Lecture 9: Listeria monocytogenes and Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
List the general features of Listeria monocytogenes
Shape
Gram Staining
Catalase _
Oxidase _
Hemolysis _
Motility _
CAMP test _
Small Gram + short rods (bacillus)
Catalase +
Oxidase -
Beta hemolysis
Small zone
Motile
Multiple flagella
Umbrella-shape in SIM
CAMP +
T/F: Listeria monocytogenes grows on McConkey agar
False, it is Gram + so it won’t
T/F: Listeria monocytogenes are environmental saprophytes
True
What are the 3 main types of Listeria monocytogenes serotypes?
1
2
4b
How does Listeria monocytogenes enter the animal? How does it travel through the body once it enters?
Through ingestion of contaminated feed
Penetrates the intestine, then spreads through the lymph and vasculature
or
Enters via dental pulp and the migrates via cranial nerves
or
Transplacentally in pregnant animals
The way L. monocytogenes enters the animal can influence the type of listeriosis that manifests
Listeria monocytogenes utilize what type of replication style?
They are facultative replicators
That means they can replicate in or out of the cell
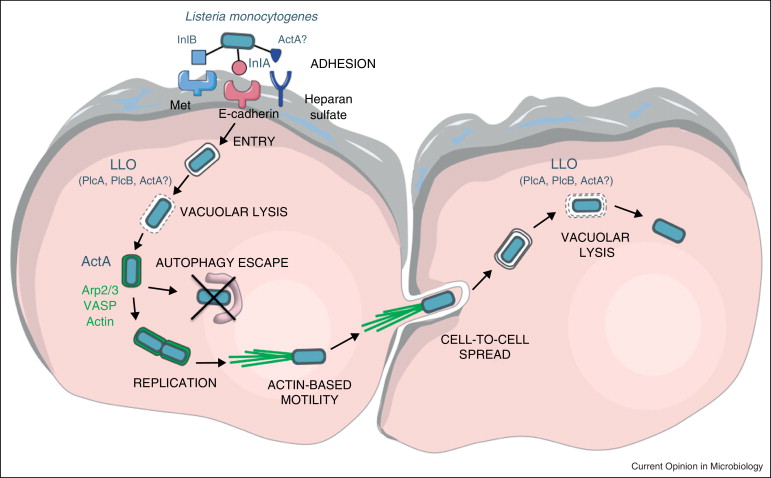
To enter the cell, L. monocytogenes uses cell invasion proteins known as ……
Internalins A and B (Inl A/B)
How does L. monocytogenes escape/avoid immune destruction?
Through escaping the phagosome once uptaken
Uses membrane damaging toxins listeriolysin and phospholipases
Once L. monocytogenes escapes the phagosome and replicates within the cell, how does it spread from cell-to-cell?
ActA
ActA induces host Actin to polymerize around L. monocytogenes and form actin comet tails
The bacteria then uses this actin to spread from cell-to-cell
What are the 3 main sources of L. monocytogenes infections in animals?
Poorly preserved/rotten silage (ph>5)
aka Silage disease
Often seen in winter or spring
Animals are feed silage that was not properly fermented
Asymptomatic carriers
Biofilms on equipment/environment
Listeriosis infections can present as 4 different forms, what are they?
Abortion/perinatal mortality
Septicemia
Neonatal ruminants and monogastrics
Meningoencephalitis
Adult ruminants
Keratoconjunctivitis and mastitis
Rare
How would you expect listeriosis to present in an adult ruminant vs a neonatal ruminant?
Adult Ruminant
Meningoencephalitis
Neonatal Ruminant
Abortion or Septicemia
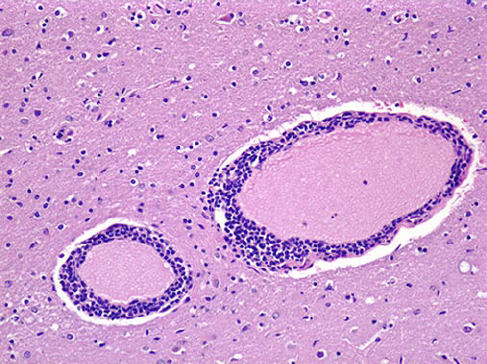
Neural listeriosis is caused by L. monocytogenes entering the host via the dental pulp/oral mucus and then entering the C.Ns to reach the brain, what are the lesions associated with this form of Listeriosis?
Marked hyperemia of B.V of leptomeninges
Micro-abscesses
Perivascular cuffing of mononuclear cells (lymphocytes, plasma cells)
Accumulation of inflammatory cells in the space around a blood vessel
Sheep/Goats that present with
Dullness
Circling
Tilting of the head
Drooling
Drooping eyelid/ear
Likely have…….
Neural listeriosis
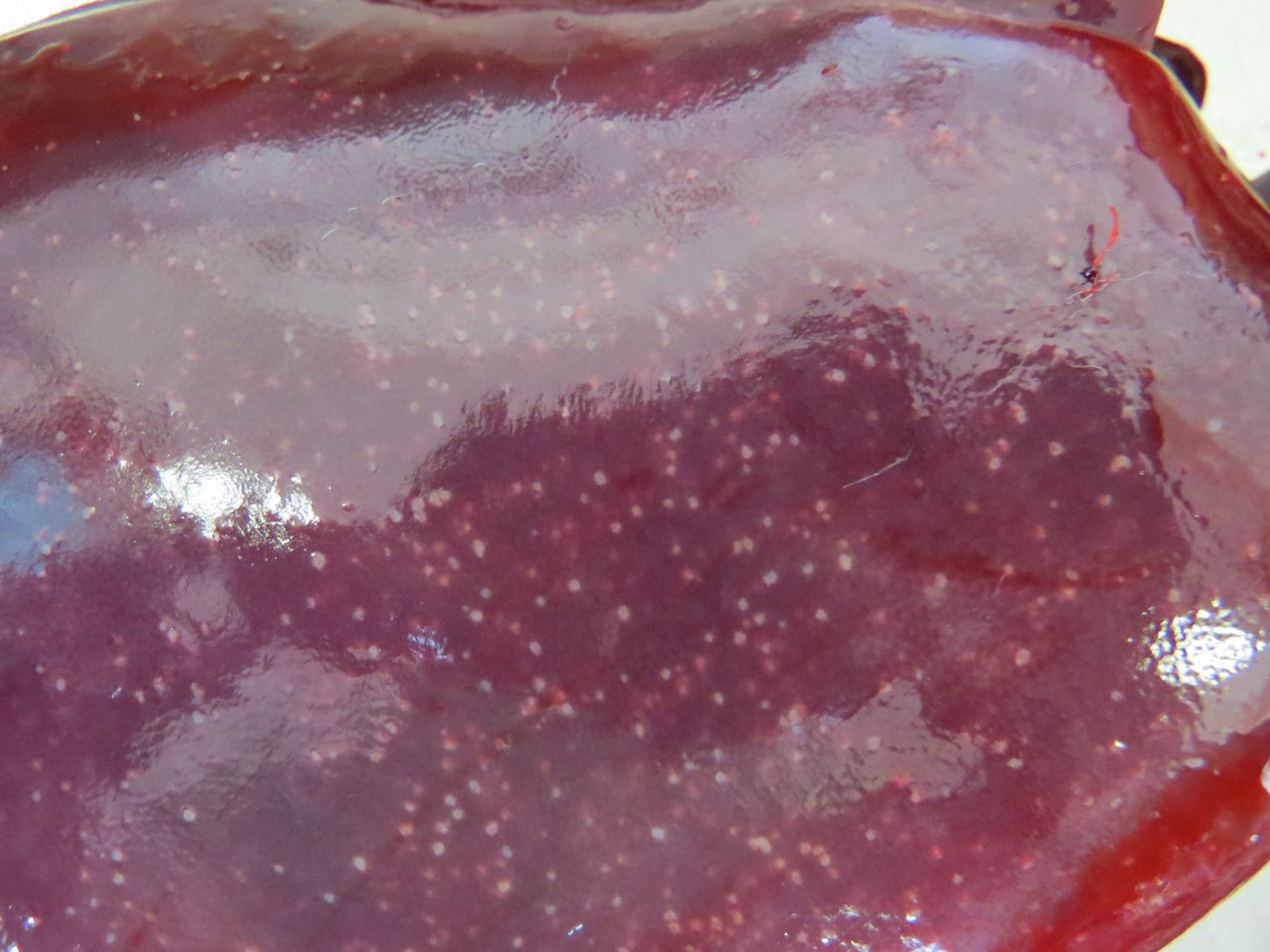
Sheep that die as a result of L. monocytogenes that became septic, usually present with what lesions?
Multifocal Hepatic necrosis (pyogranulomatous)
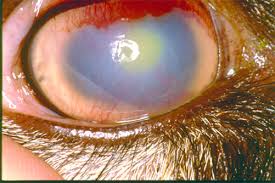
What is Silage eye? What are it’s clinical signs?
Ocular form of listeriosis
Associated with eye trauma
Clinical Signs
Uni/bilateral hyperaemic conjunctiva
Cloudy cornea
Lacrimation
How is L. monocytogenes diagnosed?
Bacterial Isolation
T/F: L. monocytogenes grows on McConkey agar
False, it’s Gram + so it won’t
Listeria selective enrichment broth improves isolation for samples taken from the ____, what is selective about this broth?
Brain, cold (4C)
How is L. monocytogenes treated? Is it always effective?
Penicillin and tetracyclines
Usually not effective for neural listeriosis
How do humans usually get listeriosis?
Indirectly via zoonotic infections
Transmission during pregnancy
What is the disease of red threads?
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
List the general features of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Shape
Gram Staining
Catalase _
Oxidase _
Coagulase _
Hemolysis _
Motility _
Short curved bacilli
Gram -
Catalase -
Oxidase -
Coagulase +
Alpha hemolytic
Non-motile
T/F: Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is zoonotic
True
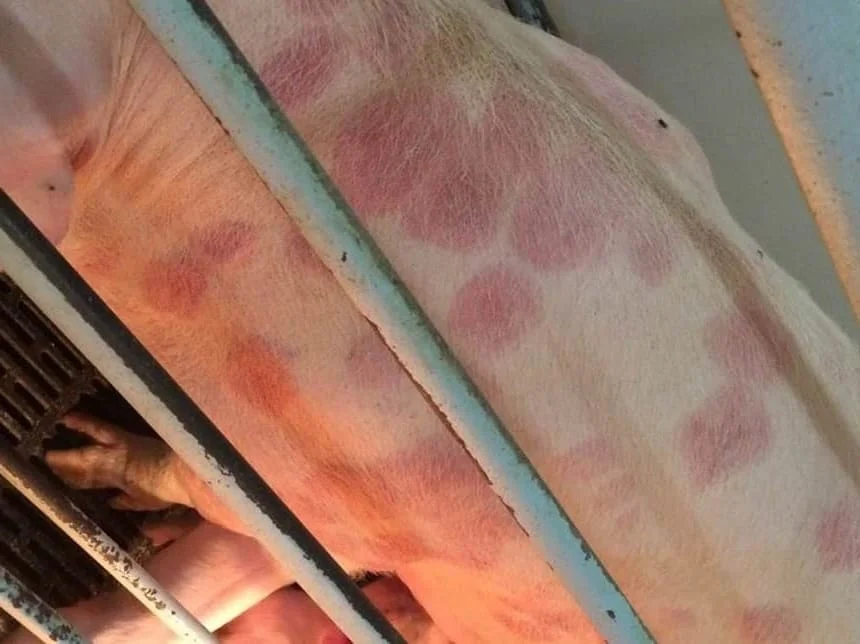
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae causes what cutaneous disease in pigs?
Diamond skin disease
What clinical signs is Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae known to cause in turkeys?
Arthritis
Valvular endocarditis
_____ are the most important reservoir of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Pigs
Infected and carriers of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae shed bacteria in ____ and ____
Feces, secretions
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae enters into the host through the _____, ___, or ____ _____
Tonsils, skin, mucus membranes
Name and described the 3 most important virulence factors to Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Capsule
Antiphagocytic
Facilitates intracellular replication
Hyaluronidase
Aids with dissemination into tissues
Neuraminidase
Adherence and invasion of endothelial cells
Damages vascular endothelial cells
T/F: Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae can cause vasculitis and thrombus formation
True!
Arthritis and Vegetative endocarditis are examples of the ____ form of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae disease in swine
chronic
How would acute or subacute Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae present in pigs?
Septicemia with sudden death
Diamond Skin Disease
Which serotypes of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae are most common in pigs and are the targets of vaccines against this bacteria?
Serotypes 1 and 2
How does Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae present in young and adult sheep?
Young
Non-suppurative polyarthritis
Caused by AG/ABs deposits in joints
Adult
Post-dipping lameness
Same idea, AB/AG deposits in joints, in this case the sheep are exposed by the dipping pools
Which bacteria causes rhomboid-shaped skin lesions in dolphins?
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
T/F: You can use porcine vaccines to prevent Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae infections in cetaceans (dolphins, porpoises, whales)
True!
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is a zoonotic pathogen, define the term Erysipeloid
A localized skin infection caused by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Also known fish handler’s disease
T/F: Listeria monocytogenes spreads between host cells by including the formation of host cell actin comet tails
True
T/F: Listeria monocytogenes brain lesions are characterized by microabscesses due to mononuclear infiltrates
False, the micro-abscesses are caused by neutrophils
Silage disease in ruminants caused by Listeria monocytogenes is due to spoiled silage with a pH<5
False, it would be caused by a pH>5 (alkaline)
T/F: Properly refrigerated cooked meats are not a risk for listeriosis in humans
False
T/F: Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae does not survive for extended periods in the environment
False
T/F: Pigs are the most important reservoir of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
True
T/F: Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae septicemia produces rhomboid skin lesions in pigs because of vasculitis and thrombosis
True