LE1 Compana Lab
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Comparative Anatomy
the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different speciesto understand evolutionary relationships.
backbones and limbs
identical structure in embryonic origin
Notochord, Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord, Pharyngeal Slits, Post-Anal Tail, Endostyle
Notable Features of Chordates
SUBPHYLUM CEPHALOCHORDATA
notochord extends into the head, filter-feeding using pharyngeal slits, and has a fish-like body, retains the notochord throughout life, lacks backbone
SUBPHYLUM UROCHORDATA/TUNICATA
marine animals with a tunic, filter feeding through a pharyngeal basket, notochord and nerve cord are present only in the larval stage, lacks backbone
SUBPHYLUM VERTEBRATA
notochord replaced by a vertebral column, well-developed head and brain, complex sensory organs, and a closed circulatory system, exhibits a backbone and complex body systems
Gill Arches for Bony Fish, Jaw and Inner Ear for Terrestrial Animals
What will the pharyngeal pouches be when the organism matures?
thyroid gland
What will the Endostyle be when the organism matures?
Central nervous system
What will the dorsal tubular nerve cord be when the organism matures?
vertebrae/backbone
What will the notochord be when the organism matures?
Tails, coccyx in humans
What will the postanal tail be when the organism matures?
Mouth
First structure that develops for protosomes
Anus
First structure that develops for deuterosomes
Vertebrates
Animals with a backbone or spinal column.
Agnatha
• do not have true jaws like other fish
• have a circular, toothed mouth
• have a cartilaginous skeleton rather than made of bone
• lack scales on their bodies
• have long, eel-like bodies
• often parasitic
Pacific Lamprey, Entosphenus tridentatus
Give the common and scientific name of this animal.

Cartilage
Skeleton of Chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes
Type of fish that is covered with placoid scales
False
True or False:
Chondrichthyes have a swim bladder.
Internal Fertilization
What type of fertilization does Chondrichthyes have?
Oviviparous or viviparous
What type of reproduction does chondrichthyes have?
Heterocercal
Tail shape of chondrichthyes
Bone
Skeleton of Osteichthyes
Osteichthyes
Its skin is soft, covered with cycloid or ctenoid scales.
True
True or False:
Osteichthyes have swim bladders
Buoyancy
What is the purpose of a swim bladder in Osteichthyes?
True
True or False:
Chondrichthyes have exposed gill slits
Operculum
What covers the gills of Osteichthyes?
Mostly external, some internal
How does Osteichthyes fertilize?
Oviparous
How does Osteichthyes reproduce?
Homocercal
Tail shape of osteichthyes
Mammals and Birds
Which groups of vertebrates are endotherms?
Fishes, Amphibians, Reptiles
Which groups of vertebrates are ectotherms?
Amphibians, Reptiles, Mammals, Birds
Which groups of vertebrates are tetrapods?
Amphibians
• characterized by their ability to exploit both aquatic and terrestrial habitats
• lays their egg on water
• typically have a thin, moist skin and rely heavily on cutaneous respiration
Aposematism
Term for bright coloration of organisms to serve warning to predators
Batrachotoxin
One powerful chemical that the specialized glands of some amphibians secrete.
Reptiles
• external covering of epidermal scales
• lay their eggs on land
False
True or False:
Snakes aren’t really tetrapods because they do not have legs.
Birds
• have feathers that provide insulation, aid in flight
• lays hard-shelled eggs
• have wings
• have beaks or bills
• have highly modified scales
• lightweight skeletons with hollow bone
Mammals
• feed their young with milk produced by the mother – “mammary glands”
• skin of many mammals is covered with sweat glands
• covered with hair or fur (some have scales)
Mammary Glands
Defining structure that makes mammals, mammals.
True
True or False:
Whales and dolphins have hair
Tubercles
Bumps found on a humpback whales’ head, mouth, and flipper.
Evolution
the change in the characteristics of a species over several generations and relies on the process of natural selection
Natural Selection
Process where individuals having more useful traits survive better and produce more progeny than individuals with less-favorable traits
Divergent Evolution
Occurs when groups from the same common ancestor split into two groups by a geographic barrier (for instance, a body of water or a migration to a new area), causing each group to develop different traits.
Convergent Evolution
Occurs when organisms that aren't closely related evolve similar traits as they both adapt to similar environments.
Coevolution
Occurs when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection
Phylogeny
study of the relationship between all the organisms on Earth that have descended from a common ancestor
Taxonomy
Branch of science of naming, describing, and classifying organisms
Taxon
any particular group of organisms is called a ____
Carolus Linnaeus
Known as the father of taxonomy because of his adoptation of Binomial Nomenclature.
Binomial Nomenclature
A system that uses a unique, two-part scientific name derived from Latin or Greek to each kind of organism
Monophyletic
includes the most recent common ancestor of a group of organisms, and all of its descendants
Polyphyletic
does not include the common ancestor of all members of the taxon
Paraphyletic
includes the most recent common ancestor of a group of organisms, but NOT all of its descendants
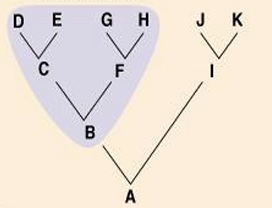
Monophyletic
What type of taxon is this?
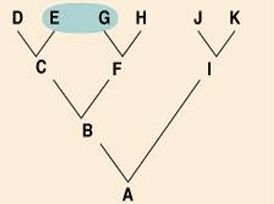
Polyphyletic
What type of taxon is this?
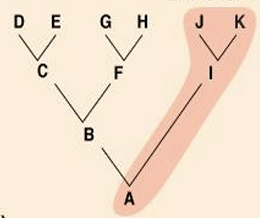
Paraphyletic
What type of taxon is this?
Liolaemus messii
Give me the scientific name of this species.

Cirrhilabrus wakanda
Give me the scientific name of this species.

Trimeresurus salazar
Give me the scientific name of this species.

Thanos simonattoi
Give me the scientific name of this species.

Boops boops
Give me the scientific name of this species.

Homologous Structures
Term for structures that have similar physical features in organisms that share a common ancestor, but the features serve completely different functions
Analogous structures
These are features of different species that are similar in function but not necessarily in structure and do not derive from a common ancestral feature
Lancelet (Amphioxus)
Wh▪ small, elongated, "fish-like" benthic filter-feeding chordates in the subphylum Cephalochordata ▪ lacks a true vertebral column, but has a notochord ▪ displays primitive features of chordates, including a dorsal nerve cord ▪ lacks well-developed sensory organs, brain, and skullat species is this?
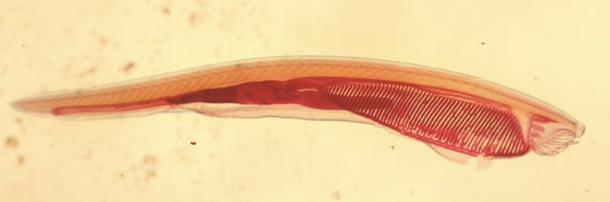
Lancelet (Amphioxus)
▪ small, elongated, "fish-like" benthic filter-feeding chordates in the subphylum Cephalochordata
▪ lacks a true vertebral column, but has a notochord
▪ displays primitive features of chordates, including a dorsal nerve cord
▪ lacks well-developed sensory organs, brain, and skull
Subphylum Cephalochordata
What type of chordate is this species?
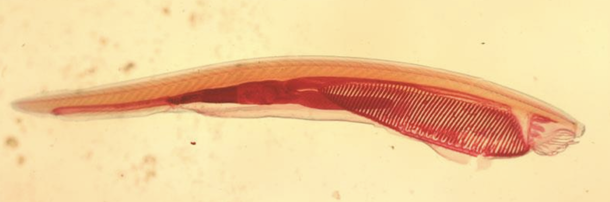
Subphylum Cephalochordata
What type of chordate is this species?

Ammocoetes (Lamprey Larva)
▪ elongated, eel-like during larval stage
▪ possesses a notochord and rudimentary vertebral elements
▪ lacks paired fins and jaws, with a sucker-like oral disk
▪ undergoes filter-feeding through gill slits
Spiracle
Small respiratory opening behind the eyes, aids in water intake for respiration when the mouth is closed
Lateral Line
Sensory organ running along the sides, detects vibrations and movements in water
Claspers
Paired reproductive organs found in males, used to transfer sperm during mating
False
True or False:
Claspers in sharks and rays can be found in male and female species.
Shark, Selachimorpha
What is the common name and scientific name of this species?
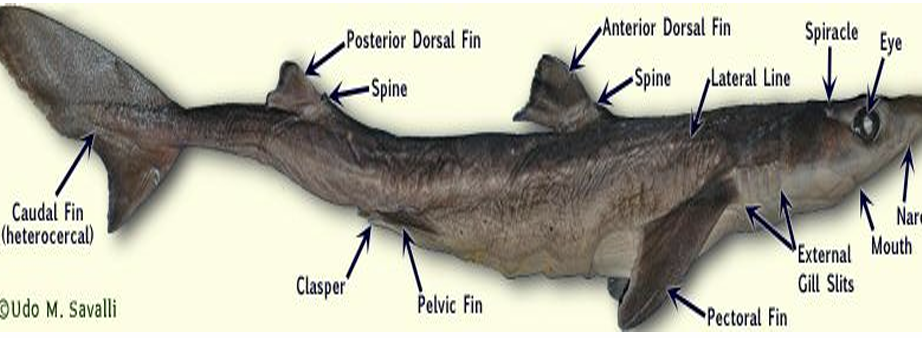
Ampullae of Lorenzini
What do you call the small black pores that are also specialized electroreceptors for detecting prey?

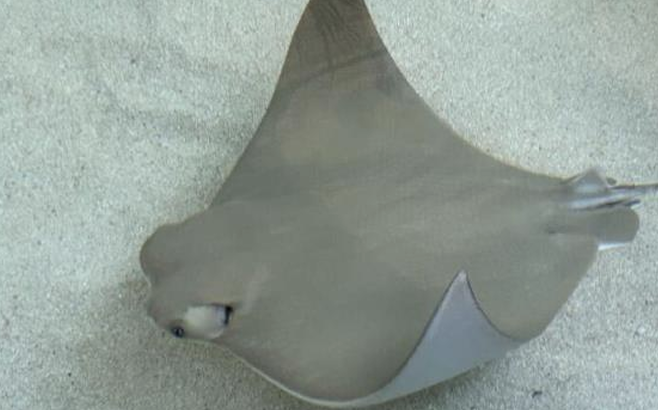
Stingray
▪ flattened, disc-shaped body adapted for bottom-dwelling
▪ ventral gill slits located on the underside for respiration
▪ barbed tail spine often equipped with venom for defense
▪ pectoral fins fused with the head, forming wing-like structures for swimming
Stingray, Myliobatoidei
What is the common name and scientific name of this species?

Placoid Scales
▪ tough, tooth-like scales found in cartilaginous fishes like sharks
▪ reduces drag and increases swimming efficiency by smoothing water flow
▪ provides protection from predators and environmental abrasions
Dentine and Enamel
What is the composition of placoid scales?
True
True or False:
Placoid scales does not overlap like other fish scales.
Milkfish, Chanos chanos
What is the common and scientific name of this species?

Milkfish
This species has:
▪ slender, streamlined body adapted for fast swimming
▪ forked caudal fin for efficient propulsion
▪ cycloid scales, smooth and thin, typical of teleosts
Cycloid scale
What type of scale is this?
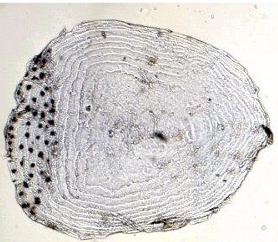
Cycloid Scale
▪ thin, round, smooth-edged scales common in bony fish
▪ growth rings visible, indicating age and growth rate
▪found in salmon, carp, goldfish, milkfish
Collagen and Calcium Salts
What is the composition of cycloid scale?
False
True or False:
Cycloid scales have enamel and dentine like placoid and ganoid scales.
Ctenoid Scales
What type of scale is in the picture?

Ctenoid Scale
▪ thin, rough-edged scales found in advanced bony fish
▪ growth rings visible, indicating fish age and development
▪ found in perch, bass, trout, sunfish
Collagen and Calcium Salts
What is the composition of Ctenoid scale?
Cteni
small tooth-like projections along the posterior edge in a ctenoid scale
Ganoid Scale
What type of scale is this?

Ganoid Scale
▪ found in primitive fish with a more ancient lineage
▪ found in sturgeon and gars
▪ thick, bony, and armor-like scales with a shiny enamel-like surface
Dentine and a Layer of Enamel
Composition of Ganoid Scales
Dermal Scales
What type of scales does a fish have?
Epidermal Scales
What type of scales does a reptile have?
Feathers (Modified Epidermal Scales)
What type of scales does a bird have?
Mostly epidermal scales, sometimes keratin scales
What type of scales does a mammal have?