Chem exam 1
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
mega
Symbol: M
10^6
kilo
symbol: k 10^3
deci
Symbol: d
10^-1
centi
c 10^-2
milli
m 10^-3
micro
u 10^-6
nano
n 10^-9
pico
p 10^-12
pure substance
A substance made of only one kind of matter and having definite properties.
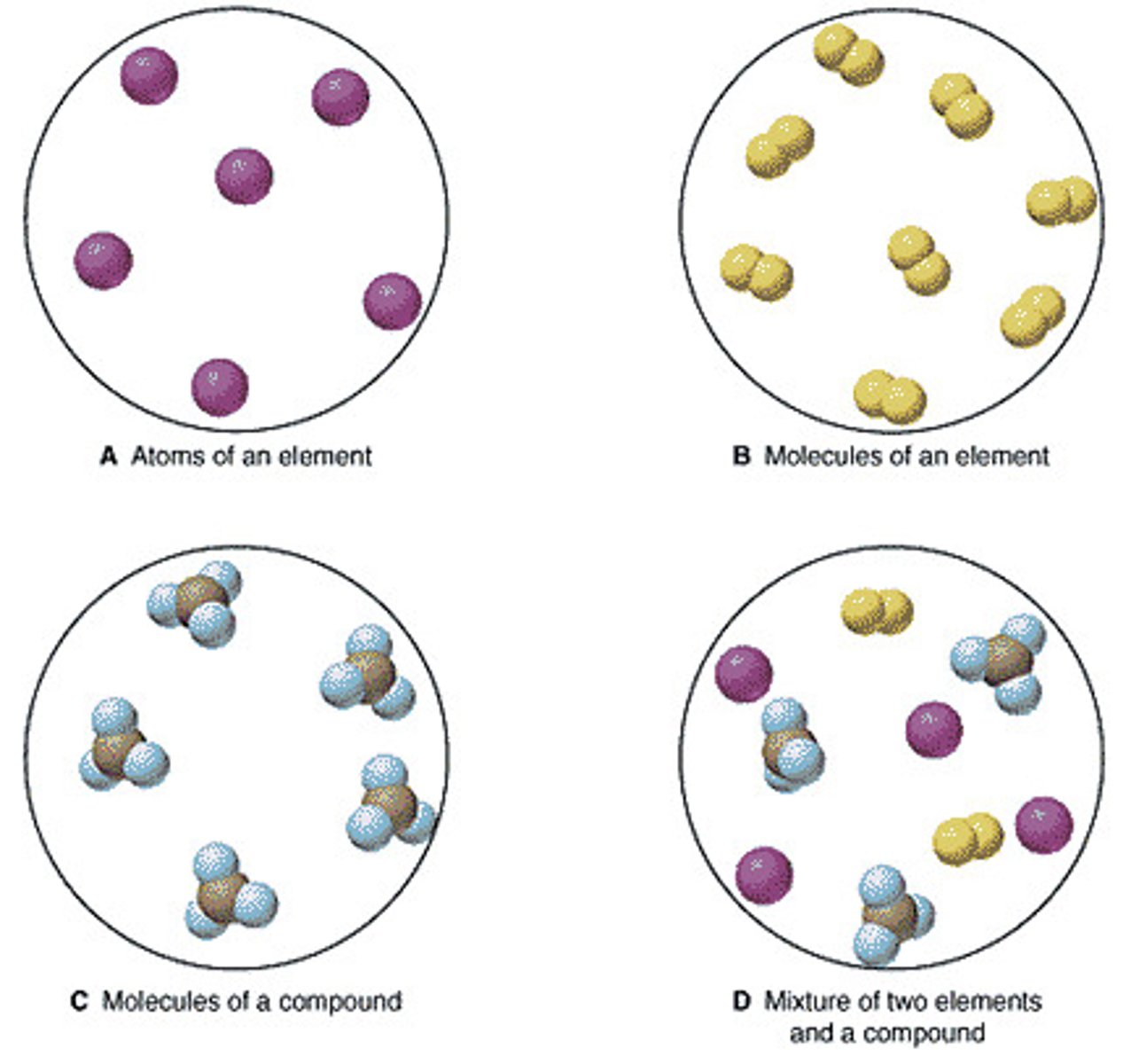
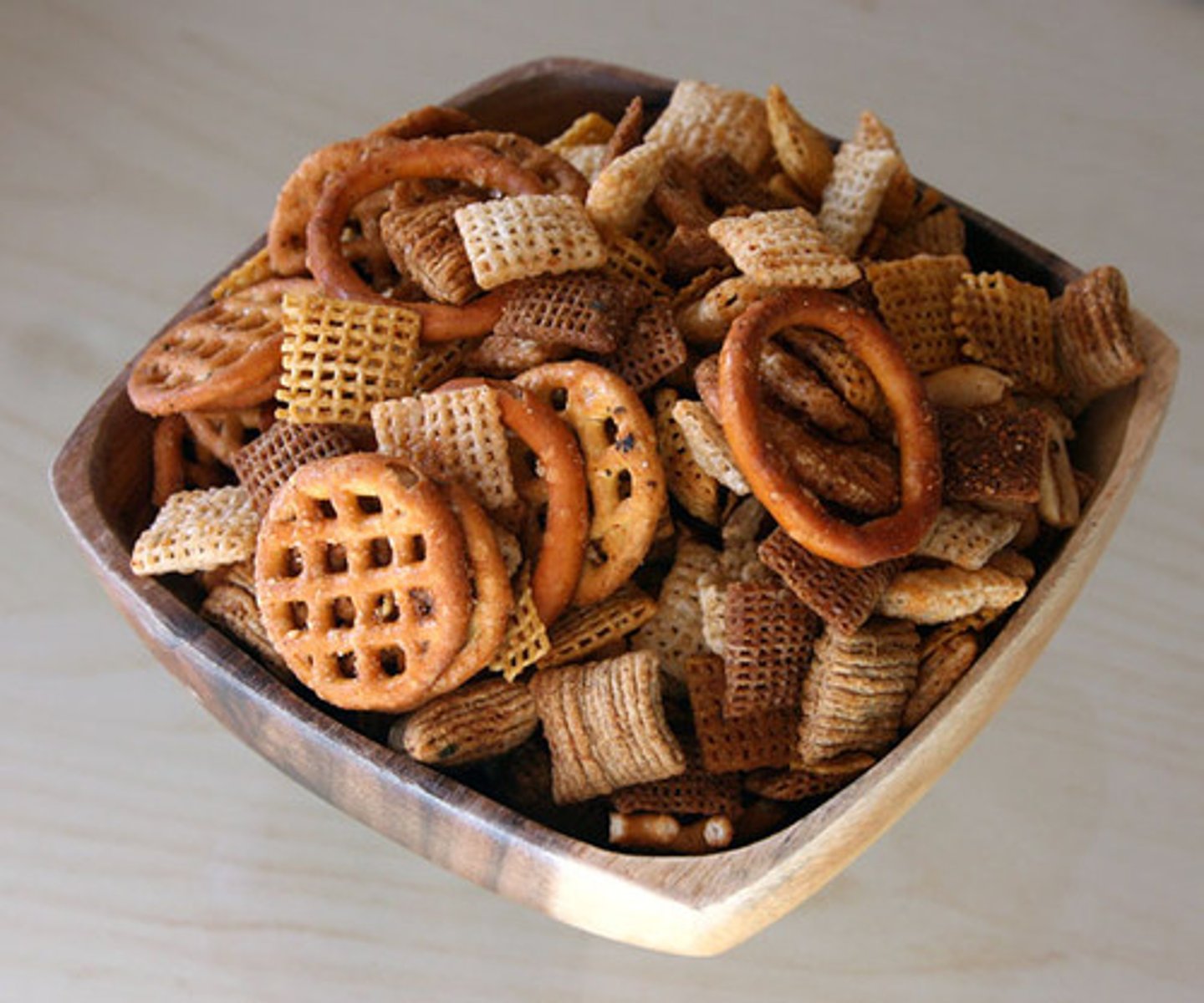
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined

Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
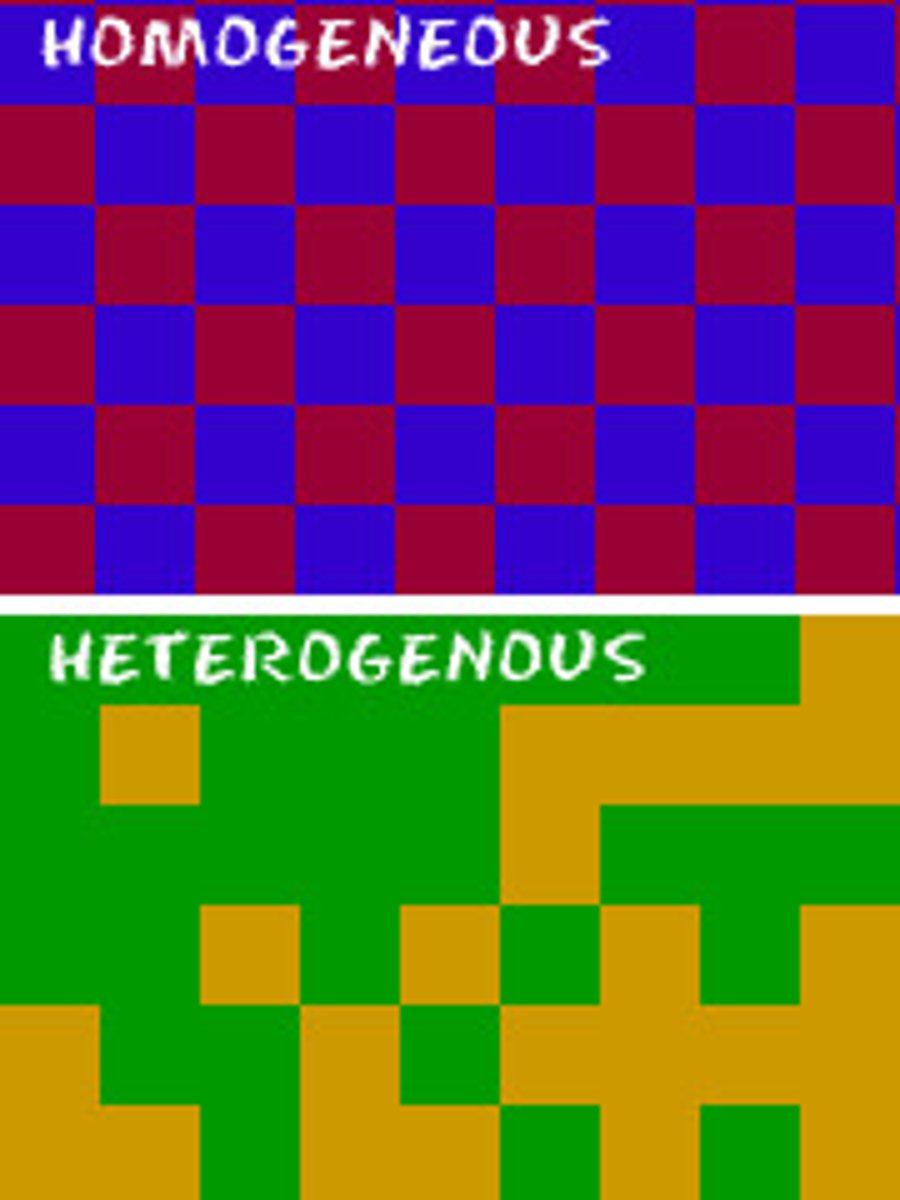
homogeneous mixture
A mixture in which substances are evenly distributed throughout the mixture
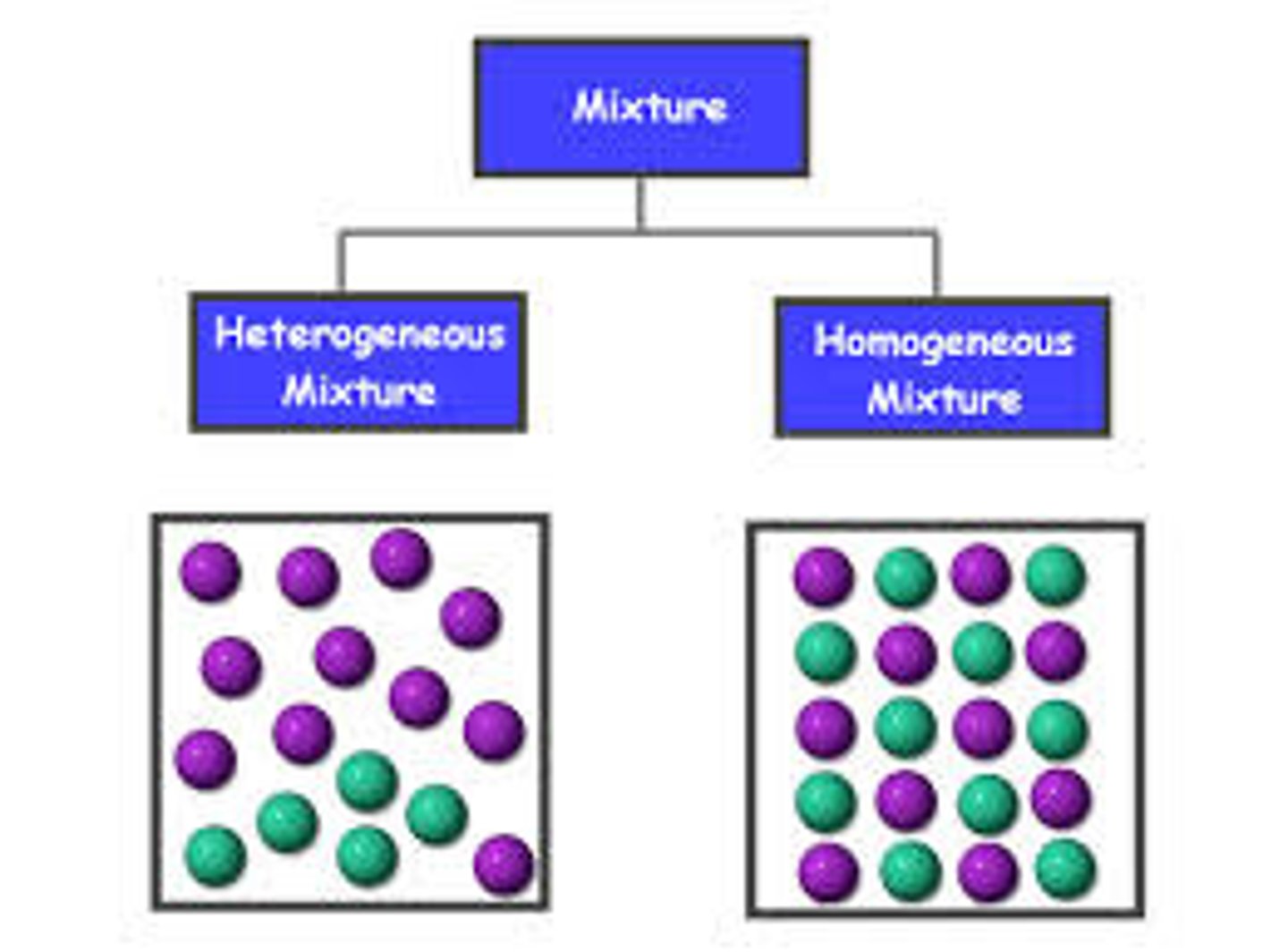
Hetergeneous Mixture
A mixture that is not uniform, in which different samples may have different compositions

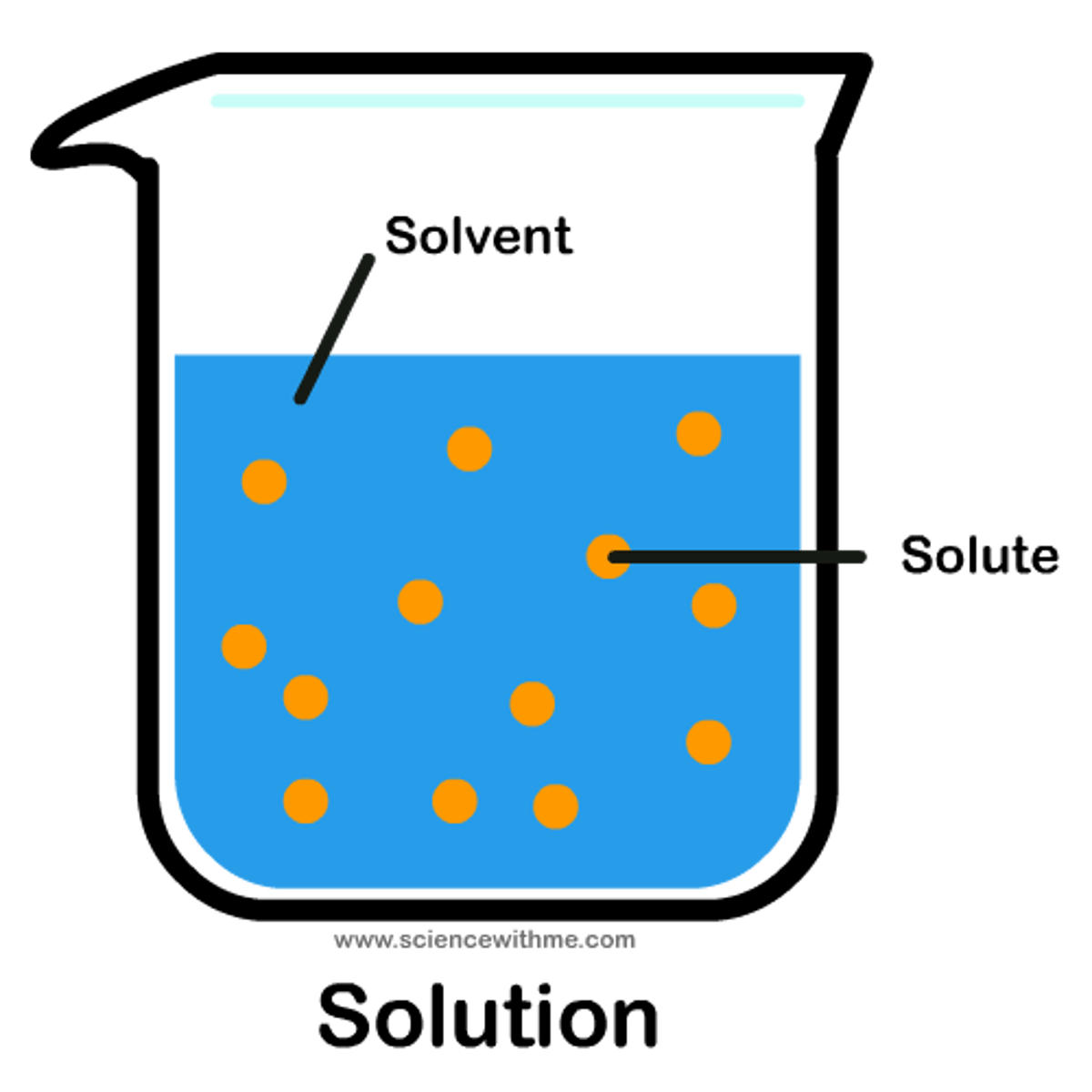
Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another.
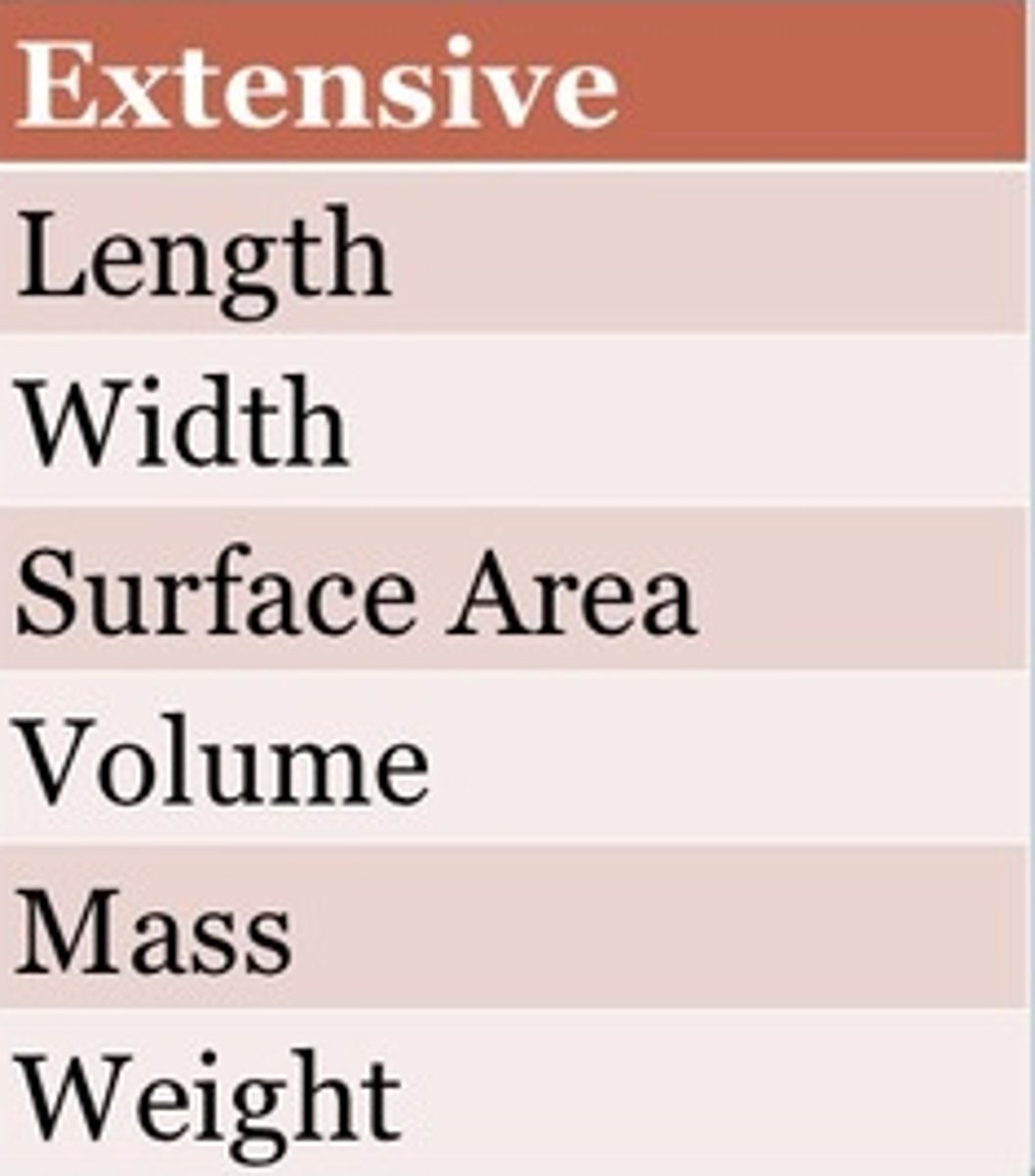
extensive property
a property that depends on the amount of matter in a sample
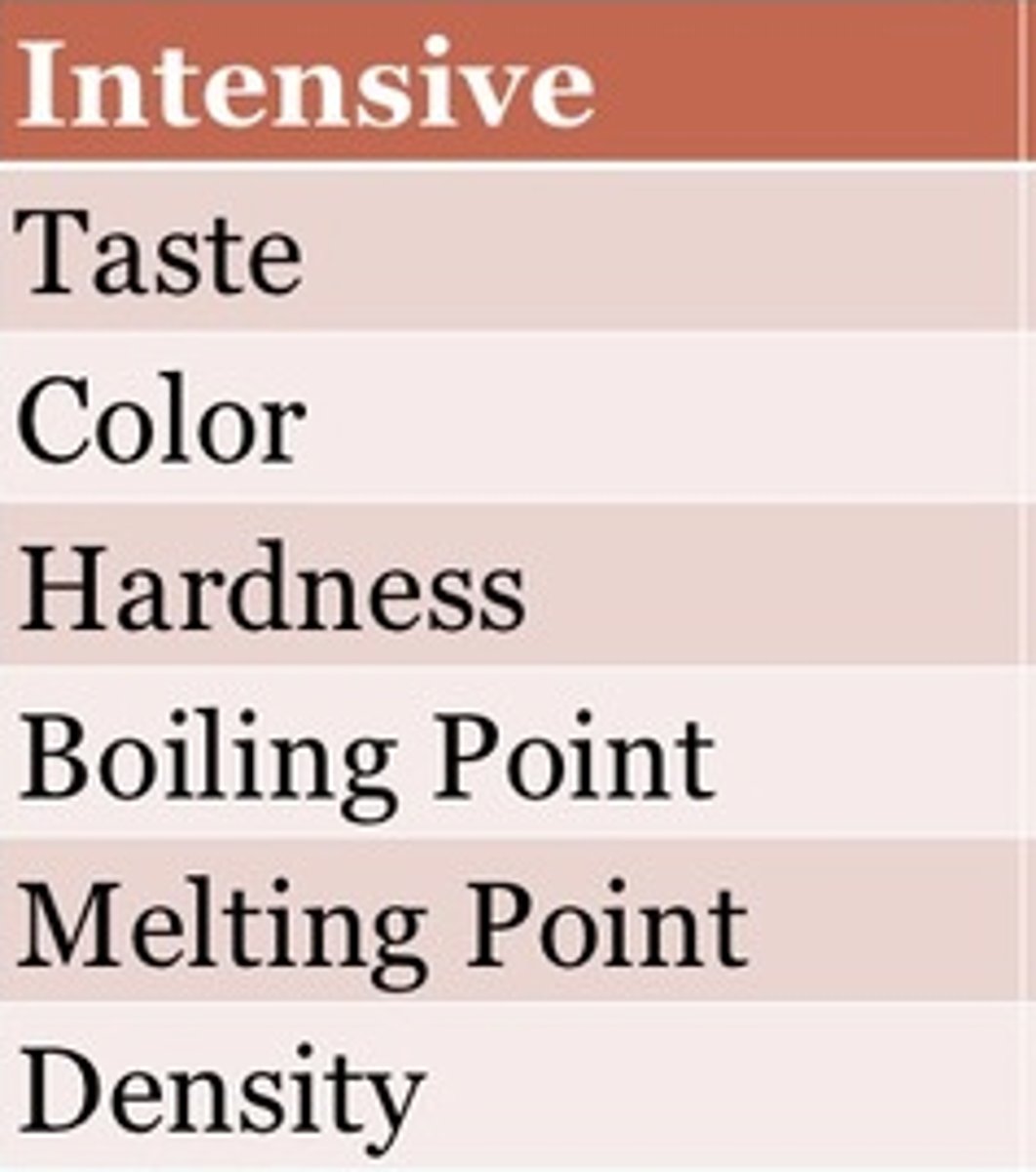
intensive property
a property that depends on the type of matter in a sample, not the amount of matter
Hypothesis
a tentative explanation that can be tested by further investigation
Theory
A hypothesis that has been tested with a significant amount of data
law
a statement that summarizes the relationship between variables
undo log(x)
10^x
undo ln(x)
e^x
in adding and subtracting questions, how do you determine sig figs?
count the numbers to the right of the decimal in the smallest number. 3.445-2.33 will have 2 sig figs.
1 mL also equals
cm^3
What does Dalton's Atomic Theory state about elements?
Elements are composed of atoms.
According to Dalton's Atomic Theory, how do atoms of the same element compare to atoms of different elements?
Atoms of the same element are identical, but differ from other elements.
What does Dalton's Atomic Theory say about the mixing of elements?
Elements can mix together.
When do atoms change according to Dalton's Atomic Theory?
Atoms only change when mixed with other elements.
Which of Dalton's theories are incorrect?
Elements are composed of small indivisible, indestructible particles called atoms
All atom of an element are identical and have the same mass and properties
J.J Thomson's
discovery of the electron using a cathode ray tube experiment.
showed that mass-to-charge ratio and that electrons are negatively charged
Plum Pudding Model
J.J Thomsons model of an atom, in which he thought electrons were randomly distributed within a positively charged cloud
proven WRONG by rutherford
Who disproved the plum pudding model?
Ernest Rutherford
Ernest Ritherford
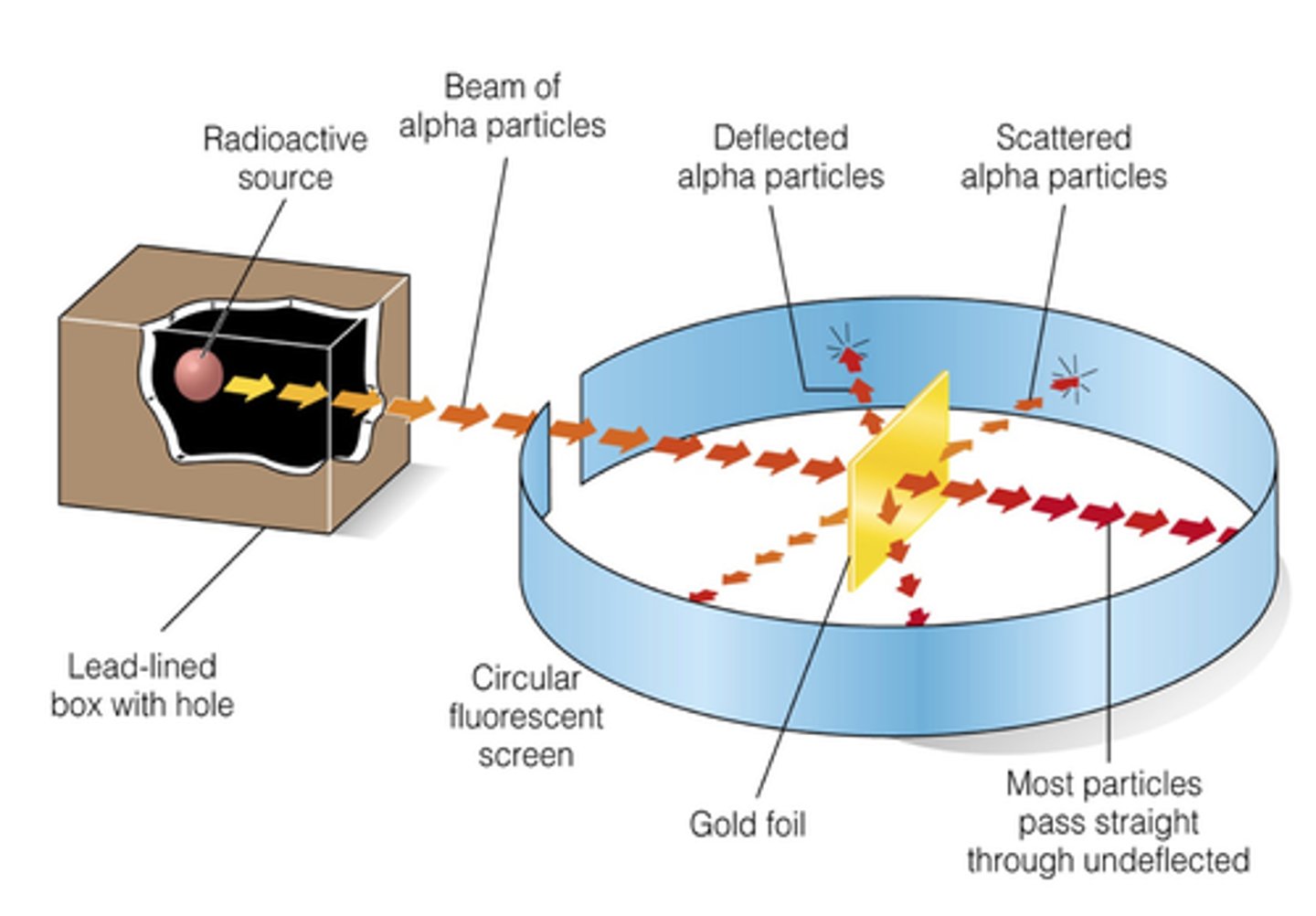
Gold foil experiment which tested plum pudding model. It disproved it and discovered the nucleus and that there were (+) charged subatomic particles.
how did Rutherford's gold foil experiment work?
-shot alpha particles through a small slit, thinking the particles would pass through
-the particles would often go straight through or a little to the side and light up the fluorescent screen
-most surprised when he saw the fluorescent screen light up in front of the gold foil, meaning the alpha particle bounced back
-proved that there is something positively charged in an atom
Robert Millikan
used the oil-drop apparatus to determine the charge of an electron. Proved e- was negative.
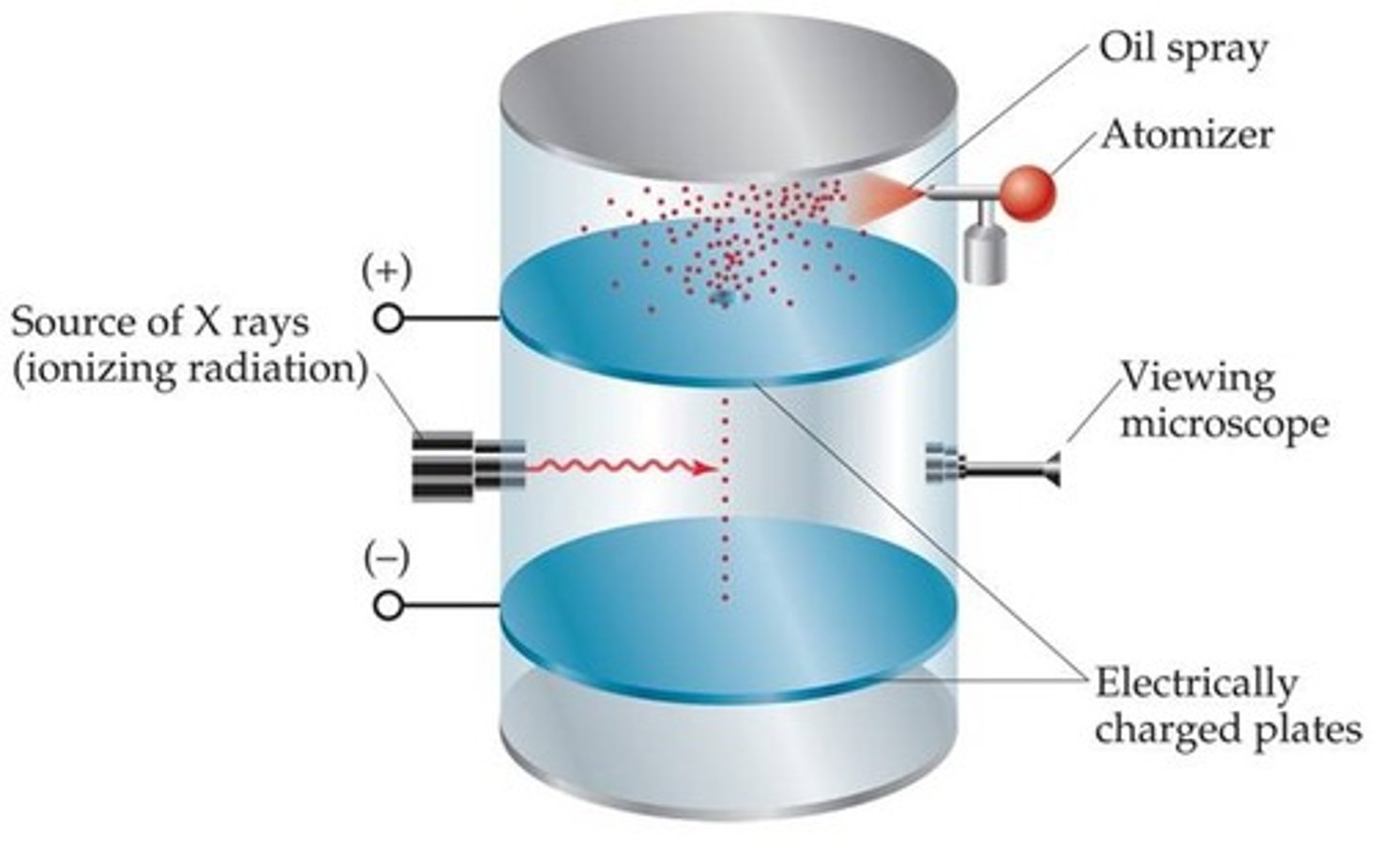
Law of Conservation of Mass
Matter is not created nor destroyed in any chemical or physical change
law of definite proportions
a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the sample or source of the compound
Law of Multiple Proportions
if two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers
Charge of first column
1
Charge of second column
2
Charge of 13th column
3+
Charge of 15th column
3-
Charge of 16th column
2-
Charge of 17th column
1-
charge of the 18th column
0
column one is known as
alkali metals
Column 2 is known as
alkaline earth metals
column 16 is known as
chalcogens
column 17 is known as
halogens
column 18 is known as
noble gases
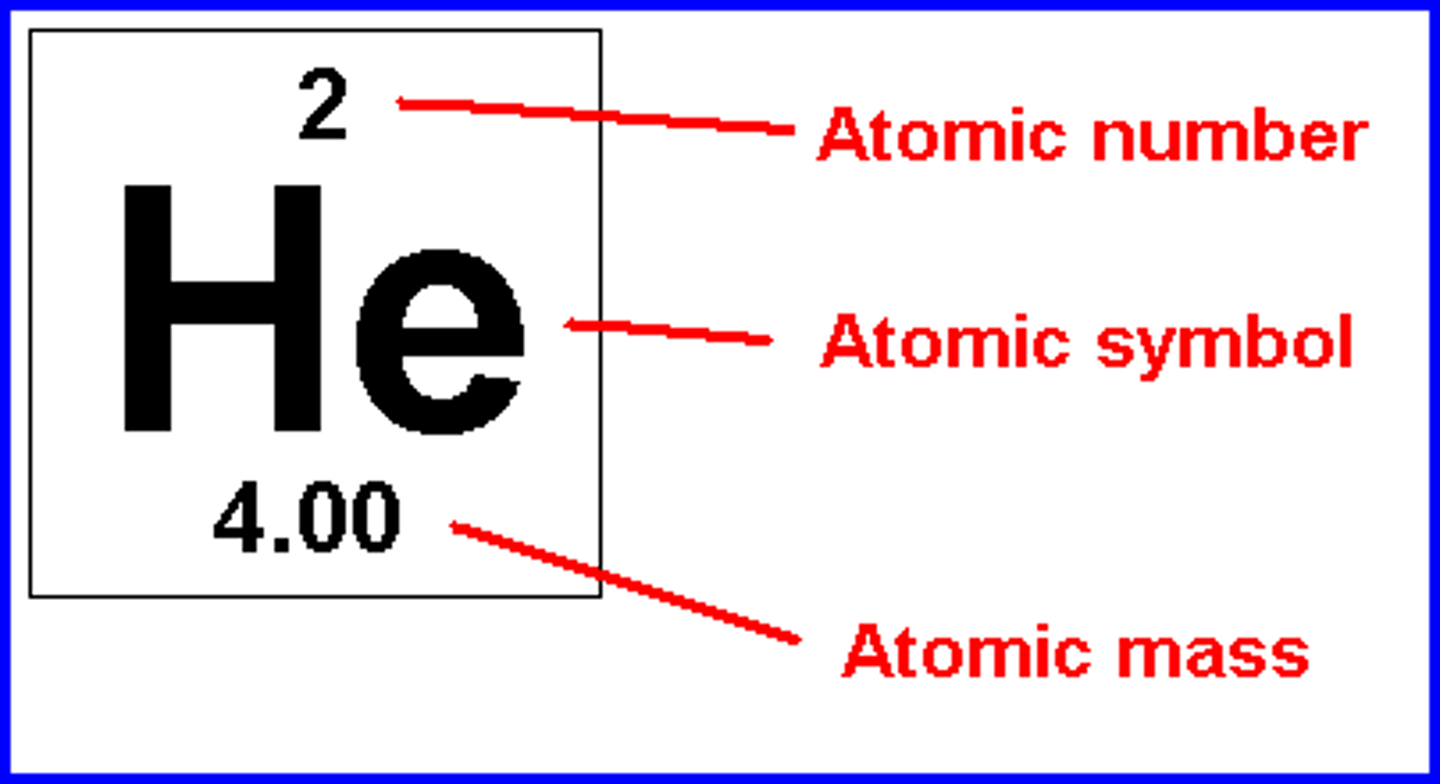
atomic mass is
protons + neutrons
what does not change in an isotope?
number of protons
where is the line of metalloids that separates metals and nonmetals?
from B to AT
mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
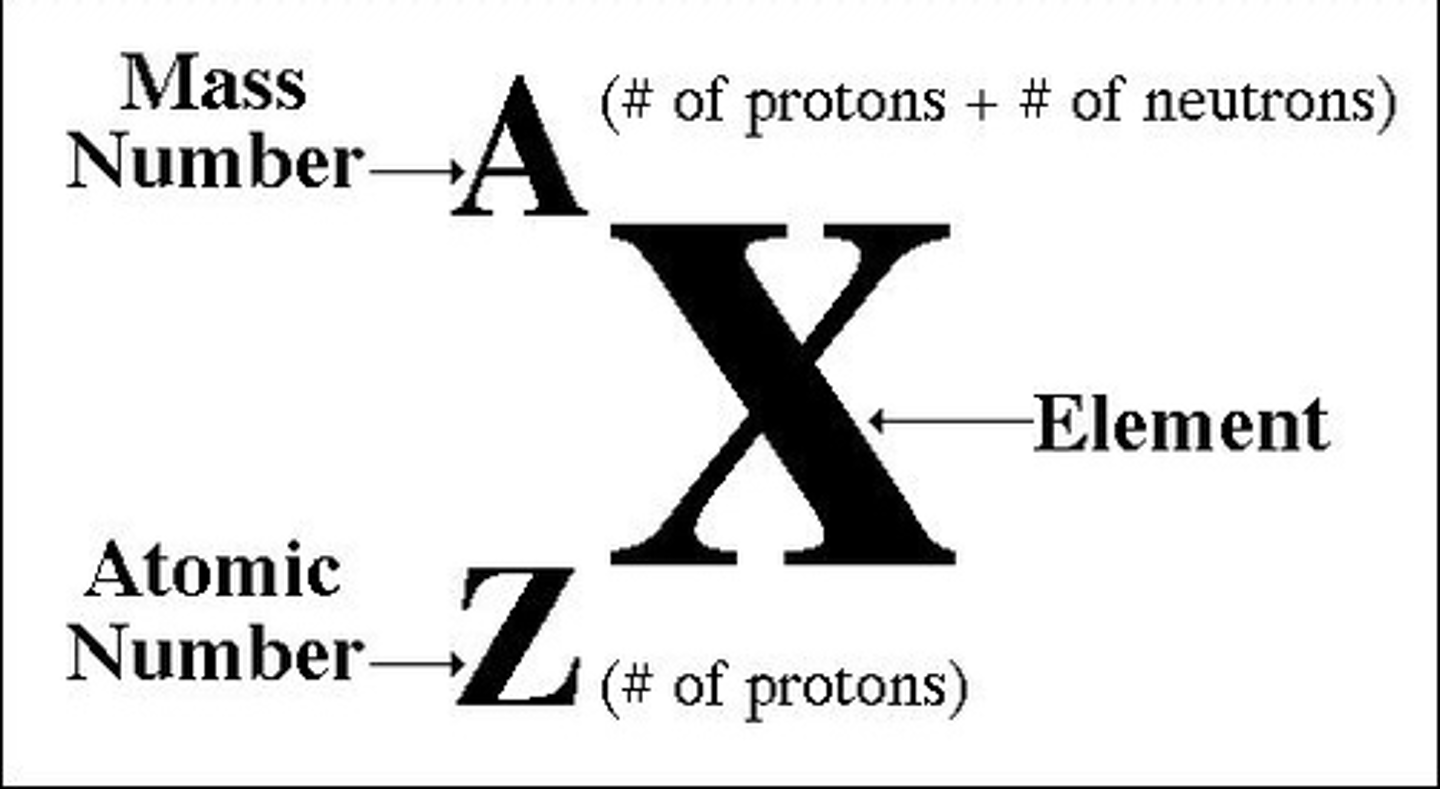
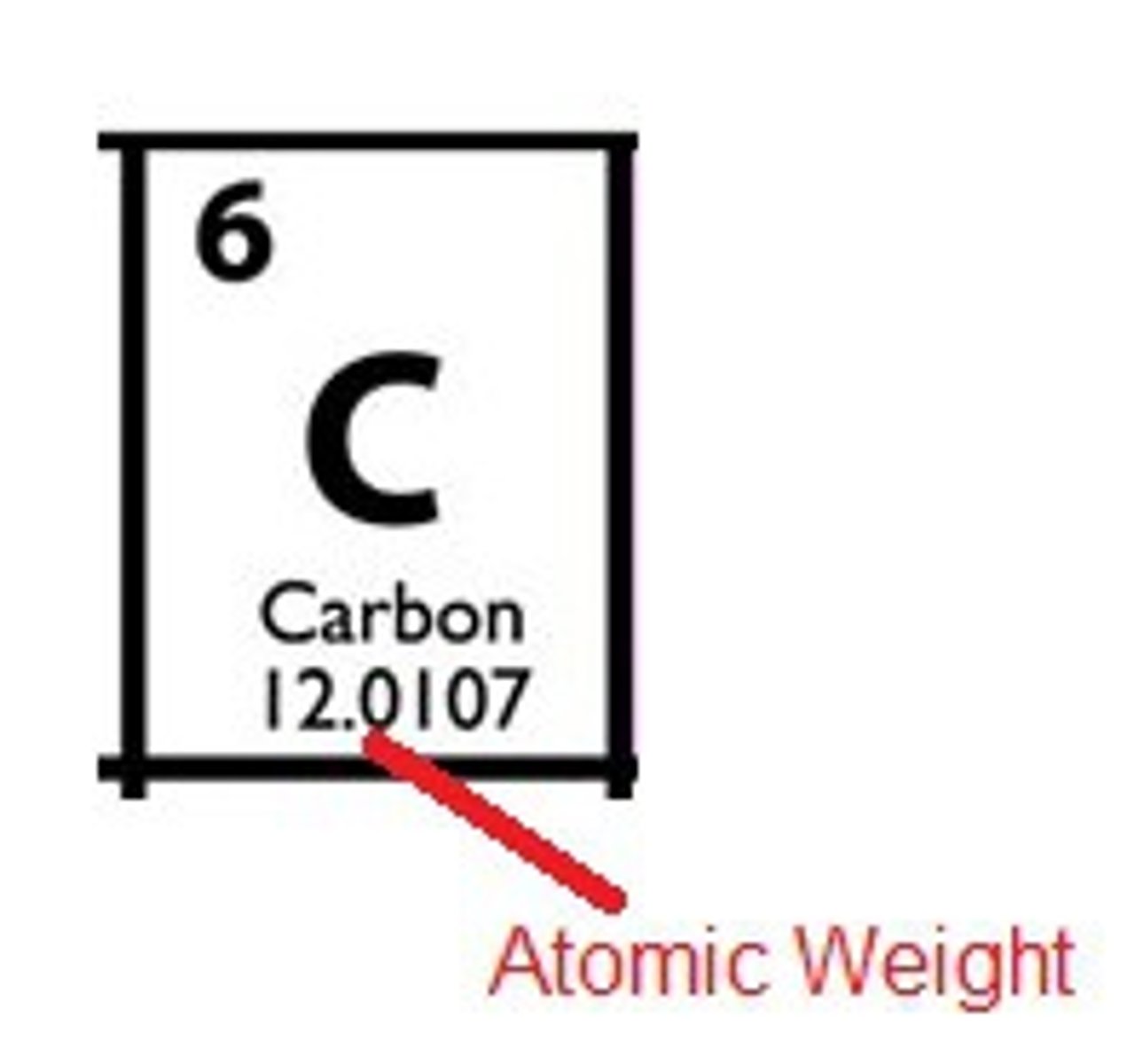
atomic weight
Average of the mass numbers of all isotopes
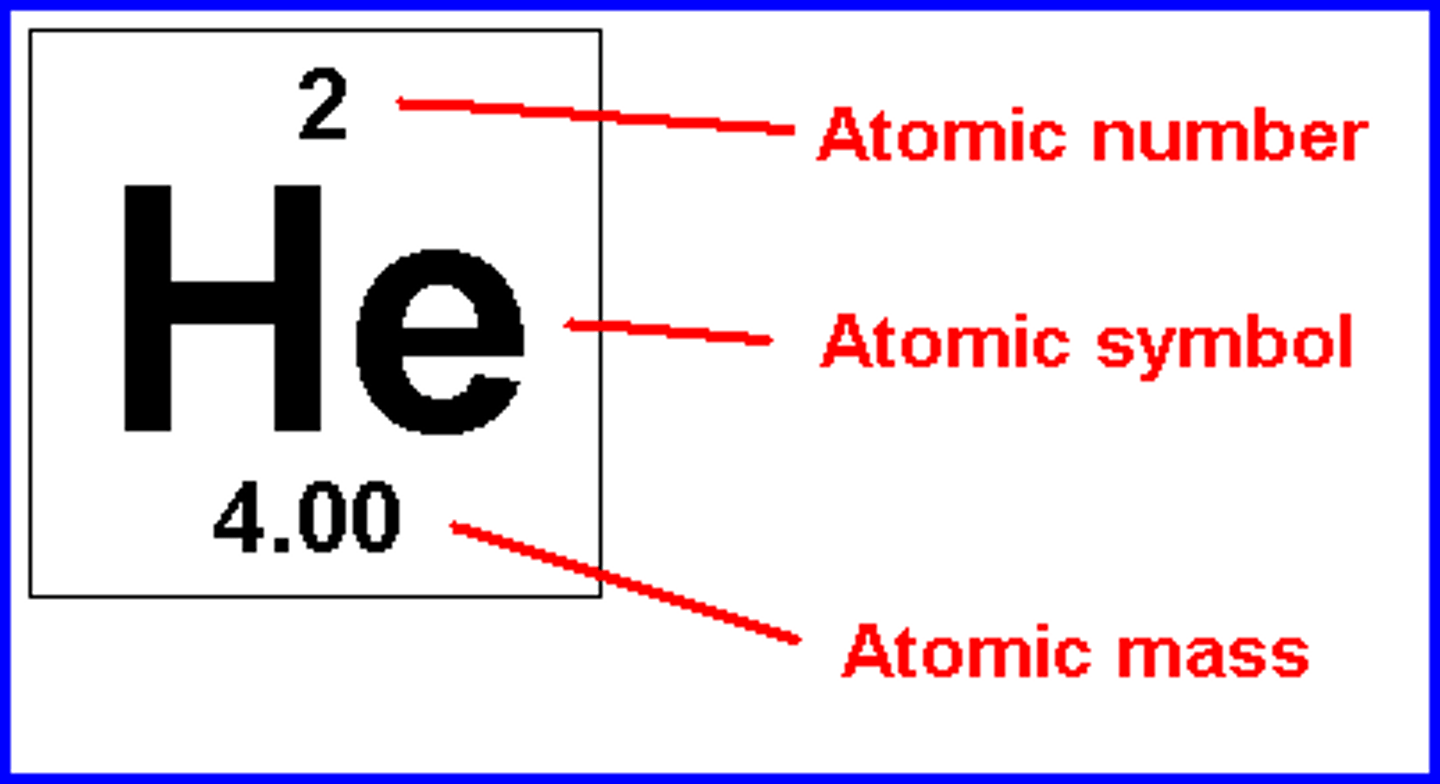
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
transition metals
groups 3-12
When starting to name a chemical, what is the first step?
determine if it is an ionic or covalent bond
ionic bond
metal and nonmetal
transfer of e-
two polar elements
covalent bond
two atoms sharing e-
two nonmetals
metallic bond
the attraction of a metallic cation for delocalized electrons
diatomic elements
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer
Hydronium
H3O+
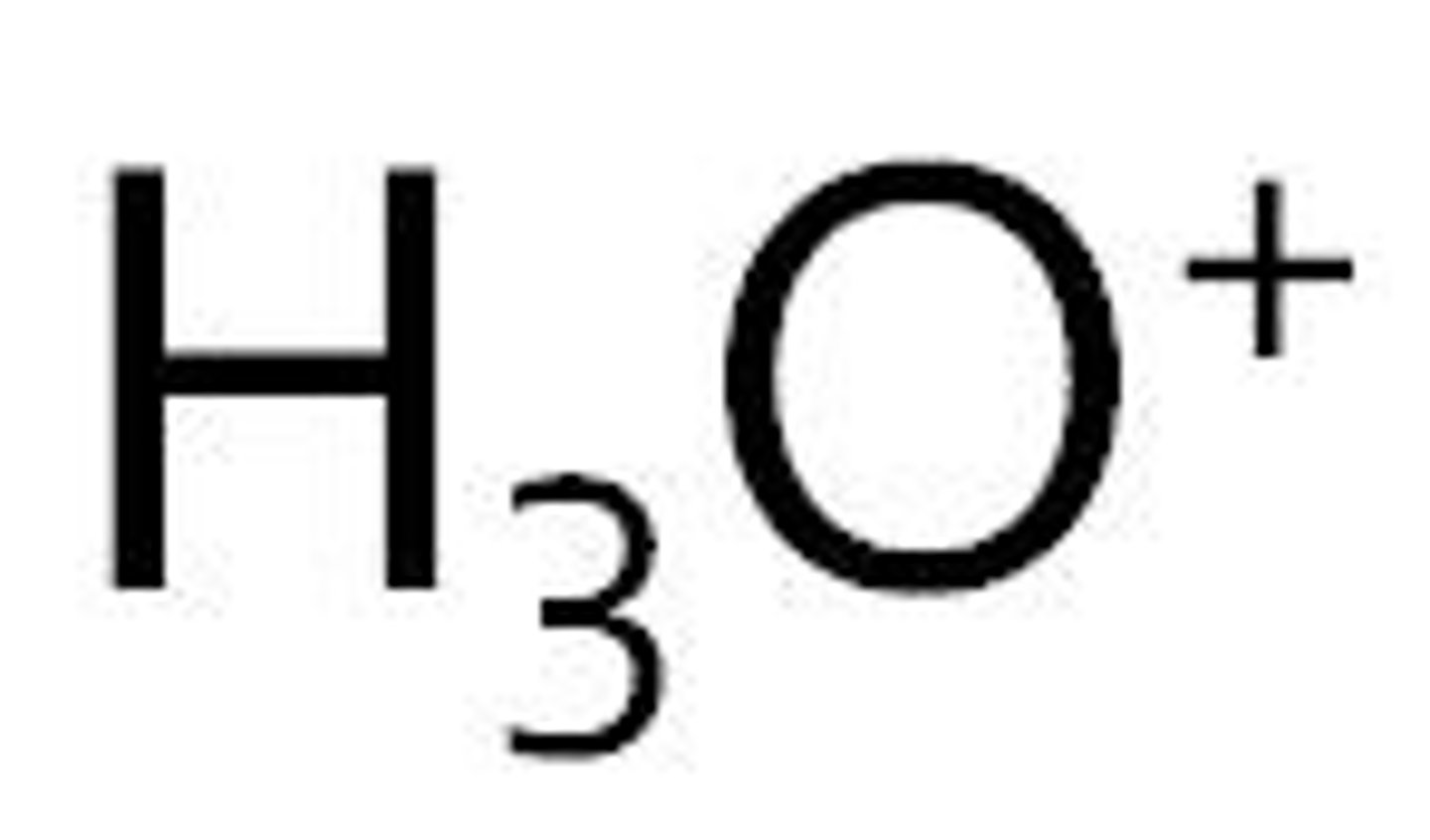
Ammonium
NH4+
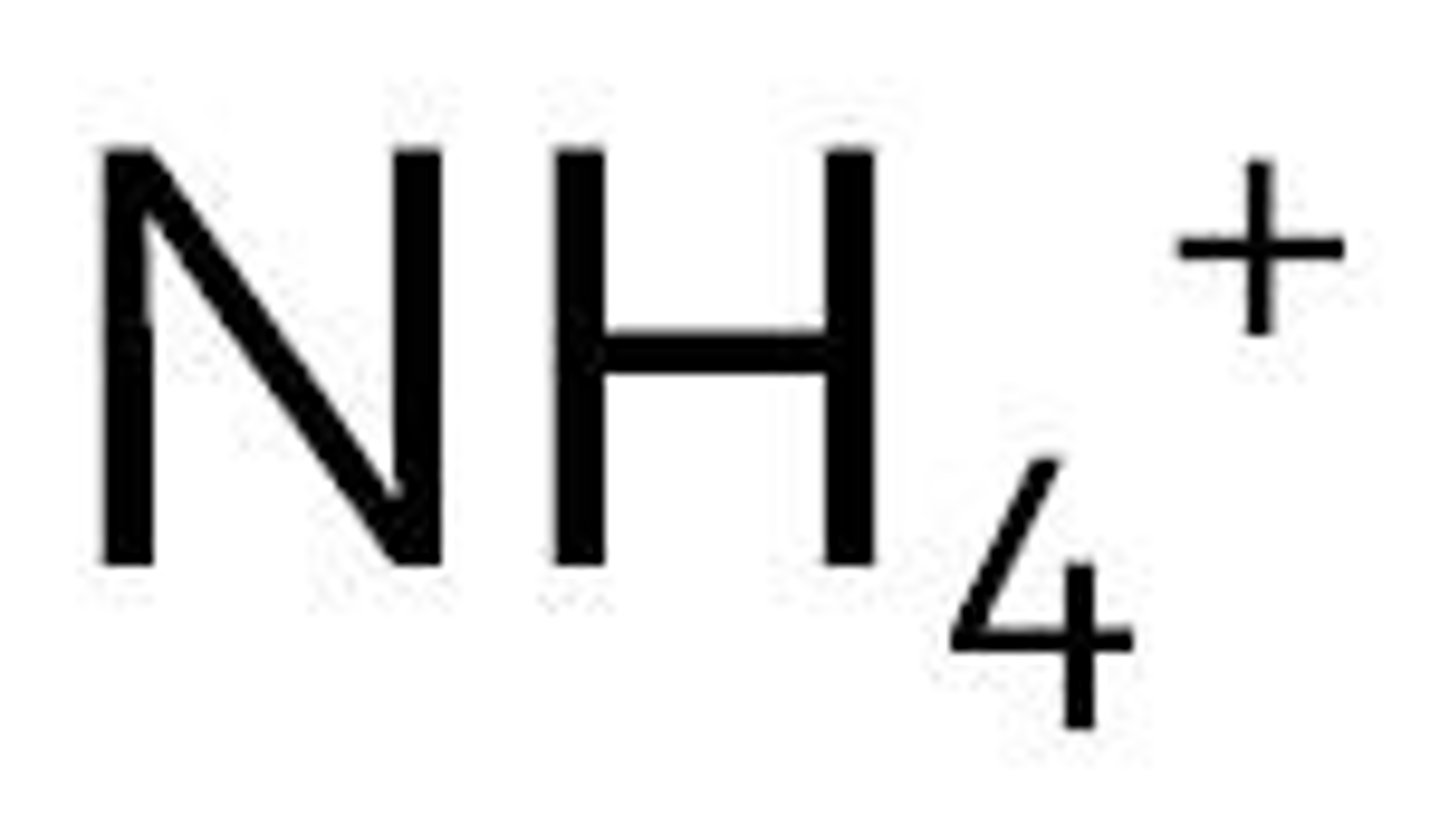
hydroxide
OH-
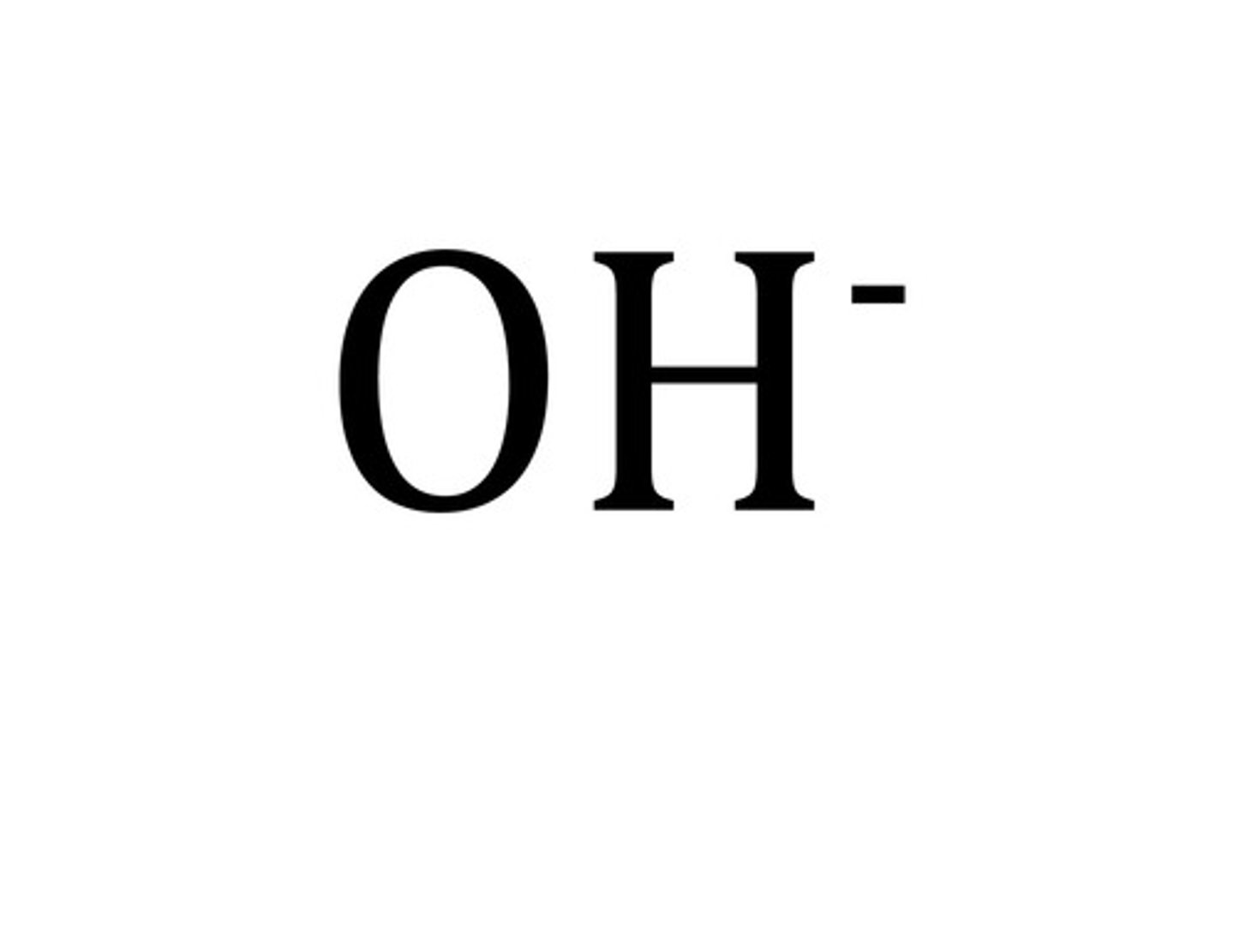
Cyanide
CN-

Nitrate
NO3-
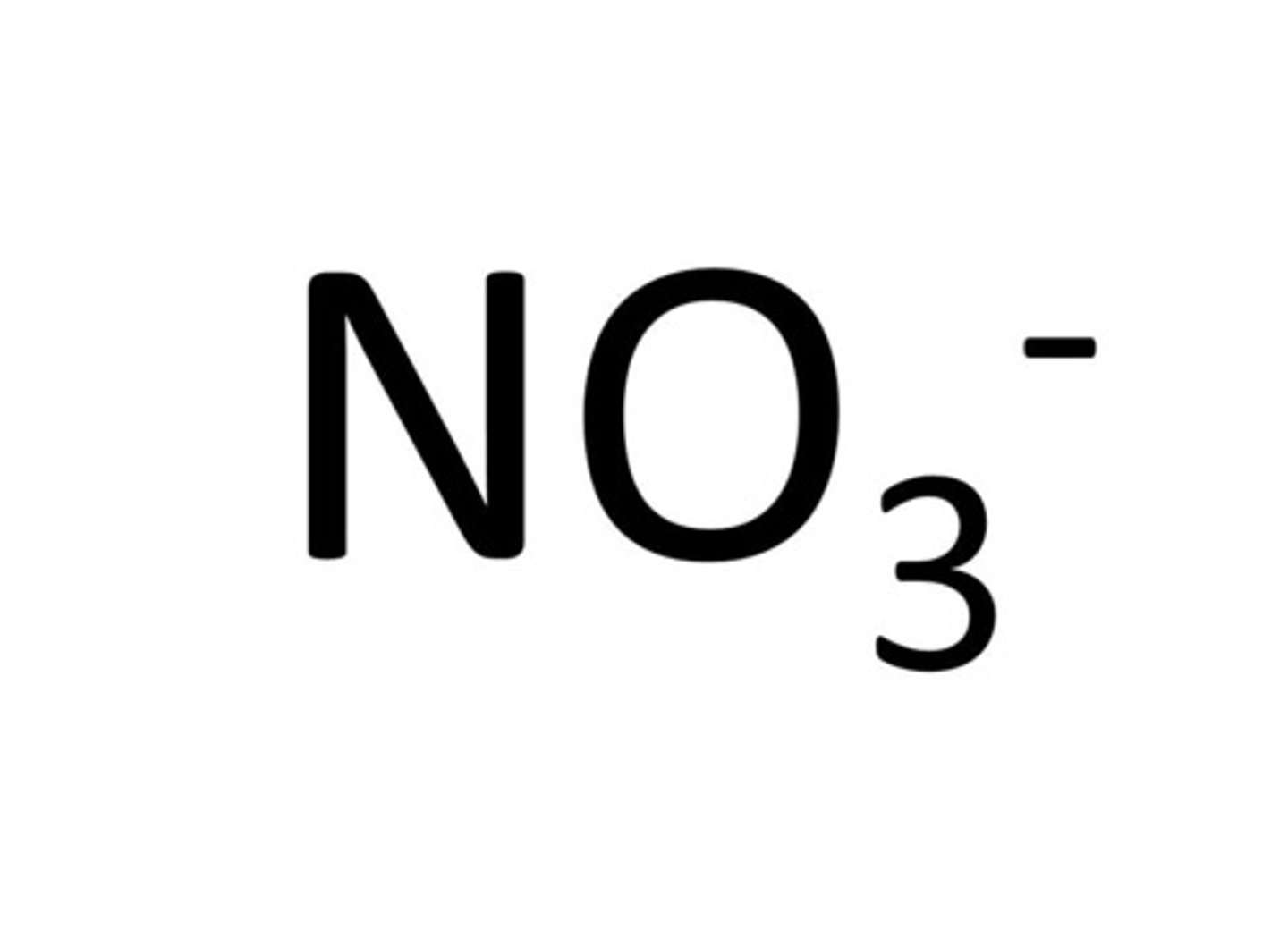
Nitrite
NO2-
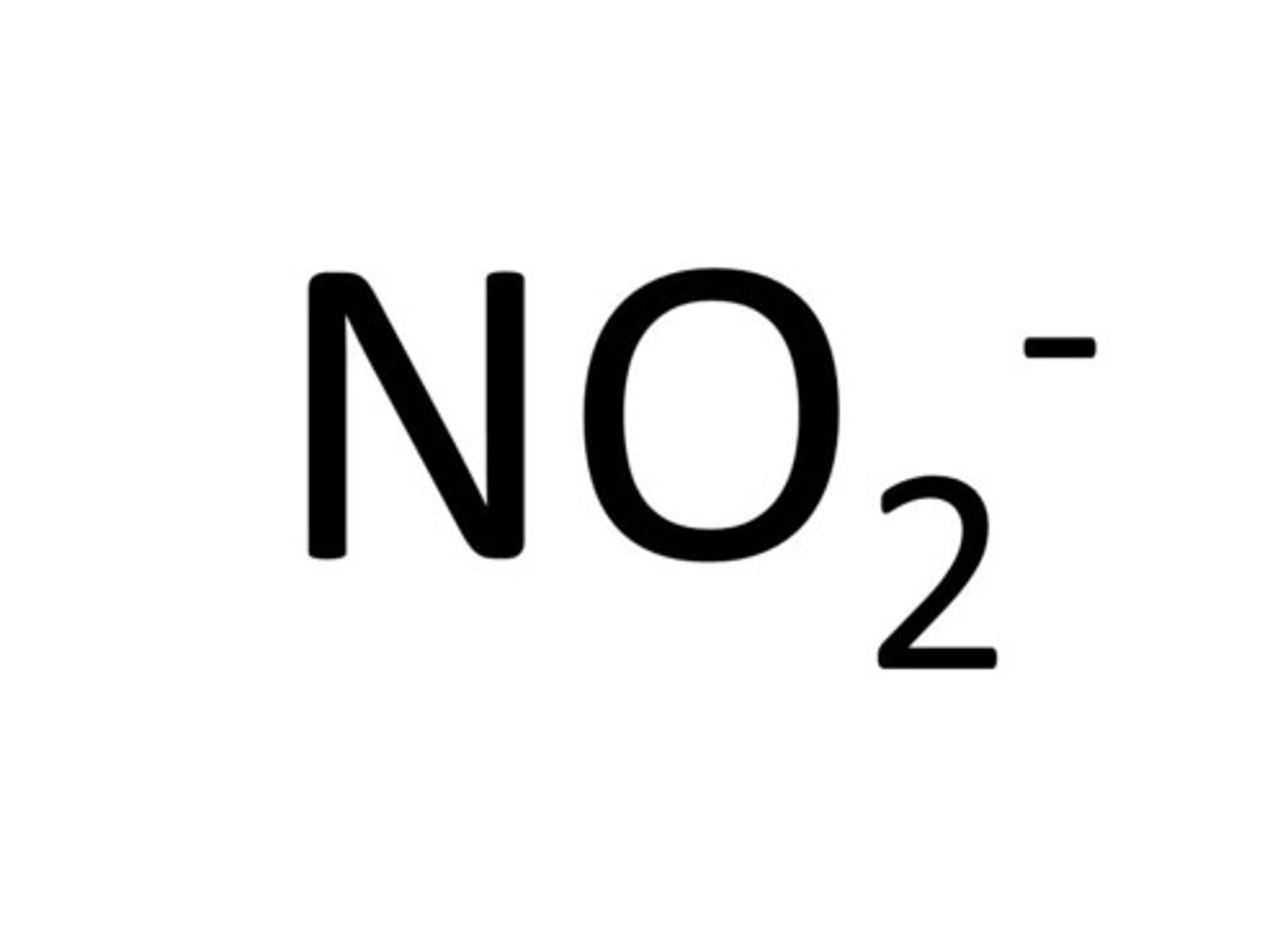
Carbonate
CO3 2-
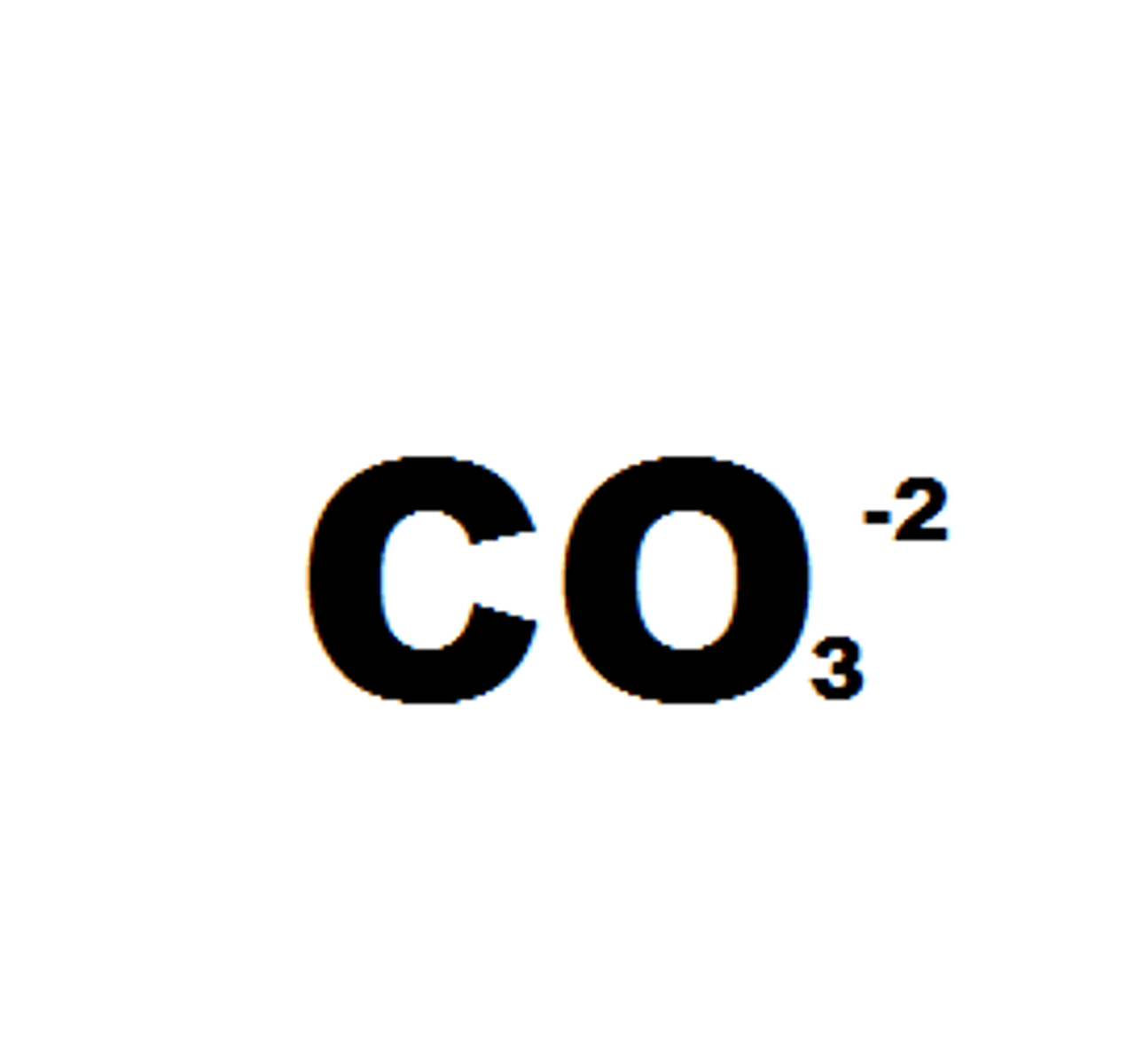
Hydrogen carbonate
HCO3-
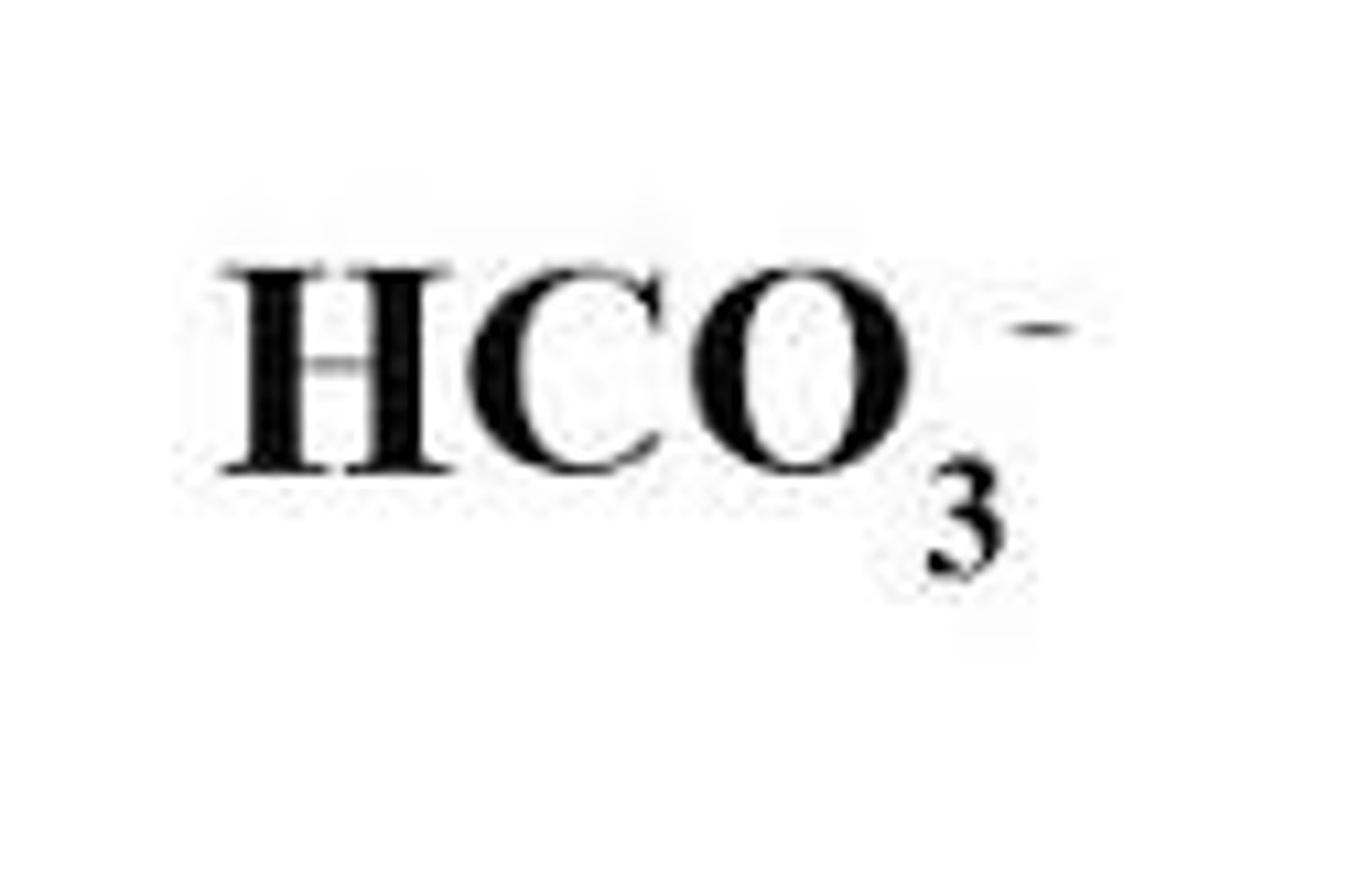
Sulfate
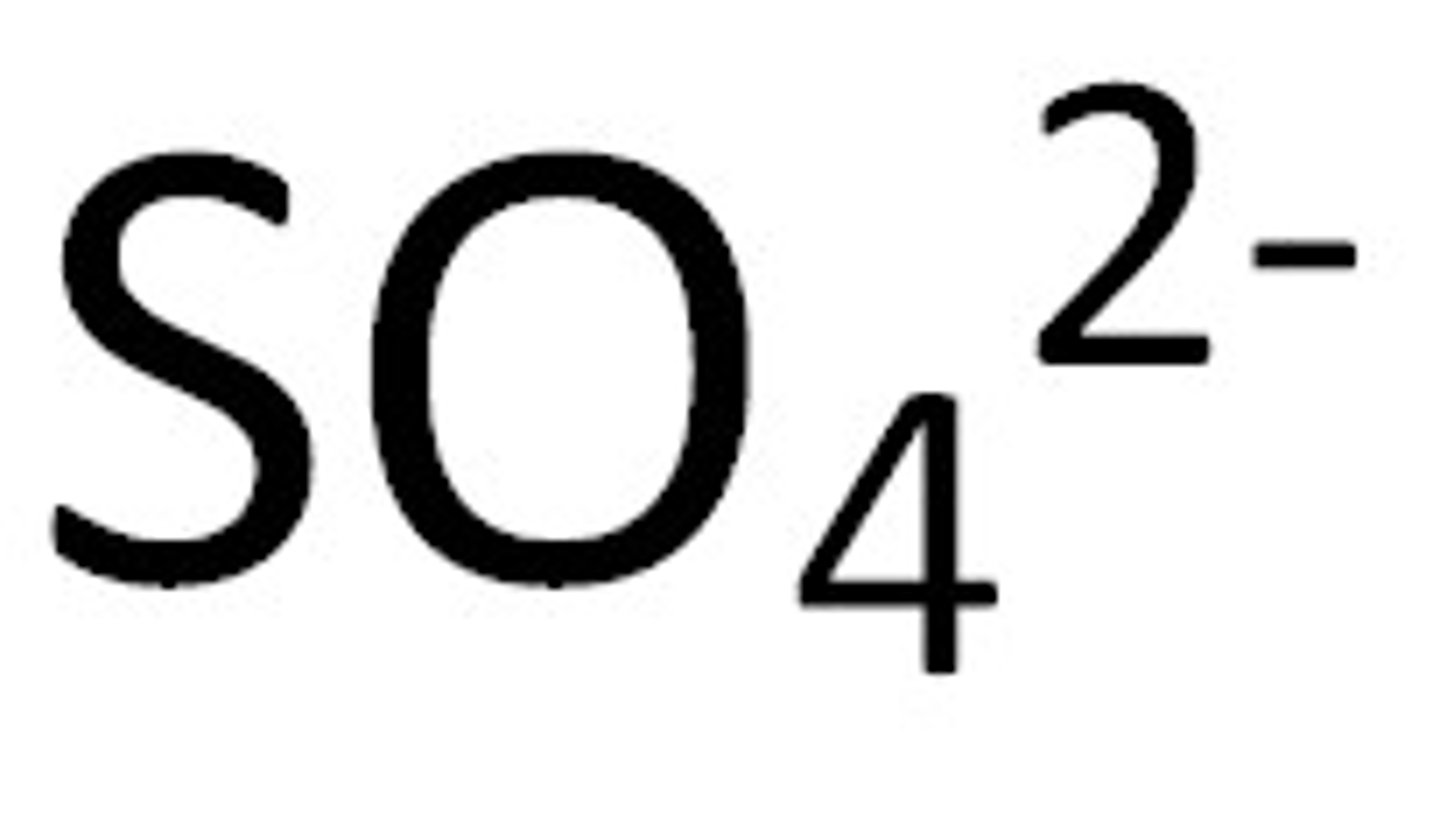
Sulfite
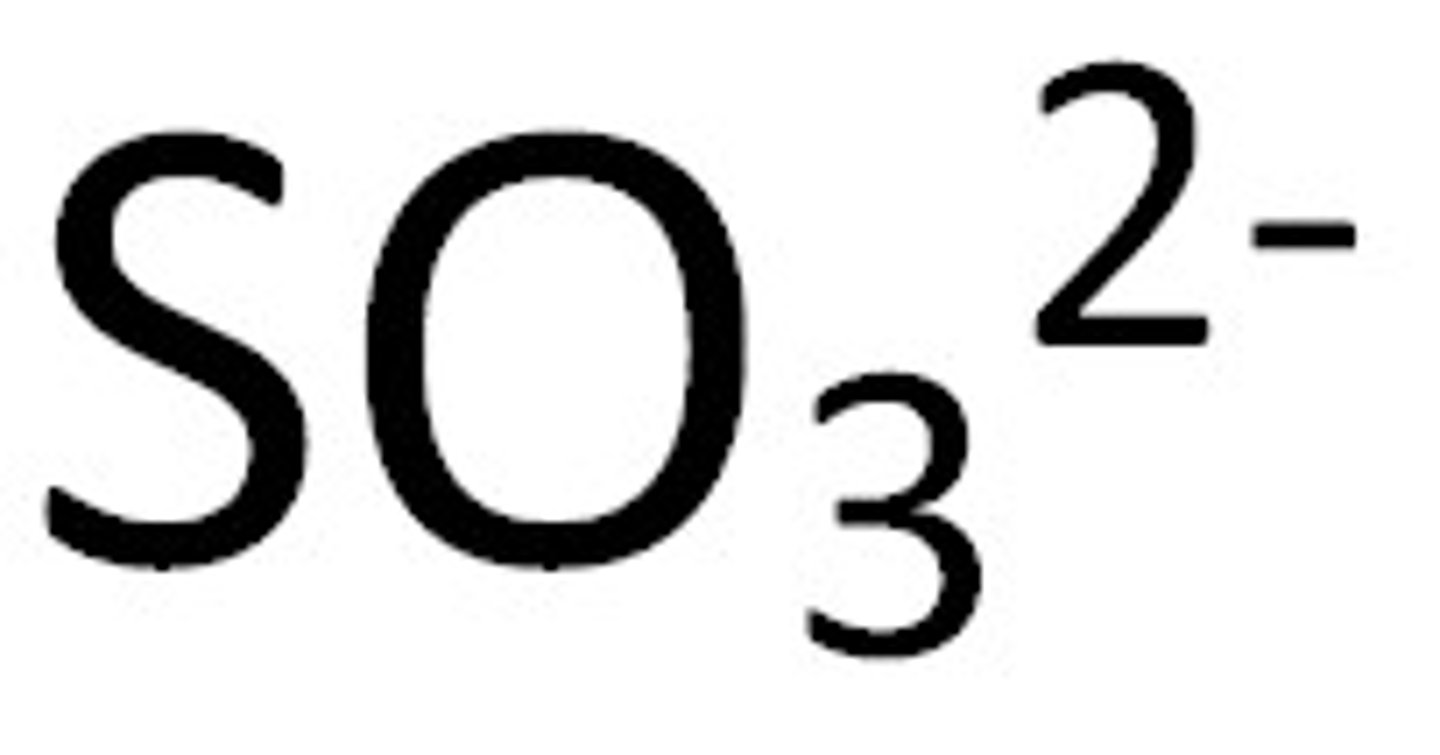
Phosphate
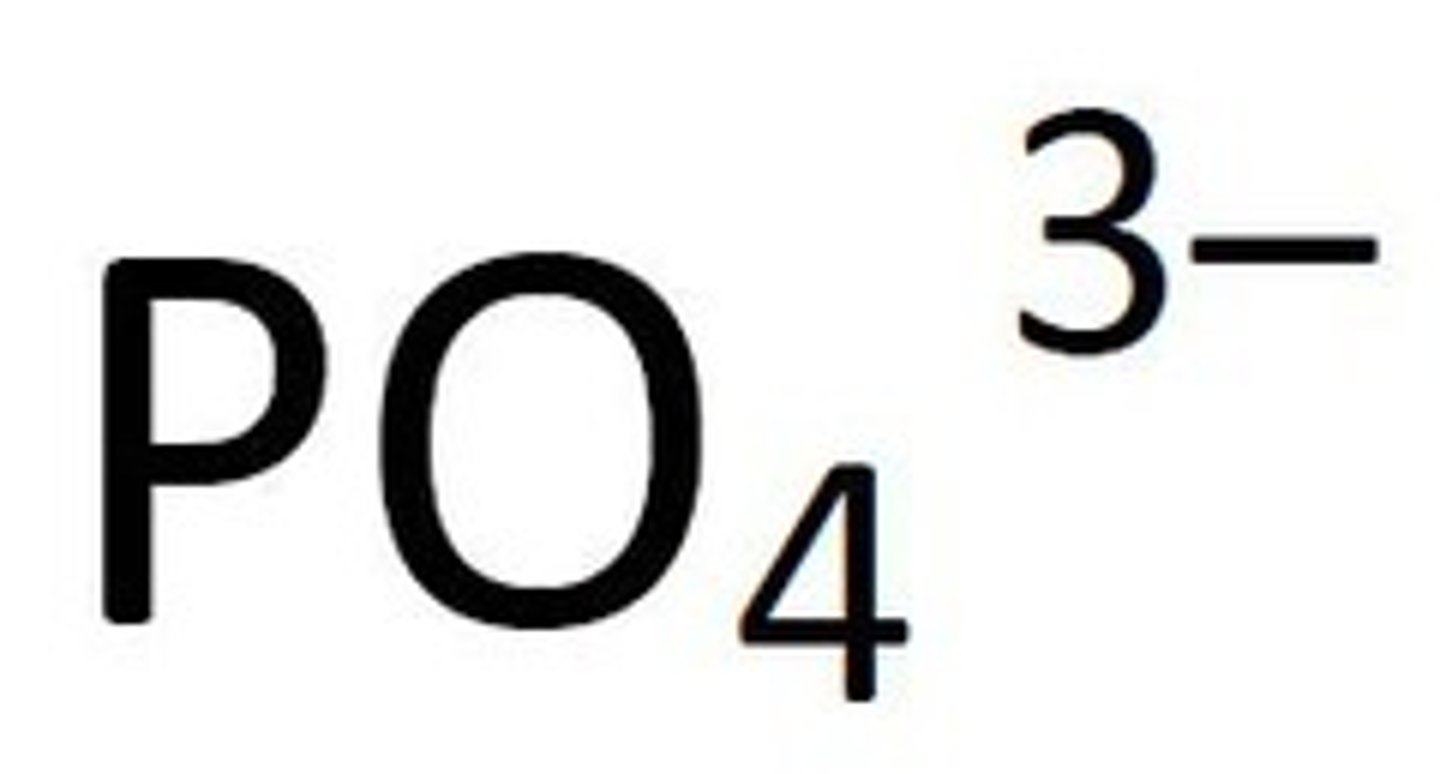
Hydrogen Phosphate
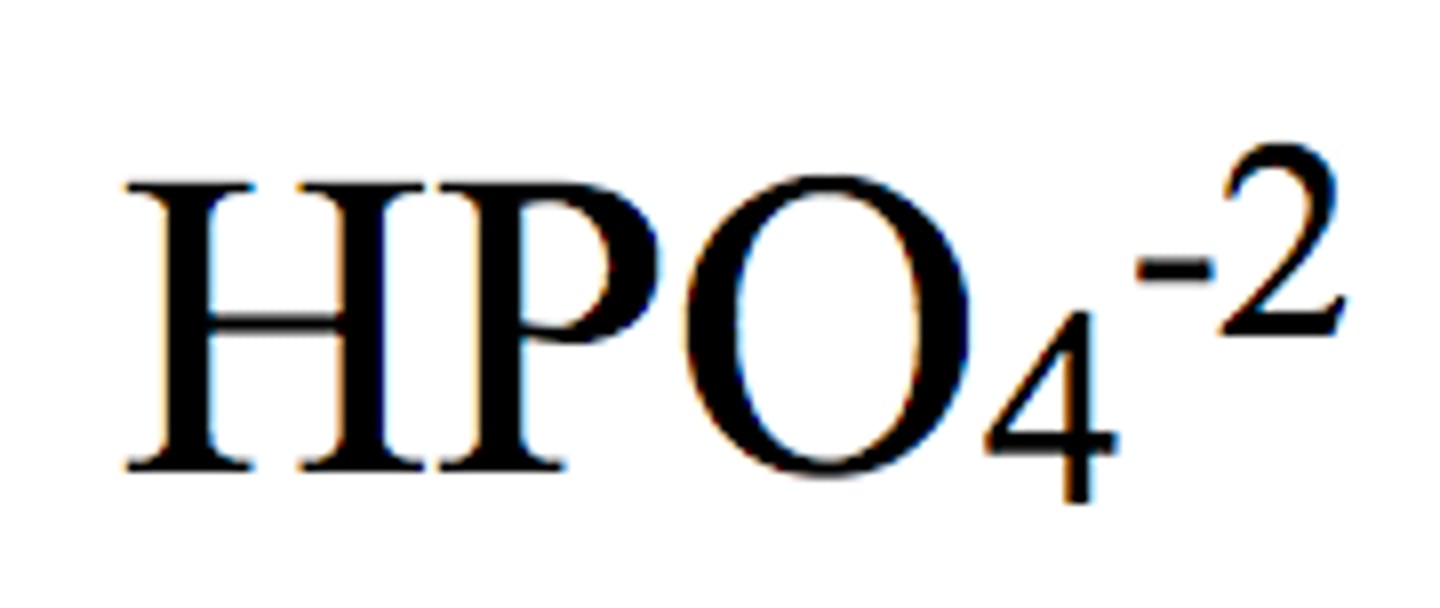
Dihydrogen Phosphate

Acetate
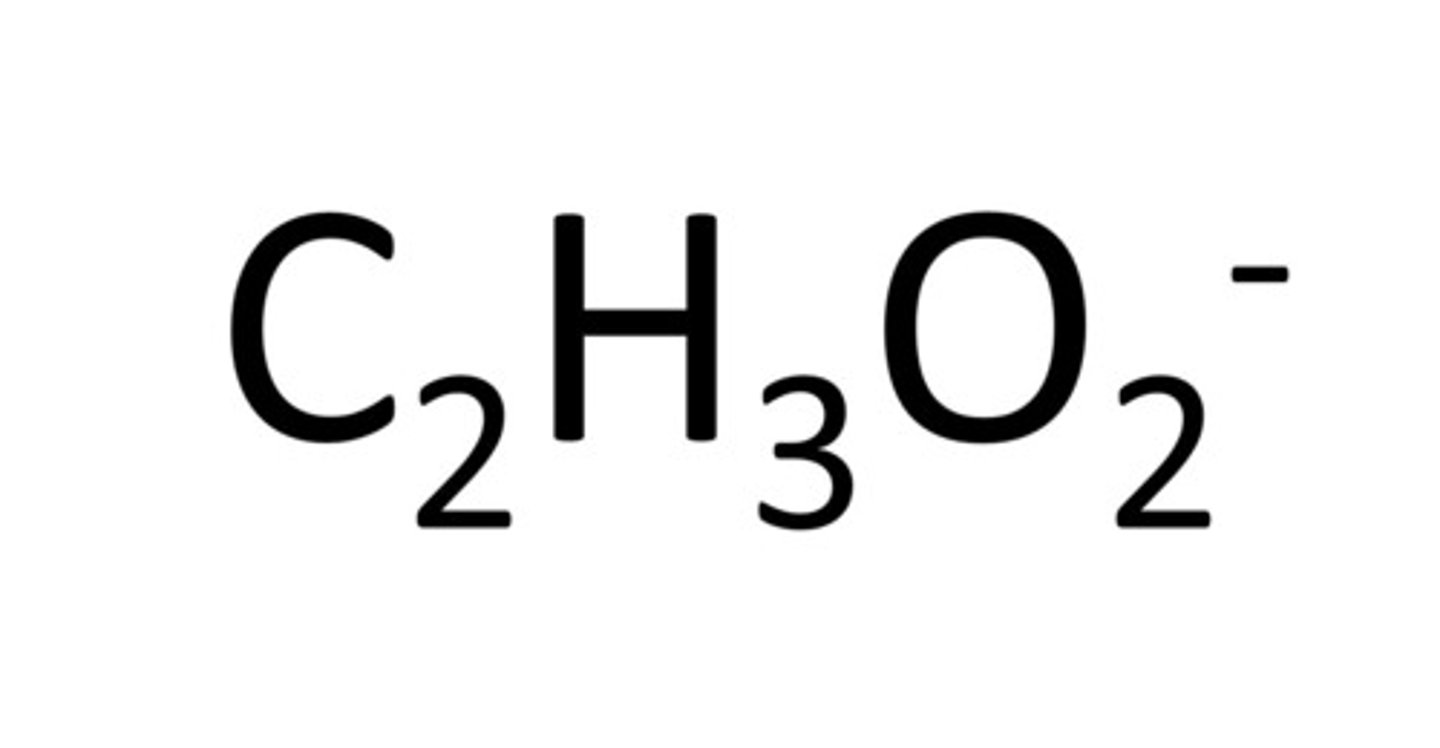
Permanganate
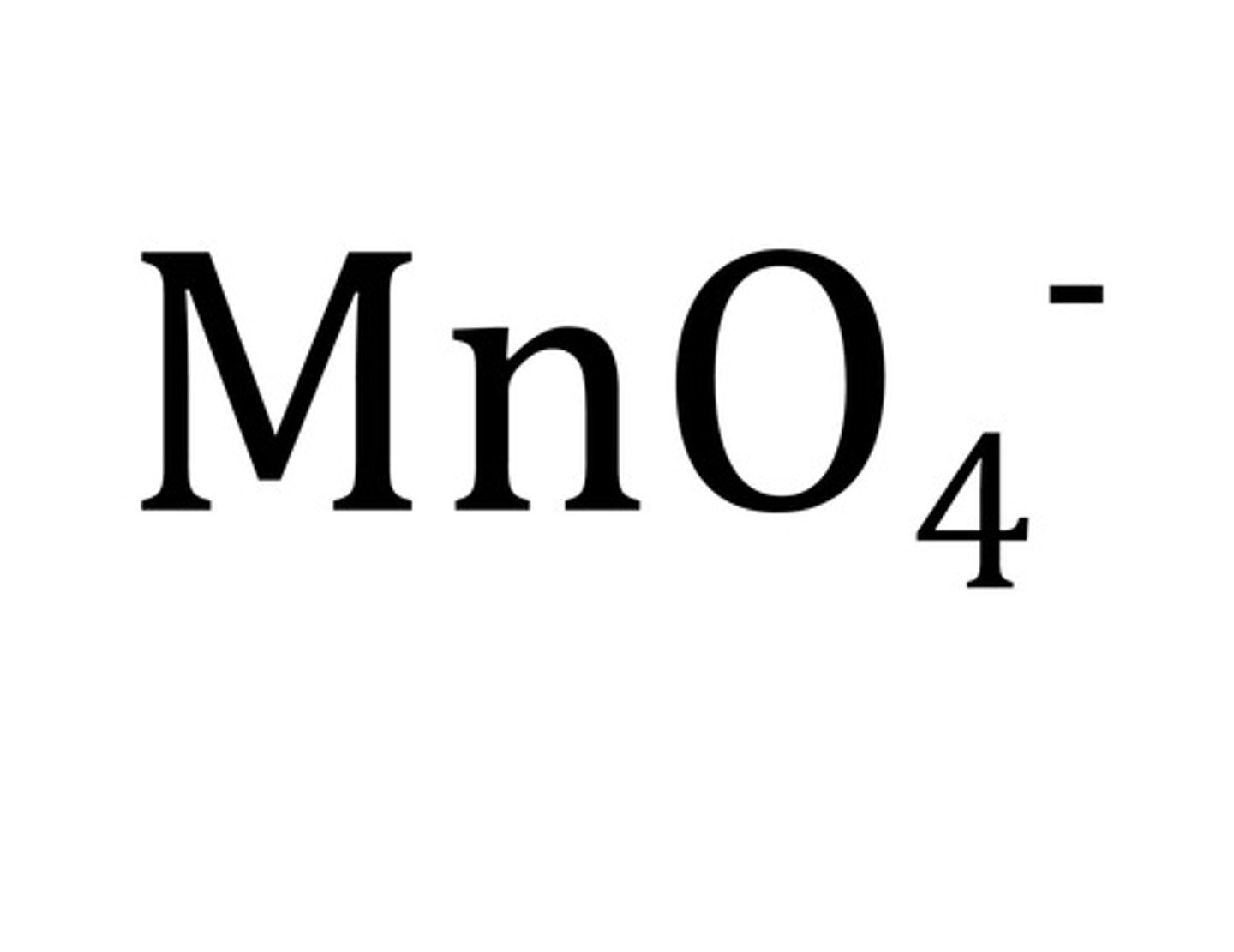
Chromate
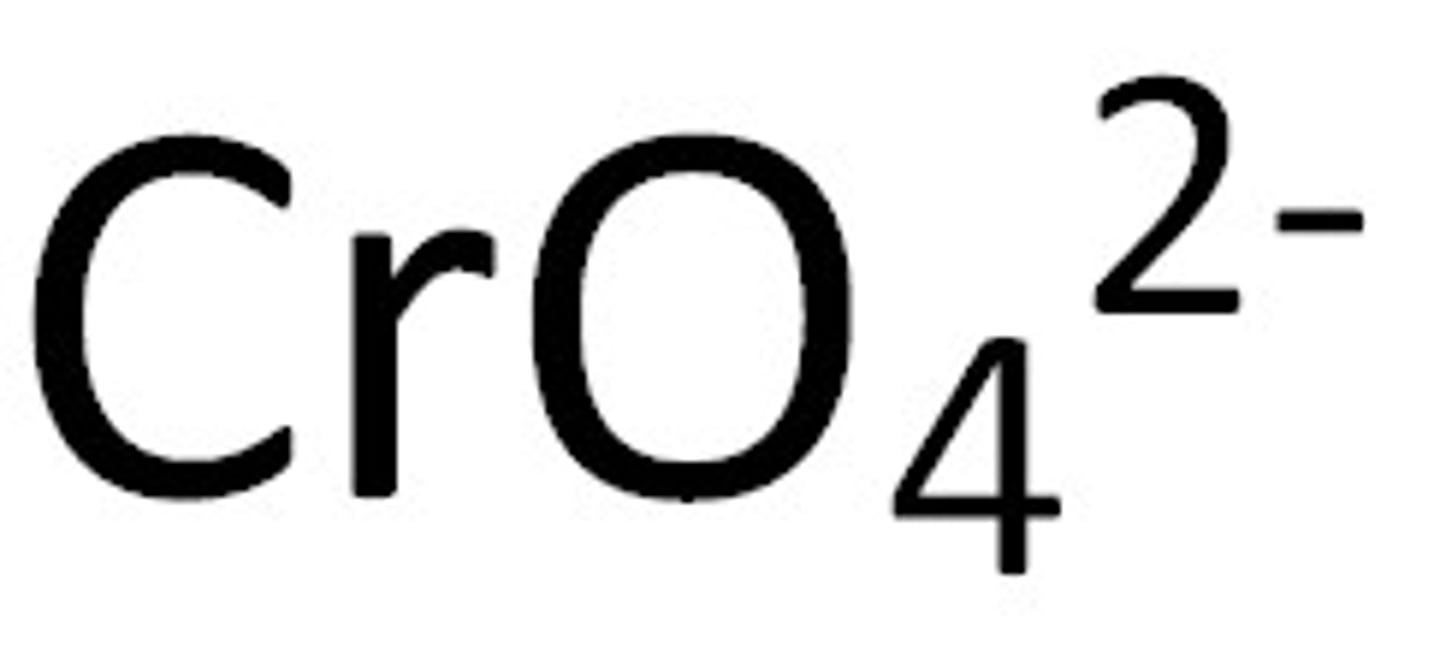
Dichromate
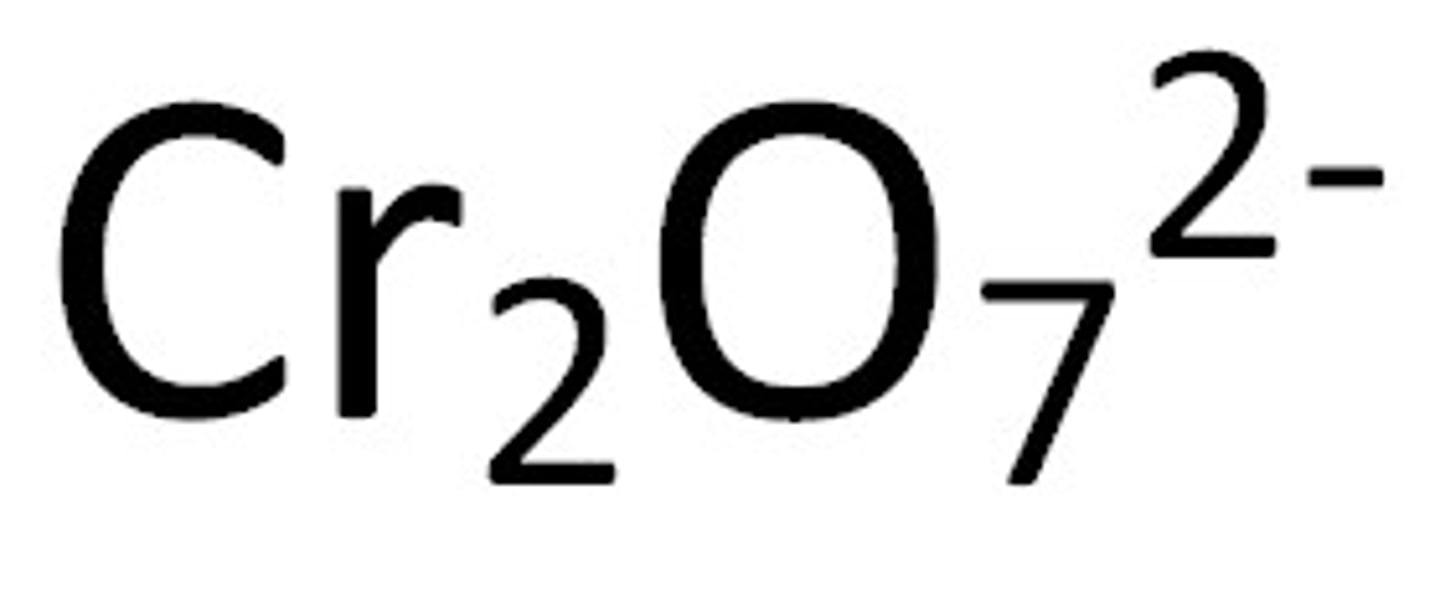
Perchlorate
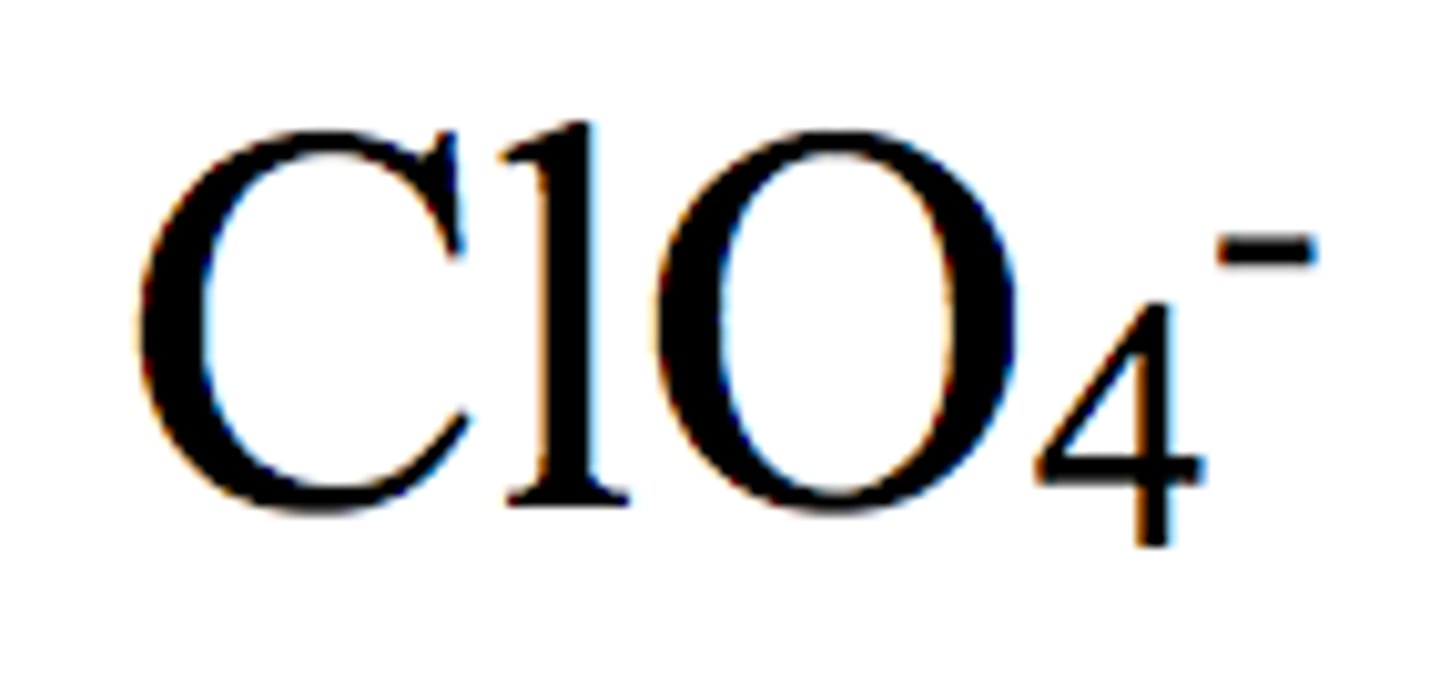
Chlorate
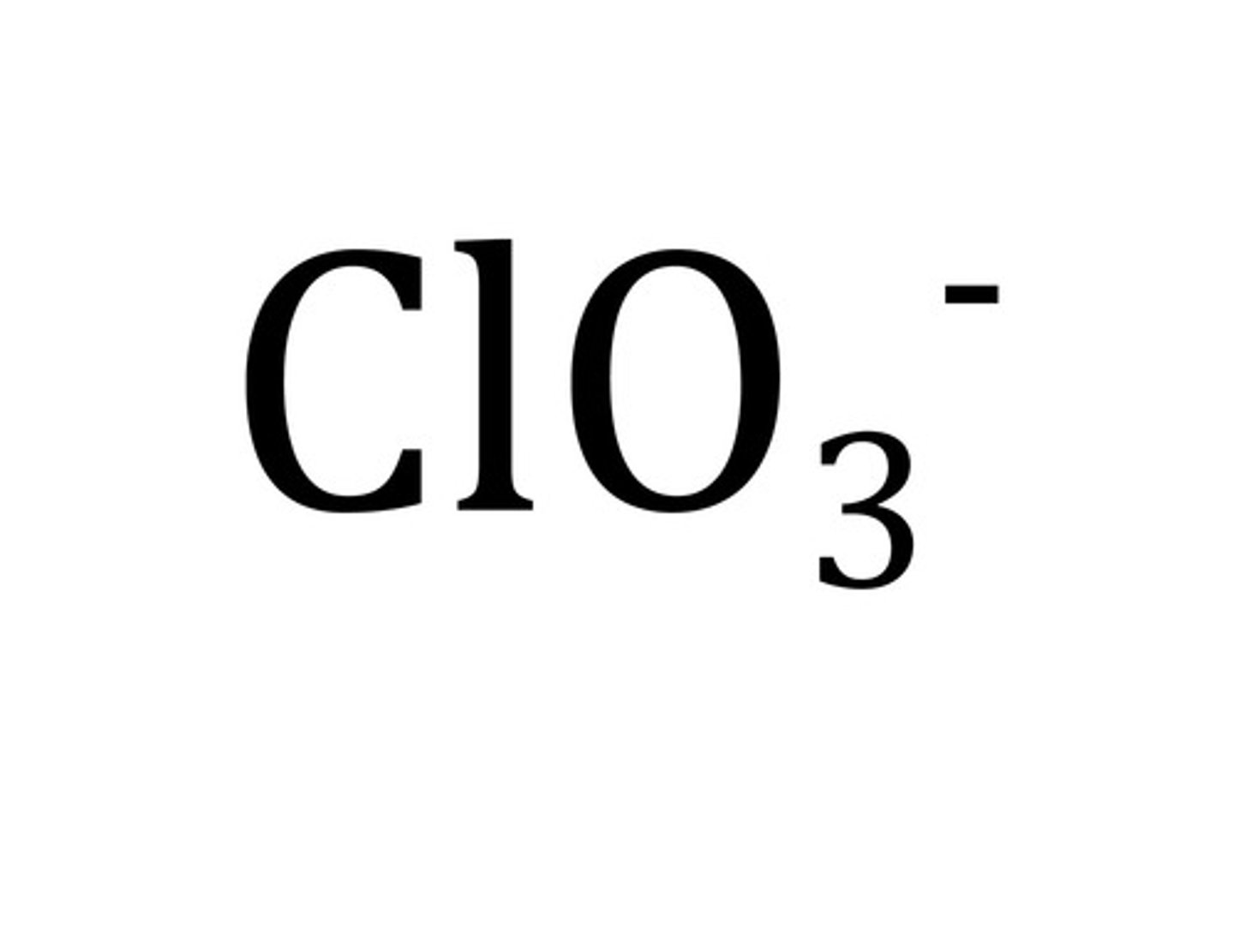
Chlorite
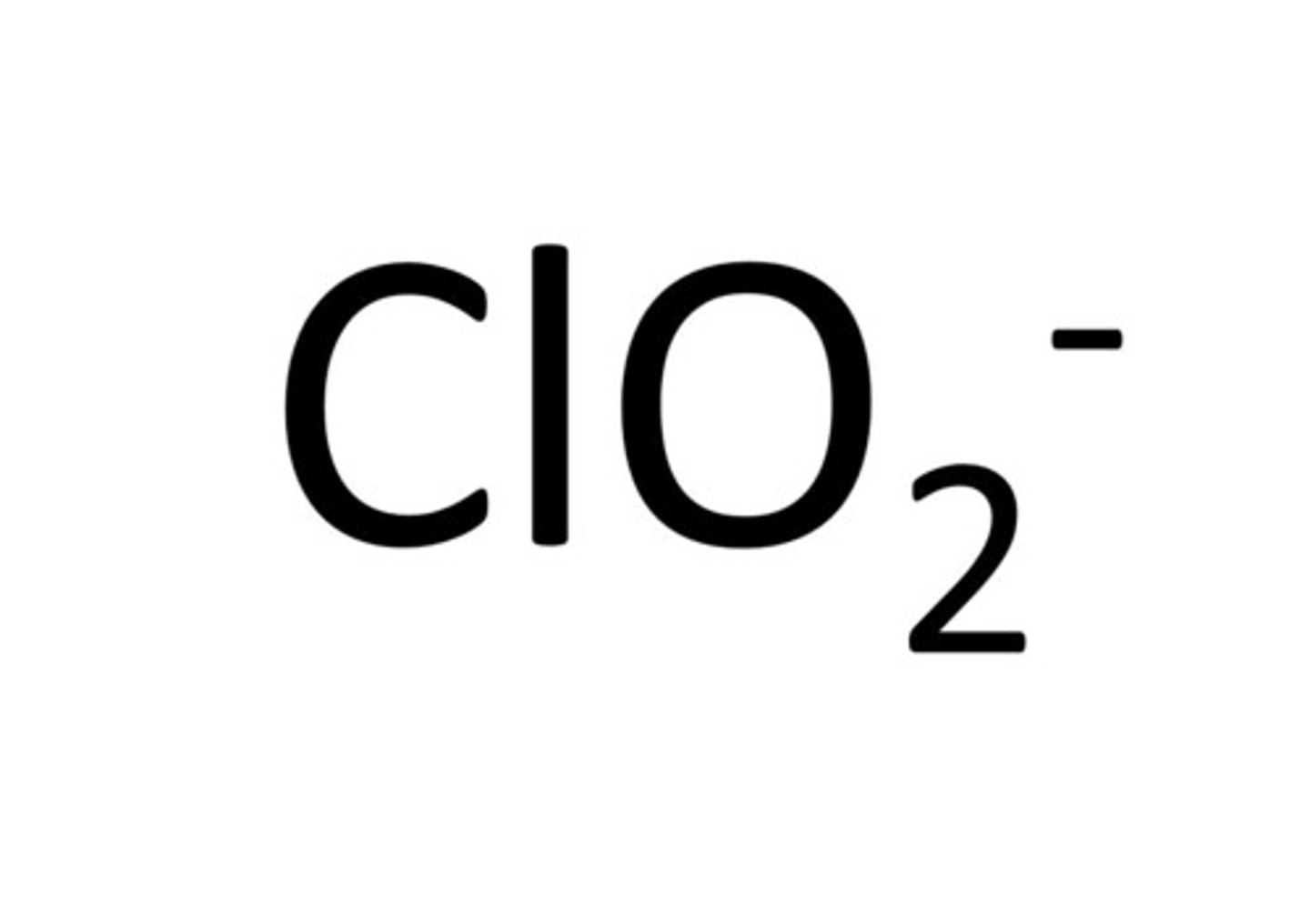
Hypochlorite
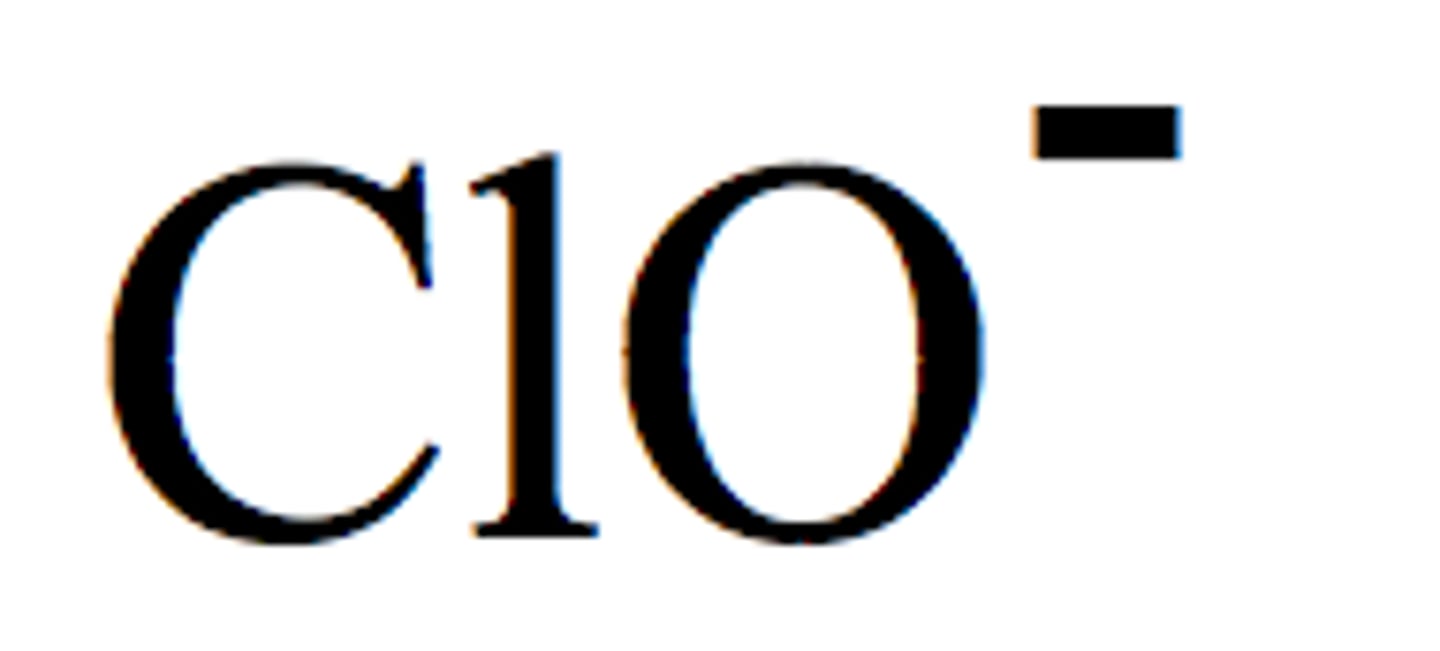
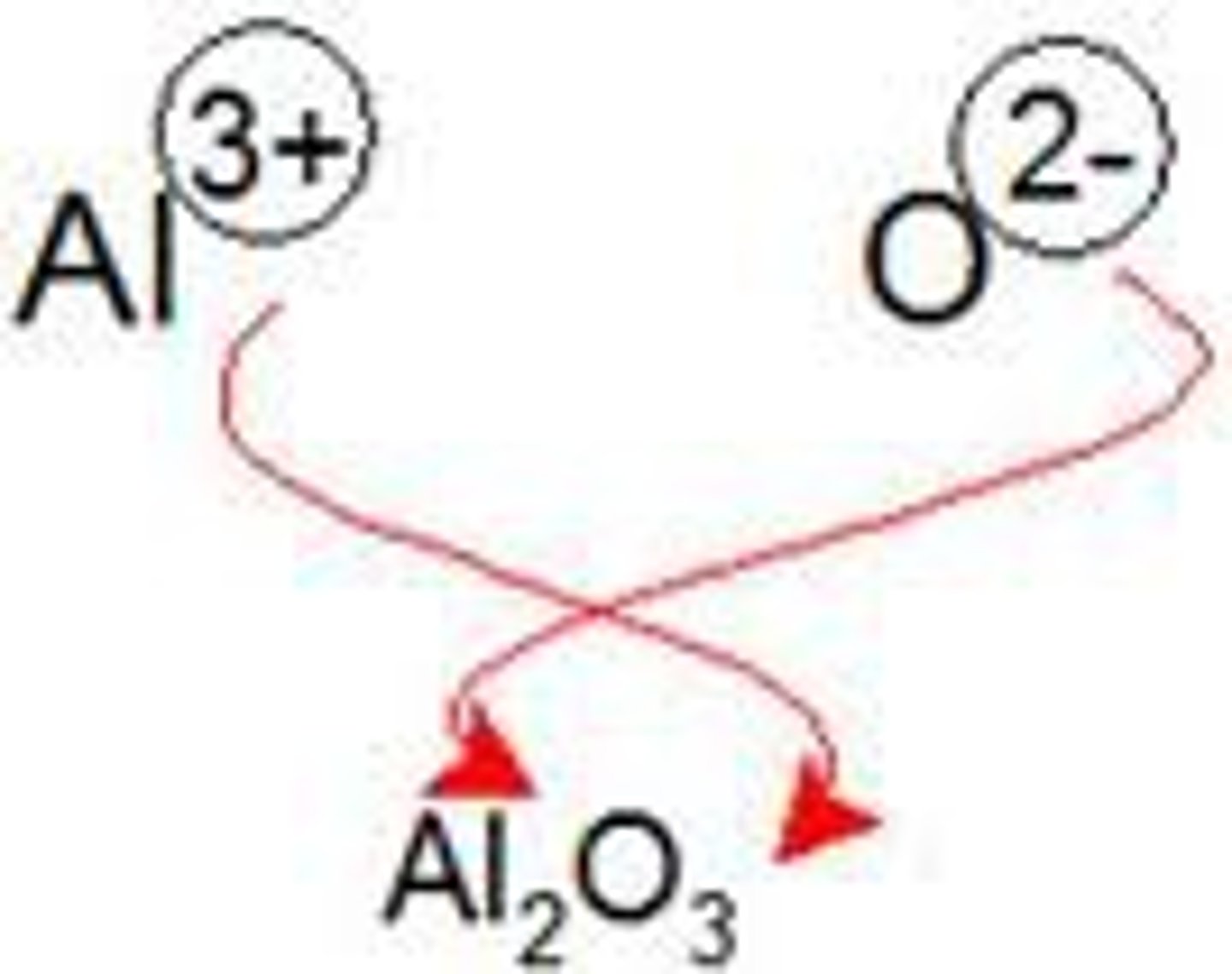
The criss-cross method is useful for
determining the ratio of ions
Do covalent or ionic compounds use prefixes?
Covalent
What if there is a transition metal in the compound. How do I name it?
It is the same as for the main group elements, except use roman numeral for the charge.
name MnBr4
Manganese(IV) bromide
start with name of metals cation, the the charge of the metals cation in roman numerals, then the base name of the nonmetals anion + ide.
polyatomic ion
a group of more than one atom joined together with covalent bonds
a group of atoms WITH A CHARGE
What do transition metals need?
a roman numeral
molecular compound
a compound that is composed of molecules with covalent bonds
when naming ionic compounds, is a prefix used to show how many atoms are present?
no
Two Binary acid (H+another element) rules:
1) add prefix HYDRO- to name of second element
2) replace last syllable in second element with "-ic" followed by acid
HF = hydrofluoric acid
main hydro_____ic acids
HF, HCl, HBr, HI, H2S
What is an oxyacid?
an acid that contains both a hydrogen atom (H+) and an oxyanion (polyatomic anion with oxygen)
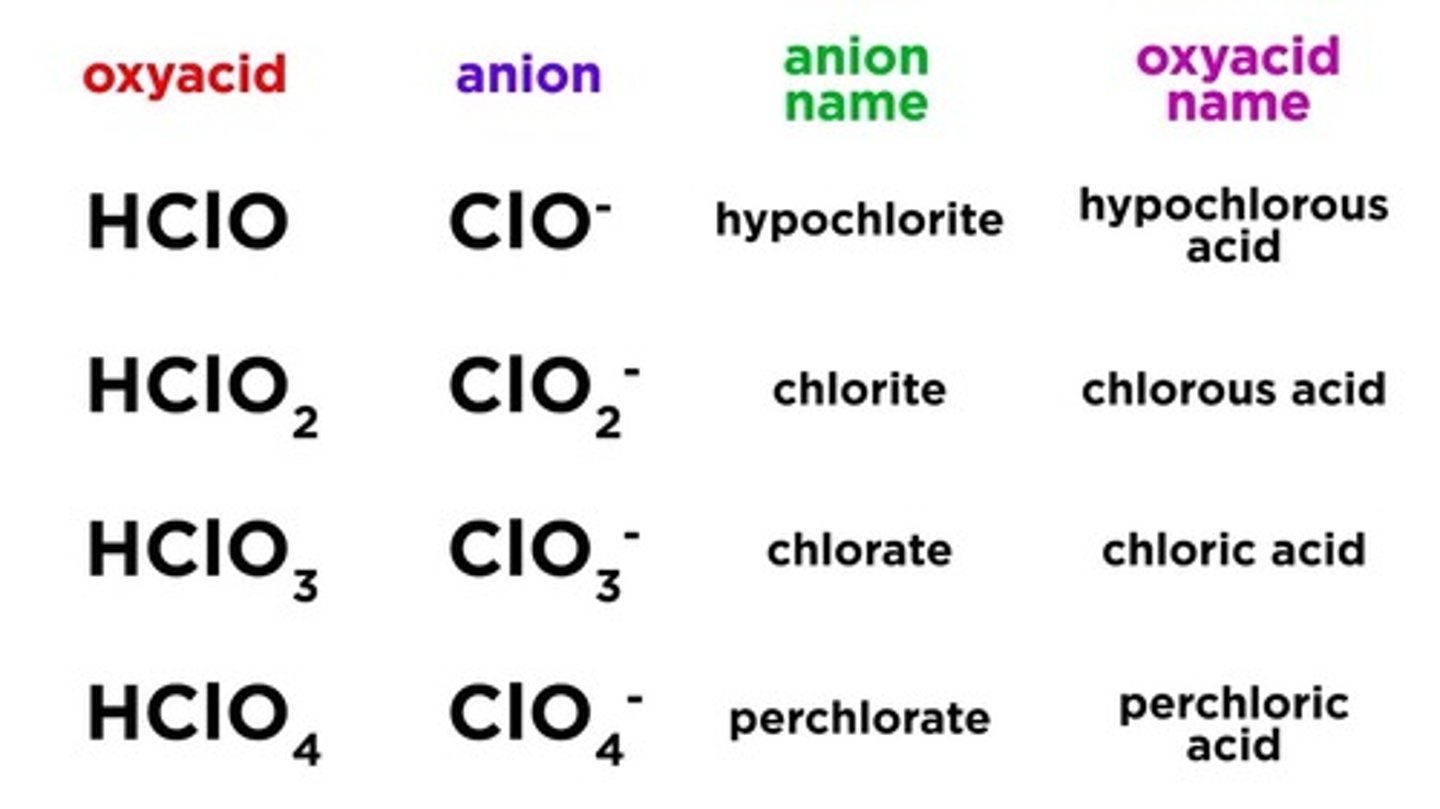
ATE endings of polyatomic ions change to
-ic
Nitrate --> nitric acid
The ITE endings of anions change to
-ous
Nitrite --> nitrous acid