AP Bio Test Chapter 43, DO2 Lab, Pill Bug, and Mean Standard Deviation SEM
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
stimulus
a signal to which an organism responds
proximate cause
the immediate cause of a particular behavior in terms of the actual stimulus
ultimate cause
the selective advantage of the behavior in terms of natural selection/evolution
when describing ultimate cause how may a behavior increase survivorship
survival of adult, increased reproductive success, increased survivorship of offspring
what is in control of natural selection
behavior which then must do with genetics
when a light shines on a planarian flatworm it heads in the opposite direction under a rock to the dark
what are the proximate and ultimate causes
the proximate cause is light and the ultimate cause is the selective advantage of finding food which increases survival, increases capability of reproduction (well fed adults reproduce better), and increases survival of the offspring by providing more food for them
many small rodents like guinea pigs are quick to jump and run erratically immediately upon hearing a sharp noise or quick movement
what are the proximate and ultimate causes
the proximate cause is the sharp noise/quick movement and the ultimate cause is running away from predators or danger to find a hiding spot (without thinking about it) which increases their survival, allows them to reproduce, and increases offspring survival with the behavior
genetic vs environmental basis of behavior is also known as what
nature vs nurture
describe the twin studies
identical twins were separated at birth with one being the control and the other being the experimental under different environmental conditions. they had similar activity patterns which shows certain behaviors are influenced by genes/nature. however parental guidance or their environmental basis allows one twin to excel at a talent such as playing a musical instrument
describe the garter snake food choice/preference experiment
the two populations were mated which showed newborns with partial preference for slugs meaning it is inherited. snakes have odor receptors in their mouth and use tongue flicks to recognize their prey. swabs were dipped in slug extract and coastal snakes (terrestrial) had higher numbers of tongue flicks.
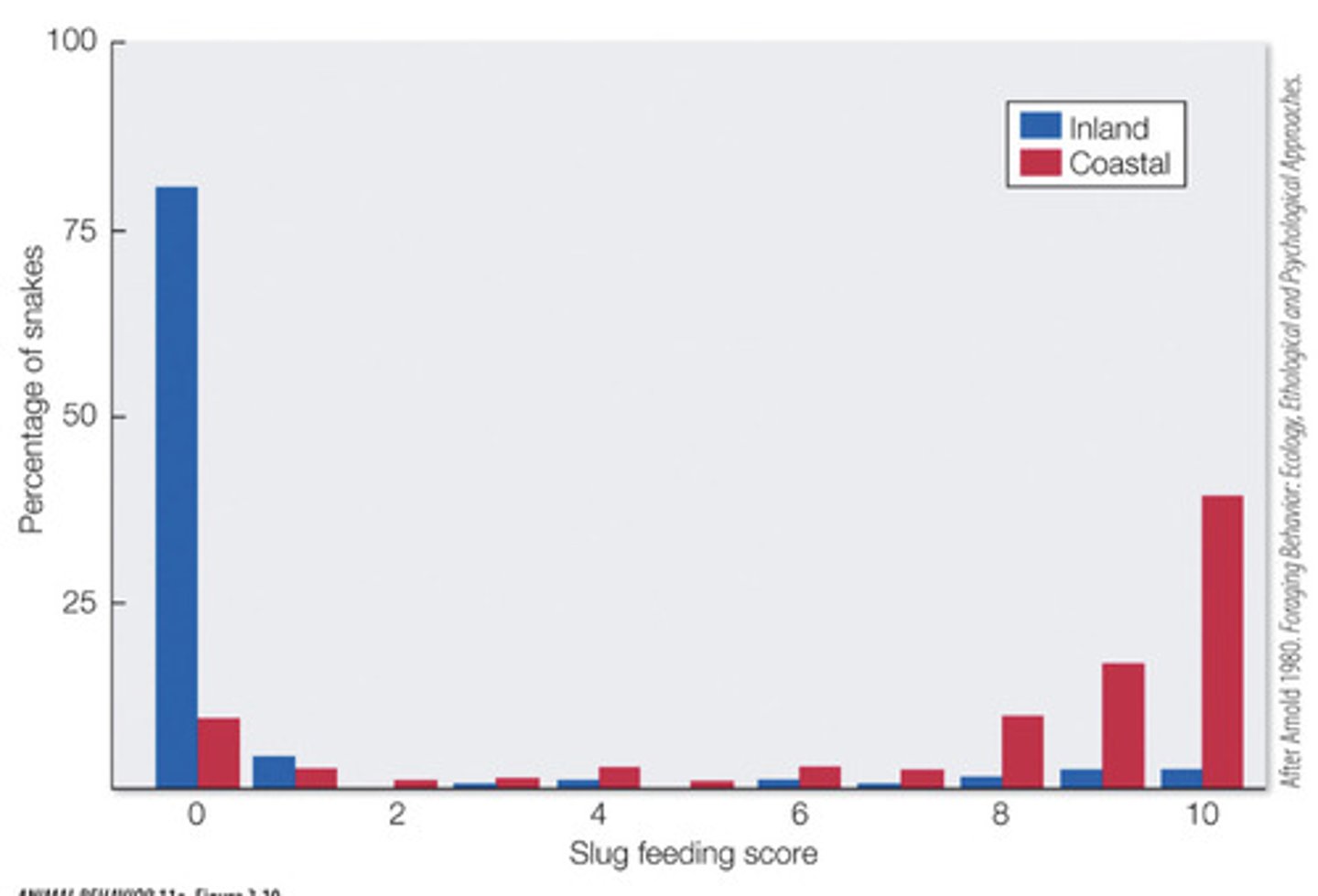
what is the independent variable in the garter snake food choice/preference experiment
type of snake
what is the dependent variable in the garter snake food choice/preference experiment
tongue flicks per minute
the gene for producing a protein smell receptor for slugs is found at a high frequency in the coastal garter (terrestrial) snake population so what is the selective advantage for these snakes to have the gene to smell slugs
slugs are a terrestrial species and are a food source for the coastal garter (terrestrial) snake while the slugs are not found in the water so the inland garter (aquatic) snake does not need to produce the protein to smell slugs
what is the genetic component for the garter snake food choice/preference experiment
gene for the ability to smell slugs
what is the environmental component in the garter snake food choice/preference experiment
aquatic vs terrestrial habitat of the species
describe the nurturing behavior in mice
maternal behavior in mice is dependent on the presence of a gene called fosB. the result is a change in the neural circuitry which manifests itself in maternal nurturing. mice that do not engage in this behavior lack the fosB alleles and will not retrieve their young when separated
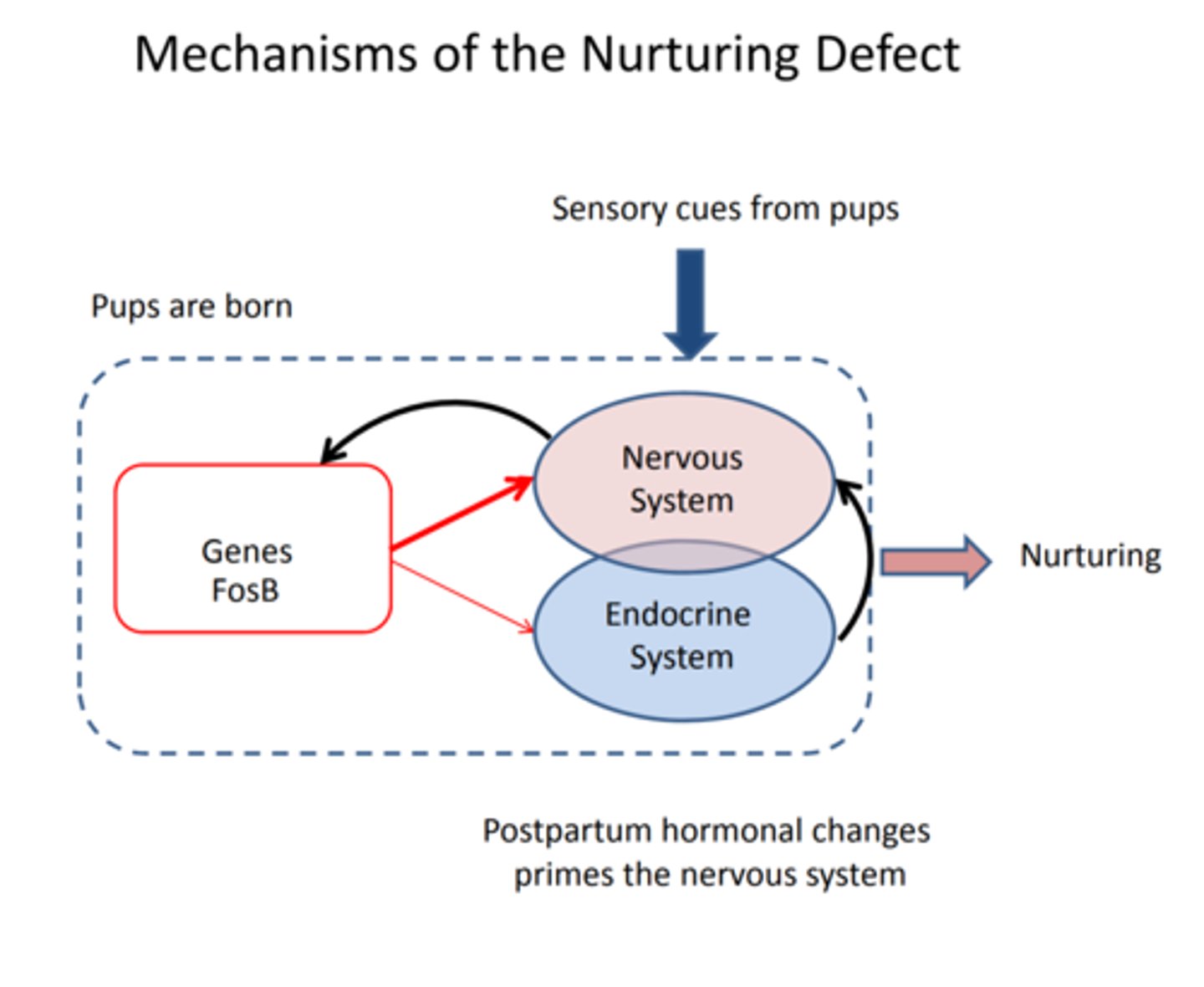
how is the nurturing behavior in mice also environmental
unloved mice treat their offspring the same way but when placed under foster care of a mouse with the maternal behavior it becomes more loved
innate behaviors
pre-programmed before birth
what is the selective advantage of innate behaviors
when an organism does not have time to learn the behavior they already know it
learned behaviors
not based on heredity but rely instead on experience and environment
every behavior is there for a reason for the organism to be what
energy efficient
fixed action patterns (FAP)
unchangeable series of actions triggered by a specific stimulus
describe the FAP of the male stickleback fish
aggressively defend a territory against other males; reacts more aggressively to any model in the experiment with a red belly like him rather than one that looks female
what are the proximate and ultimate causes of the male stickleback experiment
the proximate cause is the red belly that leads to the aggressive behavior and the ultimate cause is protecting their habitat leads to their survival which leads to the ability to reproduce with their offspring having those behaviors
describe the innate FAP of the goose retrieval experiment
the mother goose continues to try to roll the imaginary egg towards herself even after the egg is removed and it does not even have to be a goose egg it can be anything that can be pushed by her beak to fit under her
what are the proximate and ultimate causes of the goose retrieval experiment
the proximate cause is any white object and the ultimate cause is the goose gives her offspring the chance to survive and reproduce rather than being eaten by a predator
what is the FAP the Himba woman demonstrated
eye opening recognition with rapid brow and eye raising signals the baby a loving and nurturing character
because a behavior such as the one the Himba woman demonstrated is universal across all cultures what does that mean
it is probably not learned but an innate behavior
what can innate behaviors be followed by
a learned behavioral response
describe the gull chicks begging behavior example
a chick directs a pecking motion toward the parent's bill which signals the parent to regurgitate food and encourage them to eat which was tested on the day of hatching each chick was allowed to make a dozen pecks at a model
how is the gull chicks begging behavior a FAP and how is there a learned component
even if it was a model of a gull head the chicks still pecked at it and after two days the accuracy of the pecks reached more than 75%
what are the proximal and ultimate causes of the gull chicks begging behavior example
the proximate cause is the red bill and the ultimate cause is getting food from the parent to survive which equals a selective advantage
imprinting
the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life
why is imprinting innate and learned
they will imprint on an object during a critical
sensitive period of time while learning what object to imprint on because if they receive nurturing they will continue to follow that object
sensitive period
period of time in which a particular behavior develops
what are the proximate and ultimate causes of the baby birds/geese example
the proximate cause is a moving object with sound away from the babies and the ultimate cause is enabling individuals to recognize its own species and eventually find an appropriate mate
what was the hypothesis of the white crowned sparrow singing bird study
young white crowned sparrows learn how to sing from older members of their species
describe each group of white crowned sparrows and their results
-first group heard no songs and when grown sang with slight resemblance
-second group heard tapes of singing and sang in dialect as long as tapes were played in sensitive period
-third group were given adult tutor and sang song of tutor species
which group of white crowned sparrows suggest there is an innate imprinting response
the second group because they sang the correct dialect after hearing it right after being born
which group of white crowned sparrows suggest there is a social interaction learned component
the third group because no matter when tutoring began the birds sang the song of the tutor
kinesis
random movement such as pill bugs moving everywhere to eventually find a moist area
taxis
positive or negative movement to a specific stimulus such as pill bugs moving away from light
what are the proximate and ultimate causes of pill bugs
the proximate cause is light and the ultimate cause is finding the food source of detritus to survive and reproduce
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events "If I hear, see, feel, smell that...I'll get..."
what is Pavlov's example of classical conditioning
a bell rang every time the dog was given food and its salivation was measured; the dog learned to associate the bell with food and would salivate even when the food was not given
trial and error learning/operant conditioning
A form of associative learning that occurs when an animal connects its own behavior with a particular environmental response. The behavior will be repeated if the response is desirable but not if it is undesirable. "If I do this...I'll get..."
what is Skinner's example of operant conditioning or trial and error learning
when a stimulus response connection is strengthened such as rats learned to press a lever to get a sugar cube reward
animals tend to repeat the response if what
it is a positive reward and avoid it if it is harmful
migration
long distance travel from one location to another such as monarch butterflies
orientation
ability tot ravel in a particular direction such as south in the winter and north in the spring: birds use the sun and the stars
biological clock
An innate mechanism in living organisms that controls the periodicity of many physiological functions like birds know where the sun will be in relation to the direction they should be going at any time
navigation
direction in response to environmental cues
pheromones
chemical signal passed between members of the same species
doe scents signal to males they are ready to reproduce
auditory
birds have songs for distress, courting, marking territories
visual
fireflies use flash patterns to signal females
tactile
one animal cleaning the coat and skin of another cements social bonds
territory
portion of animals range defended for exclusive use
territoriality
the behavior of defending one's territory
optimal foraging model
adaptive for foraging behavior to be as energetically efficient as possible
polygamous
a single male mates with multiple females
polyandrous
a female mates with multiple males
monagomous
pair bond and both males and females help to take care of the young
sexual selection
favors features that increase an animal's chances of mating
what is the advantage of sexual selection
strongest males pass their genes on
habituation
an organism's decreasing response to a stimulus with repeated exposure to it
what is the ultimate cause or selective advantage of habituation
animal's nervous system focuses on important stimuli that signal food, mate, or real danger and ignore others that act as distractions
what is the deer example of habituation
deer grazing in backyard no longer worry about humans
describe the fruit fly courtship/mating example
-some male fruit flies possess a mutation in a gene called fruitless (fru) leading to attempting to court other male flies
-in normal males the master control gene fru codes for a protein that switches on a suite of genes responsible for male courtship behavior
without doing an experiment ho might you distinguish between a behavior that is mostly controlled by genes and one that is mostly determined by the environment
gene controlled behaviors will be the same for the species but environmentally controlled behavior will be different between different environments
social learning
process of altering behavior by observing and imitating the behavior of others
how do many predators learn to hunt
observing and imitating their mothers
what is an example of alarm calls or predator warnings
monkey infants give a general distress call then learn the call for a specific predator
signal behaviors, or cues, can produce changes in the behavior of other organisms and can result in what
increased survival and reproductive success
scent markers are signals that serve as what
no trespassing signs such as deer pee
establishing territories can provide what
exclusive access to food supplies, breeding areas, places to raise young
why is the territory of a gannet bird so much smaller than the territory of a cheetah
gannet birds use their territory for raising young while cheetahs forage or search for food
agnostic behaviors
arise over limited resources like food, mates, territories and are settled by threats, rituals, combat
primary productivity
the rate at which organic material is produced by photosynthetic organisms in an ecosystem
gross primary productivity
the amount of sugar that the plants produce in photosynthesis and subtracting from it the amount of energy the plants need for growth maintenance, repair, and reproduction
net primary productivity
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire
how might increasing limiting factors affect net primary productivity
Increasing these limiting factors like nitrogen and sulfur will increase net primary productivity. With more of these necessary nutrients, plants are able to perform more photosynthesis to balance the amount of respiration, so the ecosystem does not crash.
what could we measure to calculate productivity
the use of carbon dioxide or the production of glucose or oxygen but not water because it is hard to distinguish the amount used or evaporated
what is the purpose of having a control group
compare our results to the baseline where the independent variable is isolated
why should everything be constant except for the independent variable
if there is more than one independent variable we will not know which influenced the results and possibly made a difference
standard deviation
a measure of how spread out numbers are by finding the square root of the variance
variance
the average of the squared differences from the mean
how do you find variance
find the mean, subtract the mean from each number and square the results, and find the mean of those differences
what do you divide the variance by as a "corrective" measure
N-1
how do you find standard error
divide the standard deviation by the square root of the sample size