307 EXAM 1
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
What is The equation expressing the consumer’s indifference between various alternative choices or attributes of this choice?
Utility Function
What is the step that predicts number of trips produced and attracted by a zone
Trip Generation
What is the model commonly used to determine trip distribution
Gravity Model
What is the type of traffic assignment that results in the same travel time for different route choice
User equilibrium
What is the final product of the four-step process
Flow on links in a network
What does FHWA stand for?
Federal Highway Administration
What are: Highway, Rail, Water, Air, Pipeline
What are Transportation Modes
What are: Congestion & Safety
Critical Issues in Transportation
What is the average vehicle occupancy during peak periods in the US
About 1.1
Planning, design, and operations are what?
What are the Chronological phases of transportation projects
Headway, spacing, gap, clearance are what?
What are the microscopic traffic parameters
Speed at zero flow is what?
Free-Flow Speed
Linear relationship between speed and density is what?
What is Greenshields Model
The type of speed commonly used in traffic engineering analysis is what
What is the space mean speed
Queuing system with uniform arrival and departure is what?
What is the Deterministic Queuing System
This uniquely determines LOS for freeway basic segment is what?
What is denisty
What is the commonly used design LOS (level of service)?
What is LOS C
Lane width, lateral clearance, ramp density are what?
What are Factors affecting free-flow speed
Terrain type or grade % and length are what
What are Factors determining heavy vehicle equivalent factors
(Maximum) Freeway lane capacity is what
What is 2400pcphpl (per car per hour per lane)
What is this formula: AADT x K x D
What is Directional design hour volume (DDHV)
% of time a section of freeway is occupied by vehicles is what?
What is Percent Occupancy (Lane occupancy)
Main logic of microscopic traffic model is what?
What is Car-following and lane change
Volume, speed, travel time, delay,
accident, parking, pedestrian, … are what
What are Types of traffic studies
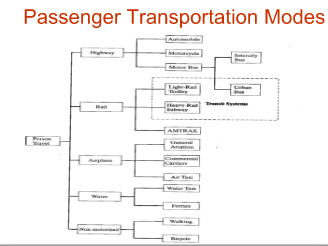
What is Intermodal Transportation
A trip that involves more than one mode of transportation

What is recurring Congestion
Caused by routine heavy traffic

What is non-recurring congestion
Caused by unexpected or unusual congestion caused by unexpected events

What are the effects of congestion
Undermines effectiveness and efficiency of the system
Cost to user: Delay, gas, accidents/crashes
Negative impacts on economic prosperity

What is Macroscopic traffic flow modeling?
Look at the flow in an aggregate sense, flow-speed-density relationship

What is Microscopic traffic flow modeling?
Consider the behavior of individual vehicles in a disaggregate manner

What are 3 macroscopic variables
Density (k)
Flow (q)
Speed (v)

What are 3 microscopic variables
(individual) speed (u)
Headway (h)
spacing (s)

What is spot Speed
The speed taken at a fixed roadside point (ui)

What is Space Mean Speed
Average speed of all vehicles occupying a given section of a highway over some specified time interval

What is Time Mean Speed
Average speed of all vehicles passing a point or short segment of highway over some specified time interval

What is Volume (V)
The actual number of vehicles passing a point during a given time interval (usually one hour or longer)
Flow rate (q):
The number of vehicles passing a point during a time interval less than one hour (usually 15 min.), but expressed as an equivalent hourly volume

What’s the equation for AADT?
AADT = # vehs observed in a year/# days in a year (365

What is Design Hourly Volume (DHV)
Demand over one hour period in peak hr
May be measure by direction
Uses of hourly volumes
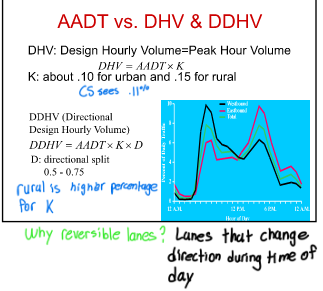
What is the difference between DHV and DDHV
DHV = AADT * K
DDHV = AADT * K * D

What’s the difference between the Peak Hour Volume (PHV) and the Peak Hour Flow Rate?
PHV = Highest Hourly volume (“Rush hour” volume)
Peak hour flow rate = Based on counts within peak hour, less than one hour in length

What is peak hour factor
Ratio of total hourly volume to the maximum 15-minute flow rate

What is Density/Concentration (K)
The number of vehicles occupying a given length of lane or roadway averaged over time
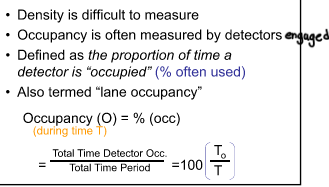
What is Occupancy?
The proportion of time a detector is “occupied” (% often used)

Density vs Occupancy
• Lv: Average vehicle length
• Measure from a specific detector in a lane
• Unit: vehicles per mile per lane

What is spacing?
Distance between two successive vehicles in a traffic stream. (From front bumper to front bumper)
Units: meters or feet

What is Headway?
Time difference (interval) between two successive vehicles as they pass a point on a roadway
Units: Seconds or minutes

What is clearance?
Distance between two successive vehicles in a traffic stream, from back bumper of the lead veh. to front bumper of the follower veh.
Units: meters or feet

What is gap:
Time interval between the back bumper of the lead veh. to front bumper of the follower veh. as they pass a point on a roadway.
Units: Seconds or minutes
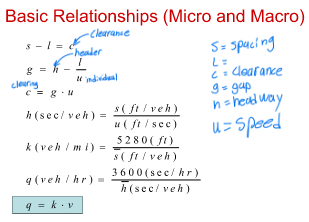
Basic Relationships
Between Micro and Macro
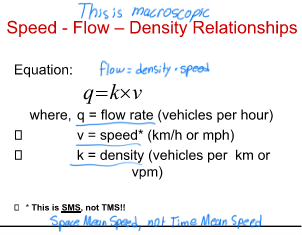
What is
Speed - Flow – Density Relationships

What are traffic studies types
• Volume study /traffic counts
• Speed study
• Travel time study
• Delay study
• Density study
• Other special studies
Crash
Parking
Pedestrian
Calibrationg

What are the travel time studies
Travel time
Runing time
Travel-time delay
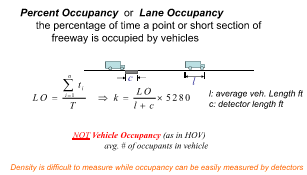
Percent Occupancy or Lane Occupancy
The percentage of time a point or short section of freeway is occupied by vehicles
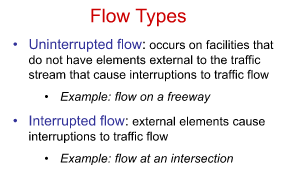
What are the two flow types
Uninterrupted flow
Interrupted flow
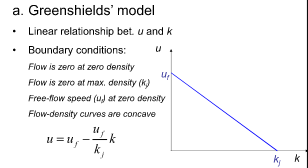
What traffic flow model is uninterrupted flow & macroscopic
Greenshields’ model

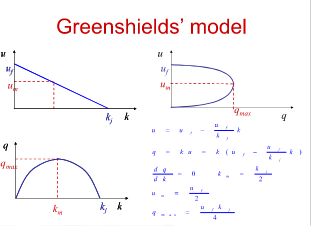
What is the Greenshields model
Different graphs
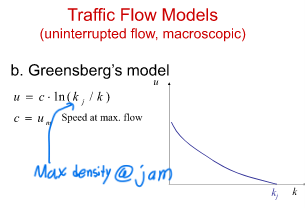
What is greensberg’s model equation
c = um = speed at max
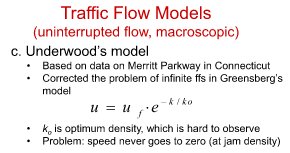
What is underwood’s model
Based on data on Merritt Parkway in Connecticut
• Corrected the problem of infinite ffs in Greensberg’s
model
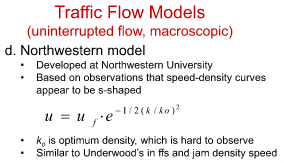
What is Northwestern model
• Developed at Northwestern University
• Based on observations that speed-density curves appear to be s-shaped
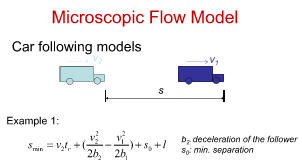
What is an example of a microscopic flow model
Car following models

What is
Example of macro/micro traffic variables
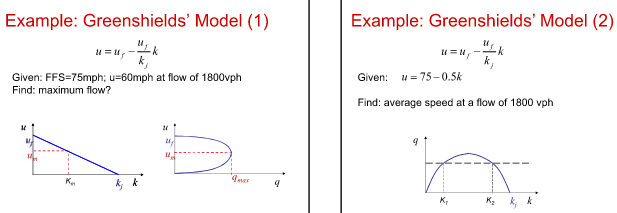
What is
Example of Greenshields’ Model
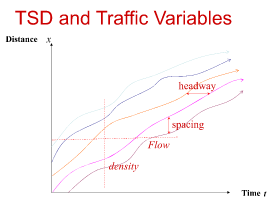
What are the
TSD and Traffic Variables on the graph

What are some queuing characteristics of
• Arrivals: lamda (rate, distribution)
• Servicing: mug (rate, distribution)
• Queue discipline: (FIFO, LIFO)
• Number of channels (m)

What are the two types of queuing
Deterministic: If both arrival and servicing rates are uniform
Stochastic: If arrival or servicing rate is not uniform
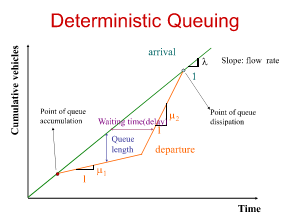
What is the deterministic queuing graph
– Arrival and servicing are uniform (same interval,
no randomness)
– arrival and service rates may vary over time
– Can be used to temporary blockage, temporary overloading, and periodical interruption

What is
Deterministic queuing example
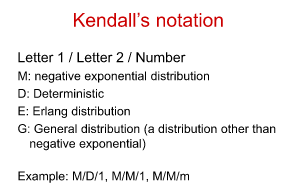
What is Stochastic Queuing and Kendall’s Notation
Letter 1 / Letter 2 / Number
– Letter 1: arrivals process
– Letter 2: service process
– Number of channels (servers)
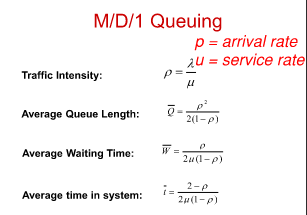
What are the
M/D/1 Queuing
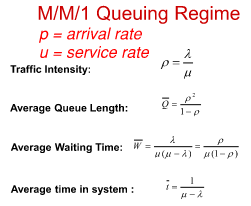
What are the M/M/1
Queuing Regime

What are
Capacity and Level of Service
What agency is FHWA
Federal Highway administration
How can you determine the directional design hourly volume (DDHV) from AADT
Multiply it by D+K, the directional distribution + density for that area (urban vs rural)
If the average demand exceeds the average capacity, what will happen when applying stochastic queueing equation?
The system will break down
What is the definition of non-recurring congestion?
Congestion caused by unexpected events like a wreck, construction lane closures, bad weather
List three examples of traffic studies
Pedestrian
Travel time
Crash
What LOS level is most commonly used for design of a basic freeway segment
LOS C
What is the most commonly used method to determine trip production and attraction?
Use ITE’s trip generation manual for that specific use
What is the relationship between space mean speed and time mean speed? Under what condition these two measures can be equal in value?
TMS is greater than SMS becasue TMS accounts for the variance in speeds. If all cars were traveling at the same speed over a section of highway, then SMS = TMS
What is a utility function?
A function that describes a user’s difference towards route choice
How should the free-flow speed be measured in the field?
Measure speed under low traffic conditions, like under 1,100 pc/hr/ln
According to HCM 2010, passenger car speeds are considered to be unaffected by the grade of a freeway segment
True
Capacity is achieved at the maximum speed.
False: at half of Free Flow Speed
Density is not easy to measure directly in the field
True
Trip distribution determines the routes for all trips
False: Trip assignment
The Greenshields’ model assumes a linear relationship between speed and flow.
False: Between speed + density
The final product of the 4-step planning process is:
Flow on links
Which of the following is NOT considered to affect the free-flow speed of a freeway basic segment according to the HCM procedure
Heavy Vehicle Percentage
Which variable is affected by the lengths of the vehicles for a given flow rate?
Gap
The following is NOT a macroscopic traffic parameter:
Headway
The variable that uniquely determines the LOS of a freeway basic segment is :
Density
List three examples of traffic studies:
Accidents
Delay
Density
What is the final product of a transportation planning process?
Flow of travel routes shown on a network
On an upgrade segment, the impact of the grade on how trucks lose speeds is assessed based on the percentage of the grade?
False
Capacity is achieved at the maximum speed;
False
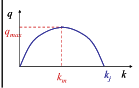
According to the Greenshields’ model, there is a nonlinear relationship between flow and density.
True: It is a parabola
Trip distribution determines the number of trips produced at and attracted to a zone
False
Logit model is often used to determine route choice
False
What is an HOV lane? What purpose does an HOV serve?
HOV lane is a traffic lane reserved for buses or vehicles with several occupants, typically marked with large diamond shapes on the pavement.