Solutions, Solubility and Colligative Properties
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
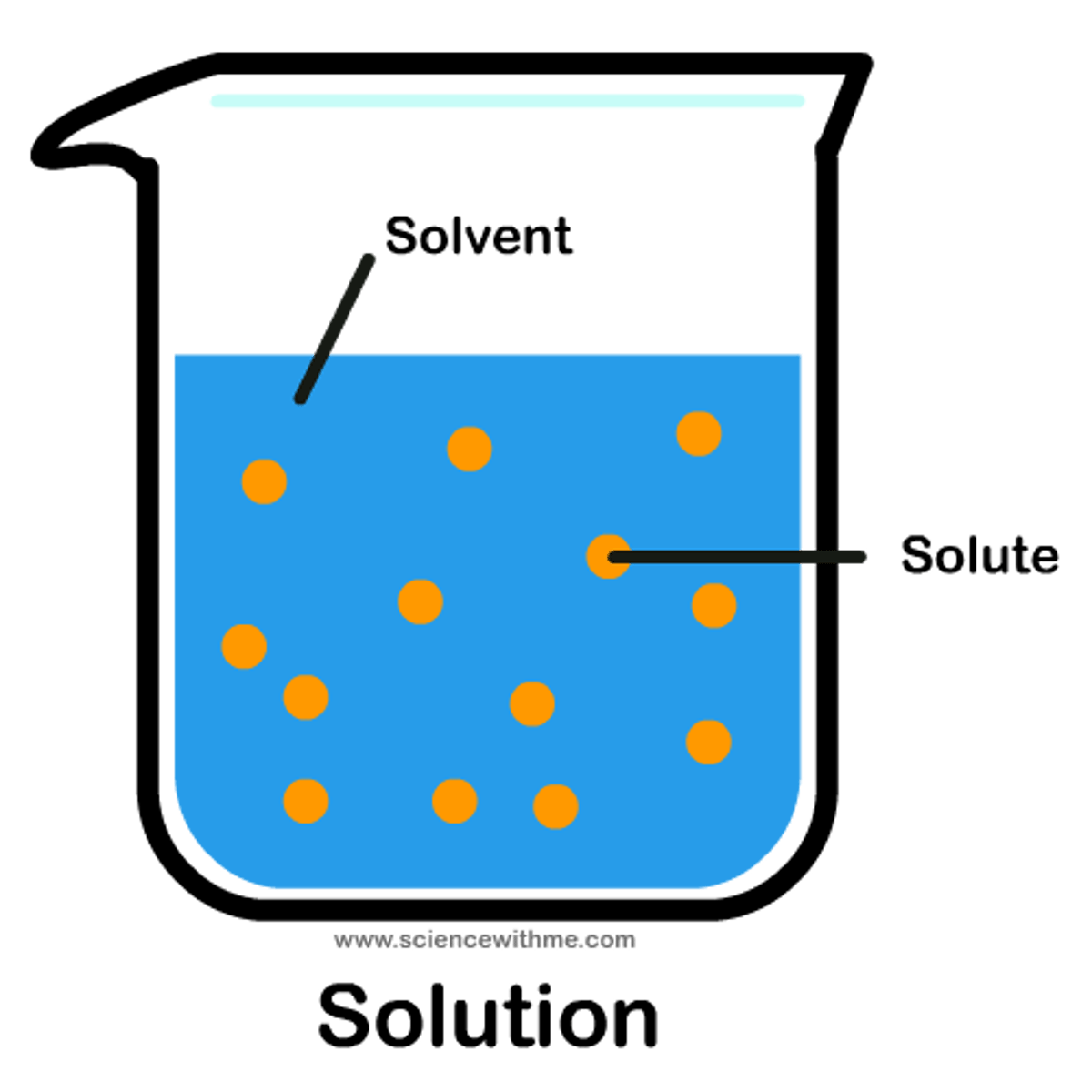
Solution
A homogenous mixture consisting of a solute dissolved
in a solvent; can be any combination of solids, liquids, and/or gases

Solute
In a solution, this is the substance being dissolved, the less abundant substance(s) in the solution
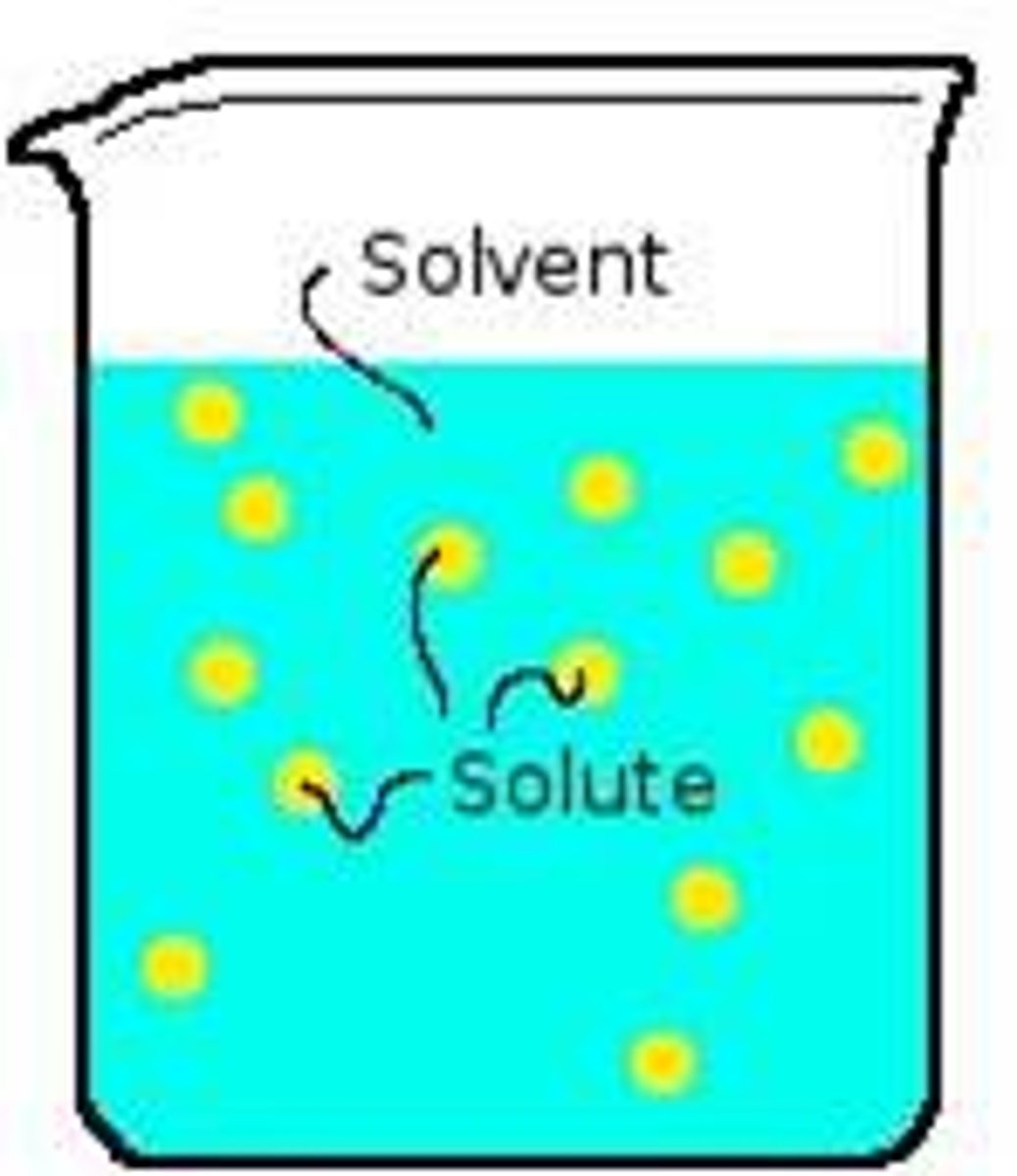
Solvent
In a solution, this is the substance doing the dissolving, the most abundant substance in the solution
Aqueous Solution
A solution in which water is the solvent
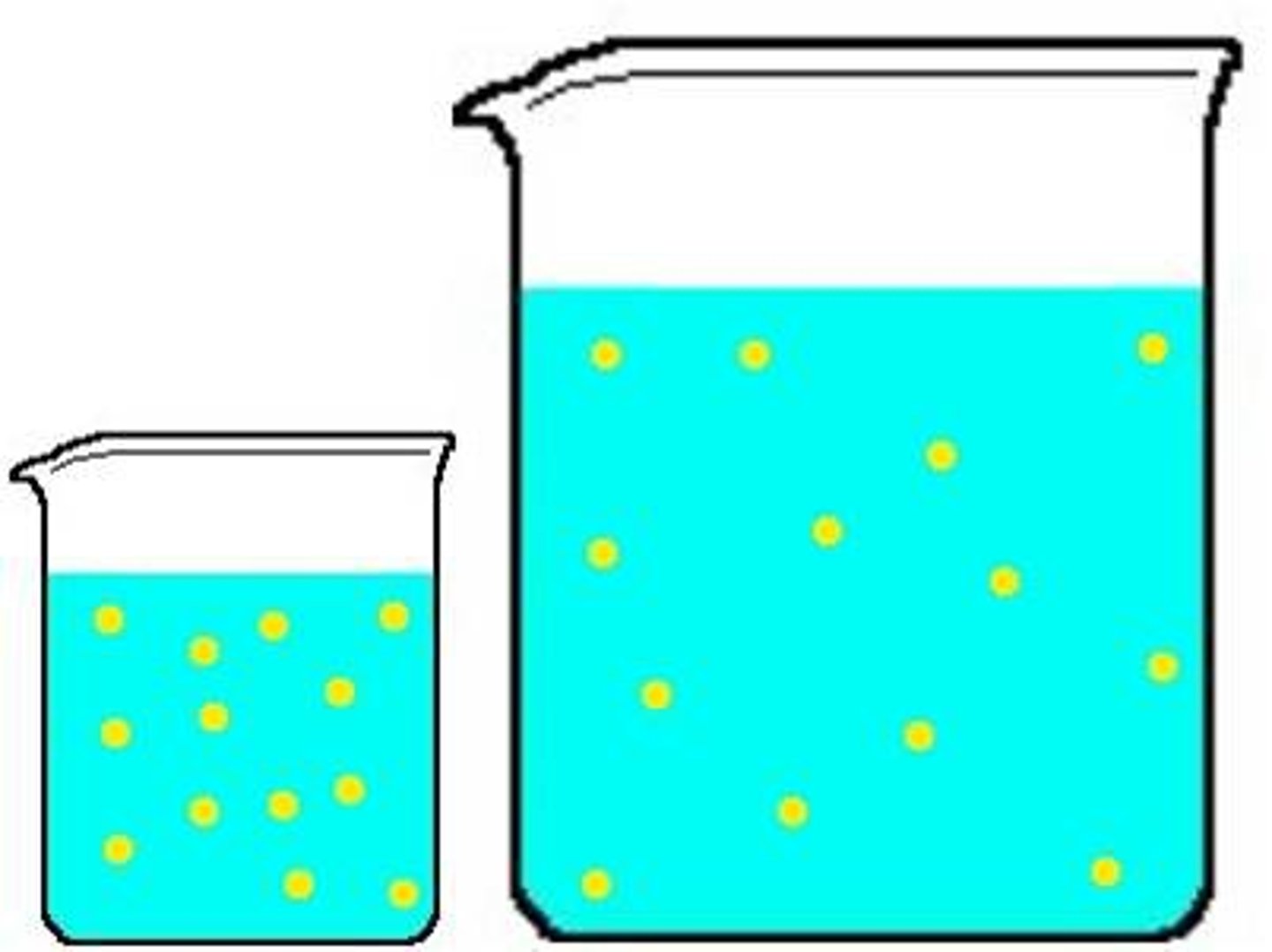
Concentration
Refers to the amount of dissolved solute in a given solution

Soluble
Can be dissolved by a particular solvent

Insoluble
Cannot be dissolved by a particular solvent

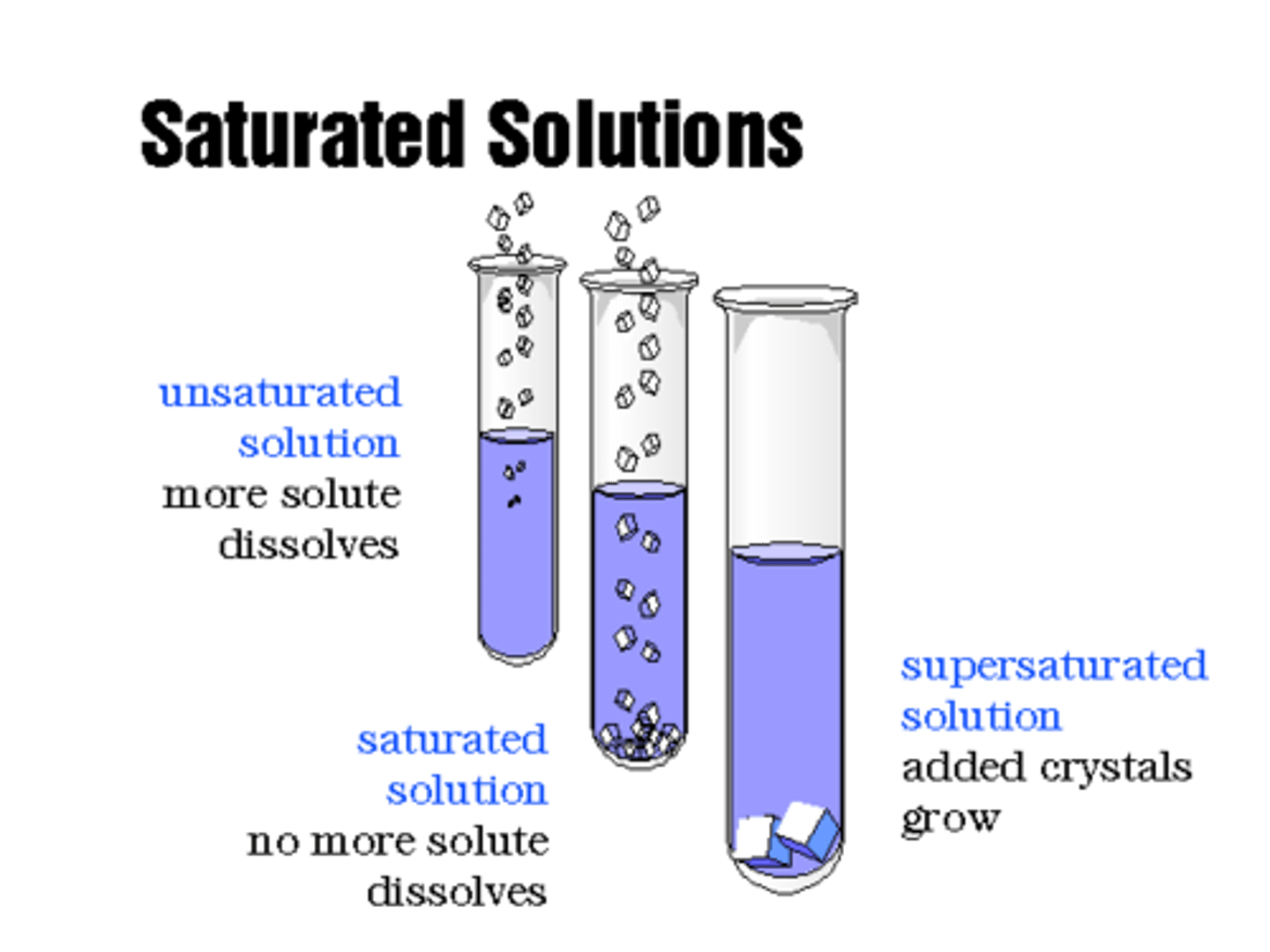
Saturated
A solution that contains the exact amount of solute that it is capable of dissolving at a given temperature
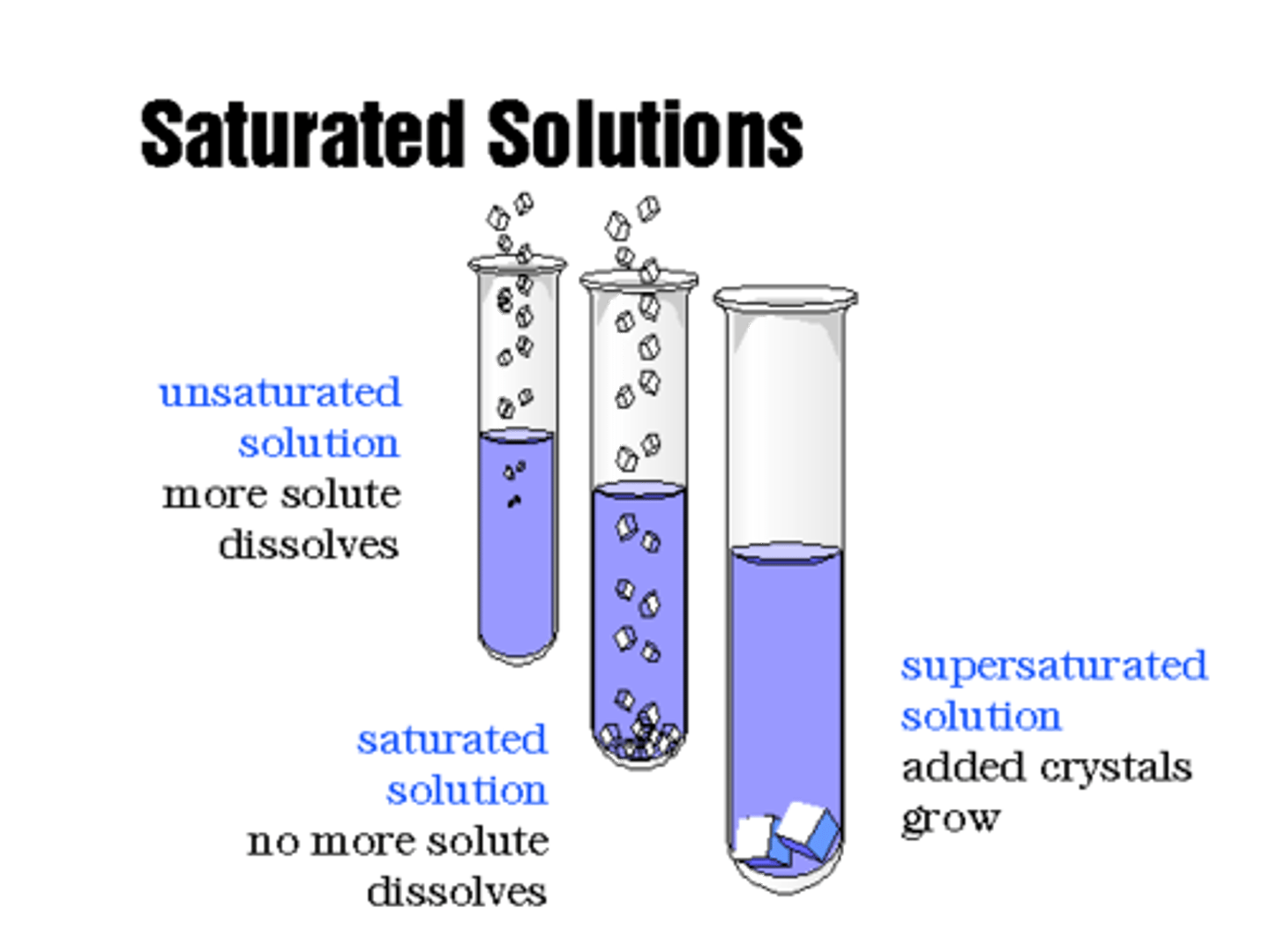
Unsaturated
A solution that contains less solute than it is capable of
dissolving at a given temperature
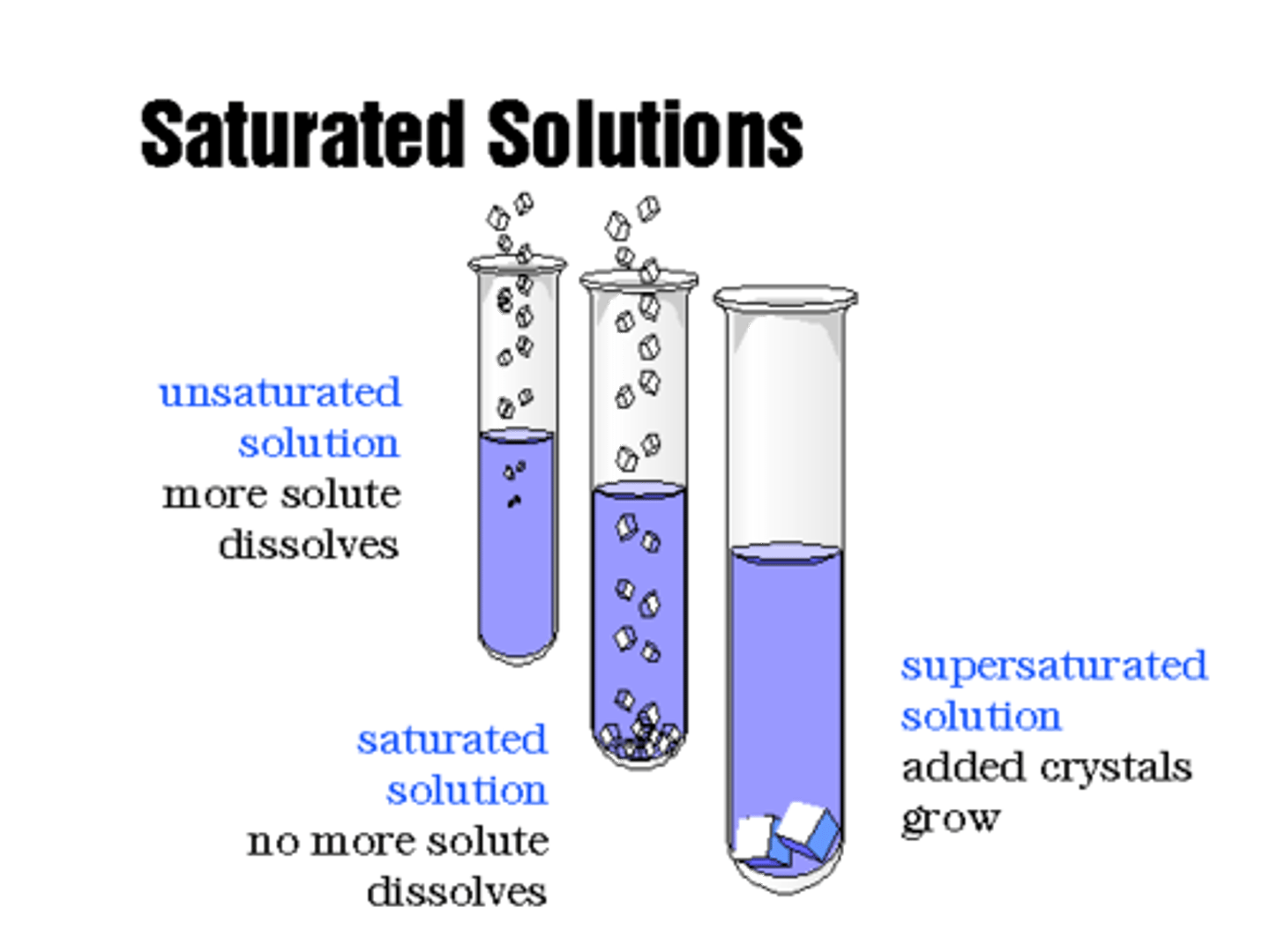
Supersaturated
A solution that contains more solute than it is capable of
dissolving at a given temperature
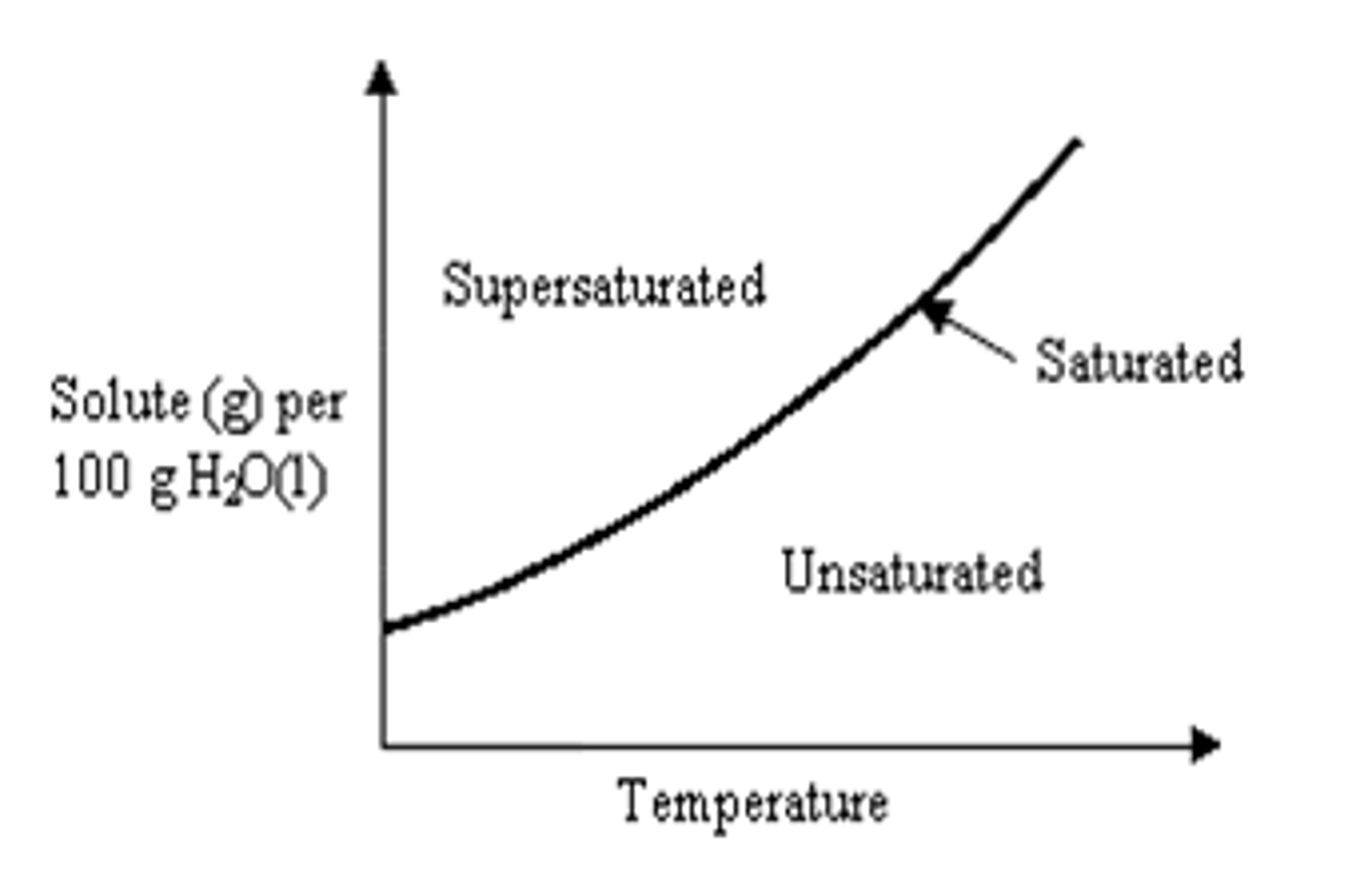
Solubility Curve
A graph showing the solubility of a substance at various
temperatures
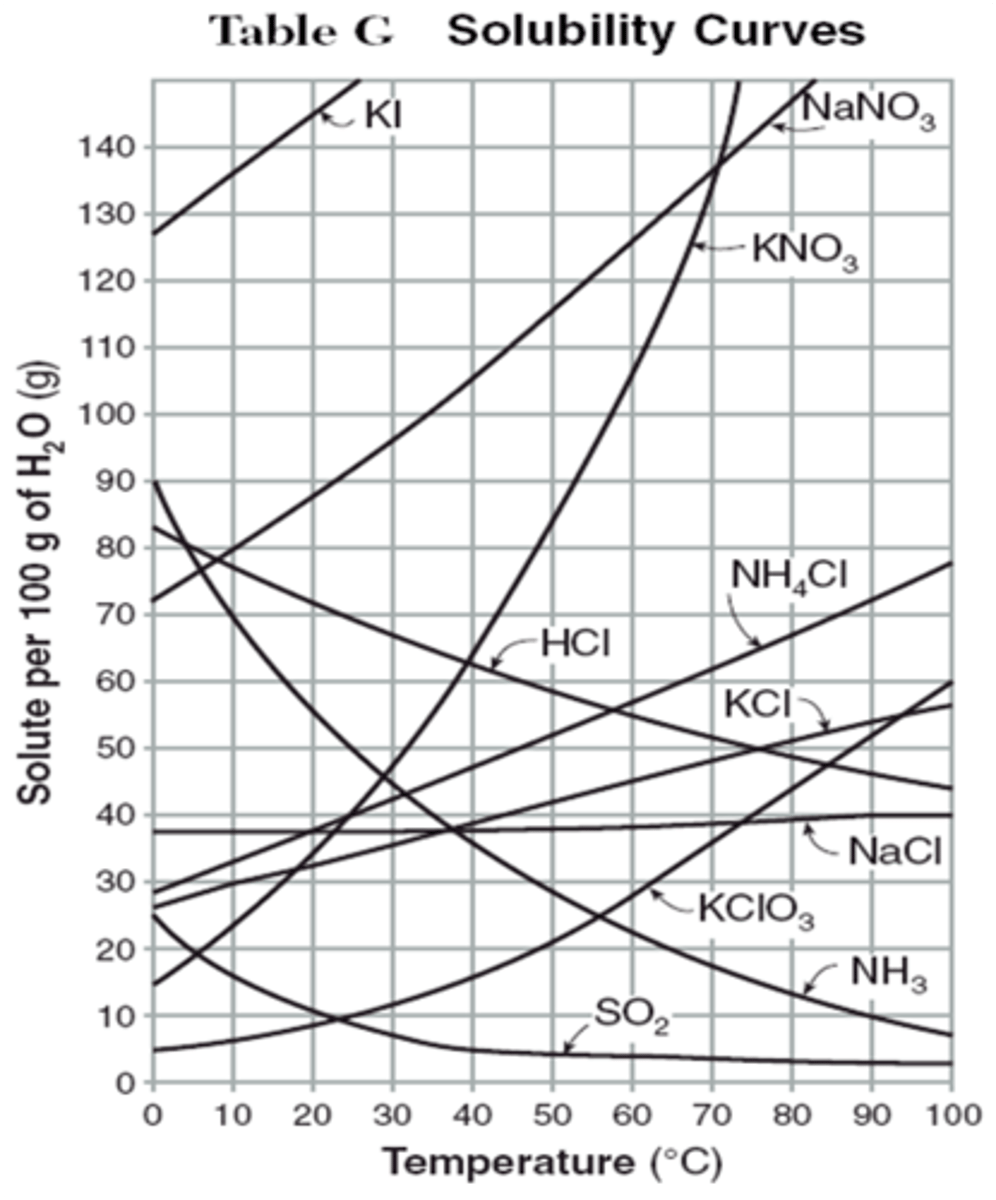
Reading a solubility curve
1. on the line is a saturated solution
2. above the line is a supersaturated solution
3. below the line is an unsaturated solution
Crystallize
The opposite of dissolving; when a substance formerly dissolved in a solution re-forms into solid crystals
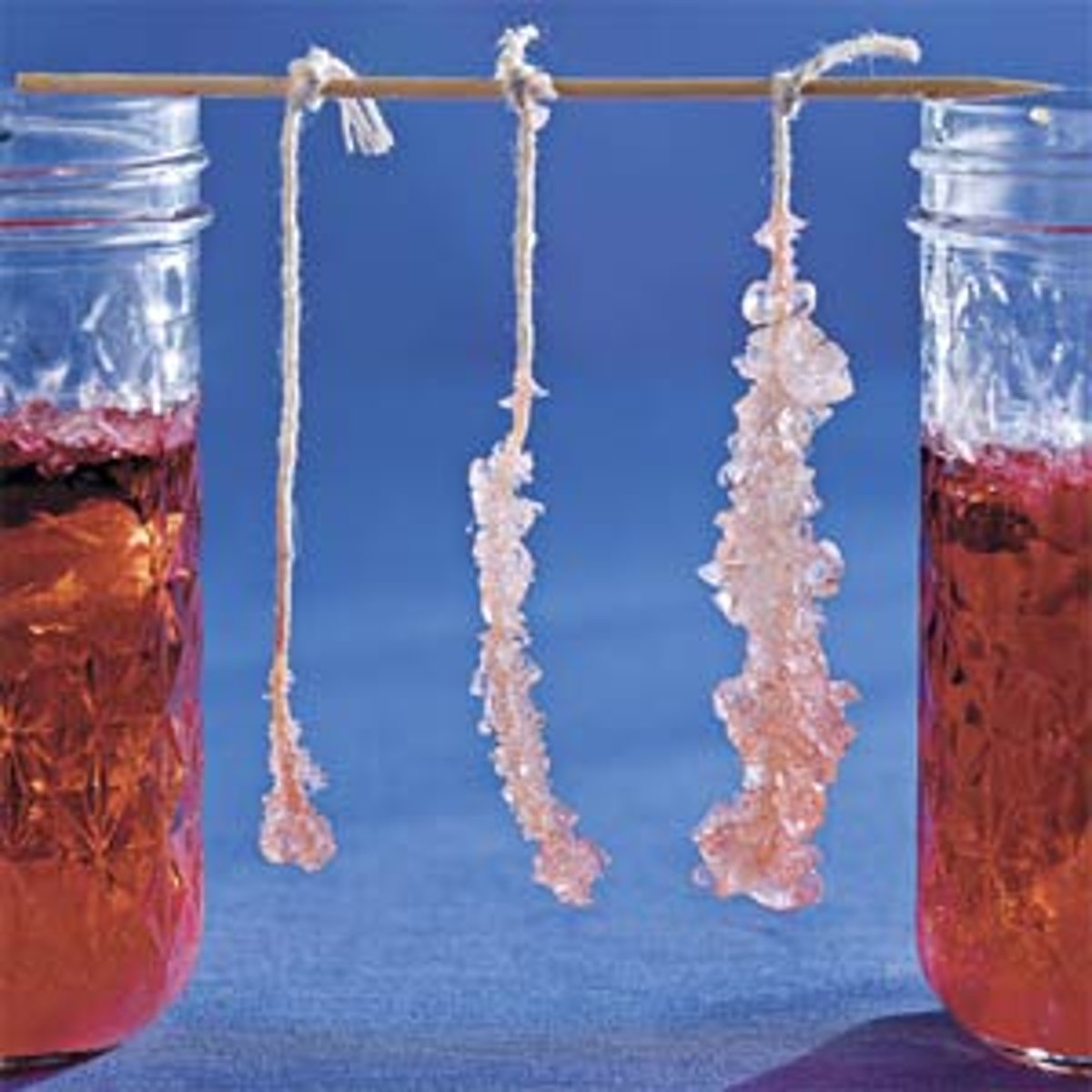

Concentrated
Describes a solution that has a relatively large amount of dissolved solute
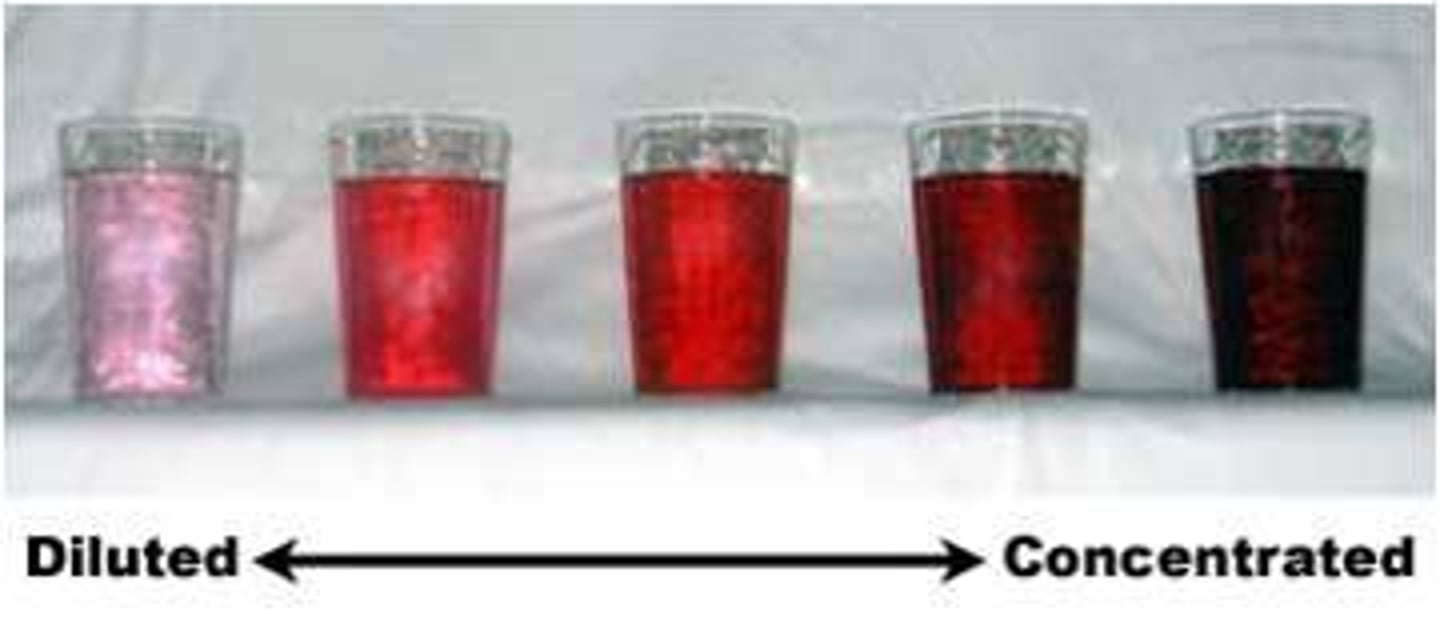
Dilute
Describes a solution that has a relatively small amount of dissolved solute
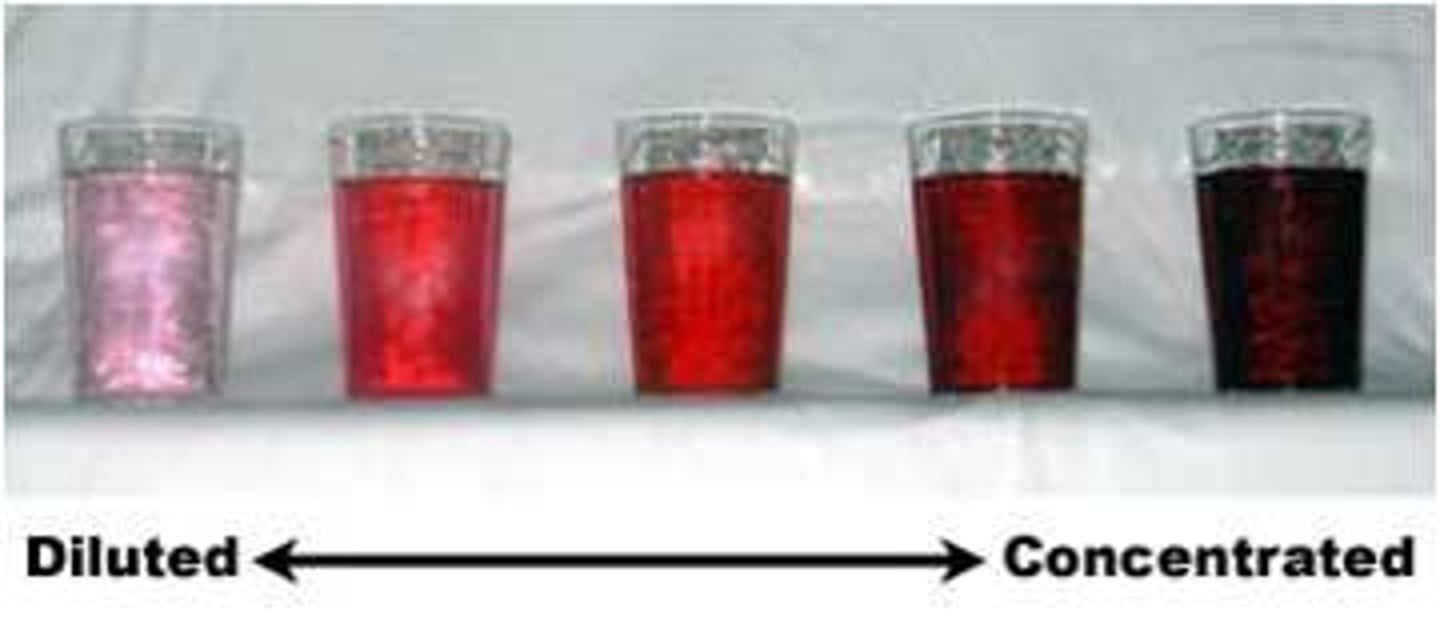
Dilution
The process of adding more solvent to a solution in order to make it less concentrated
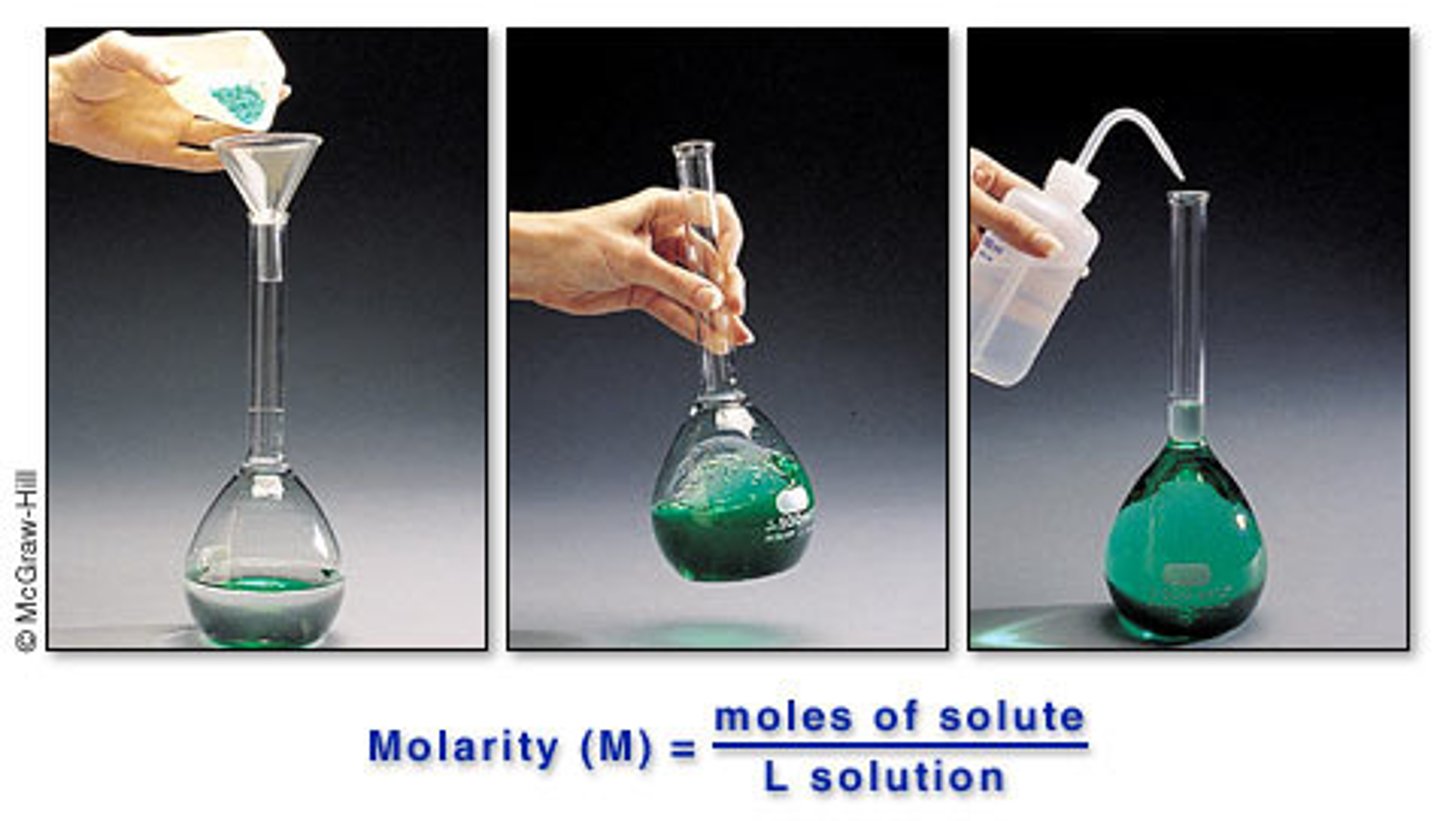
Molarity (M)
The # of moles of solute in 1.0 liter of solution

Rate of Dissolution
How fast a substance dissolves

rate of dissolving can be increased by
1. increasing temperature (heating)
2. stirring (agitation)
3. small crystal size (crushing into smaller pieces)

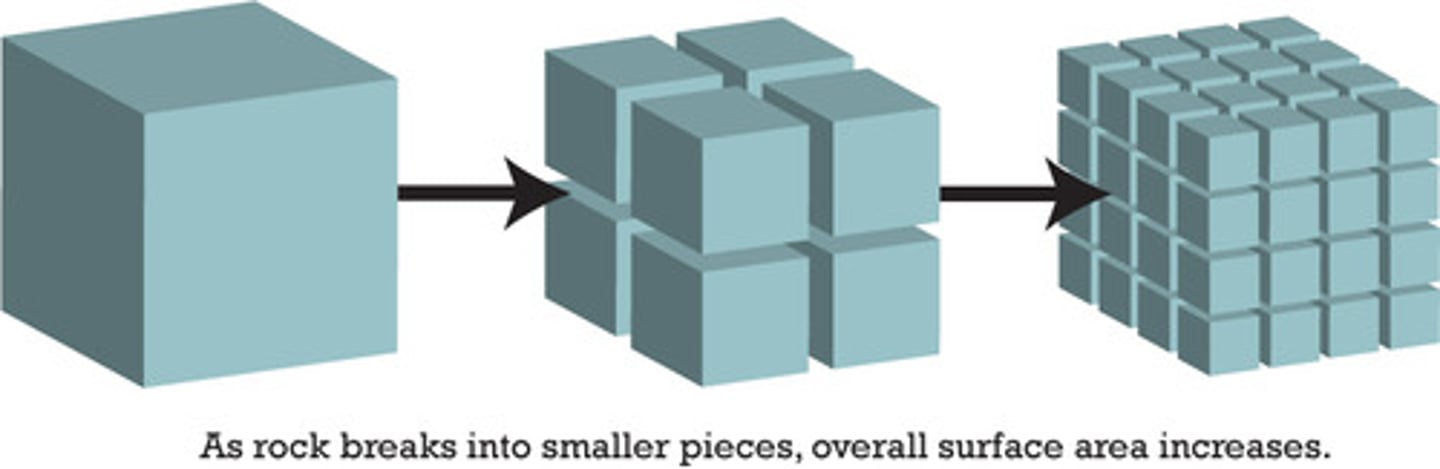
why smaller crystal sizes dissolve faster
crushing into smaller pieces increases the surface area for the solvent to be in contact with the solute
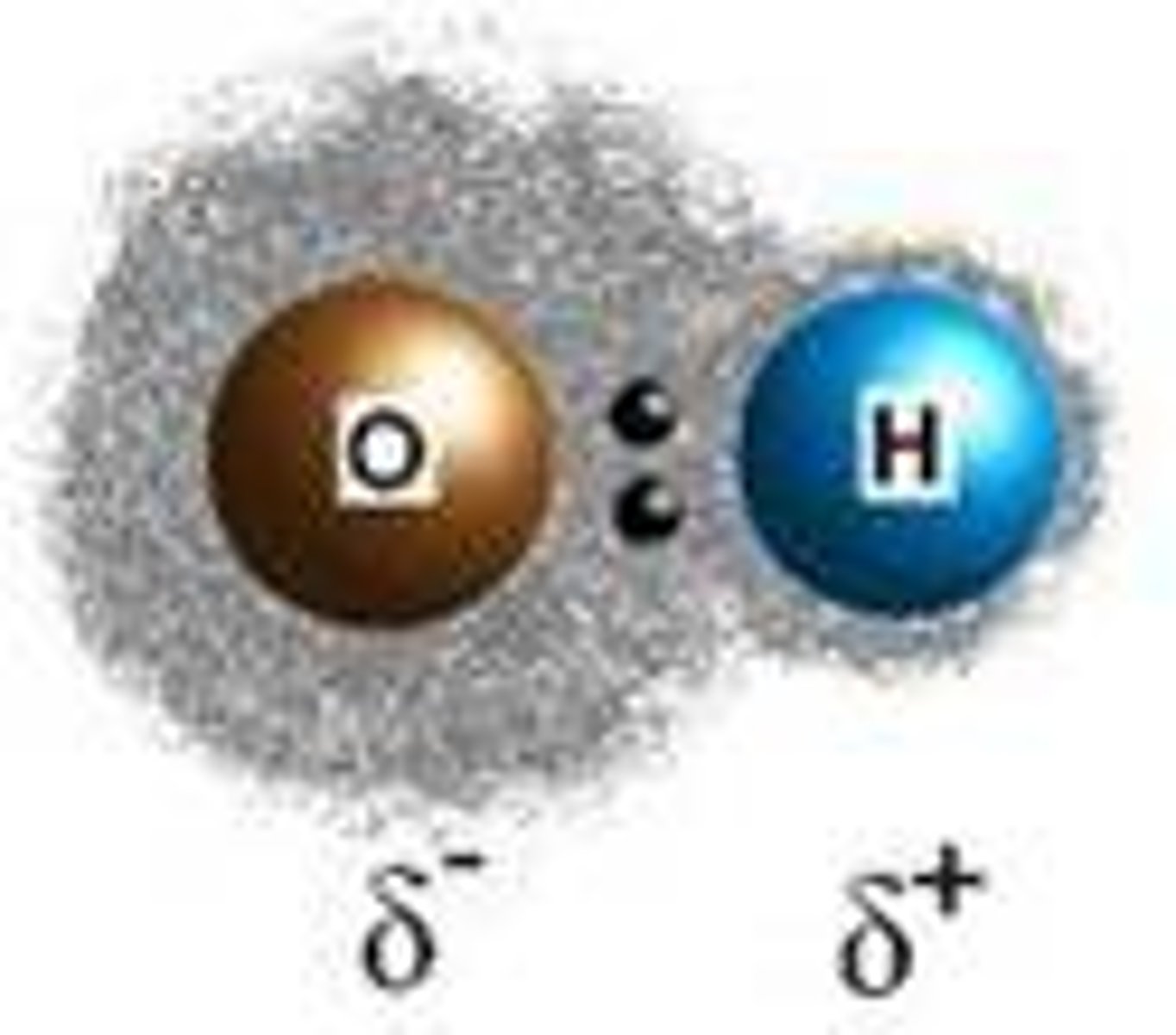
Polarity
Exists when a molecule has a clustering of negative charge on one side due to unequal sharing of electrons
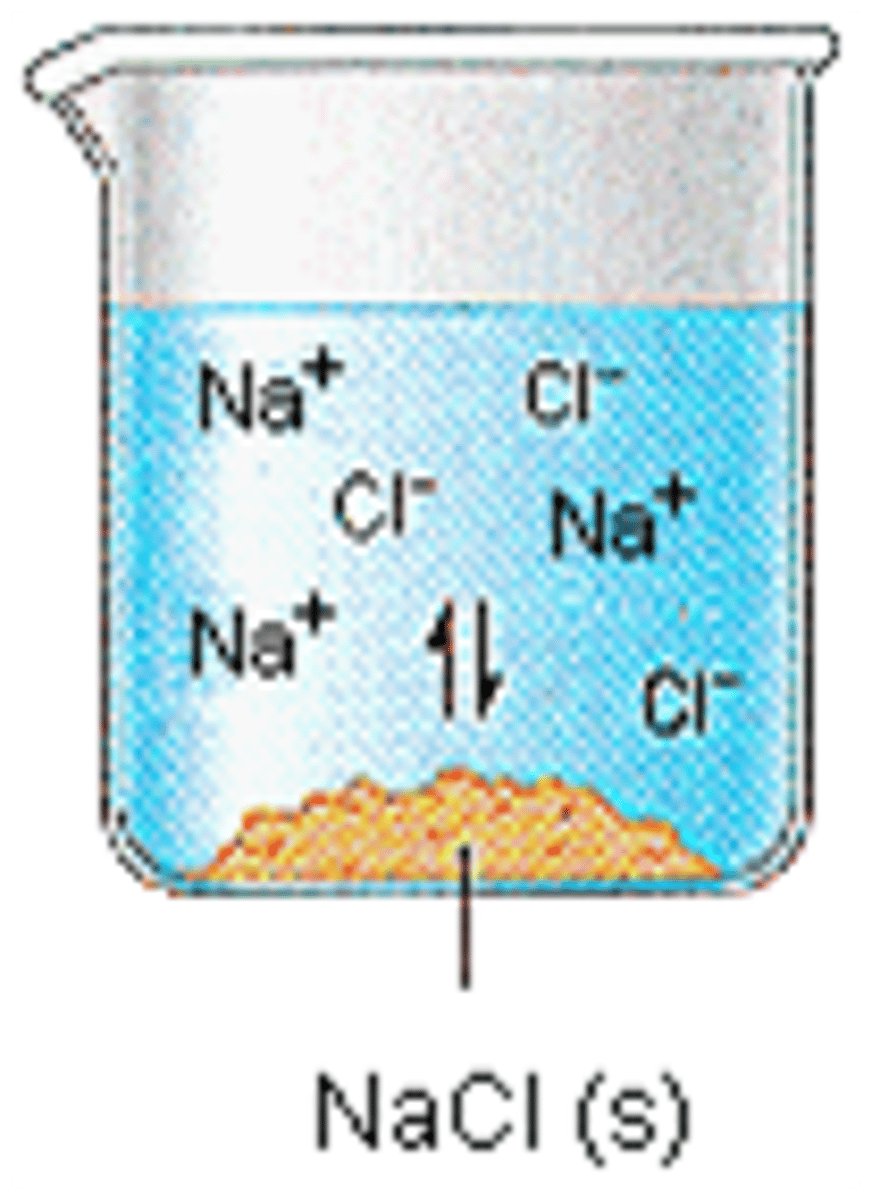
Electrolyte
A substance that conducts electricity when in the liquid (molten) state or when dissolved in
a solution because the substance ionizes when dissolved in a solvent
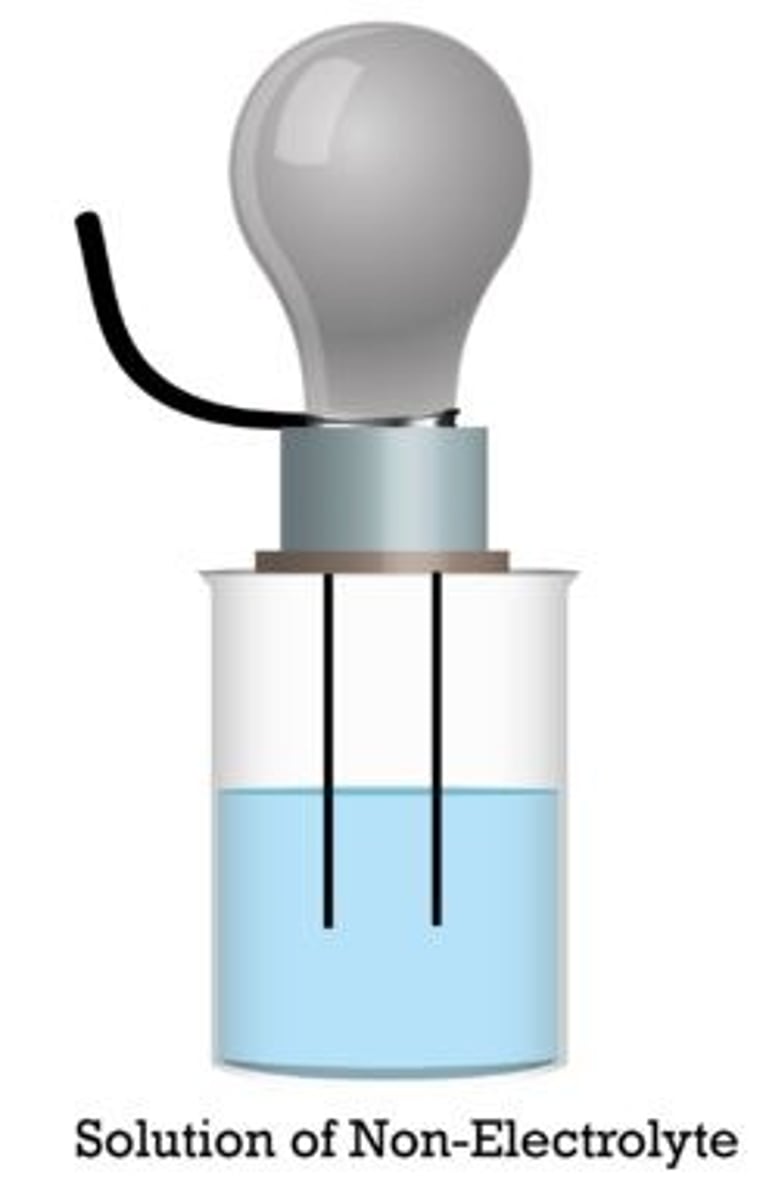
Nonelectrolyte
a compound that does not conduct an electric current in the liquid (molten) state or in aqueous solution because it does not ionize when dissolved in a solvent
Mass Percent
The # of grams of a solute in a given mass of solution expressed as a percentage
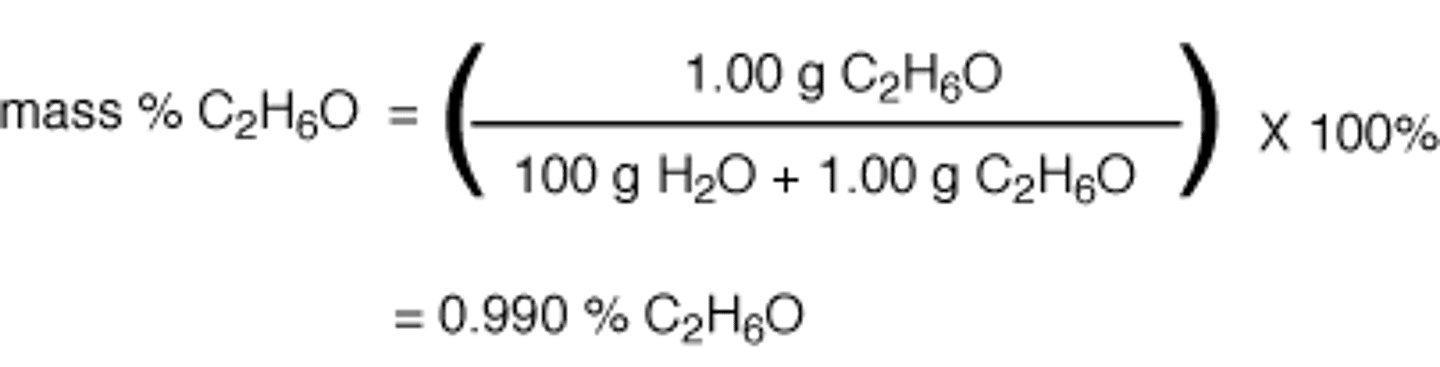
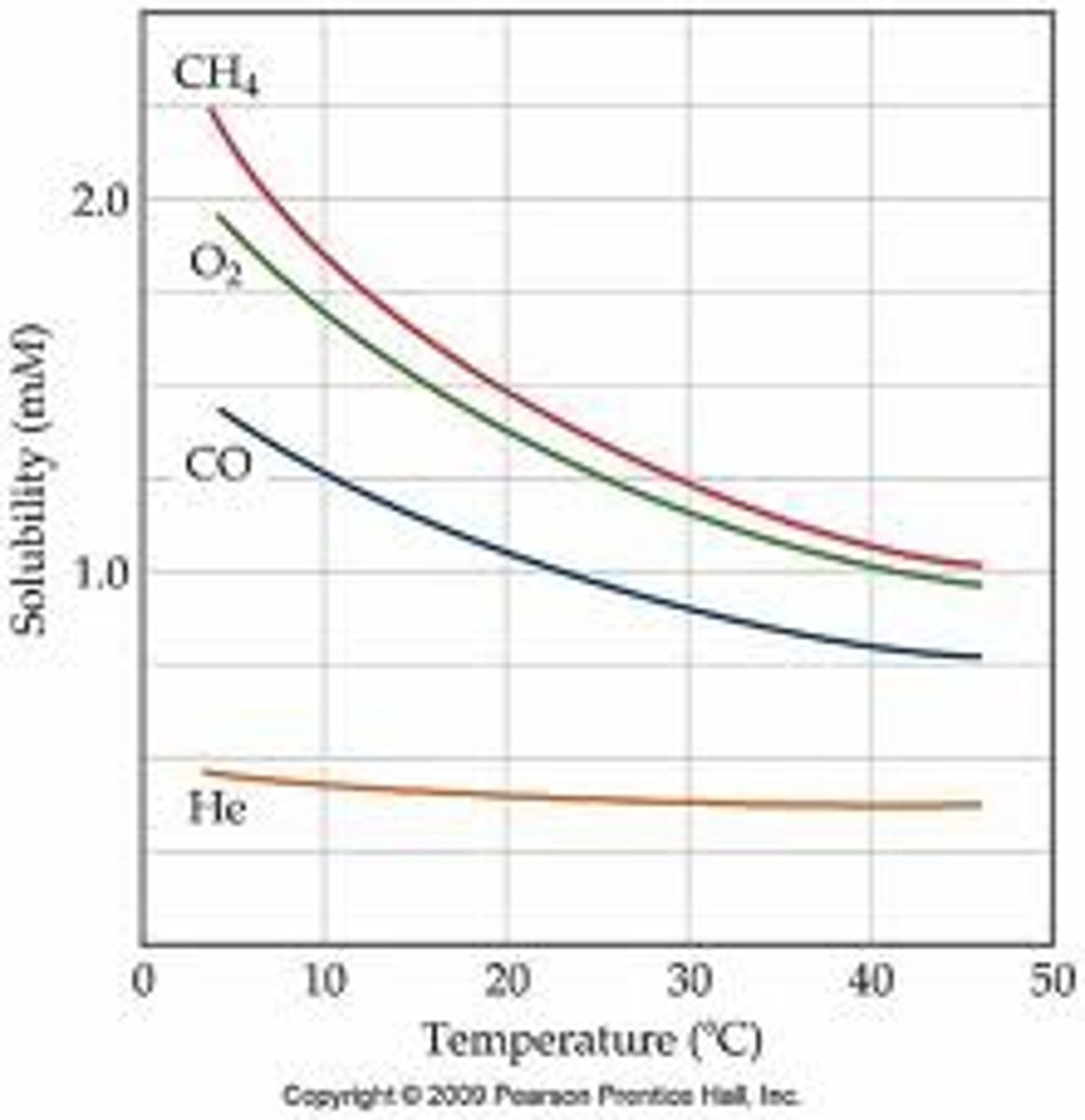
Solubility of gases
gases behave differently than solids and liquids, to stay dissolved, the number of gas particle collisions must be limited
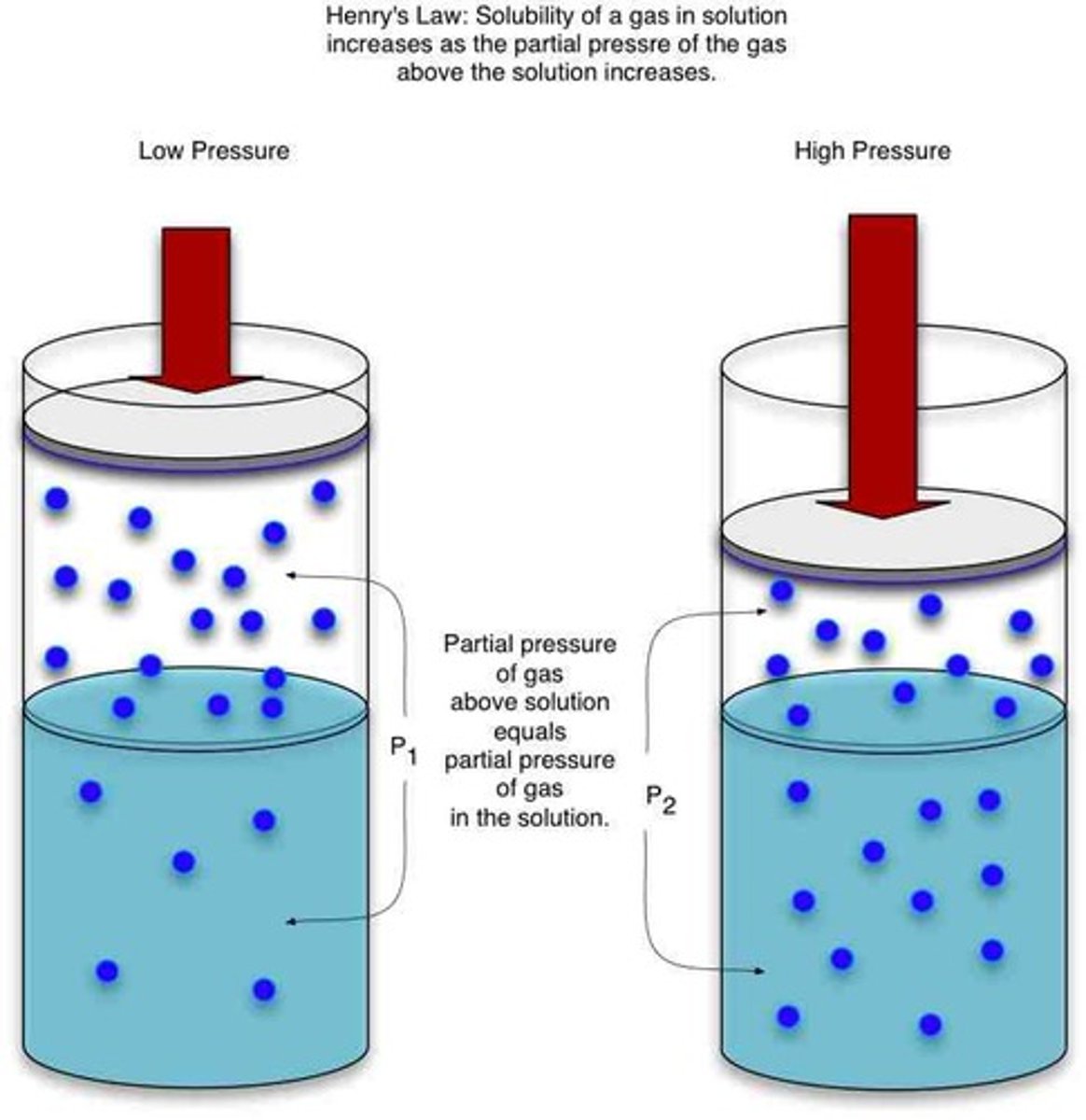
Effect of pressure on gas solubility
increases with the partial pressure of the gas on the solution
Effect of temperature on gas solubility
decreases with increasing temperature

Effect of agitation on gas solubility
generally, shaking or stirring decreases the amount of gas dissolved in a solution
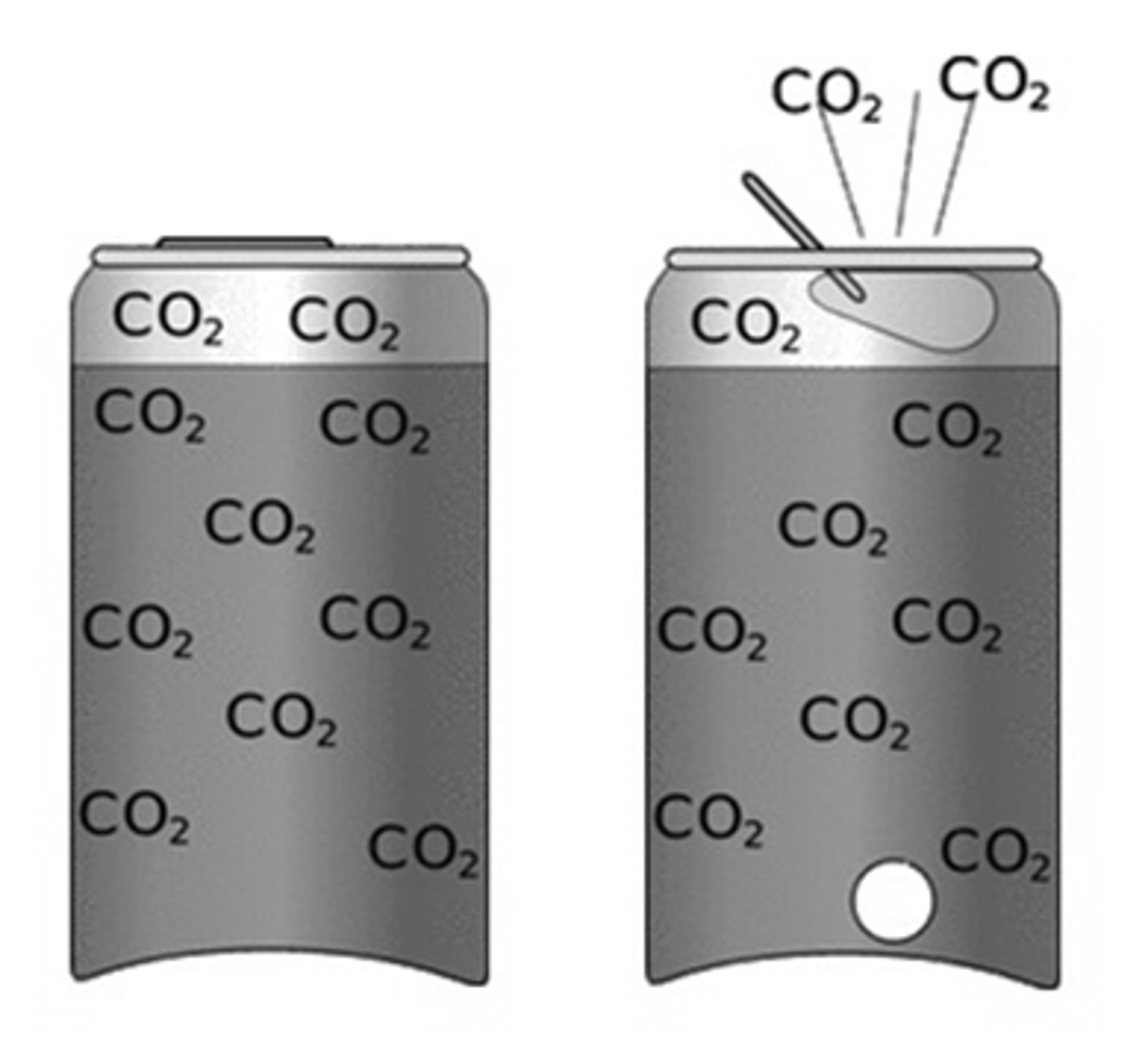
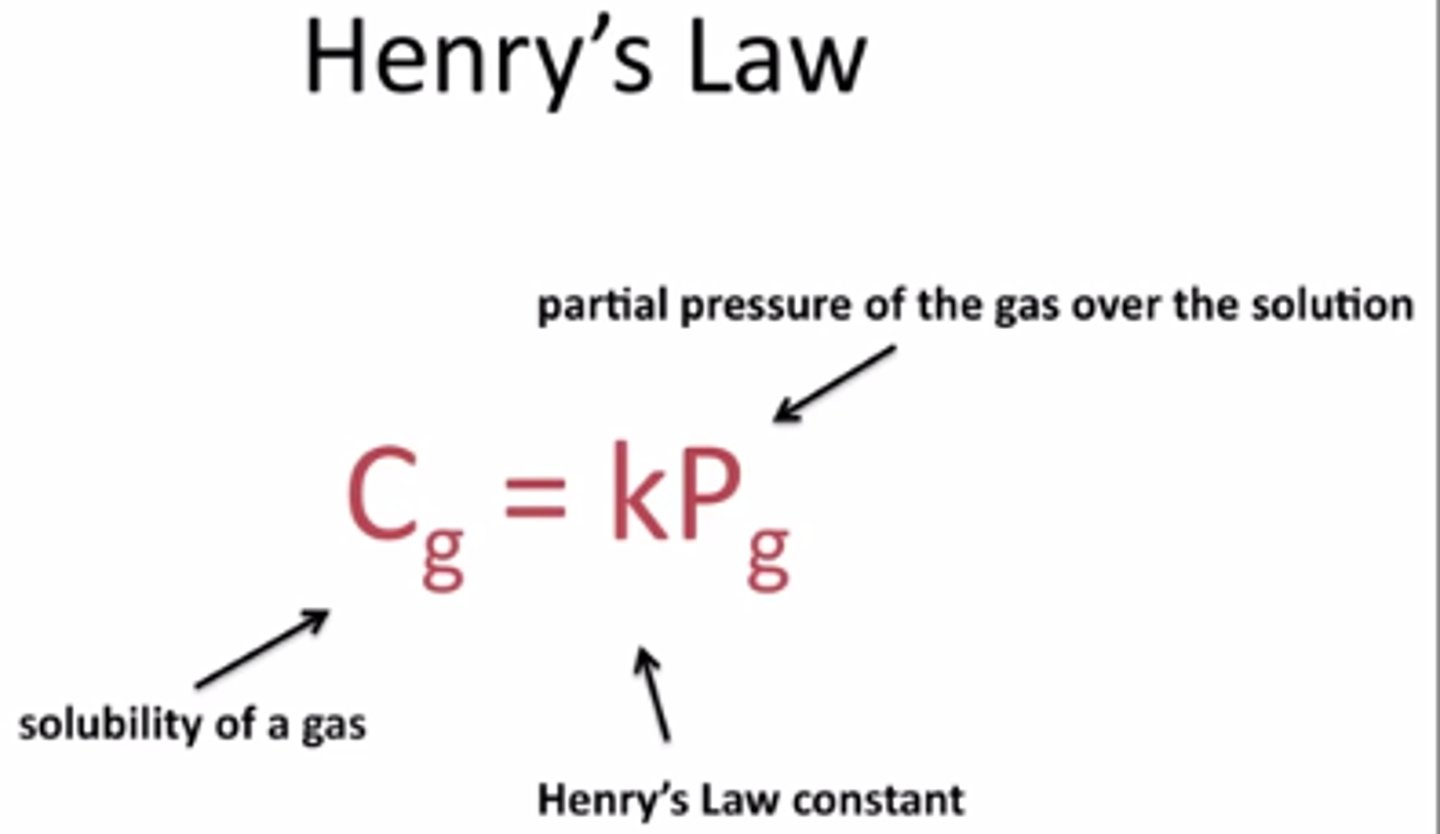
Henry's law
the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly related to the partial pressure of that gas above the liquid.
at higher pressures, more gas molecules dissolve in the liquid
Molality
moles of solute/kg of solvent
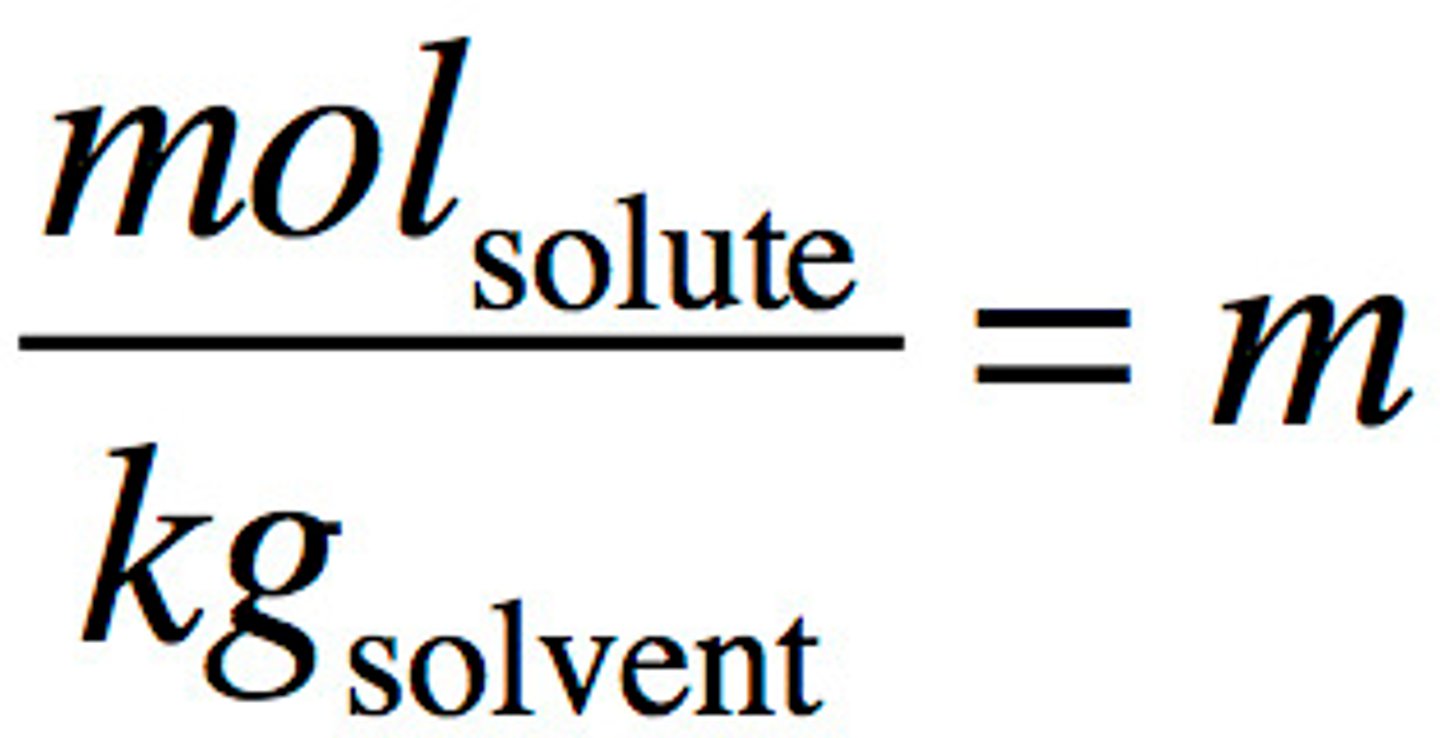
Dilution equation
M1V1=M2V2

van't Hoff factor (i)
- total # of of particles in solution
- Ex: glucose is 1
- Ex: NaCl is 2 (breaks up into 2 ions)

freezing point depression equation
ΔTf = imKf

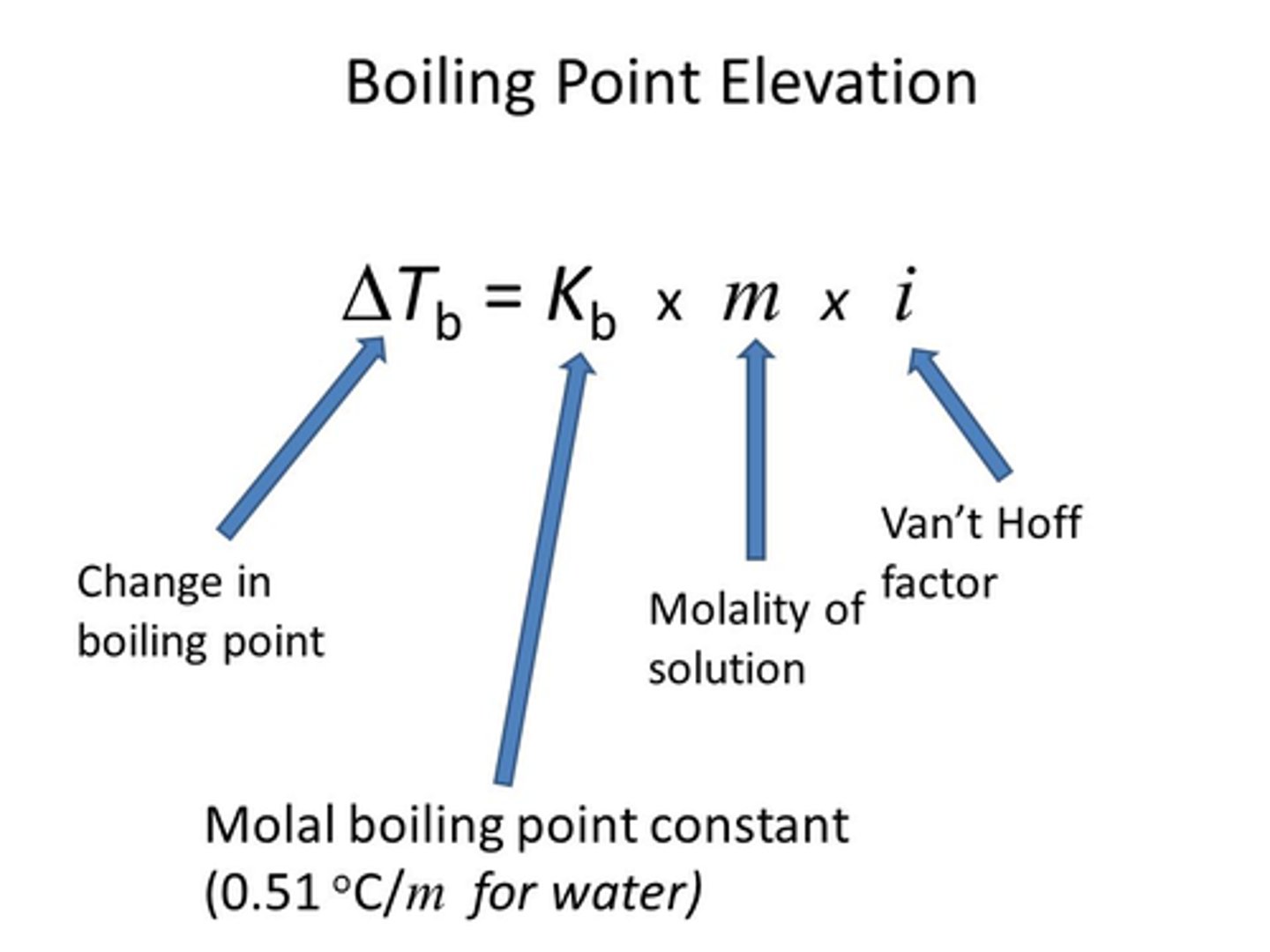
boiling point elevation equation
ΔTb = imKb
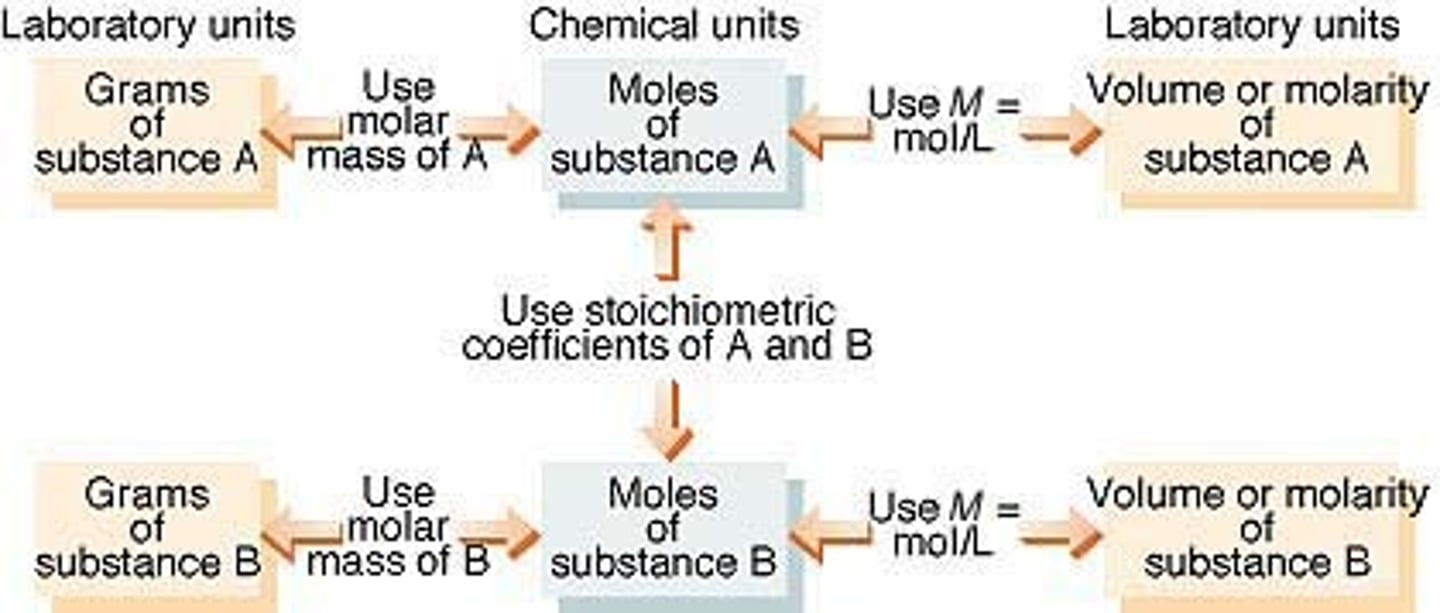
Solution Stoichiometry
Amount of A --> Moles A --> Moles B --> Amount of B