GEOL EXAM #3 QUIZ QUESTIONS
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Isobars on weather maps refer to lines of constant
pressure
Atmospheric pressure _______ with altitude.
decreases
What force causes the wind to blow?
pressure gradient force
A large air mass moves from east to west in the Northern Hemisphere mid latitude. What is the direction of the Coriolis force acting upon the air mass?
from south to north
Which of the following best describes friction?
Friction is always opposite of wind direction
If a wind is blowing from the land to the ocean, how would you call it in terms of direction?
offshore wind
What is the primary driver of large-scale winds?
pressure gradient
What is this wind direction shown on a map?
Northerly wind
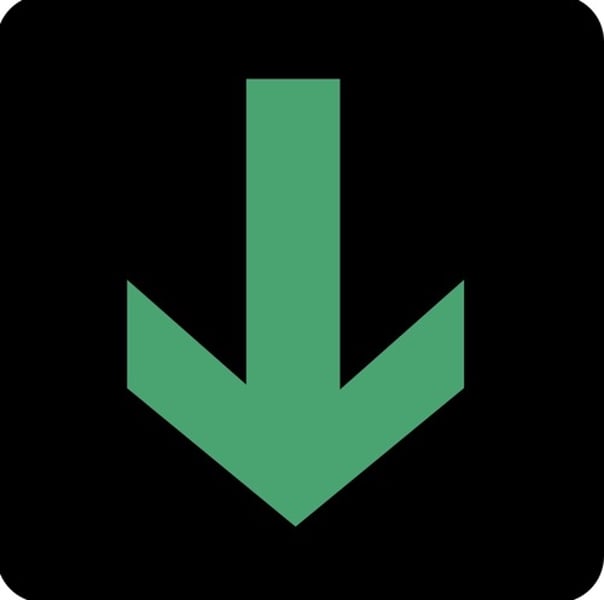

Which of the following best describes surface winds around cyclones in the Northern Hemisphere?
Counterclockwise and spinning inwards toward the center
Click on the wind band of trade winds
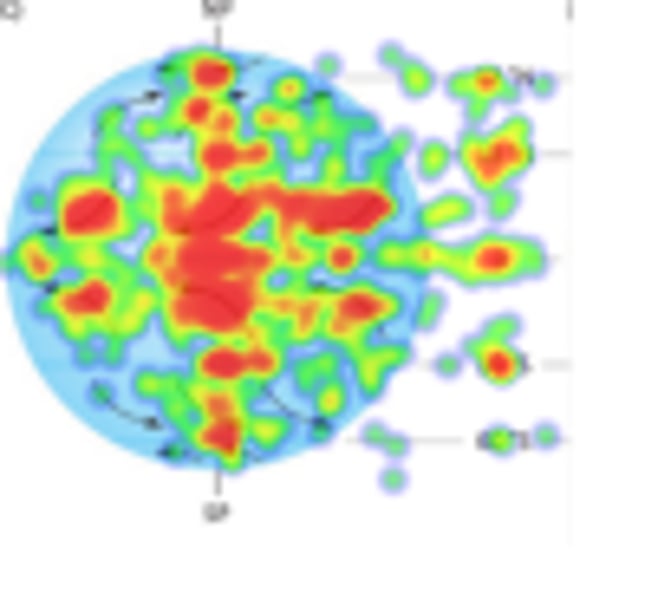
Click on where the ITCZ is.
The world's deserts are found at 30o latitude because?
of the sinking air of the subtropical highs.
Which of the following best describe the direction of northern hemisphere jet stream?
Westerly
What is meridional flow?
north-south airflow
What is the WRONG description of blocking pattern?
Blocking pattern causes fair weather
Arctic amplification refers to the fact that the Arctic is warming _______ the Northern Hemispheric mean.
faster than
Cold front is located to _____ of the cyclone center.
the south
What is the wrong description of upwelling and downwelling?
In coastal upwelling, the surface layer of warm, nutrient-deficient water thickens
Where does deep water form in the Northern Hemisphere?
North Atlantic
Atlantic meridional overturning circulation describes the primarily ______ movement of warm surface water and _______ movement of cold deep water.
northward, southward
During neutral conditions in the tropical Pacific, warmer SST is located on the _____ side of the Pacific.
west
Weaker trade winds will lead to ___ conditions in the eastern tropical Pacific and ______ will likely to arise.
warmer, El Niño
Weaker trade winds will lead to _ conditions in the eastern tropical Pacific and ____ will likely to arise.
warm, El Nino
Which of the following will occur when trade winds across the tropical Pacific strengthen?
La Nina
The biological pump in the ocean ___ CO2 in the atmosphere.
decreases
How will Sea-level change when the floating ice in the ocean melts?
does not change
Solar changes are _______ factors to the Earth's climate system.
external
With more sunspots, the Sun conveys more energy to Earth. Is it true?
yes
Which variations doesn't Milankovitch cycles include?
sunspot
In the present day volcanos affect the Earth's climate mainly through the release of _______ and ashes.
SO2
Which type of feedback is the ice-albedo feedback?
positive
Which decay of organic matter generates methane?
Anaerobic decay
The Keeling curve shows the increasing trend of which greenhouse gas in the atmosphere?
CO2
Methane release from melting permafrost is a _________ feedback
positive
Which type of aerosols exert an overall cooling effect on the climate?
sulfate
The net radiative forcing to the present climate is _______.
anthropogenic