Cytoplasm
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is cytoplasm?
An active material
Why can’t it be thought as a fluid?
Bc it is far from equilibrium: bc of the motion of particles (ATP) and meshwork of cytoplasm
Feeling of the cytoplasm
Different for ions, organelles and proteins
Why is the cytoplasm crowded?
4 types of molecules
0.1nm size particles
Ions and very small molecules (H2O)
12 to 100 atoms particles
Sugars, amino acids
10-100nm size particles
Proteins, DNA and RNA
1 micrometer size particles
Organelles
How crowded is the cytoplasm?
As crowded as a protein crystal (20-60% protein/weight)
Why is the cytoplasm a rough-and-tumble place?
Bc the particles inside it are in constant motion
Why are they in constant motion/do they follow Brownian motion?
Bc the heat generated by ATP hydrolysis causes all the particles to be in a state of constant motion
What is the diffusion coefficient?
Coefficient representative of the speed of the diffusion of a particle (inversely proportional to radius)
What other term can define Brownian motion?
Random
Why is Brownian motion random?
50/50 chance of turning left or right in 1-D
Tendency observed as the number of steps increase
Particles diffuse further away from one another
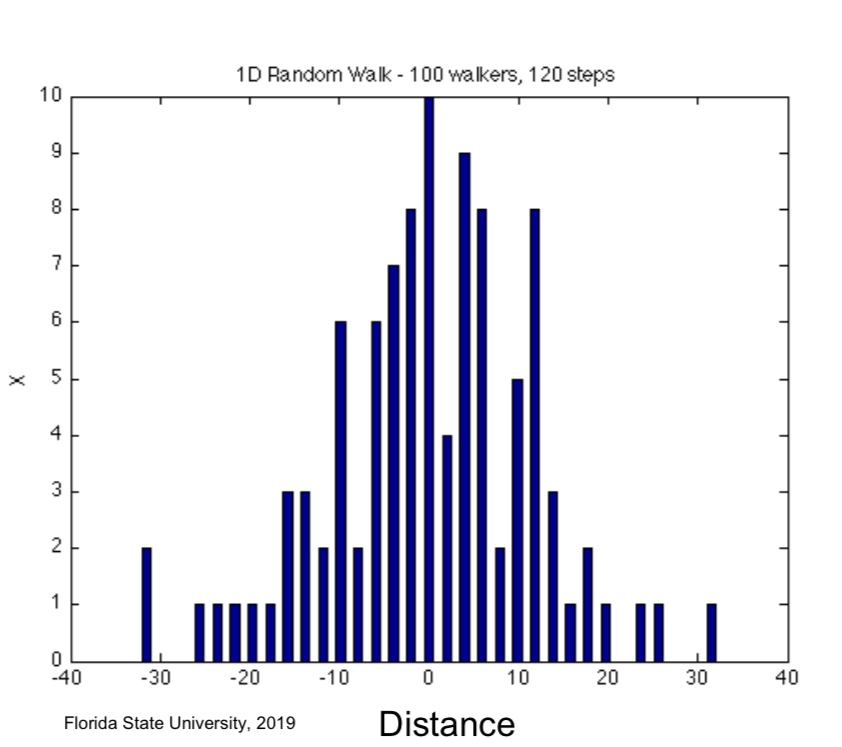
Displacement and Brownian motion
It explores a lot of space but 0 displacement (deltaX)
What does the fact that there is no displacement show?
That, as a population, the particles work to maintain a certain spatial organization
How does Brownian motion explain the time needed for a drug to act?
Even as proteins undergo conformational changes, they are also distorted by collisions
How is the viscosity of the cytoplasm quantified?
By Reynold’s number

Inertia
Resistance of an object to change in its state of motion
Viscosity
Measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow
Full formula for Reynold’s number
.
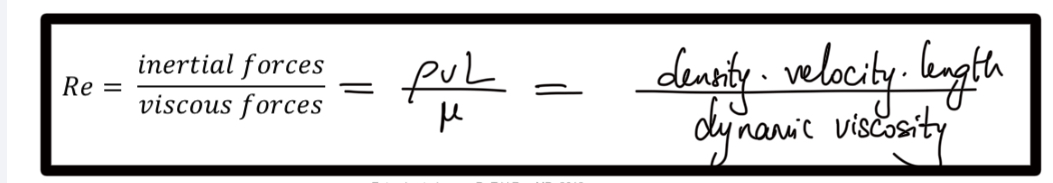
What does an Re= 10^{-4} indicate?
That there is 10 000 more viscosity than inertia for a bacteria in the cytoplasm
4th quality of the cytoplasm
Elasticity or tendency to return to its original shape after deformation
How is cytoplasm a meshwork ?
Bc of its cytoskeleton: actin filaments, organelles, polymers, etc.
What does the meshwork determine?
Pore size
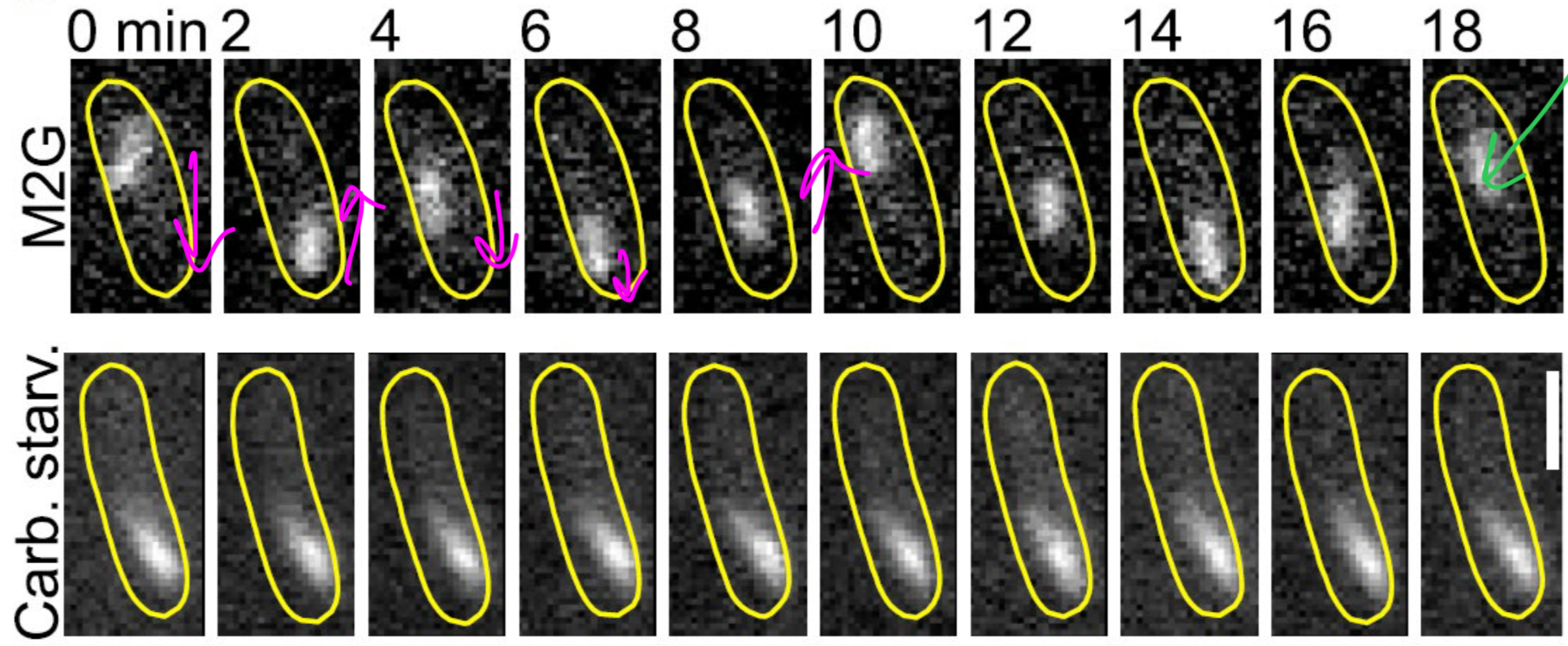
What happens when a cell is carbon deprived?
No more ATP production W
What does rapid ATP depletion cause?
Freezing of the cytoplasm (thaught to help cell save the last of its energy)