pharmacognosy- microorganisms, marine organisms and the animal kingdom
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
A Gram-positive bacterium, found worldwide in water, guts of animals, fish and mammals or even shellfish and also in soil. What is its immediate mode of action?
Blocking neurotransmission; paralysis of muscles causing vomiting, diarrhoea and severe abdominal pain; most death attributed to suffocation due to paralysis of diaphragm.
1 Gram may kill as many as 50 million people.
what is botulism caused by?
the toxins that are produced by clostridium botulinum bacteria and is rare but potentially fatal condition
common or general symptoms of botulism?
visual disturbances or blurred vision
drooping eyelids
dry mouth and speaking problems
vomiting
swallowing problems
nausea
abdominal cramps
what can botulinum toxin A and B be used to treat?
counter involuntary facial muscle spasms and muscle spasticity in children with cerebral palsy
what are the well-known marine products that have been used for many years?
marine macroalgae have been used as crude drugs in the treatment of iodine deficiency (goitre, hypothyroidism, ect)
various seaweeds have a number of uses:
-as sources of vitamins
-in treatment of anaemia during pregnancy
-various intestinal disorders
-hhypocholesterolaemic and hypoglycemic agents
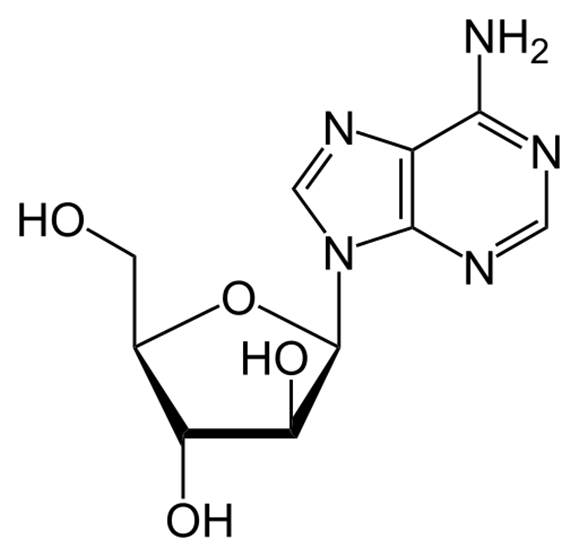
many marine organisms have been screened for the presence of anti-viral compounds, what has been reported to have significant anti-viral activity?
Vidarabine (ARA-A) has been reported to have significant anti-viral activity - Herpes vosta/simplex
ARA-A is isolated from the Caribbean sponge Tethya crypta
marine organisms
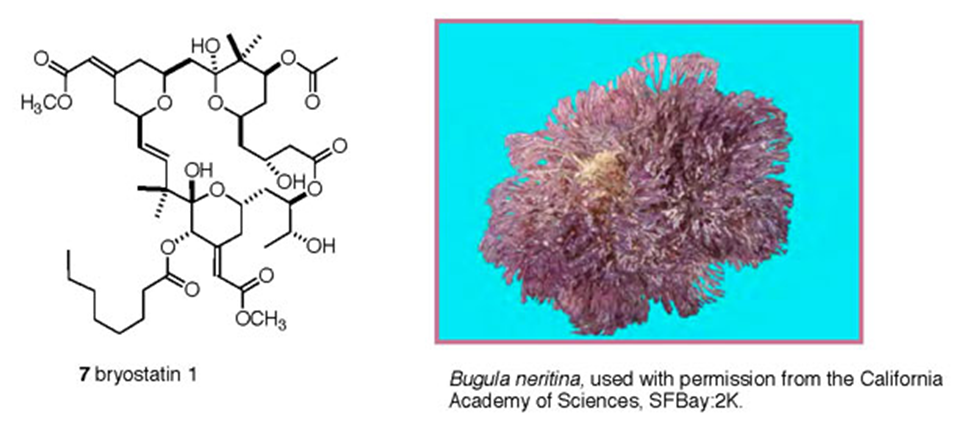
what antitumour compounds are used in combination with other chemotherapies for enhanced action?
the most important group of compounds are called macrolides of which the most significant are known as bryostatins, isolated from bugula nertina
marine organisms
antiparasitic compounds: a broad spectrum anthelmintic compound kainic acid was isolated from?
the red alga
marine organisms
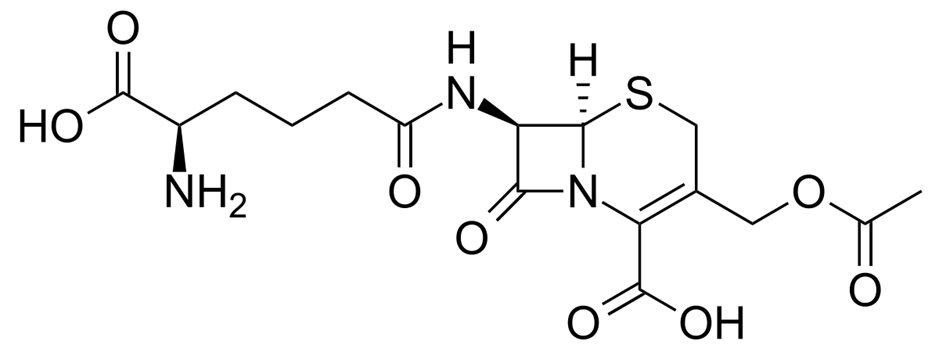
antimicrobial compounds: Cephalosporin C was isolated from?
the marine fungus Cephalosporium acremonium
the semisynthetic product- cephalothin sodium is commonly used, as are other derivatives
many animal products are still in use in traditional medicines of china, india and africa, the following are pharmaceutically important?
porifera (sponges)
coelenterata (corals)
mollusca (snails)
chordata (including mammals)
what does porifera (sponges) include in terms of medicinal properties?
bromophenols (antibacterial)
cyclic peroxides and peroxyketals (antimicrobial, cytotoxic)
modified sesquiterpenes (antimalarial, antifungal, anticancer)
what does coelenterata (corals) include in terms of medicinal properties?
sarcophyton glaucum produces sacrophytols A and B (inhibit tumour production)
Sponges and corals are currently subject of intense research
what does mollusca (snails) include in terms of medicinal properties?
cuttlefish bone (sepia officinalis) has been used in dentifrices and as an antacid
what does chordata (including mammals) include in terms of medicinal properties ?
Cod and halibut are important for their liver oils (contain vitamins A & D)
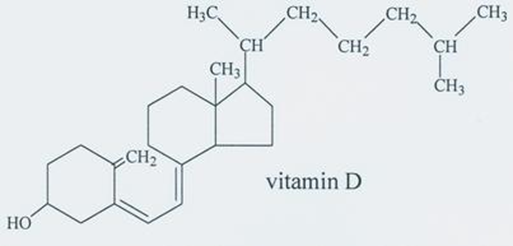
other important classes of drug from mammals include?
vaccines
blood- products
hormones
sera
examples of poison arrow frogs?
dendrobates tinctorius ‘azureus’
dendrobates leucomelas
Phyllobates terribilis (most poisonous frog known)
how much skin secretion from phyllobates terribilis frog will kill a human?
0.0000003g
contains a mix of very powerful neurotoxins
explain where the phyllobates terribilis comes from, its appearance?
Phyllobates terribilis comes from Columbia and occupies some of the wettest rainforest in the world.
There are at least four colour morphs (varieties) thought to exist: yellow, orange, green and white.
what happens when the phyllobates terribilis is touched or threatened?
when touched or threatened, the frog produces venom from glands on their backs and behind their ears.
the skin secretions include some of the most powerful toxins known to man - BATRACHOTOXIN- very complex structure
the phyllobates terribilis produces batrachotoxin, explain how batrachotoxin works and what it does?
Batrachotoxin increases permeability of outer membrane nerve and muscle cells to sodium ions, causing an irreversible electrical depolarisation. Muscles remain contracted – can cause arrhythmias, fibrillation and ultimately cardiac failure.
describe the japanese puffer fish (fugu) ?
contains an extremely potent neurotoxin called tetrodotoxin
very small amounts cause complete paralysis
very popular dish (banned in EU)