3.1.1.2 MASS NUMBER AND ISOTOPES TOF + questionsss
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
How is atomic number presented
Z and is equal to number of protons
WHAT DOES MASS SPECTROMETRY DO?
Gives accurate information about relative isotopic mass + relative abundance of isotopes
What is the relative atomic mass?
The mean mass of an atom of an element divided by one twelfth of the mean mass of an atom of the carbon-12 isotope
What is meant by an isotope
Atoms of the same element
Same. Atomic number
Different number of neutrons
Therefore different mass number
What is meant by an ion?
When an atom loses or gains electrons
No overall charge
No longer neutral
An ion with one fewer proton one fewer neutron and the same number of electrons as an atom of 129xe

A particle with 2 fewer protons two fewer neutrons and the same number of electrons as an atom of 20ne
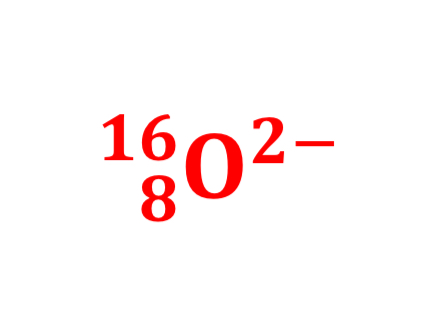
An ion with one more proton two more neutrons but the same number of electrons as an ion of 85RB+
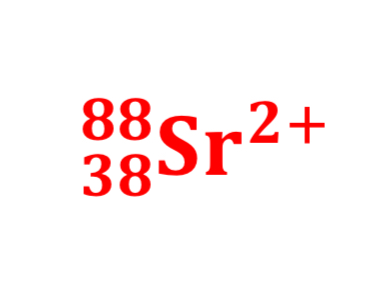
What does abundance mean?
How common each isotope is
What is mass spectrometry used for?
Molecular/ atomic Mass number
abundance of isotopes
What is TOF and what is it used for
Time of flight mass spectrometry
Differentiates molecules based on time taken for them to travel through the machine
What are all the stages called to T.OF
First it’s vapouriest to become a gas then placed into the spectrometer where its ionised
Ionisation
Acceleration
Ion drift
Detection
Describe the different types of ionisation
ELECTRON BEAM IONISATION - electron gun used to fire HIGH ENERGY ELECTRONS at sample
Electrons repel each other + TAKE ONE ELECTRON OFF ATOM OR MOLECULE + 1+ ion
(Used for low MR components and elements)
Electro spray IONISATION
SAMPLE IS DISSOLVED INTO A VOLATILE SOLVENT
Injected through a HYPER DERMIC NEEDLE turns sample into a mist at end of needle - HAS A HIGH VOLTAGE - CAUSES PARTICLES TO GAIN A PROTON = ION
X(g) + H(g)^+ >. XH(g)
Used for hgh Mr compounds EG PROTEIN
Describe acceleration
Accelerated by an electric field ( due to them being charged)
Negative on front (acceleration plate) to attract ions and positively charged at back (to repel further down)
AFTER THIS ALL PARTICLES HAVE SAME INETIC ENERGY
Would a heavier mass or lighter mass be have a higher velocity
LIGHTER MASS ISOTOPES OR MOELCULES WILL HAVE HIGHER VELOCITY
What happens in ion drift?
Positive ions endete Right tube
How are ions then detected in DETECTIONSTAGE
Negatively charged plate which makes a current produced when ions hit the place
MORE IONS= BIGGER CURRENT
Mass of ions hitting the detection plate can be picked up and forms the time of flight
What has to happen for detection to work?
PARTCILES MUST BE CHARGED
So that they can be attracted to negative and positive plates and move down the spectrogram
What is the layout of the mass spectrum
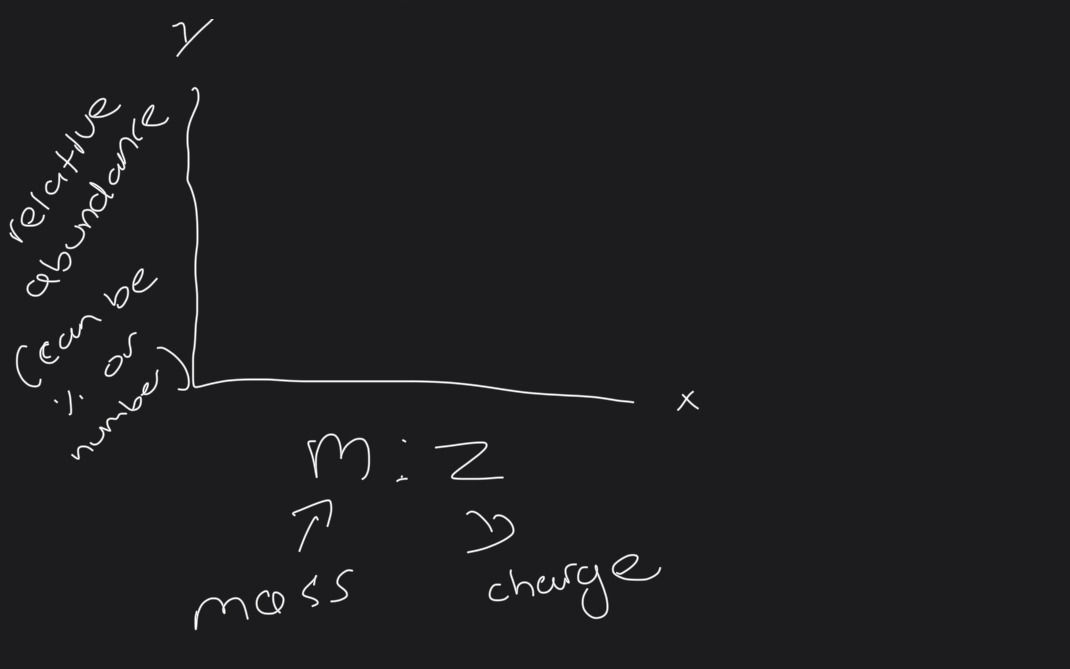
What is normally the charge?
+1
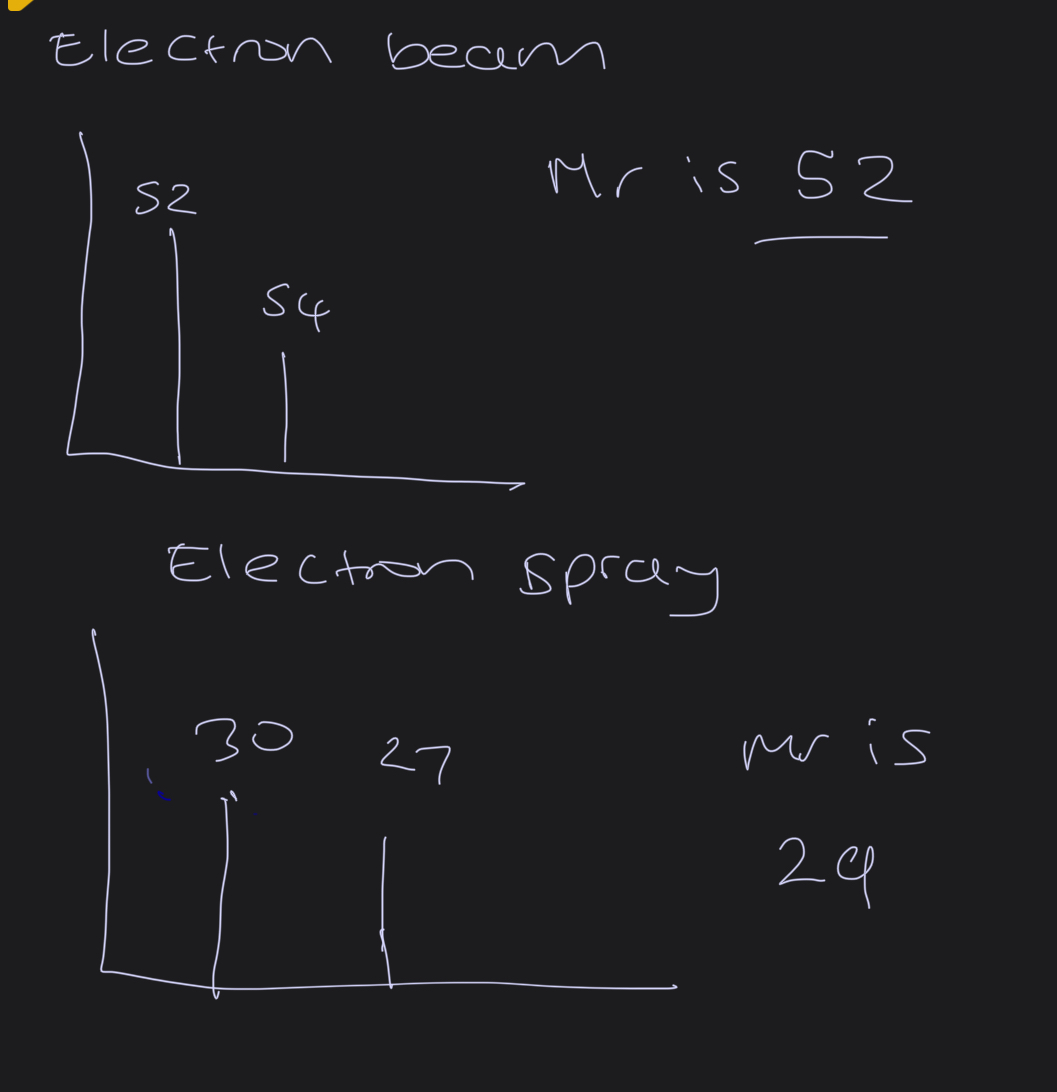
So in electron BEAM the peak equals the relative mass of isotope
ELECTRON SPRAY. - the peak is one unit greater than relative mass ( cux of the H+ ION so make sure to minus one) -..
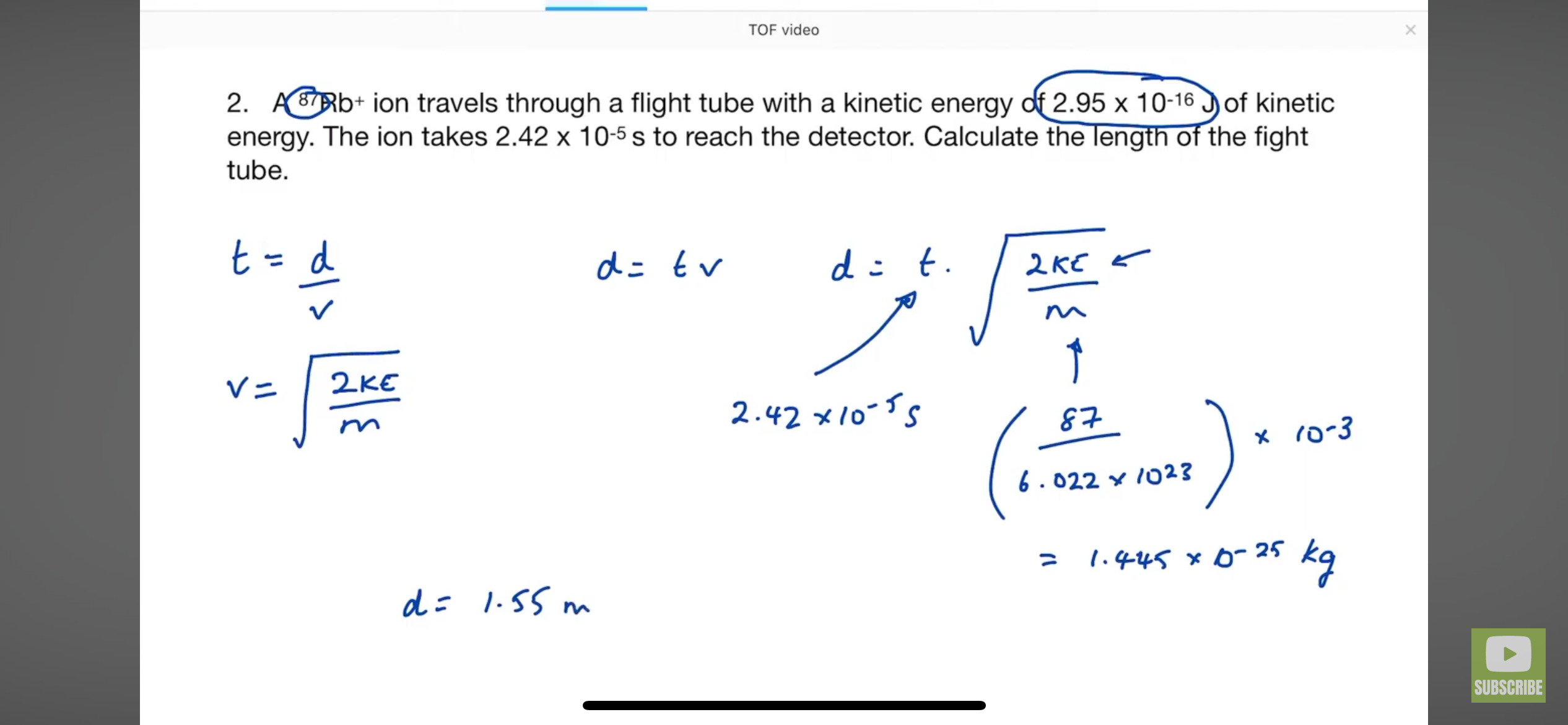
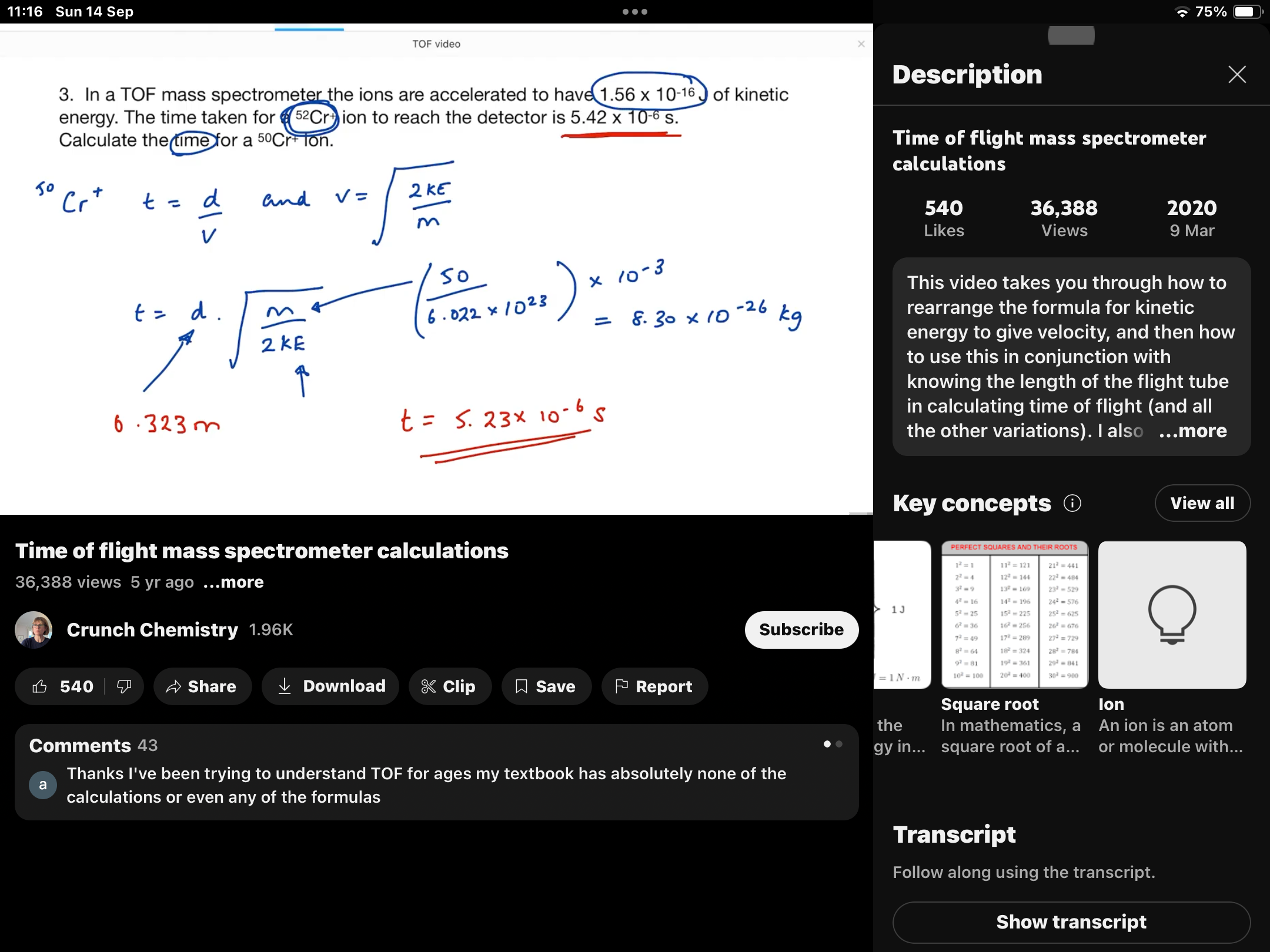
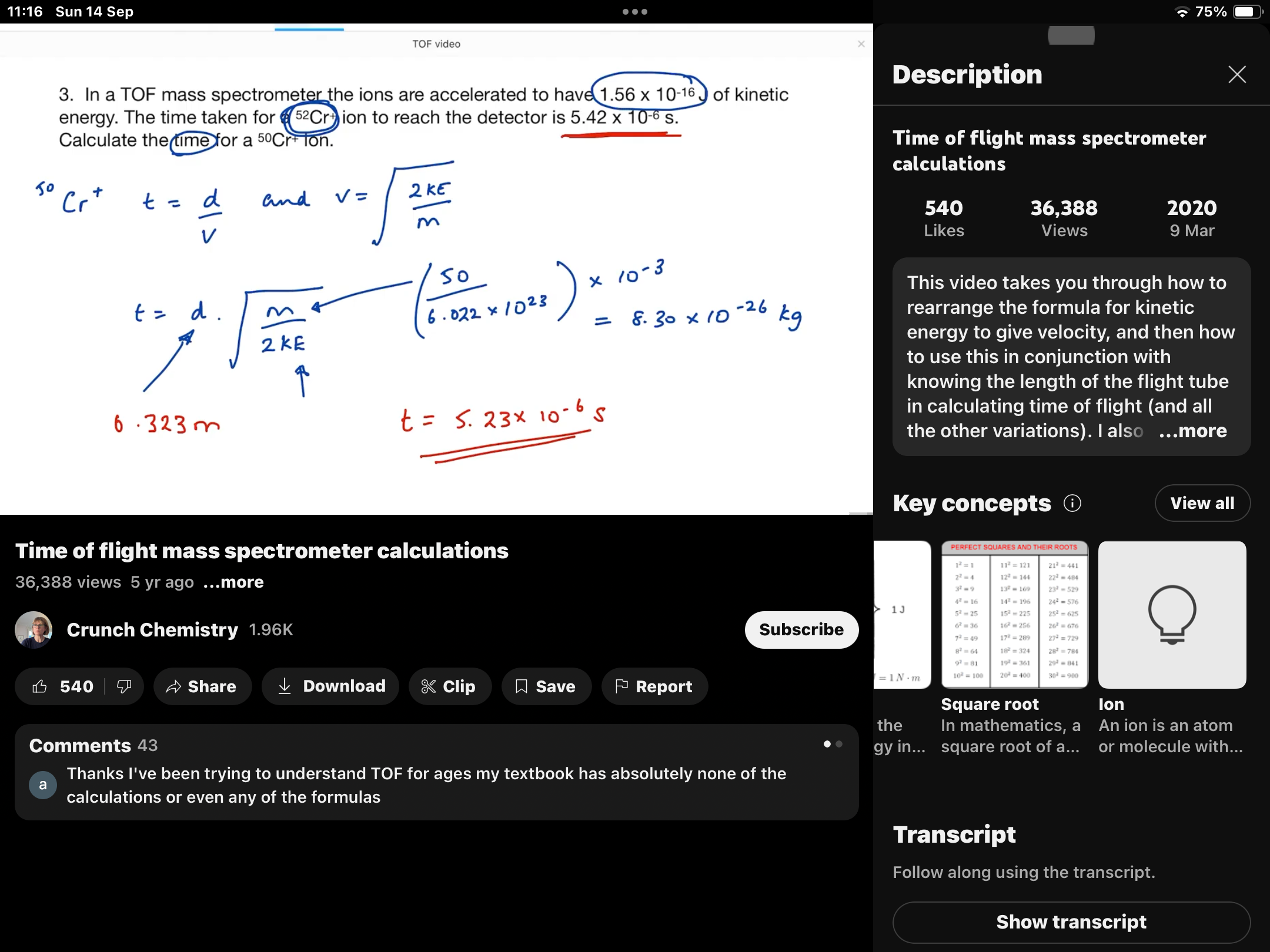
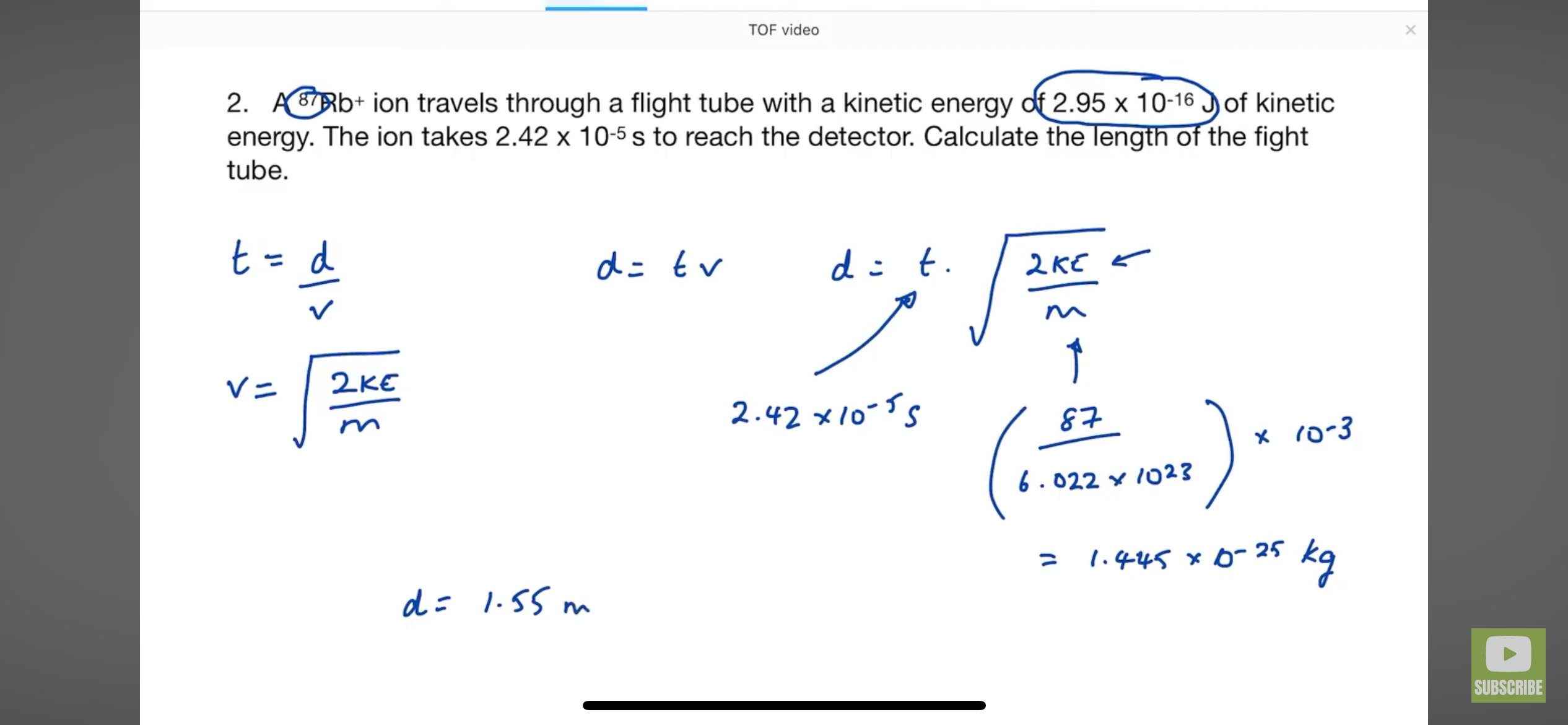
How to get mass of an element to be used in the kinetic energy equation
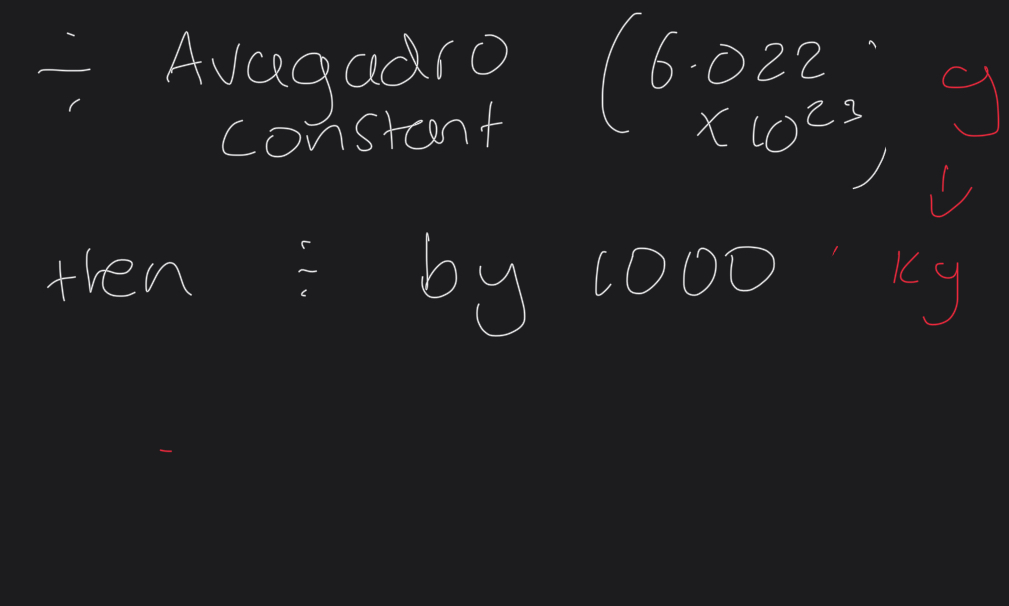
How to get the time of flight equation? FROM KINETIC EQUATION AND SPEED DISTANCE TIME
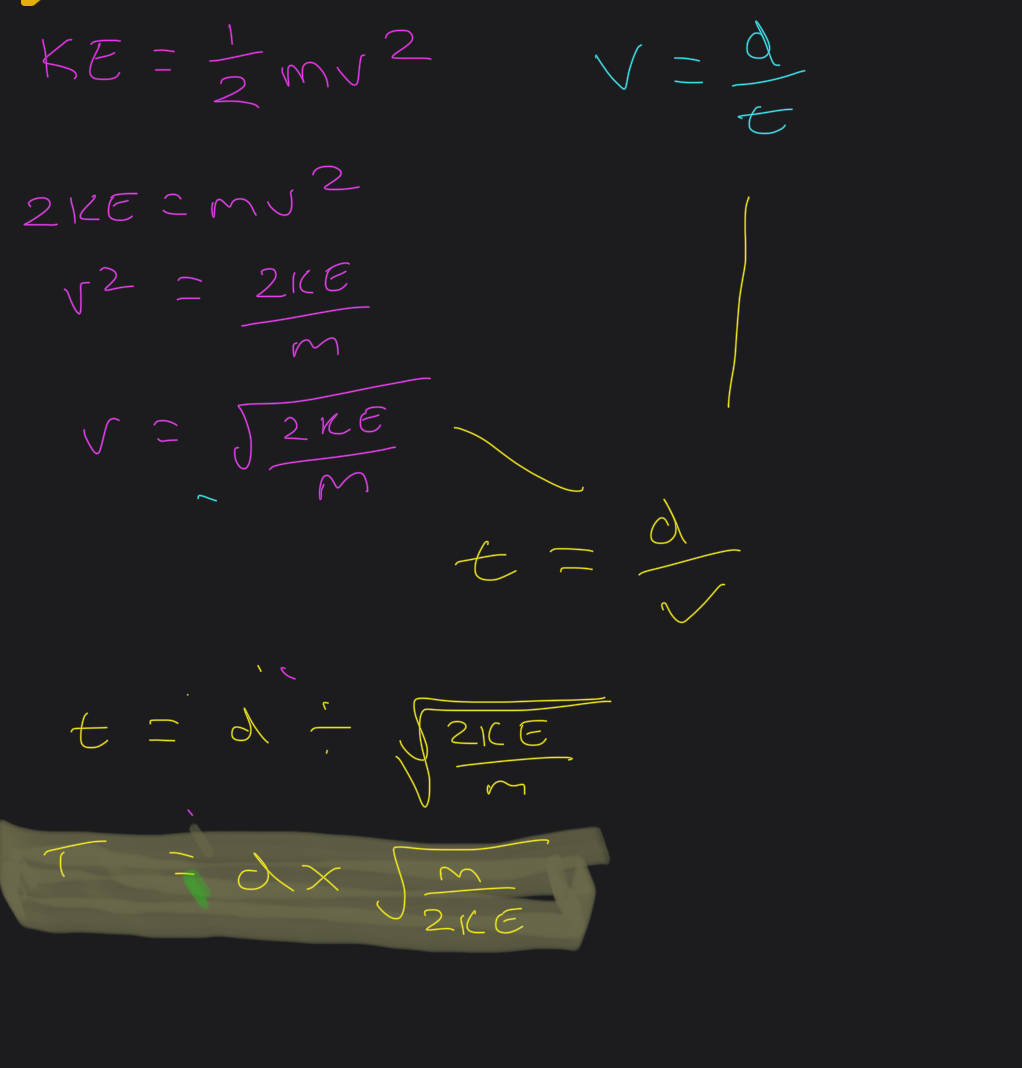
HOW TO GET RELATIVE ATOMIC MASS
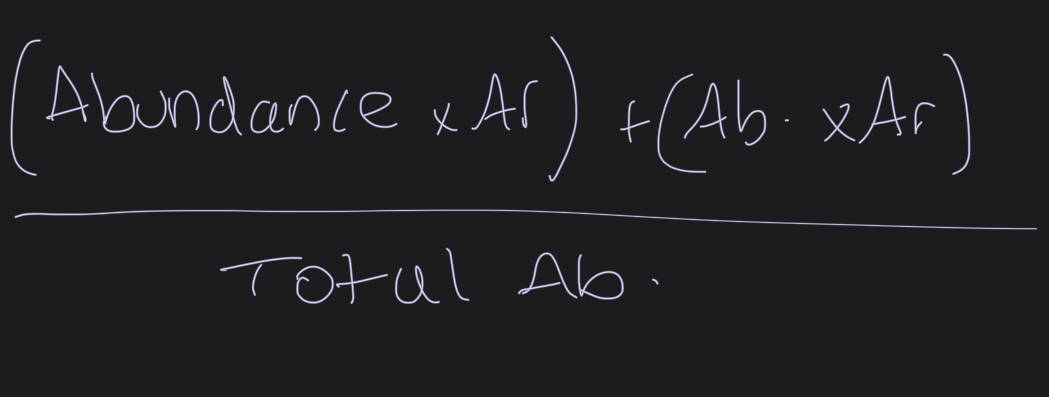
What does species mean?
Specific type of atom or ion in the molecular compound
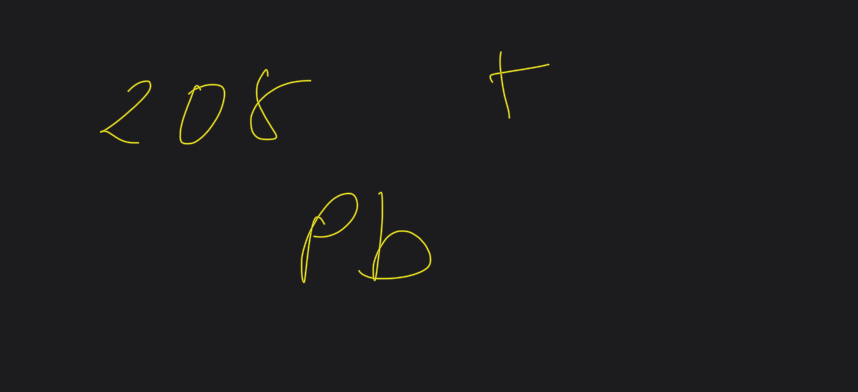
What does m+ mean
Positive ion when electron is knocked of in ionisation
The m is the parent element
What is hydrogen 2 called
Deuterium
It has one proton and one neutron
An isotope of hydrogen

Explain what a small peak can be( m+1)
It’s one added to mass number

Explain what m+2 can be?
:.
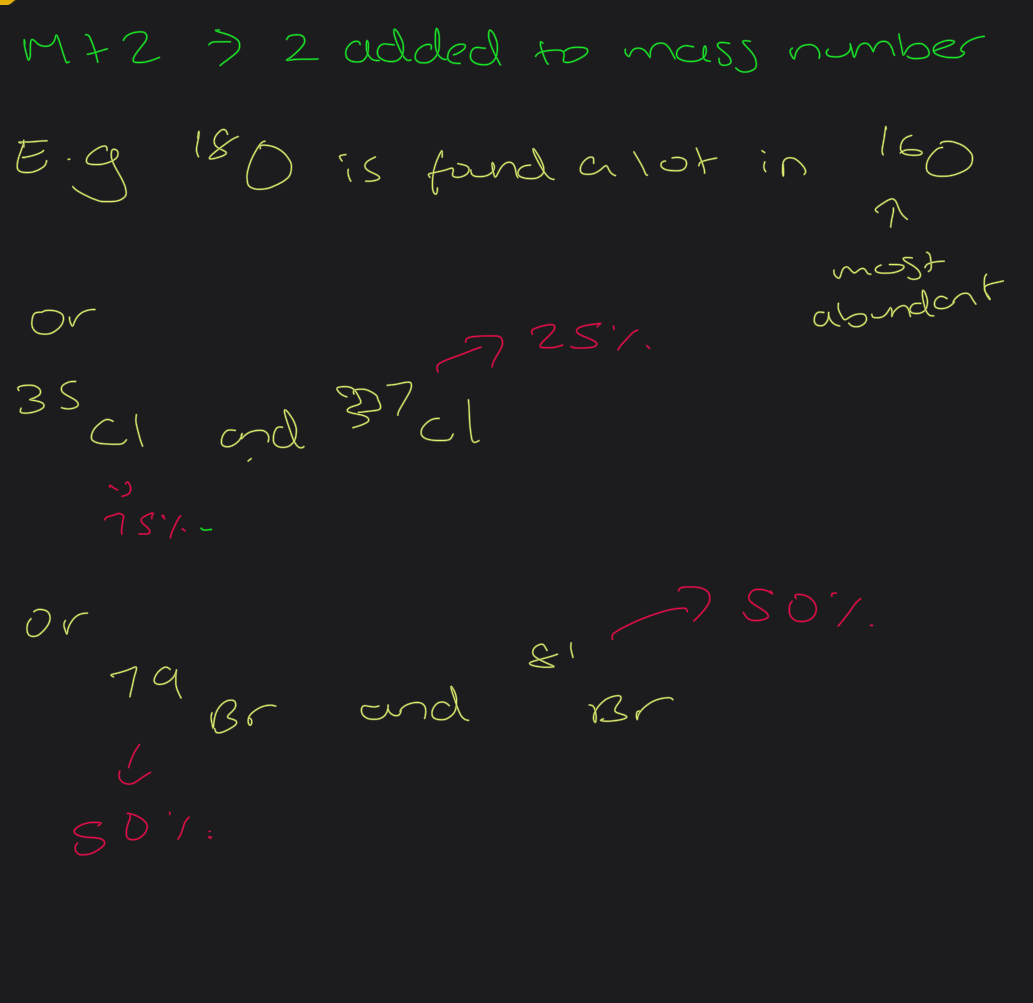
Why is m+1 peaks higher than m+2 peaks
Abundance of it is higher ( likelihood of an m+1 is more)

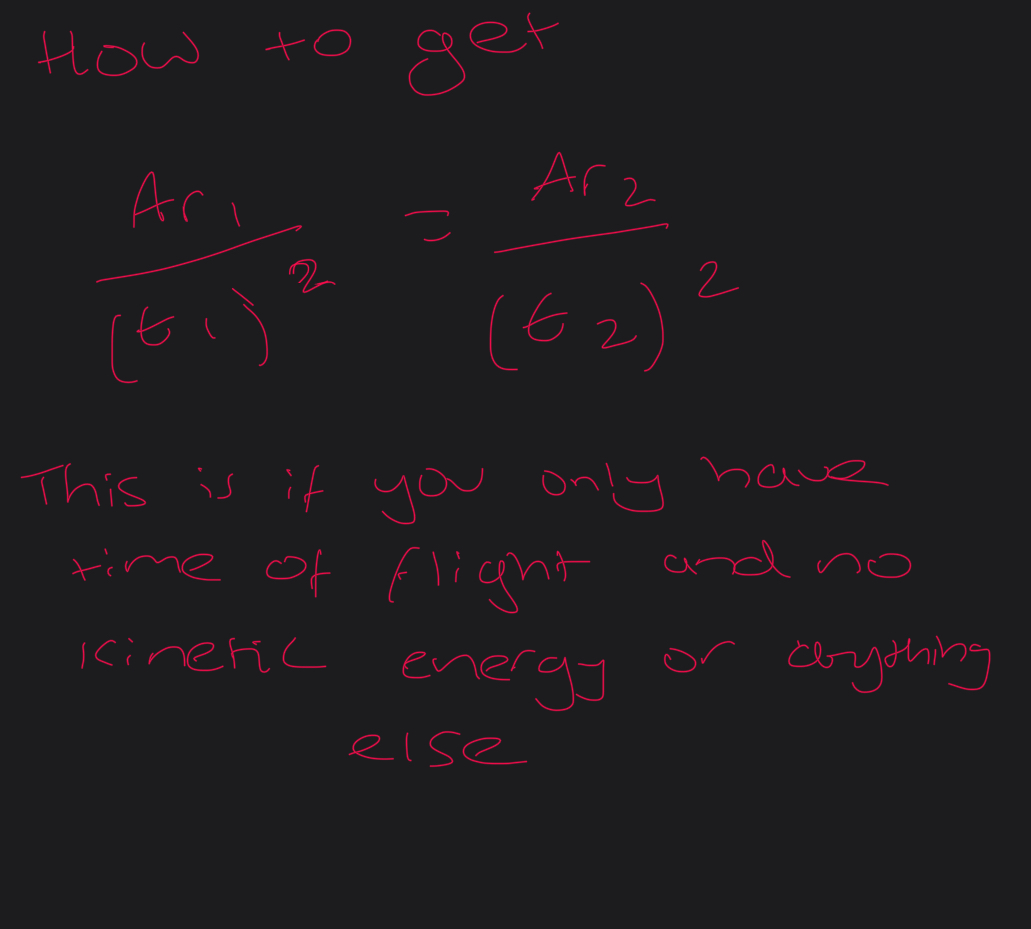
Questionnn
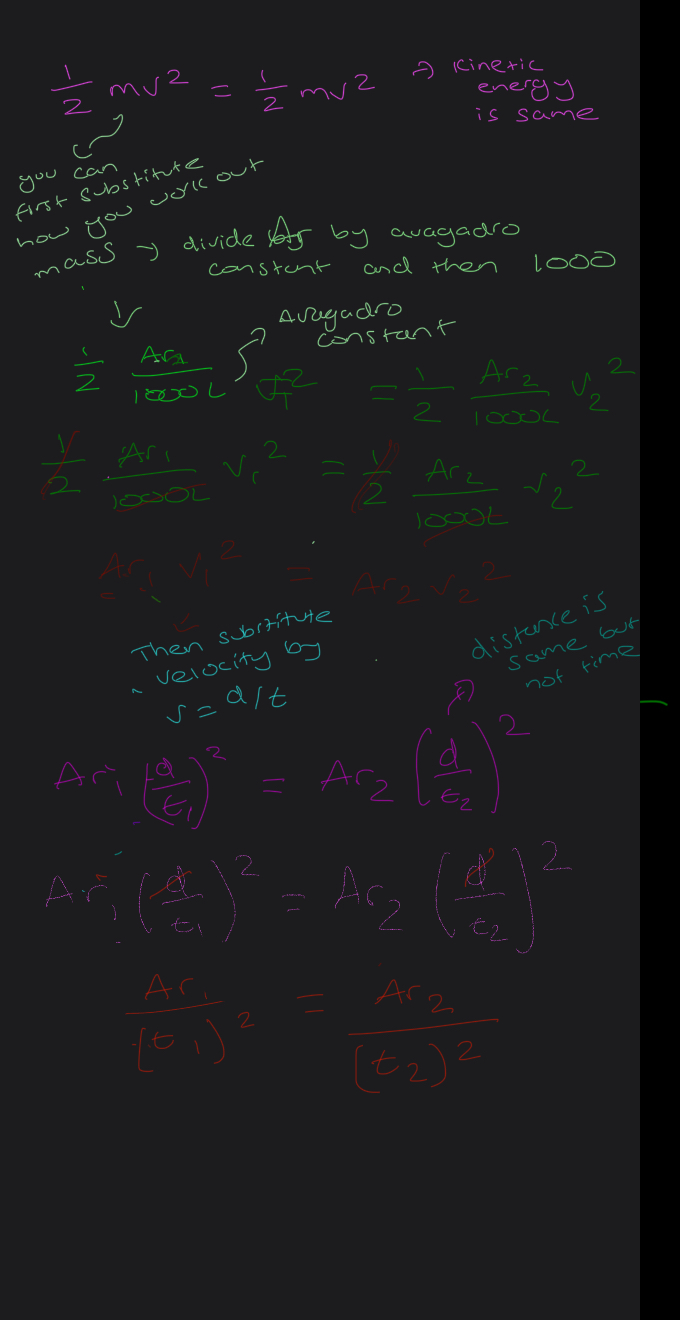
The element bromine is made of diatomic molecules. THERE are 2 isotopes of bromine namely 79br and 81br of roughly equal abundance. Sketch what the time of flight mass spectrum of the element bromine will look like?
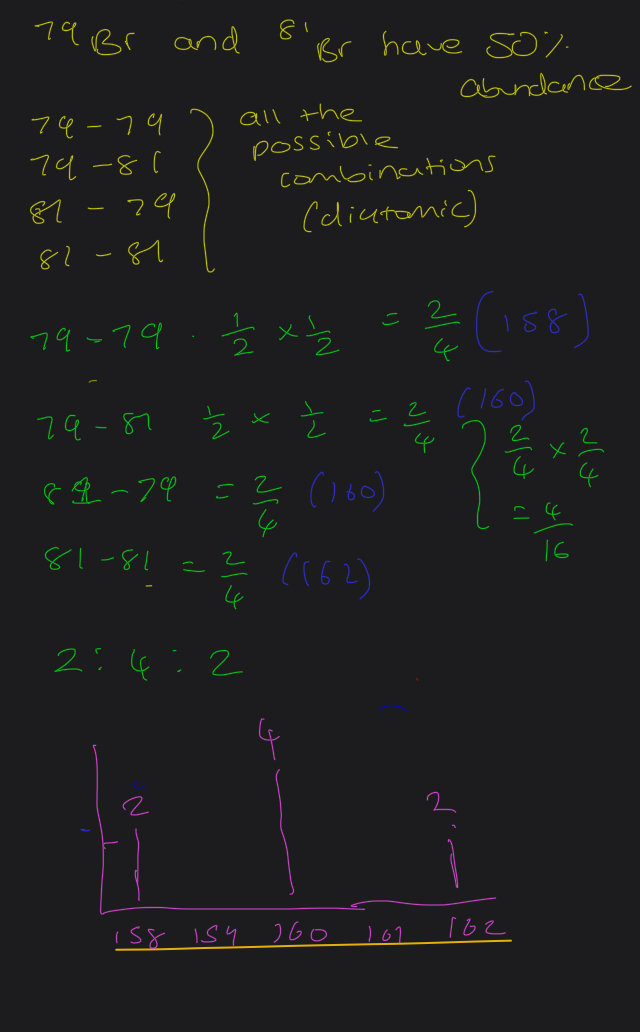
Question
.
Question