18.1 carboxylic acids
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
State the ways in which carboxylic acids can be produced
oxidation of primary alcohols and aldehydes
Hydrolysis of nitriles
Hydrolysis of esters
Oxidation of primary alcohols & aldehydes
Acidified KMnO4 and reflux
First oxidised to aldehyde then to carboxylic acid
Acid Hydrolysis of nitriles
Hydrolysis by dilute acid results in the formation of a carboxylic acid and ammonium salt
Alkaline hydrolysis of nitriles
Hydrolysis by dilute alkali results in the formation of a sodium carboxylate salt and ammonia; Acidification is required to change the carboxylate ion into a carboxylic acid
Hydrolysis of esters
Hydrolysis of esters by dilute acid or dilute alkali and heat followed by acidification will reform the alcohol and the carboxylic acid
Acid vs alkaline hydrolysis of esters
Hydrolysis by dilute acid is a reversible reaction where an equilibrium is established
Hydrolysis by dilute alkali is an irreversible reaction as all the ester is broken down to form a sodium carboxylate salt and an alcohol; acidification is required to change the carboxylate ion into a carboxylic acid
Describe the ways in which carboxylic acids can react
Redox reactions with reactive metals
Neutralisation. Reaction with alkalis
Acid-base reaction
Esterification
Reduction
Redox reaction of carboxylic acids with reactive metals.
Produces salt and hydrogen gas
Neutralisation reaction with alkali
Salt and water
Acid base reactions with carbonates
Produces salt and water and carbon dioxide
Esterification with alcohols
H2SO4 as catalyst
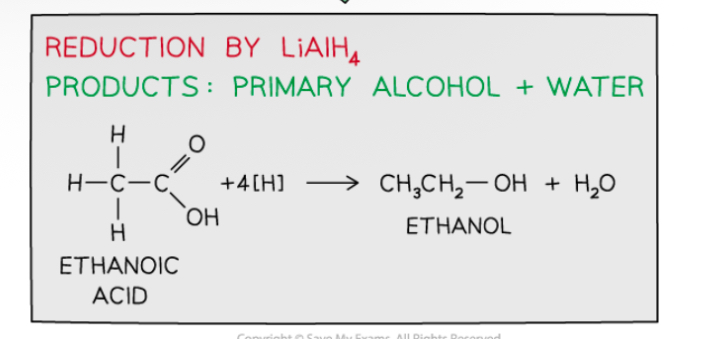
Reduction by LiAlH4
Produced primary alcohols and water