Pharm E1- HIV & STIs
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
What are the 3 main phases of HIV infection?
acute (retroviral syndrome or mono like illness), chronic, terminal (AIDs)
When monitoring HIV patients, you want CD4 count _____ and viral load _____
high ; low
What would indicate a maximal and durable suppression of HIV replication (tx is working)?
undetectable viral load
What does CD4 count indicate?
extent of immune damage
What do plasma HIV RNA levels (viral load) indicate?
magnitude of replication
When should treatment for HIV be started?
ASAP - regardless of CD4 count (reduces transmission, fewer AIDs events)
What are the main drugs classes used to treat HIV?
Nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Non nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Protease inhibitors
Integrase Inhibitors
Entry/fusion inhibitions
Coreceptor inhibitors
What class of drugs?
used in treatment of HIV
based off purine and pyrimidine nucleotides/nucleosides
targets reverse transcriptase
acts as chain terminator to prevent viral RNA from being copied & incorporated into our DNA
NRTIs
Which NRTIs do not have as many side effects?
abacavir, tenofovir, emtricitabine, lamivudine (newer agents)
Which NRTIs are the side effects more pronounced with?
stavudine, didanosine, zidovudine
What are SE associated with NRTIs?
peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis, lipoatrophy, myopathy, anemia, lactic acidosis w/ fatty liver
*monitor liver function
Before starting treatment, which drug requires testing for a HLA-B5701 mutation that causes a hypersensitivity reaction to the drug?
Abacavir
Which drugs belong to the nucleoside (nucleotide) reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) class?
Stavudine
Zidovudine
Emtricitabine
Lamivudine
Abacavir
Didanosine
Tenofovir
Which class of drugs?
treats HIV
binds to reverse transcriptase forcing conformational change preventing DNA production
(can’t read viral RNA anymore)
NNRTIs
What drugs belong to the non nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) class?
Delavirdine
Efavirenz
Nevirapine
Etravirine
Rilpivirine
What SEs are associated with NNRTIs?
rash, transaminitis
*monitor liver function
With which class of drugs used to treat HIV would a single viral mutation confer resistance to the entire class (lose whole category of drugs)?
NNRTIs (except etravirine)
Which class of drugs?
used to treat HIV
inhibits protease enzyme preventing virus from making mature proteins
most metabolized in liver, often given w/ boosters (CYP3A4 inhibitors)
Protease inhibitors (PIs)
What drugs belong to the protease inhibitor class?
Atazanavir
Darunavir
Fosamprenavir
Indinavir
Lopinavir
Nelfinavir
Ritonavir
Saquinavir
Tipranavir
What SEs are associated with protease inhibitors (PIs)?
GI distress, elevated lipids, glucose intolerance, altered fat distribution (buffalo hump / lipodystrophy)
Why are strong CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ritonavir or cobicistat given along with protease inhibitors?
utilize the drug interaction to increase drug levels for less frequent dosing (better for compliance)
What drugs belong to the fusion inhibitor class?
Enfuvirtide (Fuzeon)
What class of drugs?
inhibits HIV1 envelope fusion (no activity for HIV2)
not PO, given SC injection
injection site rxns common - pain, erythema, nodules
fusion inhibitors
What drugs are CCR5 antagonists?
Maraviroc (Selzentry)
What class of drugs?
treats HIV1-2
blocks human receptor to prevent virus from getting in
works on human cell NOT virus
can only use against correct strain → must test BEFORE starting tx
CCR5 antagonist
What side effects are associated with CCR5 antagonists (Maraviroc)?
rash and hepatotoxicity
What drugs are Integrase Inhibitors (InSTI)?
Raltegravir
Dolutegravir
Elvitagravir (coformulated w/ cobicistat)
Bictegravir (coformulated w/ emtricitabine + tenofovir [Biktarvy])
What class of drugs?
treats HIV
often with booster to reduce frequency of dosing
effective and better tolerated - most pts start on these
bind to integrate & prevent viral DNA incorporation into chromosomal DNA
Integrase inhibitors
What are side effects associated with integrate inhibitors?
rash, N, HA
Efavirenz, Etravirine, and Nevirapine ______ CYP3A4
induce (lower drug levels)
Most protease inhibitors ______ CYP3A4
inhibit (increase drug levels)
What should be the initial treatment regimen for a new diagnosis of HIV?
(**test question, know drugs in each class)
minimum of 3 antiretroviral agents- 2 must be NRTIs
Ex: InSTI + 2 NDRTIs, PI + 2 NRTIs, NNRTI + 2 NRTIs
What is the current preferred initial regimen for HIV?
integrase inhibitors + 2 NRTI
(Dolutegravir + tenofovir + emtricitabin or lamivudine or biktarvy)
What should be used whenever possible in HIV treatment to increase compliance?
combo formulas (ex- Atripla, genvoya, Complera, biktarvy)
What would elevated viral loads indicate after being on treatment?
virus is resistant to drug regimen or patient is not compliant with meds
Which resistance testing for HIV treatment provides the most information but is more expensive and has a slower turnaround?
phenotype testing
Which resistance testing for HIV treatment is easier and faster but not as informative?
genotype testing
Which HIV medication should be avoided in pregnancy due to risk of neural tube defects (spina bifida)?
efavirenz
Which drug is recommended intrapartum to prevent HIV transmission to fetus?
Zidovudine
What should fetuses receive if their mother is HIV+?
zidovudine 4-6 wks
Should HIV+ mothers breastfeed?
no
What is the post exposure prophylaxis after high risk HIV exposure?
Tenofovir, emtricitabine, raltegravir x 4 wks
start ASAP
What is the HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis for serodiscordant couples, NSN, or IV drug abusers?
(*must be seronegative before starting)
daily tenofovir/emtricitabine (Truvada)
What integrase inhibitor is started orally then converted to long-acting IM and given every 2 months (good for noncompliant patients and patients who can’t tolerate oral medications)?
Cabotegravir (Vocabria)
When should CD4 counts and HIV RNA loads be measured?
before treatment initiation and every 3 months
What are reasons for changing HIV treatment regimen?
intolerable SEs, tx failure (viral RNA > 200), resistance to drugs
As CD4 count drops ______
risk of opportunistic infx increases (life threatening)
What is immune reconstitution syndrome (IRIS)?
ART therapy initiation → major increase in inflammatory cascade (immune system starts working) → OI symptoms start showing (worsening fever & OI manifestations)
What is the MC life threatening OI in AIDs patients?
PCP
What is the treatment for PCP?
bactrim x 21 days
When is PCP prophylaxis indicated?
CD4 < 200 or hx of oropharyngeal candidiasis or hx PCP PNA
What is the prophylaxis for PCP?
bactrim 3x weekly (MWF)
What is the treatment for candidiasis (thrush) in AIDs patients?
Fluconazole (Diflucan) IV/PO 7-21 days OR
Nystatin oral liquid QID (*not recommended for esophageal infx)
What is the recommended treatment for gonorrhea?
Ceftriaxone 500 mg IM (single dose to ensure compliance)
What should also be treated in a gonorrhea patient due to high rate of co infx?
chlamydia
What is the treatment for chlamydia?
Doxy 100 mg PO BID x 7 days (preferred) OR
azithro 1g PO single dose
What is used for gonorrhea eye infection in infants?
topical erythromycin
What is an alternative treatment option for gonorrhea in patients with cephalosporin allergy?
no good alternative option; possible high dose azithromycin + gentamicin
What are alternative treatment options for chlamydia?
tetracyclines or FQs (avoid in pregnancy)
What is the treatment for chlamydial ophthalmia infection in children?
oral erythromycin
What is the treatment for syphilis?
Benzathine PCN G (Bicillin) single dose
alt: doxy or tetra x 2-4 wks
What is the treatment for advanced cases of syphilis (neurosyphilis)?
aqueous PCN G (IV)
Why is HSV a major public health risk?
many are asx & viral shedding occurs in absence of lessons
What are the goals of treatment for HSV?
relieve sx, shorten clinical course, prevent complications & recurrence, dec transmission
How can pain and discomfort associated with HSV infections be treated?
warm saline baths, analgesics, antipyretics, antipruritics, & good hygiene to prevent bacterial superinfection
What is the recommended treatment for the first episode of an HSV infection?
acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir x 7-10 days (start ASAP)
*topical tx not recommended
What is the treatment for immunocompromised patients with HSV?
IV acyclovir
What side effects is the IV form of acyclovir more associated with?
renal, bone marrow, & CNS toxicity
What is the episodic therapy regimen for HSV infections?
initiate 6-12 hrs after onset of prodrome sx (no later than 24 hrs after lesions appear)
What is the recommended treatment for patients with HSV who have prolonged recurrences & severe sx?
episodic therapy
Which HSV treatment regimen reduces frequency of recurrences by 80% and has less asymptomatic viral shedding?
chronic suppressive therapy
What is the treatment for trichomoniasis?
single 2g dose of either Metronidazole or Tinidazole
(*tx partners also)
What drug is an anti protozoal used to treat Trichomoniasis by damaging the DNA?
Tinidazole
What infection is usually acute & self limiting and confers immunity?
Hepatitis A
What is the post exposure prophylaxis for hepatitis A?
immunoglobulin (saved for extremes of age or immunocompromised)
What is the best form of prevention for Hep A?
vaccine (kids at 12 mos) & practice good hygiene
What infection is 50-100x more infectious than HIV?
Hepatitis B
What does a chronic hep B infection increase the risk for?
cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma
What indicates a chronic HBV infection & cure is no longer possible (MC in perinatal infections)?
persistent antigen levels > 6 months
Which virus has a low vaccine response and requires 3 doses for optimal protection?
Hep B
What are the goals of treatment for hepatitis B?
maintain viral suppression, seroconversion to anti-HBeAg and lose HBeAg, & prevent progression to hepatic complications
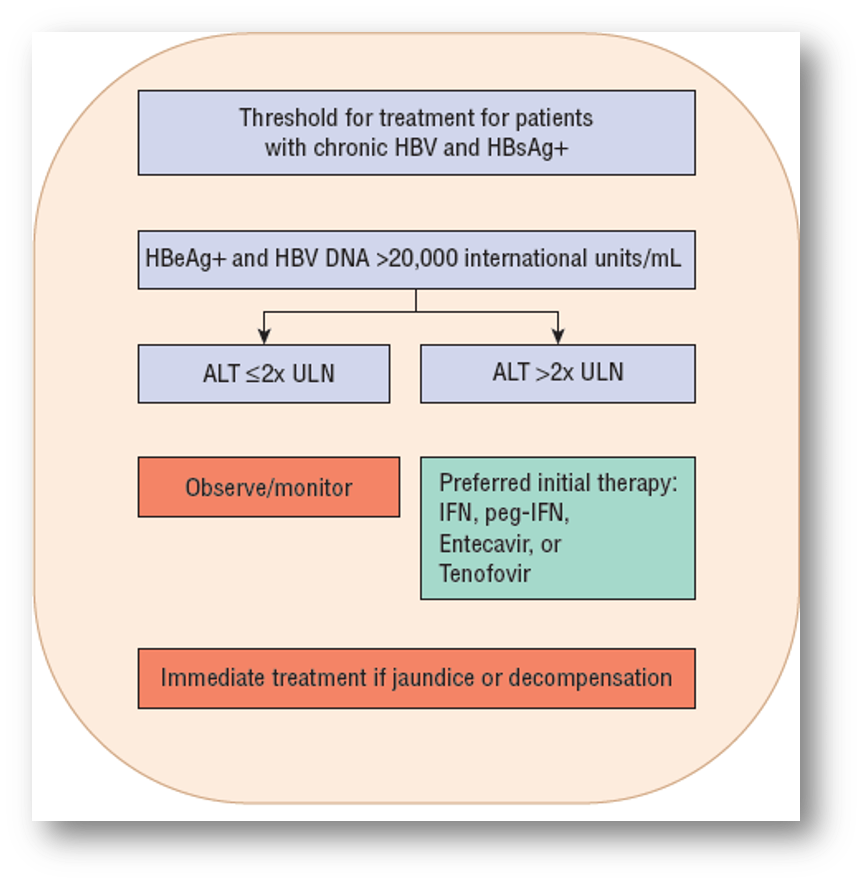
When should a patient relieve treatment for hepatitis B?
(* possible test Q
HBeAg positive & HBV DNA >20,000 AND
ALT >2x ULN
What drug?
first approved therapy for HBV
acts as a host cytokine
stimulates host immune system to mount defense (antiviral, antiproliferative, & immunomodulatory effects)
required 3x weekly injections
Interferon-alfa (Intron A)
What are adverse effects of Interferon alfa?
black box- fatal neuropsychiatric, autoimmune, ischemic, & infectious disorders
also anaphylactic risk, flu sx, depression, SI, aggression, blood dyscrasias
What drug?
activity against HV but not recommended first line
can be given indefinitely but concerns of relapse & resistance
Lamivudine (Epivir)
What drug?
activity against Lamivudine resistant HBV
nephrotoxic- monitor serum creatinine
Adefovir (Hepsera)
What drug?
considered first line for HBV due to safety & low resistance
used in lamivudine resistant strains
Entecavir (Baraclude)
What drug is more effective than Lamivudine against HBV but has a high rate of resistance?
Telbivudine
What drug?
also first line for HBV
low resistance rates
Tenofovir (Viread)
What are the goals of treatment for hepatitis C?
eradicate infection (undetectable viral load 12 wks after end of tx) & prevent progression to end stage liver disease
What patients should receive treatment for Hep C?
all patients
What is the current standard regimen for HCV treatment?
all oral meds x 12-14 wks (depending on viral genotype)
What drug?
treats HCV
binds to NS5A to prevent viral RNA replication & vision assembly
disrupts protein structure/function- can’t produce new RNA
no adjustment in renal/hepatic insufficiency
SE: HA, fatigue, N, D
expensive
Daclatasvir (Daklinza)
What drug?
treats HCV
work synergistically to inhibit NS5A to block viral replication
no organ dose adjustment needed
SE: HA and fatigue
expensive
Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir (Harvoni)
What drug?
treats HCV
inhibits NS3/4A protease
SE: rash/photosensitivity, pruritus, N
espensive
can’t be used alone (give w/ sofosbuvir or interferon/ribavirin)
Simeprevir (Olysio)
What drug?
treats HCV
give in combo with Paritaprevir, Ritonavir, Technivie, or Dasabuvir
Ombitasvir
What drug?
injectable to treat HCV
MOA not fully understood
used for complicated cases
has bad SE
Ribavirin (Rebetol)
What drug is pregnancy category X, requiring women to use 2 forms of birth control for 6 months AFTER treatment ends?
Ribavirin (rebetol)
What are SEs of Ribavirin (Rebetol)?
SI, depression, insomnia, dyspnea, hemolytic anemia, pregnancy category X
What class of drugs are mainly used to treat HCV?
direct acting antivirals (DAAs)