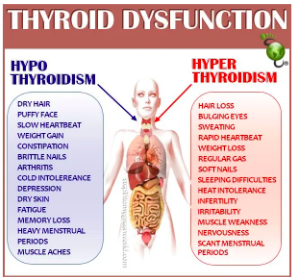
Thyroid Gland - Autoimmune Disease
Graves Disease (hyperthyroidism)
- Characterized by: unexplained
weight loss, nervousness,
increased heart rate, and the
protrusion of the eye
Hashimoto Disease
(hypothyroidism)
- Characterized by: large goiter,
primarily affects middle-aged
women, fatigue, puffy face,
hoarse voice, depression, pain in
joints
Pituitary Gland – Master Gland
ANTERIOR LOBE:
Glandular part
Secrets hormones for 6 targets
HORMONES
Growth hormone (GH)
follicle-stimulating (FSH)
luteinizing hormone (LH)
adrenocorticotropic
hormone (ACTH)
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Prolactin (PRL) – non tropic
POSTERIOR LOBE:
Neural part
Secrets 2 hormones
Signal from Hypothalamus
Hormones
- Oxytocin
- Antidiuretic (ADH)
Anterior Pituitary: HGH
Hormone: Human Growth Hormone(hGH)
Function:
Peptide hormone stim growth
speeds up the breakdown of fat (lipids)*
shifts cell’s use of nutrients away from carbohydrates (glucose) and towards lipids as an energy source*
GH and insulin function as antagonists*
Cell reproduction/regeneration
Regulates body composition, body fluids
Mental function
Bone & muscle growth
Diseases:
Acromegaly
Gigantism
Pituitary Dwarfism
quiz question: are GH and insulin synergists? FALSE

Anterior Pituitary: ACHT
Hormone: adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Function:
Maintains the growth and development of the adrenal gland
Regulates levels of Cortisol
ACTH Secreted by pituitary gland
ACTH Stimulates Adrenal Cortex
Diseases:
Cushing’s Disease
Characterized by: upper body obesity, rounded face, increased fat around the neck, and relatively slender arms and legs.
Anterior Pituitary: TSH
Hormone: thyroid stimulating
hormone (TSH)
Function:
- stimulates production of
Thyroxin(T4) and
Triiodothyronine (T3) by Thyroid gland
* T4 must be converted to T3 for body to use
(Liver main area – Selenium required to remove molecule of Iodine
Anterior Pituitary: PRL
Hormone:
prolactin (PRL)
Function:
Stimulates the mammary glands to secrete milk for lactation
Anterior Pituitary
Hormone: follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Function:
Females: initiates development of oocytes (stimulates growth of ovarian follicles)
Males: initiates development of sperm
Hormone: luteinizing hormone (LH)
Function:
Females: stimulates secretion of estrogen/progesterone
Males: stimulates secretion of testosterone
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
F: FSH
L: LH
A: ACTH
T: TSH
P: Prolactin
I: Ignore
G: Growth Hormone
Posterior Pituitary Gland: Two Hormones
Two Hormones made by axons of the Hypothalamus (Neural)
1. Oxytocin
stimulates uterine contraction, birth hormone (increases contraction)
men also secrete it
Antidiuretic (ADH) = vasopressin, stimulates kidneys to absorb water
prevents the formation of a large volume of water and conserves water
Diabetes Insipidus – hyposecretion
quiz question: birth hormone relates to which gland? Pituitary
Posterior Pituitary
Hormone: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or vasopressin
Produced in Hypothalamus
Released by Post Pituitary
Function:
It helps the Kidney manage the amount of water in the body
If ADH levels are low – it increases Urine output
Pineal Gland
Hormone: melatonin
Function:
Body’s biological clock
Wake sleep cycle
Sunlight goes down, and melatonin rises
Parathyroid Gland - On top of the Thyroid
Hormone: parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Function:
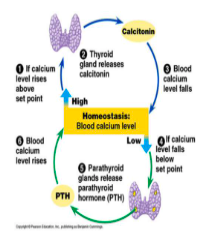
Works with calcitonin to help control blood Ca+ levels (calcitonin: decreases reduces blood calcium levels while PTH increases blood calcium)
Does the opposite of calcitonin*
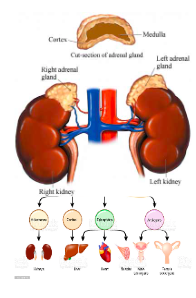
Adrenal Gland
Located on top of each kidney
- Produce hormones you can not live without
- Mediate short- and long-term responses to stress
Two Parts:
Adrenal Cortex
outer part
Adrenal Medulla
inner part
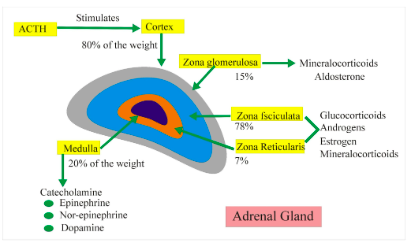
Adrenal Gland: Adrenal Cortex
Hormones:
Cortisol
Aldosterone
Adrenal androgens
Function:
Increases blood glucose levels, reduces inflammation, increases blood pressure, and increases the storage of (visceral) fat
Adrenal Cortex: Cortisol
A Flight or Fight Hormone
Steroid Hormone
Controls body response to Stress
Controls Salt and water balance
Immune system
Manages how body uses carbohydrate, fats and proteins
Increases blood sugar level (glucose)
Disease:
Cushing Syndrome – too much (Hyper)
Addison’s Disease – too little (Hypo)
Adrenal Cortex: Aldosterone
Steroid Hormone
Essential for Sodium (Na+) conservation in kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands and colon
Secretion of Potassium (K+)
Increases blood volume
Increases blood pressure
Hyperaldosterone – fluid retention, Increased BP, weaknness, cause loss of K+ and retention of Na+
Hypoaldosterone – Low Na+ (hyponatremia), High Pa+ (hyperkalemia), and too much acid (metabolic acidosis)
Conn’s Syndrome – very rare, too much (Hyper)
Adrenal Cortex: Androgen
Steroid Hormone
Play a role in male traits and reproductive activity
Kick starts puberty
Present in both males and females
Adrenal Medulla- core of Adrenal gland, inner part
Flight or Fight response & Extension of the Autonomic nervous system
Main Hormones
Epinephrine- adrenaline (increases HR, dilate airways, dilates blood vessels, acts on histamine)
Norepinephrine (alertness, BP regulation, mood regulation- SNRIs)
Dopamine (pleasure, motor control, mood, attention, vasoconstriction)
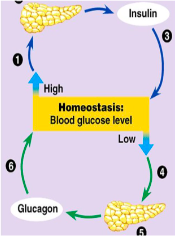
Pancreas
Maintains homeostasis of blood glucose levels
Releases directly into blood
Dual Functioning
Produces 2 antagonist Hormones
Insulin – lowers BS, moves glucose into cells
Glucagon – increase BS
(^ antagonists)
Type I DM – shortage of Insulin; impaired insulin production
Type II DM – lack of receptors in target cells'; impaired insulin secretion
MOST COMMON ENDOCRINE DISORDER*
Heart
Hormone: atrial natriuretic peptide or hormone (ANP/ANH - promotes sodium loss)
Function:
Targets Kidneys & Cardiovascular System
Released from R Atrium
blood volume/pressure
causes salt to move from the blood to the kidney
Increase urinary excretion
Gland: Testes
Hormone: testosterone
Function: Growth and maintenance of male sexual characteristics and for sperm production
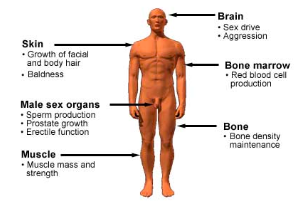
Gland: Ovaries
Hormone: estrogen
Function: development and maintenance of female sexual characteristics
Hormone: progesterone
Function: maintenance of uterine lining for pregnancy
Sex hormones are produced by: the testes, ovaries, and adrenal glands (androgens)*
Gland: Placenta
Hormone: human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Function: Stimulates development of fetus, and hormone secretion by maternal ovarian tissue for first trimester of pregnancy
Digestive Glands
Hormone: leptin
Gland: adipose tissue - plays a role in energy balance*
Function: Signal of how much fat is stored and Stimulates reduction of appetite
Hormone: ghrelin
Gland: stomach
Function: Stimulates hunger and is also linked to reward and pleasure in the brain
GI Tract
In the mucous lining of the _____, other cells secrete ___ hormones that play a regulatory role in ___ process
Ex. secretin
Antagonists: Calcitonin and Parathyroid Hormone
Calcitonin
reduce blood calcium levels
inhibits the activity of osteoclasts to break old bone
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
increase blood calcium levels
promotes the breakdown of old bone
quiz question: parathyroid can cause an increase in ossification: false