BME 302
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
stroke volume is proportional to end-diastolic volume
the Frank-Starling law states:
vasoconstriction, platelet plug, exposed collagen, thrombus
the steps of hemostasis are
filtration, leaky cell junction, solute concentration, absorption
in capillaries, hydrostatic pressure drives _____ through ____ ____ ____, whereas osmotic pressure depends on _____ ______ and drives _____
fill in the blanks

skeletal, cardiac, smooth
muscle cell types listed in order of twitch speed from fastest to slowest
false
true or false: smooth muscle has sarcomeres
acetylcholine
which neurotransmitter is released by somatic motor neurons
true
true or false: muscle fibers run the whole length of the muscle
phasic, tonic
what are the two types of smooth muscle contraction patterns?
cell, axon terminal
in single-unit smooth muscle; in multi-unit smooth muscle, each ___ has a ___ ___
false
true or false: smooth muscle has nebulin and titin
tropomyosin, actin binding site
the power stroke of the myosin head begins when _____ moves off of the ____ ____ ____
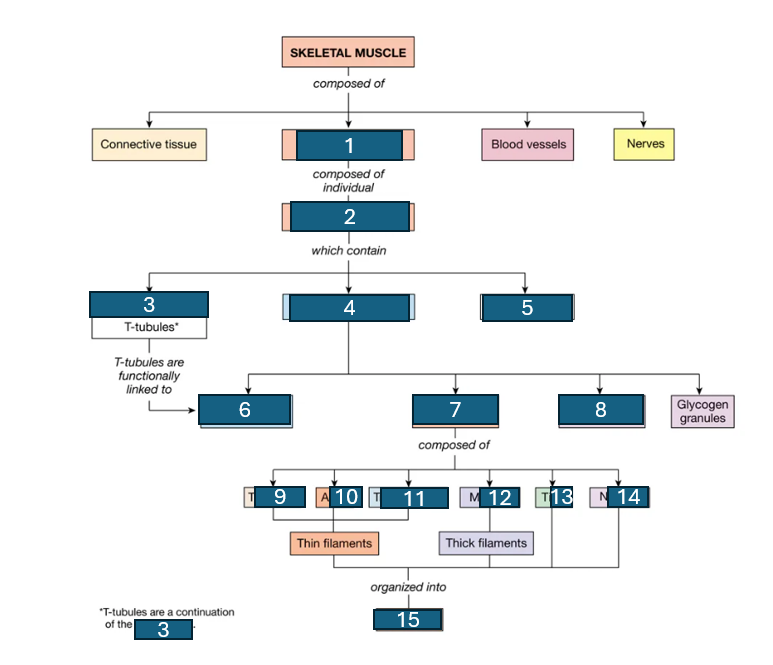
muscle fasicle, muscle fiber, sarcolemma, sarcoplasm, multiple nuclei, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibrils, mitochondria, troponin, actin, tropomyosin, myosin, titin, actin, sarcomere
fill in the blanks
ATP, myosin, myosin, ATP, power stroke, myosin, ADP
steps of the contraction cycle
__ binds to __
__ hydrolyzes __
__ __ begins
__ releases __
ATP, ADP, myosin, myosin, G-actin
in the rigor state, no __ or __ is bound to __, and the __ are tightly bound to __ -__ molecules
G-actin
F-actin is the result of multiple polymerized ____ molecules
false
true or false: the Hagen-Pousille equation is applicable to gases
I band, H zone, A band, Z disks
during contraction of a sarcomere, the ___ and ___ shrink, while the length of the ___ remains constant, bringing the ___ of the sarcomere closer together
A band, I band, H zone, Z disk, M line
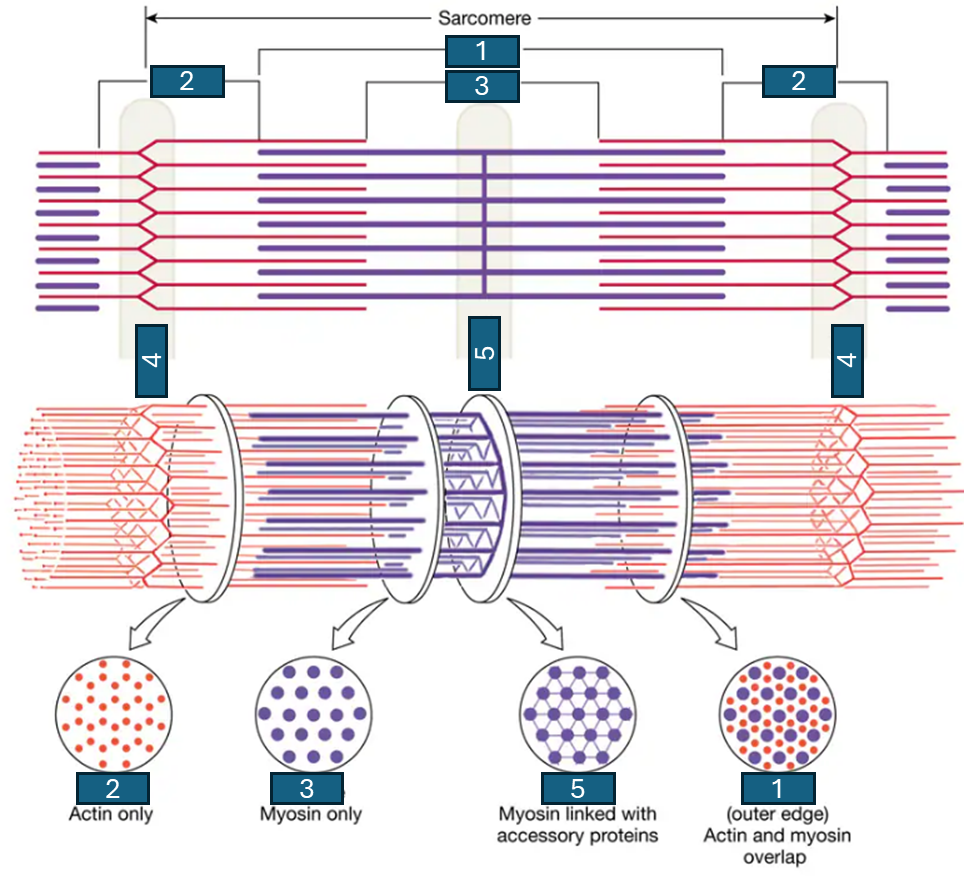
fill in the blanks
titin, nebulin
the two accessory proteins that ensure alignment of filaments within a sarcomere are ___ (which is ___) and ___ (which is ___)
phosphocreatine
which molecule is the backup energy source for muscles?
central fatigue is caused by the ___, while peripheral fatigue can arise from communication failure at the __ ___ or failure of the ___ ___ ___
false
true or false: lack of ATP is a factor in muscle fatigue
slow-twitch fibers, fast-twitch oxidative glycolytic fibers, fast-twitch glycolytic fibers
what are the 3 types of muscle fibers
myoglobin, mitochondria, capillary blood
slow-twitch oxidative muscle has more red ____, ____, and ___ ___supply compared to fast-twitch glycolytic muscle
events at neuromuscular junction, excitation-contraction coupling, Ca2+ signal, contraction relaxation cycle, muscle twitch, sliding filament theory
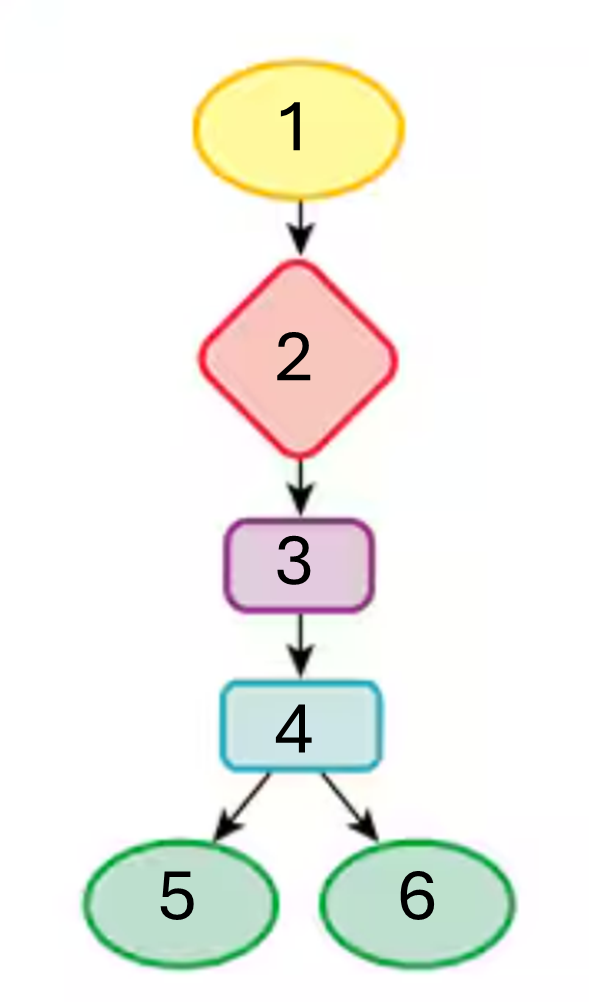
fill in this map of the events in muscle contractions
true
true or false: all muscle fibers in a single motor unit are of the same fiber type
muscle twitch
a single contraction-relaxation cycle is also known as a __ __
ACh, Na+, ACh, action potential
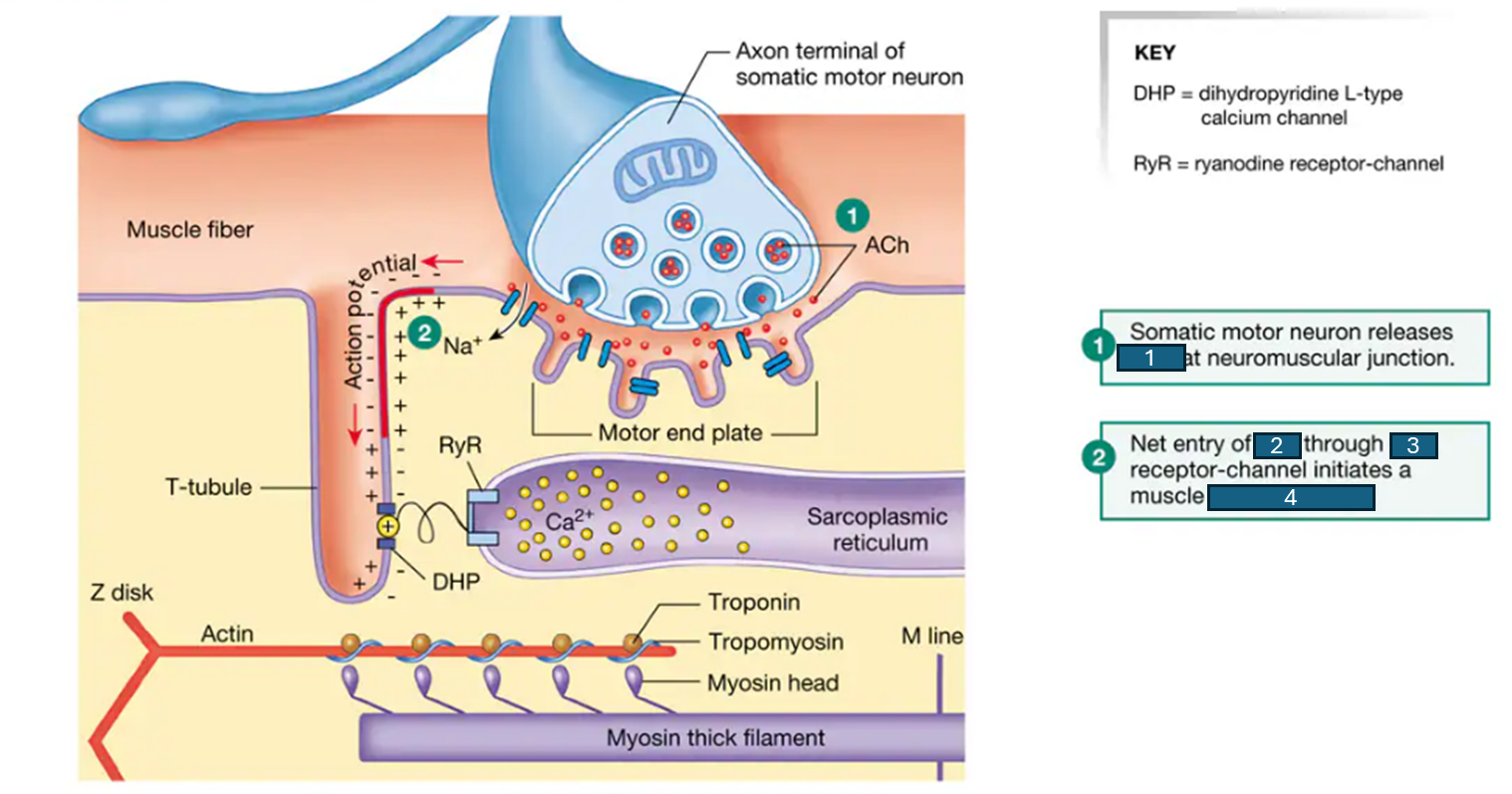
steps of muscle AP initiation: fill in the blanks
t-tubule, DHP, Ca2+, sarcoplasmic reticulum, Ca2+, cytoplasm, Ca2+, troponin, actin-myosin, myosin, actin, sarcomere
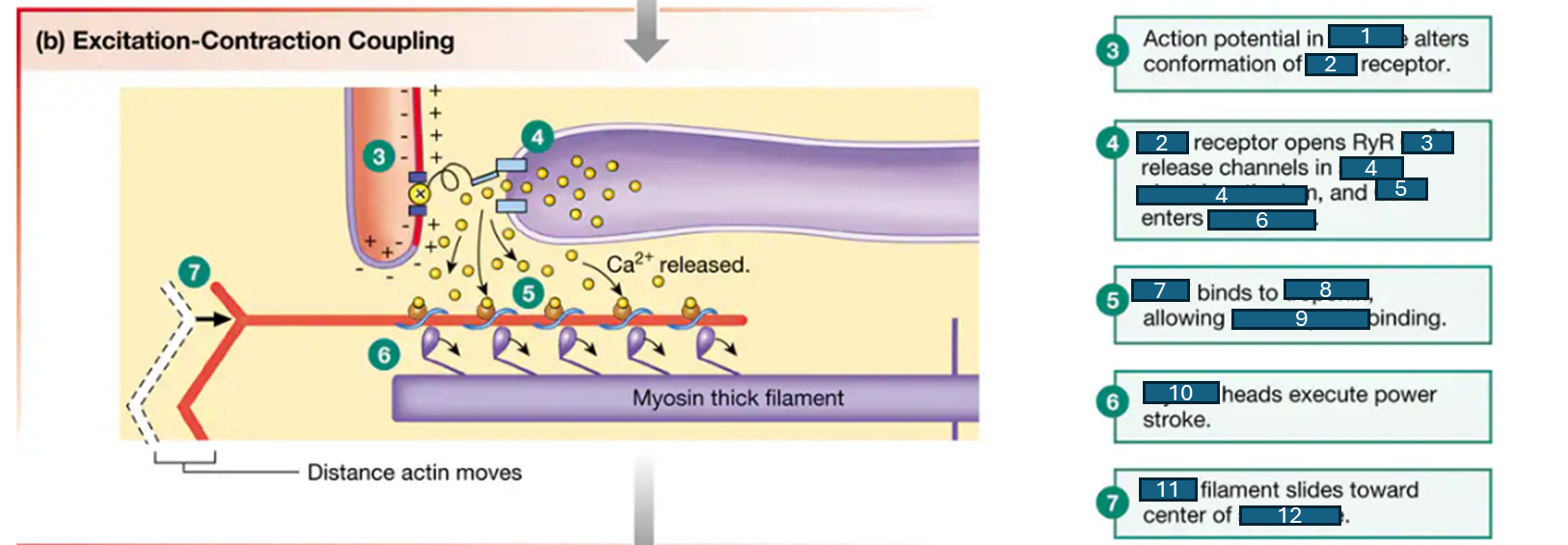
steps of excitation-contraction coupling: fill in the blanks
Ca2+ATPase, Ca2+, Ca2+, troponin, tropomyosin, myosin
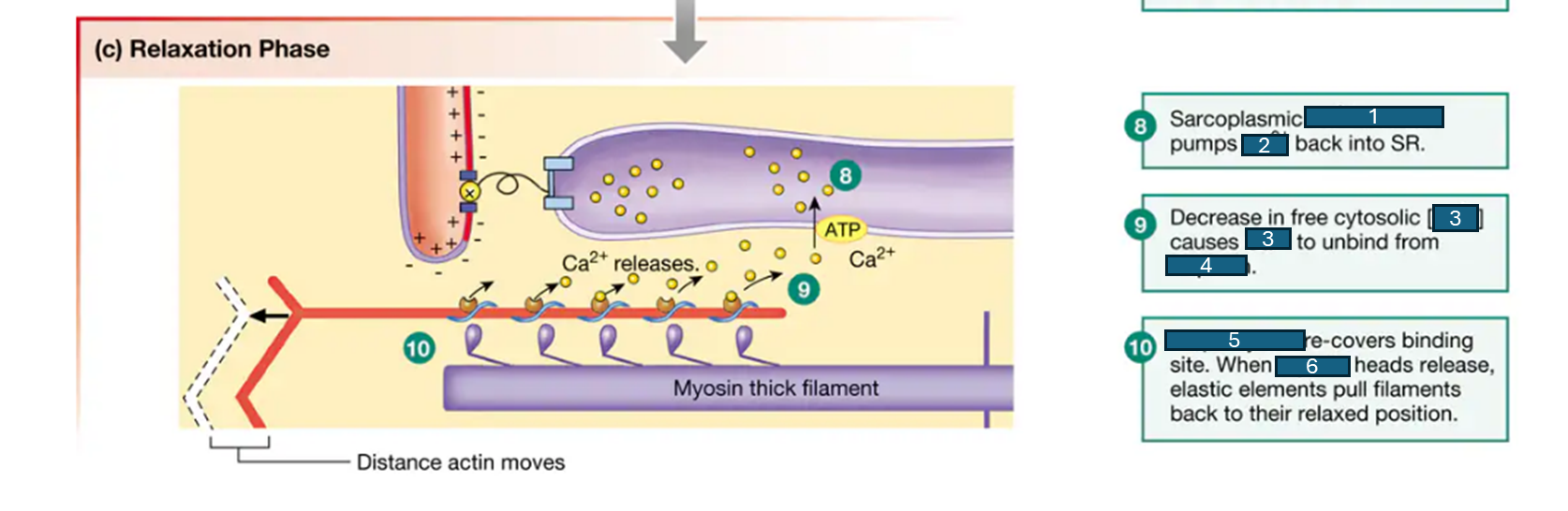
relaxation phase: fill in the blanks
skeletal, cardiac
muscle types that are striated
smooth muscle, cardiac muscle
muscle types that are electrically linked
cardiac muscle
muscle type with gap junctions in intercalated disks
is equal to
blood flow to the lungs _____ blood flow to the rest of the body
I, II
type ___ alveolar cells are responsible for gas exchange, while type __ alveolar cells produce surfactant
flow, pressure
pulmonary circulation is high ___, low ___
macrophages, phagocyte
alveolar ____ ingest foreign material within the alveoli (they are a type of _____)
tidal volume
____ ____ is the volume that moves during a respiratory cycle
inspiratory reserve volume
____ ____ ___ is the additional volume above tidal volume
expiratory reserve volume
__ ___ ___ is the volume forcefully exhaled after the end of a normal expiration
IRV, ERV, VT
vital capacity is the sum of ____, _____, and _____
VC, RV
total lung capacity is the sum of ____ and ____
pleural pressure
_____ _____ is the constant negative pressure that keeps the lungs “inflated”
surface tension, smaller, pressure
the law of LaPlace states that if two bubbles have the same ____ ____, the _____ bubble will have higher ____
dead space
total pulmonary ventilation is greater than alveolar ventilation because of ___ ___
CO2, exhaled air
bronchiole diameter is mediated primarily by ___ levels in ___ ____ passing through them
dilate
as PCO2 increases, the bronchioles and systemic arteries _____ (dilate/constrict)
hypoxia, hypercapnia
_____ means too little oxygen, and _____ means increased concentrations of CO2
emphysema
what disease state does this represent

fibrotic lung disease
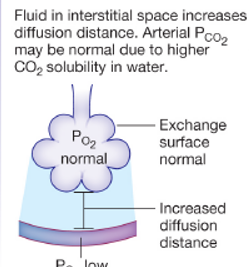
what disease state does this represent
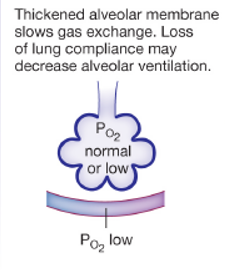
pulmonary edema
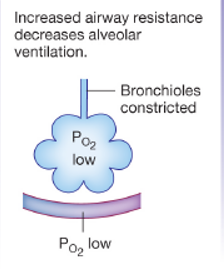
what disease state does this represent
asthma
what disease state does this represen
oxygen, carbon dioxide
____ (carbon dioxide/oxygen) is NOT very soluble in liquids, but _____ is (oxygen/carbon dioxide)
increasing, decreasing, increasing, 2,3 BPG
the following parameters shift the oxygen-hemoglobin binding curve right: ____ pH, ___ PCO2, ___ temperature, ___ amount of the metabolic compound ___
L * viscosity, r^4
resistance to air flow within a tube is proportional to…?
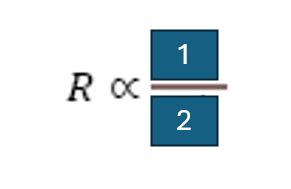
excretion, lumen, outsider the body, filtration, blood, lumen, reabsorption, lumen, blood, secretion, blood, lumen
the four processes of the kidney, list in alphabetical order, are
_______, involving movement from ____ to _____
_______, involving movement from ____ to _____
_______, involving movement from ____ to _____
_______, involving movement from ____ to _____
anaerobic
_______ (anaerobic/aerobic) metabolism is FAST but INEFFICIENT
glucose, lactic acid
anaerobic metabolism requires ______ and produces _____
false
true or false: myosin heads are released in unison at the end of a powerstroke
asynchronous
______ recruitment of motor units helps avoid fatigue
right
everything associated with an increase in metabolism (decrease in PO2, increase in PCO2, increase in pH, decrease in shifts the hemoglobin saturation curve to the ____
kidneys
erythropoietin is produced by the ____
hypertonic, hypotonic
red blood cells shrink in a ______ medium and grow in a _____ medium
plasma, hemoglobin
O2 dissolves in ____ first before being taken up by ______
true
true or false: temperature within the lungs more or less always remains at 37 C
venous return
end diastolic volume can be increased by increasing _______ _____
preload, contraction
_____ is the degree of stretch of the heart just before ______
carbaminohemoglobin, bicarbonate, carbonic anhydrase
while some carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin as _________, most carbon dioxide exists as ______ in the blood, lowering pH when protons are removed by _________
filtration, absorption
most capillaries show a transition from net ________ at the arterial end to net ________ at the venous end