The Adrenal glands
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Adrenal Cortex
Derived from mesoderm of same region that gives rise to gonadal tissue; makes up 90% of the adrenal gland at age 3, the 3 layers develop
Adrenal Medulla
Functionally part of sympathetic nervous system developing from neural crest cells give rise to postganglionic sympathetic neurons; secretes catecholamine hormones
Classification of arteries
Short capsular arterioles, intermediate cortical arteries (long branches that go through cortex to the medulla), medullary sinusoids
Adrenal Gland physiology
Produces regulatory hormones
Adrenal Cortex physiology
Mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, anabolic and sex hormones
Adrenal Medulla physiology
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, stress-response hormones under direct autonomic nervous system control
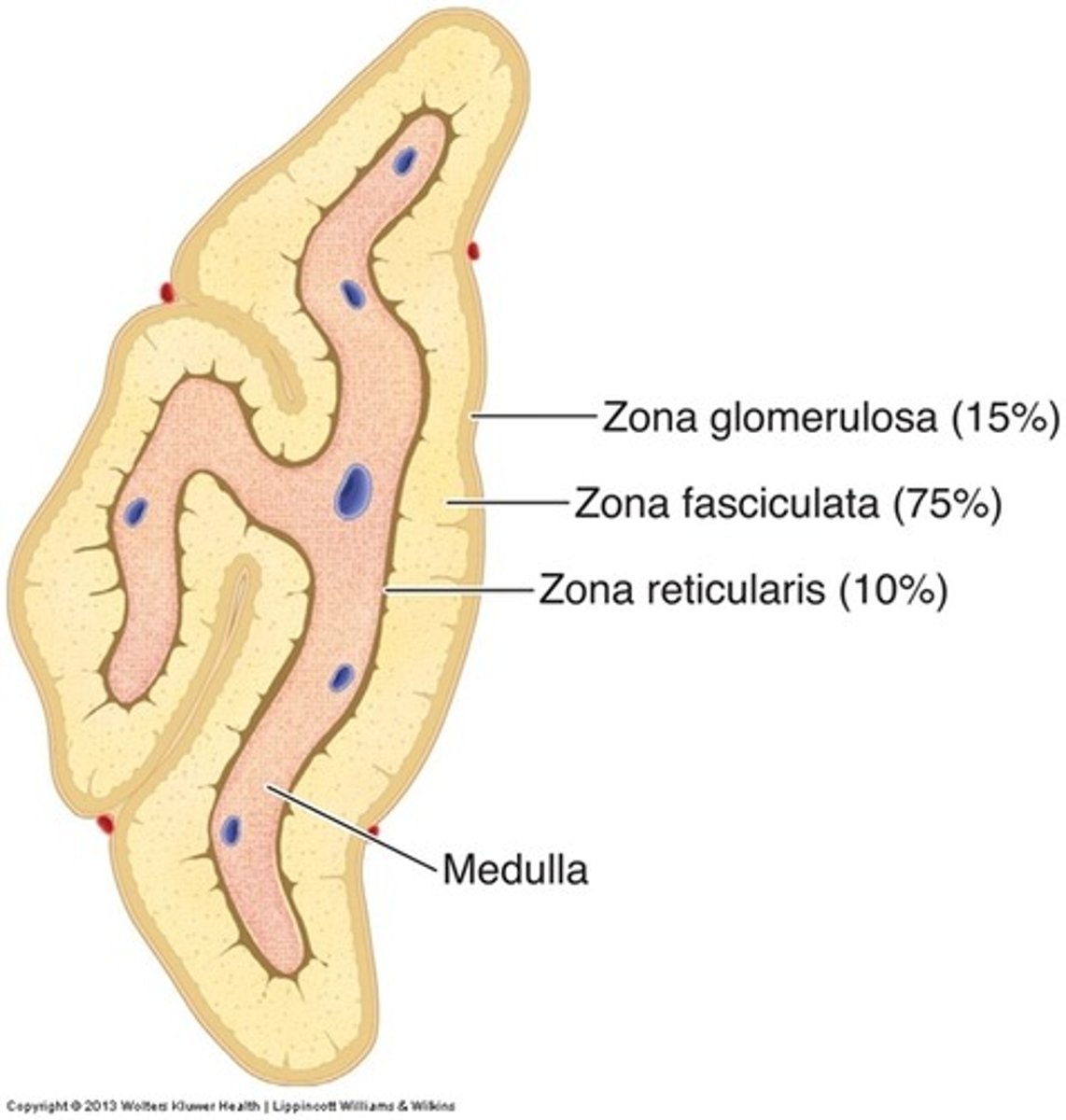
Zona glomerulosa hormone
Aldosterone: responsible for 95% of mineralocorticoid hormone activity
Zona glomerulosa function
Regulates sodium and potassium levels, which affect fluid and electrolyte homeostasis, including extracellular fluid volumes. Primary activation through renin-angiotensin system
Zona glomerulosa regulation
Complex process; release triggered by: dehydration, sodium deficiency, hemorrhage or elevated potassium levels. ACTH has minor role in stimulation secretion
Zona fasciculata hormone
Glucocorticoids, including cortisol or hydrocortisone (most abundant), cortisone, and corticosterone
Zona fasciculata function
Major effect on metabolism of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates; encourages fat storage. When more energy is required, assists in gluconeogenesis, which helps resist both mental and physical stress. Hormones trigger anti-inflammatory and immune-suppress responses
Zona fasciculata regulation
High stress or low blood concentration (negative feedback mechanism)
Zona reticularis hormone
Secretes male & female gonadocorticoids (estrogens & androgens)
Zona reticularis function
Promotes normal development of bones and reproductive organs; affects secondary sex characteristics but not as much as hormones from ovaries and testes
Zona reticularis regulation
Low blood concentration (negative feedback mechanism)
Hormones secreted by Adrenal Medulla
Catecholamine, Epinephrine (adrenaline) 80% and norepinephrine (noradrenaline),
Release of epinephrine and norepinephrine
Stimulated through sympathetic nervous system
Hormone secretion is controlled by
Autonomic nervous system
Testing medullary function
24 hour ruined samples used for catecholamines, metanephrines measured in urine, dopamines measured via blood or urine samples
Agenesis
Most important congenital disorders are adrenocortical hyperplasias; causes alterations and increases in steroid synthesis
Anecephalic fetus
Usually stillborn, adrenal gland consists only of provisional cortex with no fetal zone; causes either cerebral pituitary or hypothalamic
Cytomegalic type
Unknown cause, unusual adrenal cortex made up of large eosinophilic cells, gland weighs <1 g; with early diagnosis, replacement steroid therapy promotes long-term survival
Ectpopy
Consist mainly of accessory cortical material and can occur anywhere from diaphragm to pelvis including: kidney, liver, retroperitoneal tissues, ovary, testes and tissues accompanying spermatic cord