Planet Earth Exam 1
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
James Hutton
Hypothesized that ancient rocks formed like those in ocean/stream features, that the Earth was older was older than previously thought.
Uniformitarianism
A principle that geologic processes that occurred in the past can be explained by current geologic processes
Catastrophism
A principle that states that geologic change occurs suddenly
Charles Lyell
Wrote Principles of Geology, revived uniformitarianism.
Earth System Science
Views the planet as a combination of systems with complex relationships.
geosphere
The solid part of the earth consisting of the crust and outer mantle.
atmosphere
The envelope of gases surrounding the Earth or another planet.
hydrosphere
All the water on earth.
cryosphere
Frozen water on earth.
biosphere
Consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists, including land, water, and the atmosphere.
lithification
The process that converts sediments into solid rock by compaction or cementation.
continental crust
30 mi thick, composed of igneous and sedimentary rock, low density (buoyant).
oceanic crust
6 mi thick, composed of igneous basalt rock, high density.
tectonic plates
made of crust and a portion of the upper mantle, forming the lithosphere.
mantle
extends 1800 mi, mostly solid and composed of peridotite. upper part is hot and flexible.
core
2200 mi thick, composed of iron and nickel, consists of liquid outer and solid inner. rotations within generate earth's magnetic field.
silicates
stony materials that incorporate Si and O.
lithosphere
mechanical layer of earth; solid, rigid, strong like cold butter.
aesthenosphere
mechanical layer of earth; ductile, soft like warm butter.
Original Horizontality
states that because sediments settle out of a fluid by gravity, they tend to accumulate in horizontal layers.
Superposition
in an undeformed sequence of layered rocks, each bed is older than the one above and younger than the one below.
Lateral Continuity
sedimentary strata and some volcanic deposits often form in laterally-extensive horizontal sheets. erosion dissects these layers.
Cross-Cutting Relations
younger features truncate (cut across) older features. faults, dikes, erosion, etc. must be younger than the material that is faulted, intruded, or eroded.
unconformity
a time gap in geological time from nondesposition or erosion.
angular unconformity
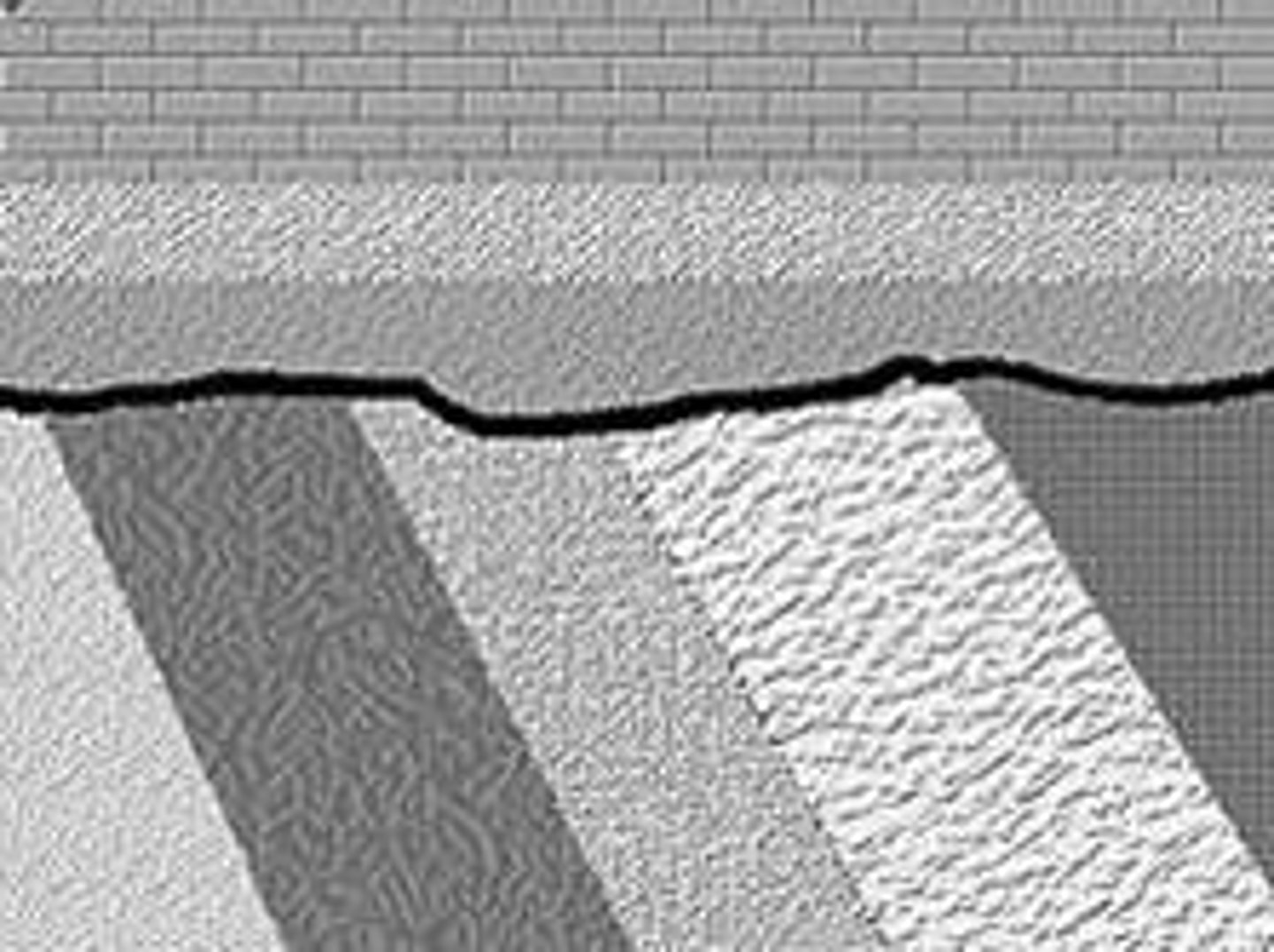
non-conformity
igneous/metamorphic rocks capped by sedimentary rocks
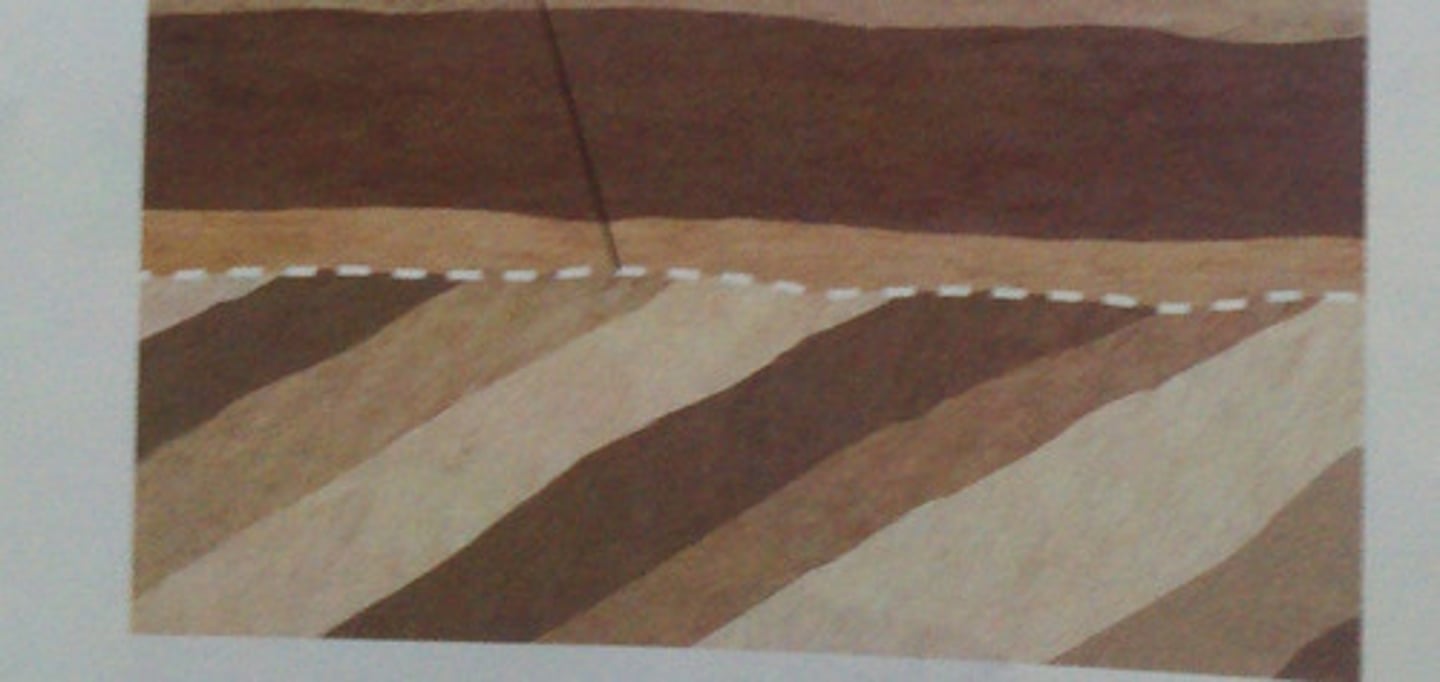

disconformity
sedimentary layers which have been eroded away.
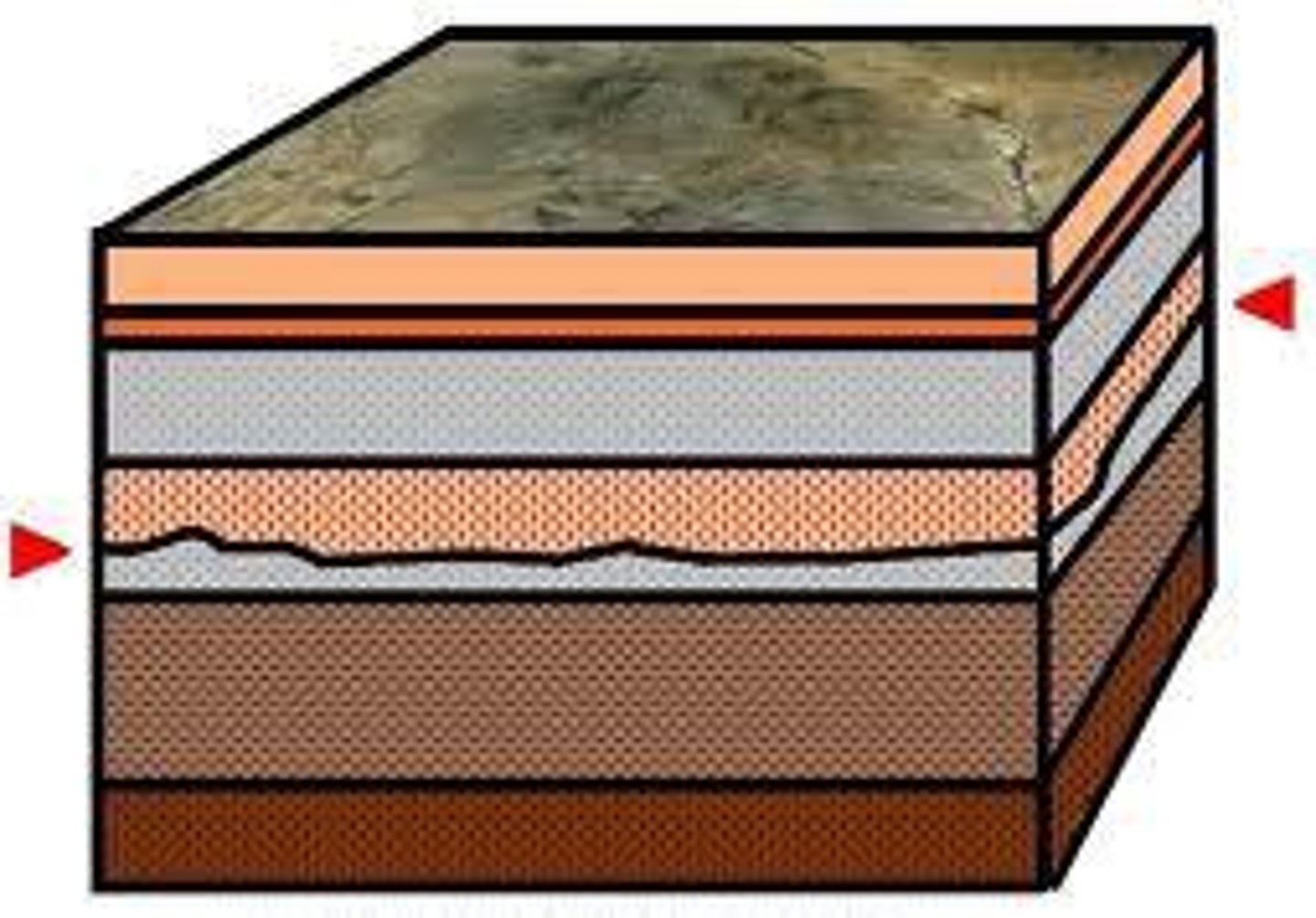
relative dating
the process of determining if one rock or geologic event is older or younger than another, without knowing their specific ages.
stratigraphy
study of layered sedimentary rocks.
Principle of Inclusions
when one rock formation contains pieces of inclusions of another rock, the included rock is older than the host rock.
Principle of Fossil Succession
assemblages of fossils contained in strata are unique to the time they lived and can be used to correlate rocks across a wide geographic distribution.
Lithostratigraphy
"rock time", classified in formations or groups, described spatially (ie upper/lower)
Chronostratigraphy
"time time", classified in periods, eras, or epochs, described temporally (ie late/early)
isotopes
slight variations of the same element/compound.
alpha decay
releases alpha particle (2 protons, 2 neutrons).
beta decay
neutron breaks down to a proton and an electron.
electron capture
electron + proton = neutron.
half-life
the time it takes for half a substance to break down.
radiocarbon dating.
dating technique that uses carbon-14, which decays to nitrogen-14 via beta decay.
isochron techniques
dating techniques that bypass assumptions about starting ratios of parent and daughter isotopes.
luminescence dating
dating technique that measures the time elapsed since some silicate minerals were last exposed to light or heat at the surface of the Earth.
fission track
dating technique that relies on damage to the crystal lattice produced when unstable uranium-238 decays to the daughter product and releases an alpha particle and leaves a visible track of damage.
actual preservation
a rare form of fossilization where actual materials of the organism or hard parts are preserved.
permineralization
occurs when an organism is buried and elements in groundwater impregnate all spaces within the body.
carbonization
occurs when the organic tissues of an organism are compressed, the volatiles are driven out, and everything but the carbon disappears, leaving a carbon silhouette of the original organism.
trace fossils
indirect evidence (ie burrows/footprints).
ionic bond
forms between a positive ion and a negative ion when
covalent bond
forms when atoms share electrons so that all have filled electron cells.
1st mineral characteristic
naturally-occurring.
2nd mineral characteristic
(mostly) inorganic.
3rd mineral characteristic
solid
4th mineral characteristic
crystalline structure.
5th mineral characteristic
definite chemical composition.
solidification.
when molten rock material cools and forms minerals.
precipitation.
when minerals form out of a fluid.
biomineralization.
when minerals are produced by living organisms.
diffusion.
when minerals form slowly through the migration of atoms through the crystal while the crystal remains in a solid state.
the three ways minerals are destroyed.
melting, dissolving, chemical reactions.
Minerals are classified by their ________ ___________ and __________ _________.
chemical composition, crystalline structure.
silica tetrahedron
the SiO4 unit, a fundamental building block of silicate minerals.
silicate minerals
the most dominant substances comprising Earth's crust and mantle.
isolated tetrahedra
silicate minerals with this do not share any oxygen atoms and are bonded by cations.
single-chain silicates
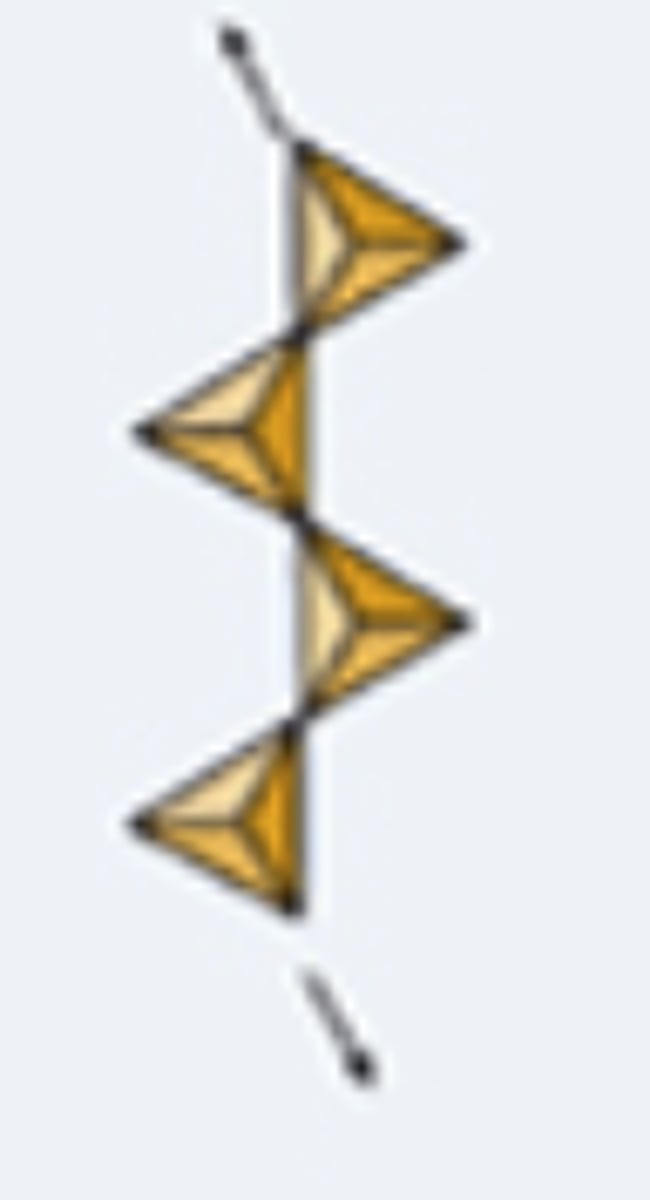

double-chain silicates
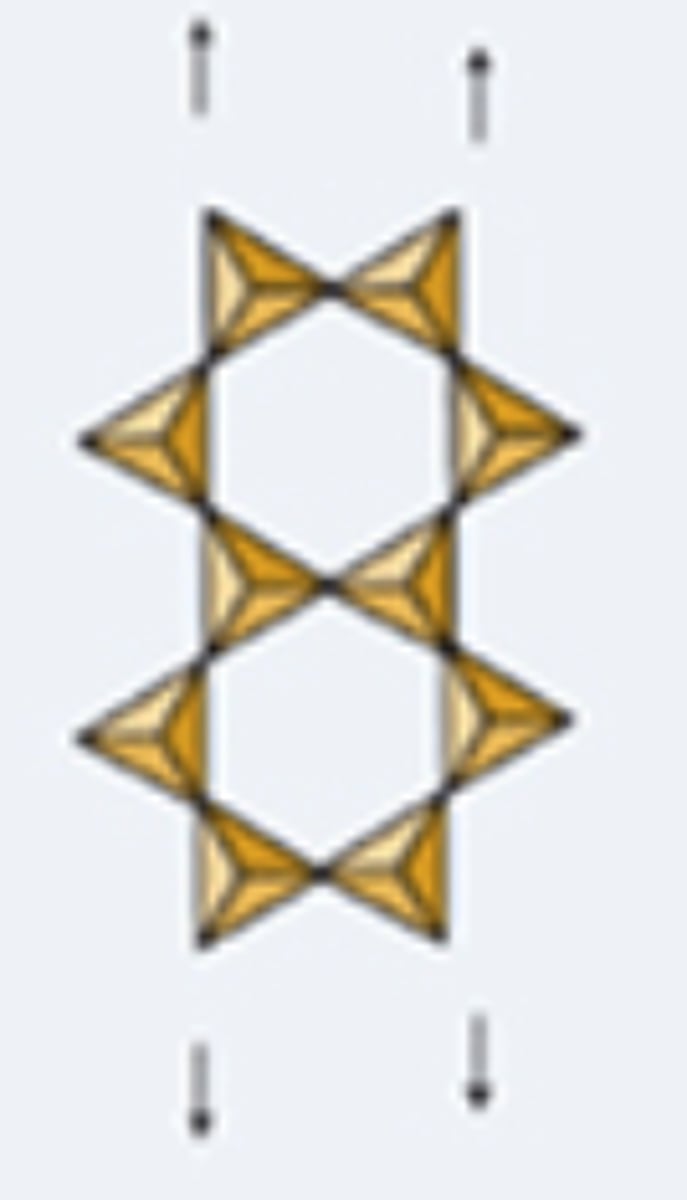
sheet silicates
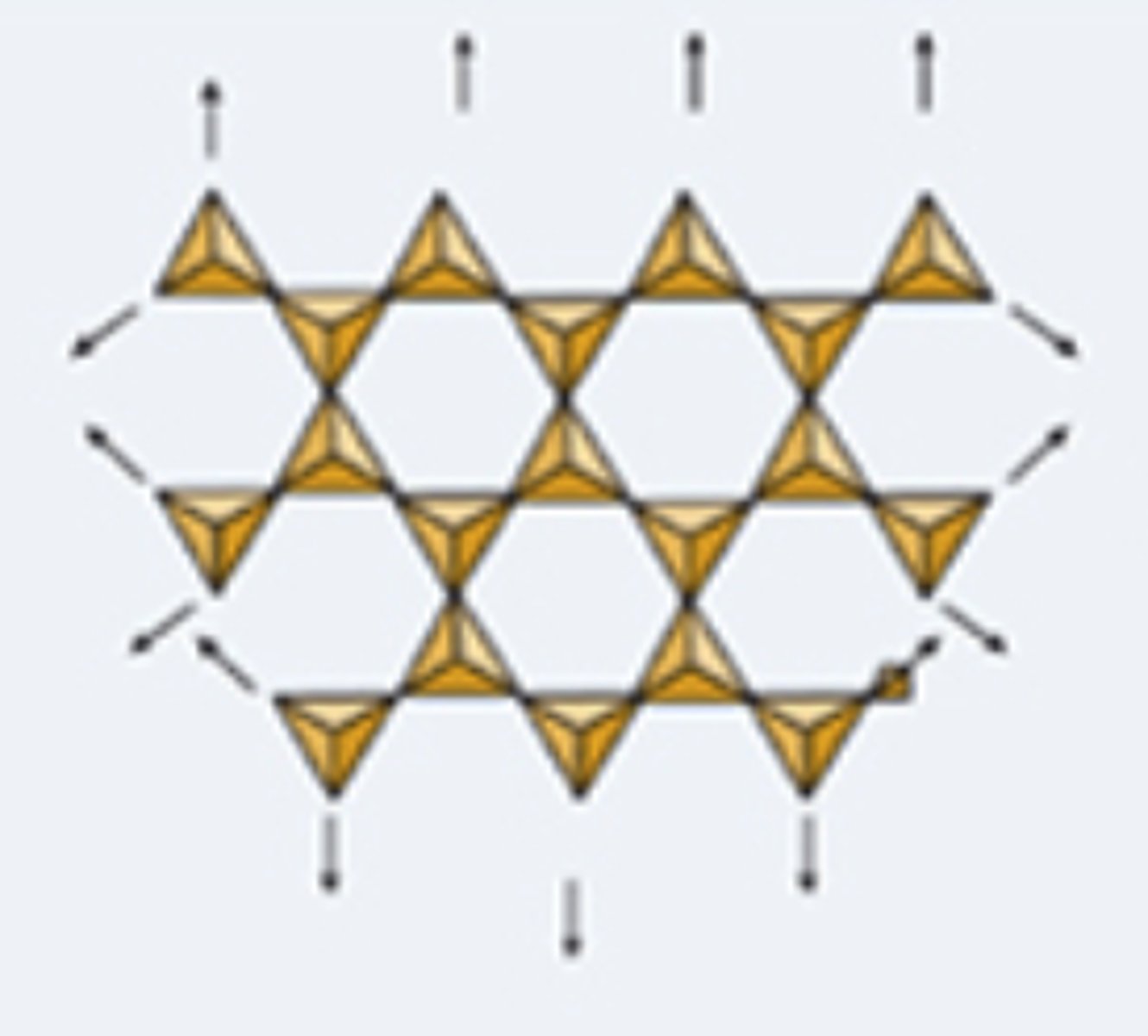
framework silicates
mineral identifiers.
color, streak, luster, hardness, density, crystal shape, cleavage, reaction to acid, fracture tendency.
rock
a coherent, naturally occurring solid, consisting of an aggregate of minerals or a mass of glass.
clastic rocks
held together by cement.
crystalline rocks
held together by interlocking crystals.
bedrock.
attached to Earth's crust. an exposure is called an outcrop.
rock composition
proportions of chemicals that make up the rock and affect minerals present in rocks.
rock texture
the configuration of grains in a rock and how those grains connect.
rock layering.
rock identification, defined by bands of different compositions, grain sizes, textures, or alignment of grains.
rock foliation.
rock identification, defined by the difference in mineral composition.
igneous rock
forms from molten material.
sedimentary rock
forms by cementation or precipitation, form layers like book pages, record history of ancient events/environments.
metamorphic rock
forms when pre-existing rocks change character due to a change in temperature and/or pressure conditions; can be any type of rock.
Plate Tectonics
A theory stating that the earth's surface is broken into plates that move.
Alfred Wegener
A German scientist who proposed the theory of continental drift.
Continental Drift
The hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations.
Glacial striations
scratches and grooves on bedrock caused by glacial abrasion.
Glacial deposits
found in regions where glaciers do not occur today.
Coal deposits
produced in equatorial swamplands, but are found at much cooler latitudes today.
The same fossil organisms occur on many of the southern continents? T/F
true
Rafting Hypothesis
previous theory to explain fossil distribution - organisms on large pieces of land drift out and colonize new area.
Isthmian Links Hypothesis
previous theory to explain fossil distribution - long, narrow land bridges between continents.
Island Stepping Stones Hypothesis
previous theory to explain fossil distribution - organisms hopped between islands.
HMS Challenger
The first major oceanographic expedition, 1872-1876, discovered the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Marie Tharp
A geologist and an oceanographer who mapped the ocean floor and proved plate tectonics.
Global Seismic Network
created during Cold War to detect atomic bombs but used for earthquakes as well.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Tracks vertical and horizontal movement of Earth's surface; tracks the motion of tectonic plates at rates of 1-10 mm/yr.
Arthur Holmes
geologist/physicist proposed convection was the driving force behind continental drift.
divergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other.
narrow continental rift
zone of extension, but NOT a divergent plate boundary until oceanic lithosphere is formed. Ex: East African Rift.
wide continental rift
zone of extension, but NOT a divergent plate boundary until oceanic lithosphere formed. Ex: US Basin.
oceanic spreading center
divergent plate boundary between oceanic plates. Ex: Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
convergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other.
subduction
One plate going under another plate, can be continental-oceanic or oceanic-oceanic.
collision
occurs between continental-continental lithospheric plates.