Behavioral Neuroscience Exam 1
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Generalization vs Reduction
Generalization refers to applying findings from specific instances to broader contexts, while reduction involves breaking down complex phenomena into simpler components for analysis.
Mind-Body Question: Monism vs Dualism
Monism posits that mind and body are one entity, while dualism argues they are distinct and separate substances.
Galvani's Experimental Findings
Galvani discovered that electrical stimulation of frog muscles caused contraction, leading to the understanding of bioelectricity in nerves.
Selective Advantage
A selective advantage is a genetic trait that improves an organism's chances of survival and reproduction in a specific environment.
Mutations
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can lead to variations in traits and may affect an organism's fitness.
How are human brains different/special compared to other animals?
Human brains have a larger neocortex relative to body size, allowing for advanced cognitive functions like reasoning, problem-solving, and language.
Axoplasmic Transport
Axoplasmic transport is the process by which materials are transported along the axon of a neuron, essential for neuron function and maintenance.
Anterograde vs Retrograde
Anterograde transport moves materials from the cell body to the axon terminal, while retrograde transport moves materials from the axon terminal back to the cell body.
Kinesin vs Dyenin
Kinesin is a motor protein that transports materials along microtubules towards the axon terminal (anterograde), while dyenin transports materials back to the cell body (retrograde).
Synaptic Transmission
Synaptic transmission is the process by which signaling molecules are released from a neuron and bind to receptors on another neuron, facilitating communication between them.
What is the messenger?
In synaptic transmission, the messenger typically refers to neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals across synapses.
What are the cells before and after the synapse referred to?
The cell before the synapse is called the presynaptic neuron, and the cell after the synapse is called the postsynaptic neuron.
What is the result of transmission?
The result of transmission is the propagation of an electrical signal in the postsynaptic neuron, leading to potential action potentials.
Excitation: postsynaptic neuron becomes more likely to fire
Inhibition: postsynaptic neuron becomes less likely to fire
How does a signal move down a neuron (by each part of the neuron)?
A signal moves down a neuron through the dendrites (receiving signals), soma (processing), axon (conducting action potentials), and finally to the axon terminals (transmitting signals).
How do sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons play a role in simple behaviors?
Sensory neurons transmit information from sensory receptors to the central nervous system, interneurons process this information, and motor neurons carry commands from the CNS to muscles for response.
Sodium-Potassium Pumps - What is their function?
Sodium-potassium pumps maintain the resting membrane potential by actively transporting sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell; this process maintains resting membrane potential, resets neuron and prevents swelling
Nodes of Ranvier - What is their purpose?
Nodes of Ranvier are gaps in the myelin sheath that facilitate rapid conduction of action potentials through saltatory conduction.
Saltatory Conduction
Saltatory conduction is the process by which action potentials jump from one node of Ranvier to another along myelinated axons, increasing the speed of signal transmission.
Reuptake and Enzymatic Degradation
Reuptake is the process by which neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron, while enzymatic degradation involves the breakdown of neurotransmitters by enzymes(acetylecholine)
Meninges
Meninges are protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, consisting of three layers: dura mater: outerlayer very thick and close to skull, arachnoid mater: middle layer weblike and contains cerebrospinal fluid, and pia mater: innermost layer very thin and hugs brain.
Afferent vs Efferent
Afferent pathways carry sensory information to the central nervous system (arrive), while efferent pathways carry motor commands from the CNS to the body (away)
Sympathetic vs Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses, while the parasympathetic nervous system promotes 'rest and digest' activities.
What are their functions?
The sympathetic nervous system increases heart rate and energy expenditure, while the parasympathetic nervous system decreases heart rate and conserves energy.
Experimental ablation
Experimental ablation is a technique used to remove or damage specific brain areas to study their functions.
Ionotropic vs Metabotropic receptors
Ionotropic receptors are ligand-gated ion channels that mediate fast synaptic transmission, while metabotropic receptors are G-protein coupled receptors that mediate slower, longer-lasting effects.
What makes up the central nervous system?
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
Blood-Brain Barrier
The blood-brain barrier is a selective permeability barrier that protects the brain from harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients to pass through.
Neural Integration
Neural integration is the process by which multiple signals are combined and processed by the nervous system to produce a coherent response.
Key Components:
Summation- combining signals
EPSP- depolarizing neuron making it closer to firing
IPSP-hyperpolarize the neuron making firing less likely
Contralateral vs Ipsilateral
Contralateral refers to structures on opposite sides of the body, while ipsilateral refers to structures on the same side.
What are the five glial cells and their functions?
The five glial cells are astrocytes (support and nourish neurons), oligodendrocytes (form myelin in the CNS), Schwann cells (form myelin in the PNS), microglia (immune defense), and ependymal cells (produce cerebrospinal fluid).
Label Neuron
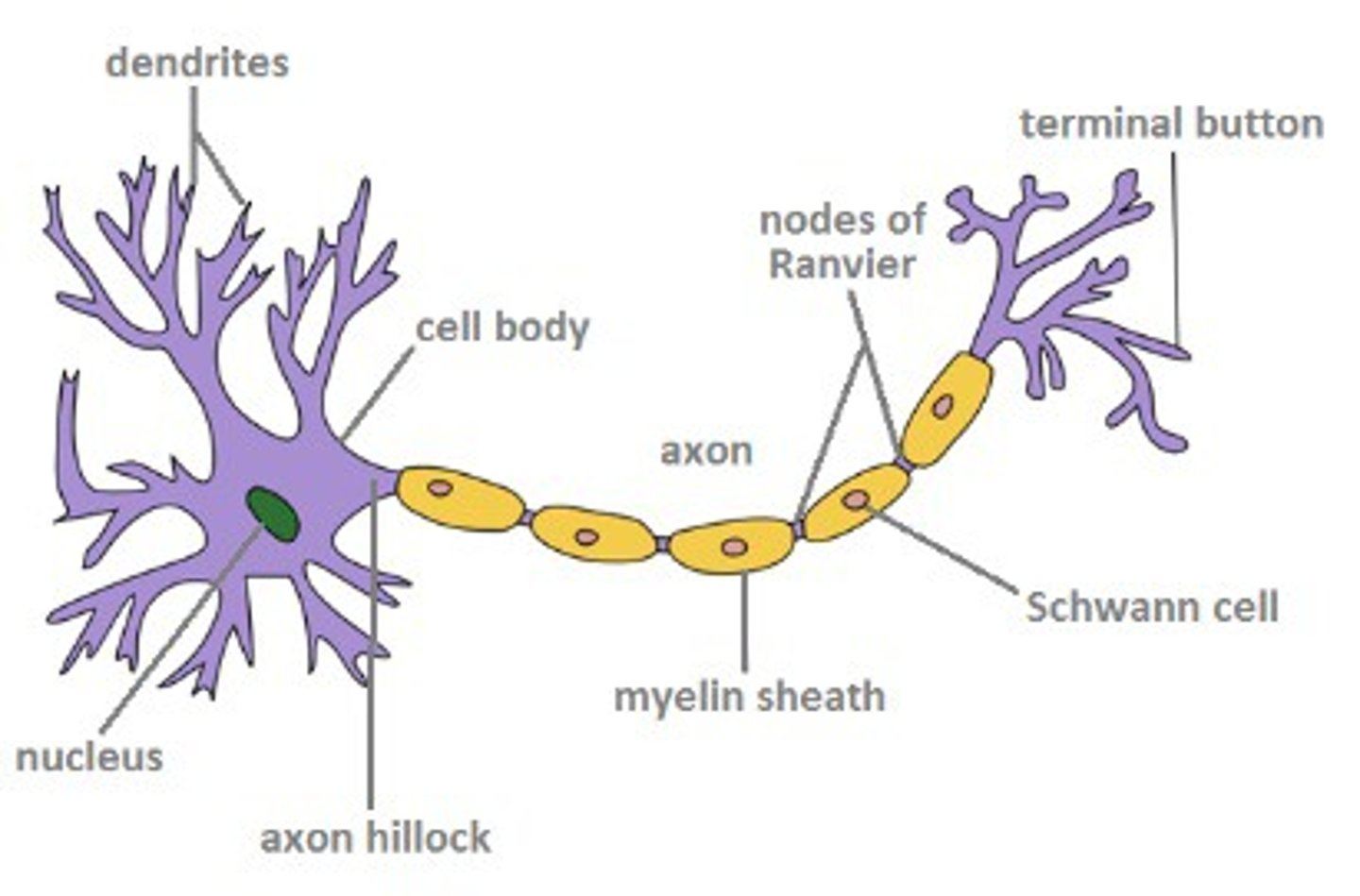
What was Cajal's contribution to Neuroscience?
used Golgi staining technique to examine individual neurons of the brain (had detailed drawings of neurons and nervous system)
Hyperpolarization vs. depolarization
Depolarization--> sodium channels open (na+ rushes into cell) neuron fires
Hyperpolarization--> inside of neuron becomes more negative than resting potential; potassium channels stay open (k+ flows out of cell) neuron cannot fire
What is rate law?
how neurons represent the intensity of a stimulus; size of action potential does not change but how often the action potential occurs changes
Anatomical directions in the brain
Anterior/ rostral: front Posterior/ claudal: back Ventral: bottom Dorasl: top Lateral: to the sides Medial: towards the middle
Gyrus vs. Sulcus
Gyrus: raised fold on cerebral cortex( bump) increases brain surface area Sulcus: grooves in gyri (valley) divides brain into regions
What are ventricles and list 4 main types
Connected system of cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid; Lateral (right and left), third ventricle, fourth ventricle; Function: produce cerebrospinal fluid, protects brain, maintains homeostasis, removes waste, circulates nutrient
Diffusion vs Electrostatic pressure
Diffusion: particles naturally move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration (k+ moves out) Electrostatic Pressure: force where opposite charges attract and similar like charges repel each other (Na+ pulled in)
Describe the human advantages according to Dr. Suzana Ted Talk
we have largest number of neurons in cerebral cortex and we cook; no other animal cooks
Concentration of ions inside and outside of cell
Inside: high potassium; low sodium and CL Outside: high Salt and CL and CA; low potassium
What are the lobes of the brain and their functions?
Frontal: decision making, problem solving Parietal: somatosensory information and spatial awareness Temporal: Hearing and language comprehension Occipital: Visual processing
What is the function of cerebral cortex and corpus callosum?
Cerebral cortex is outer layer of brain involved in thinking, decision making, and voluntary movement; Corpus Callosum is thick band of nerve fibers that allow for coordination of bilateral activities
What is the function of the limbic system?
Limbic cortex helps regulate emotional responses and attention; Hippocampus allows for new memories to form; Amygdala is emotional processing center; Fornix: a fiber tract connecting hippocampus to other limbic structures and helps with memory recall; Mammillary bodies are involved in recollective memory
What is the function of the basal ganglia?
Movement regulation, procedural memory, and motor planning
What is the function of the diencephalon, including thalamus and Hypothalamus?
Diencephalon is a relay hub for autonomic functions, endocrine activity, and sensory integration; Thalamus: relays sensory information and helps coordinate motor signals; Hypothalamus: controls autonomic nervous system and regulates homeostasis
What is the function of the midbrain?
Helps coordinate our reflexes for survival
List the functions of the hindbrain
Helps maintain vital life functions, coordinates movement and regulates sleep; Cerebellum controls balance and posture; Pons helps regulate sleep and breathing; Medulla controls autonomic survival functions including heart rate; Brain stem regulates basic life support systems