RA - Bones, Muscles, & Face shapes
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Occipitofrontalis
•Two (left and right)
•This muscle covers the top of the skull. It is named after its two parts: occipitalis (back part of the head) and frontalis (front part of the head)
•It draws the scalp posteriorly and anteriorly, causing eyebrows to raise and wrinkles to form on the forehead.
Temporalis
•Two (left and right)
•This muscle arising in the temporal cavity and inserting in the mandible
•A muscle of mastication and is the strongest chewing muscle. It closes the mandible and assists in side to side movement of the mandible
Masseter
•Two (left and right)
•This muscle arising from the zygomatic arch and inserting in the mandible
•Muscle of mastication. It closes the mandible
Orbicularis oculi
•Two (left and right)
•This sphincter muscle surrounds the eye socket
•Closes the eyelid and compresses the lacrimal sac
Corrugator
•Two (left and right)
•A pyramid shaped muscle of facial expression. This muscle lies beneath the frontalis and orbicularis oculi. Also known as the frowning muscle
•Draws eyebrows inferiorly and medially, as in frowning
Levator palpebrae superioris
•Two (left and right)
•This muscle of facial expression that runs from the inside of the eye socket to the upper tarsal plate of the eyelid.
•It raises the upper eyelid
Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
•Two (left and right)
•A muscle of facial expression
•Raises the upper lip and dilates nostrils
Levator labii superioris
•Two (left and right)
•A muscle of facial expression
•Elevates and extends the upper lip
Levator anguli oris
•Two (left and right)
•A small muscle at the angle of the mouth
•Elevates the angle of the lip
Zygomaticus minor
•Two (left and right)
•A muscle of the face
•Draws upper lip
1. superiorly
2. laterally
Zygomaticus major
•Two (left and right)
•A muscle of the face
•Draws upper lip
1.Posteriorly
2.Superiorly
3.laterally
Buccinator
•Two (left and right)
•The principle muscle of the cheek. It makes up part of the angulus oris eminence
•Compresses the cheek and it pulls the anguli oris posteriorly. It is called the trumpeter muscle and is used when sucking
Risorius
•Two (left and right)
•Extends from the skin over the masseter muscles to the corners of the mouth
•Draws the corners of the mouth posteriorly
Depressor anguli oris
•Two (left and right)
•A muscle of facial expression that arises from the mandible to insert into the anguli oris
•Depresses the angle of the mouth
Platysma
•Two (left and right)
•A thin layer of muscle covering the anterior aspect of the neck
•Wrinkles the skin of the neck and chest also depresses the mandible and anguli oris as in pouting
Sternocleidomastoid
•A thick muscle that originates from the head of the sternum and clavicle, and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone
•Rotates and depresses the head
Digastric
•A double bellied muscle of the neck which attaches to the mastoid process and the mandible
•Draws the hyoid bone posteriorly
Frontalis
What is this?
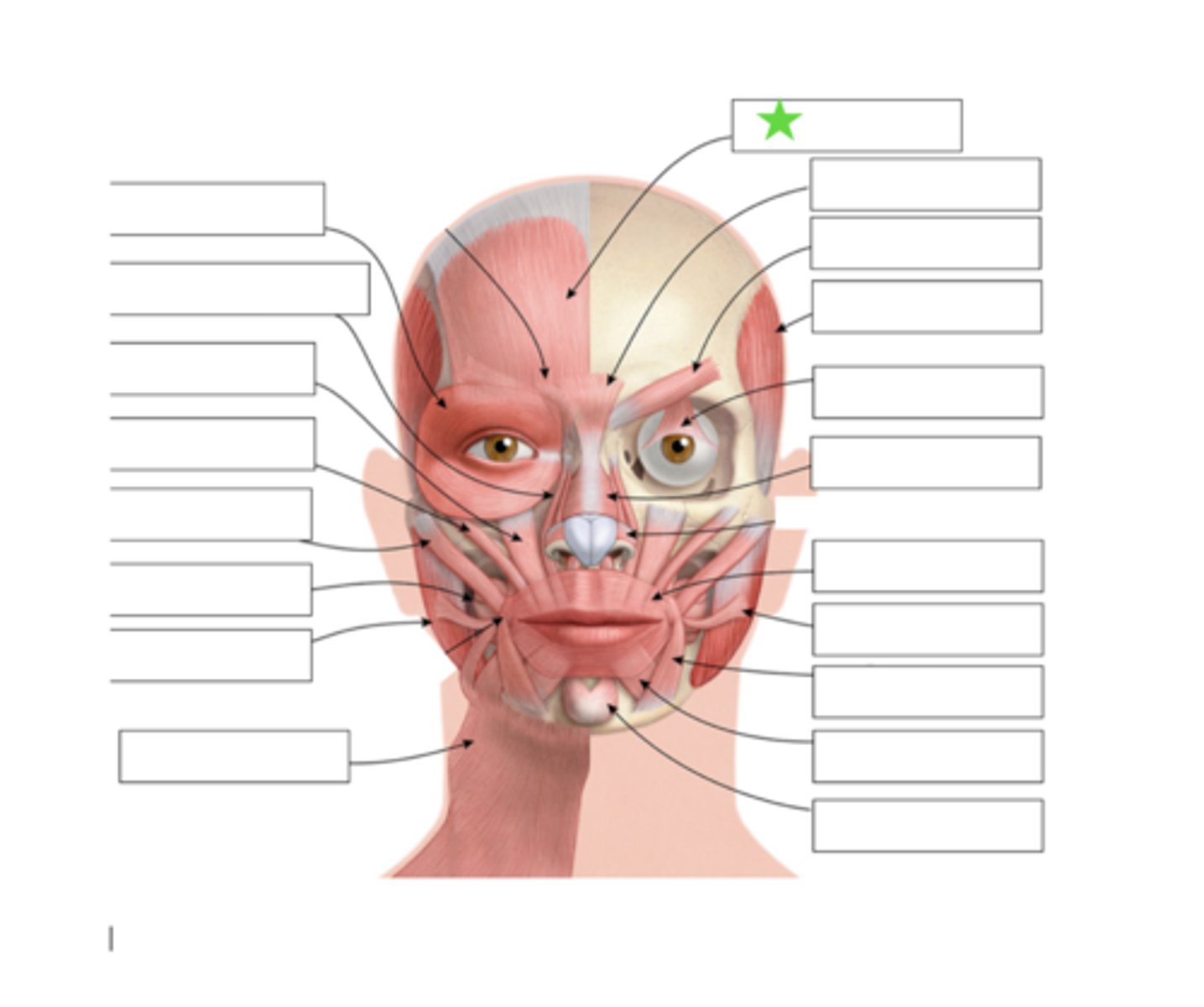
Procerus
What is this?
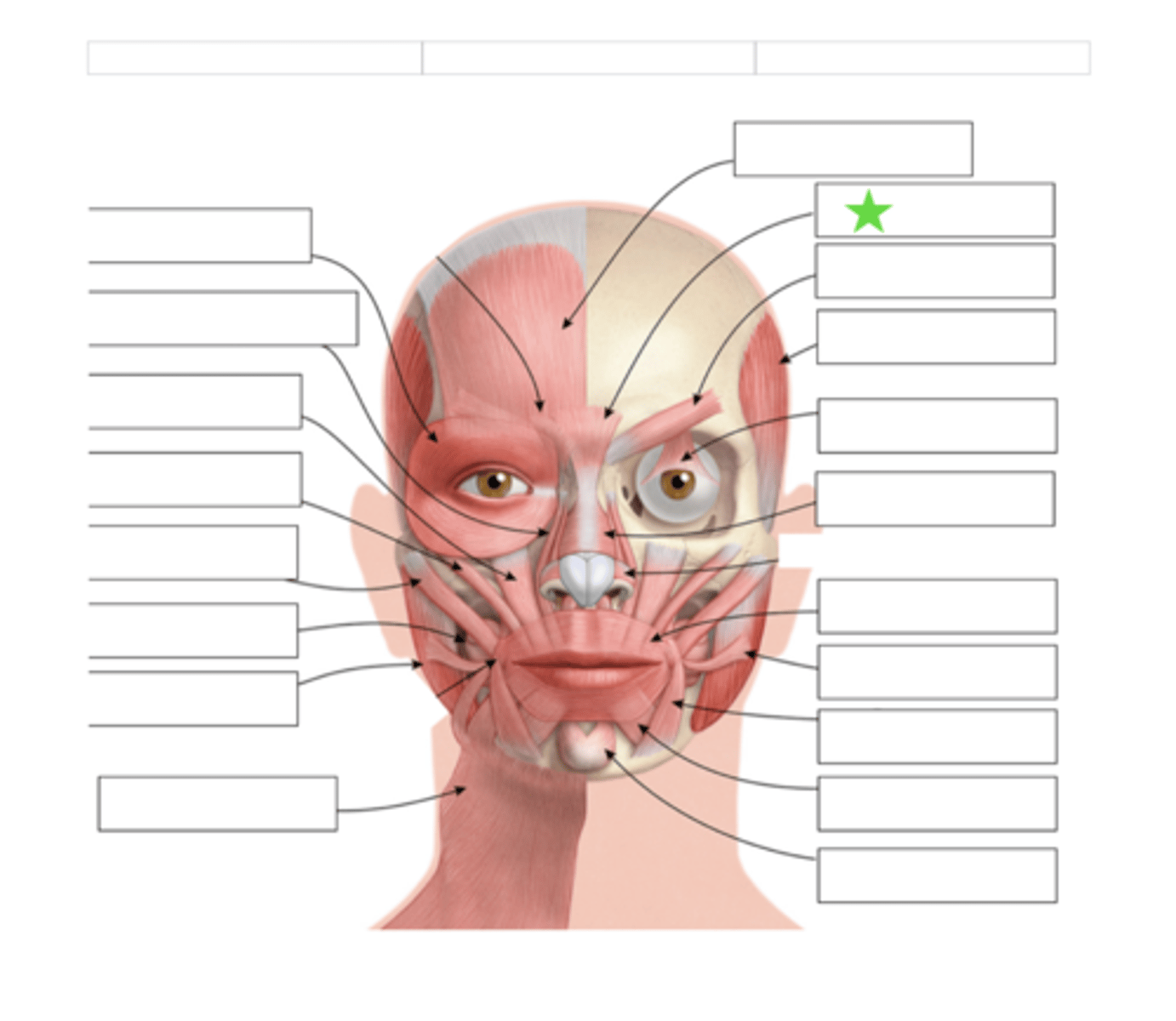
Corrugator
What is this?
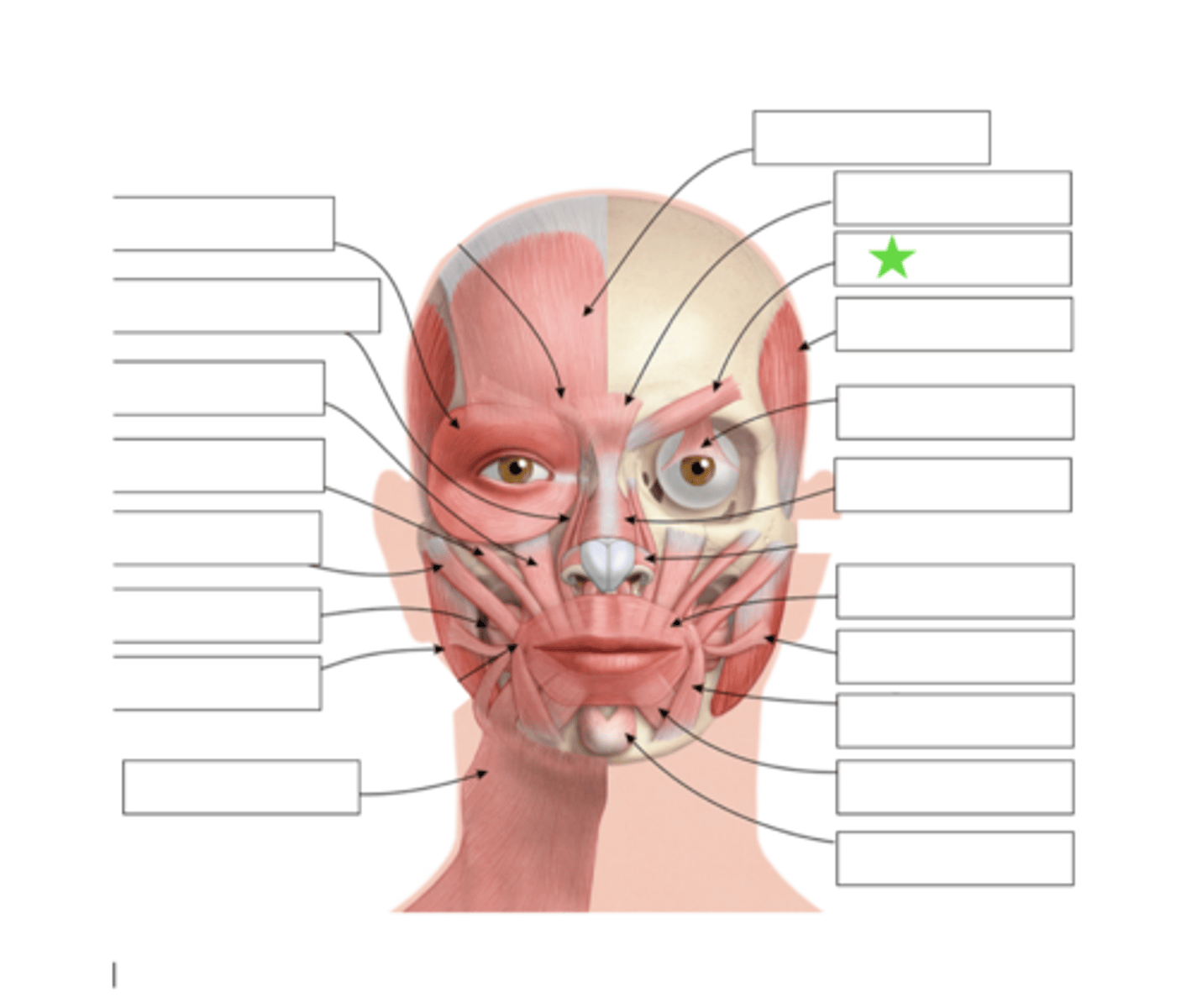
Temporalis
What is this?
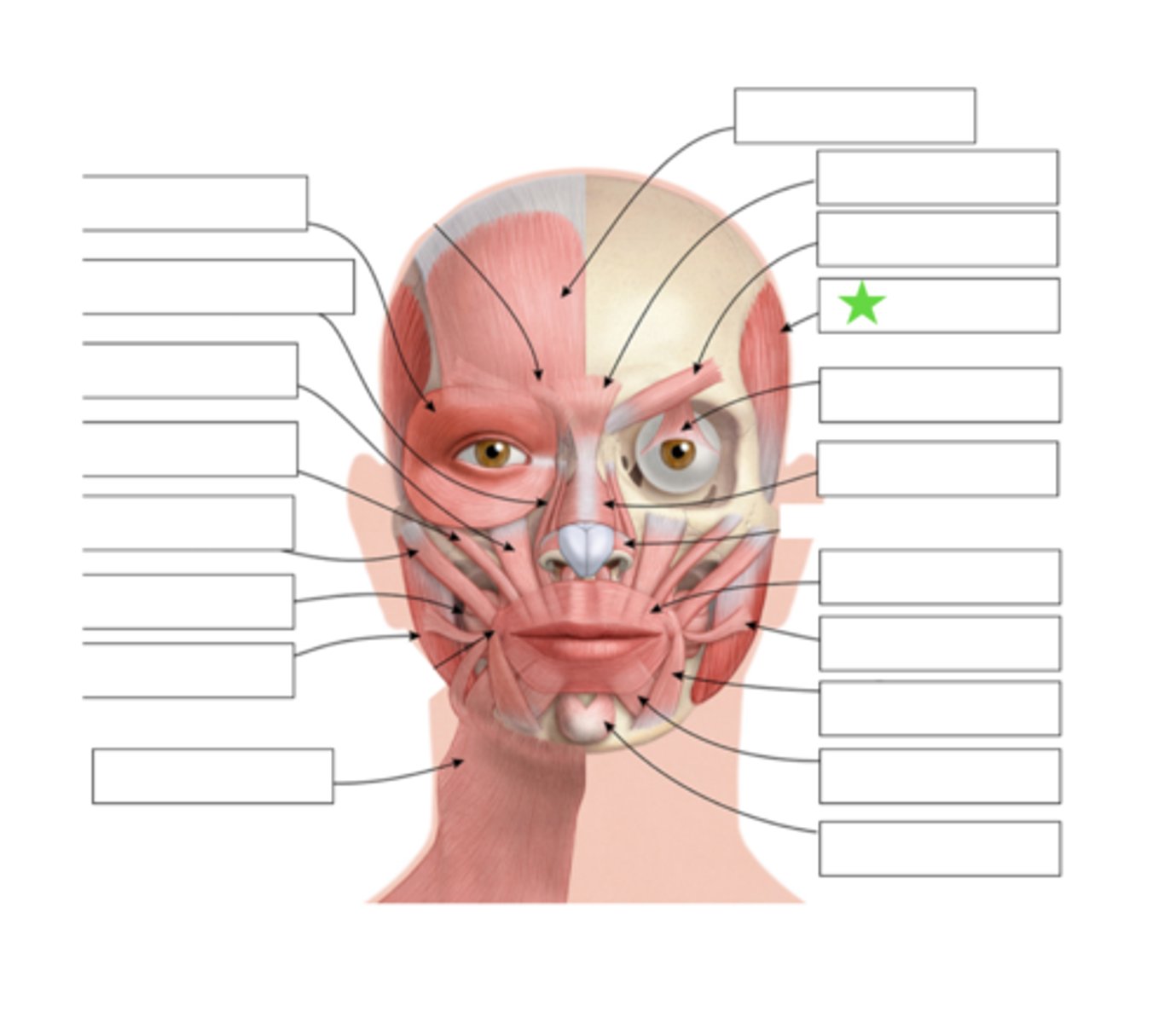
Levator palebra Superioris
What is this?
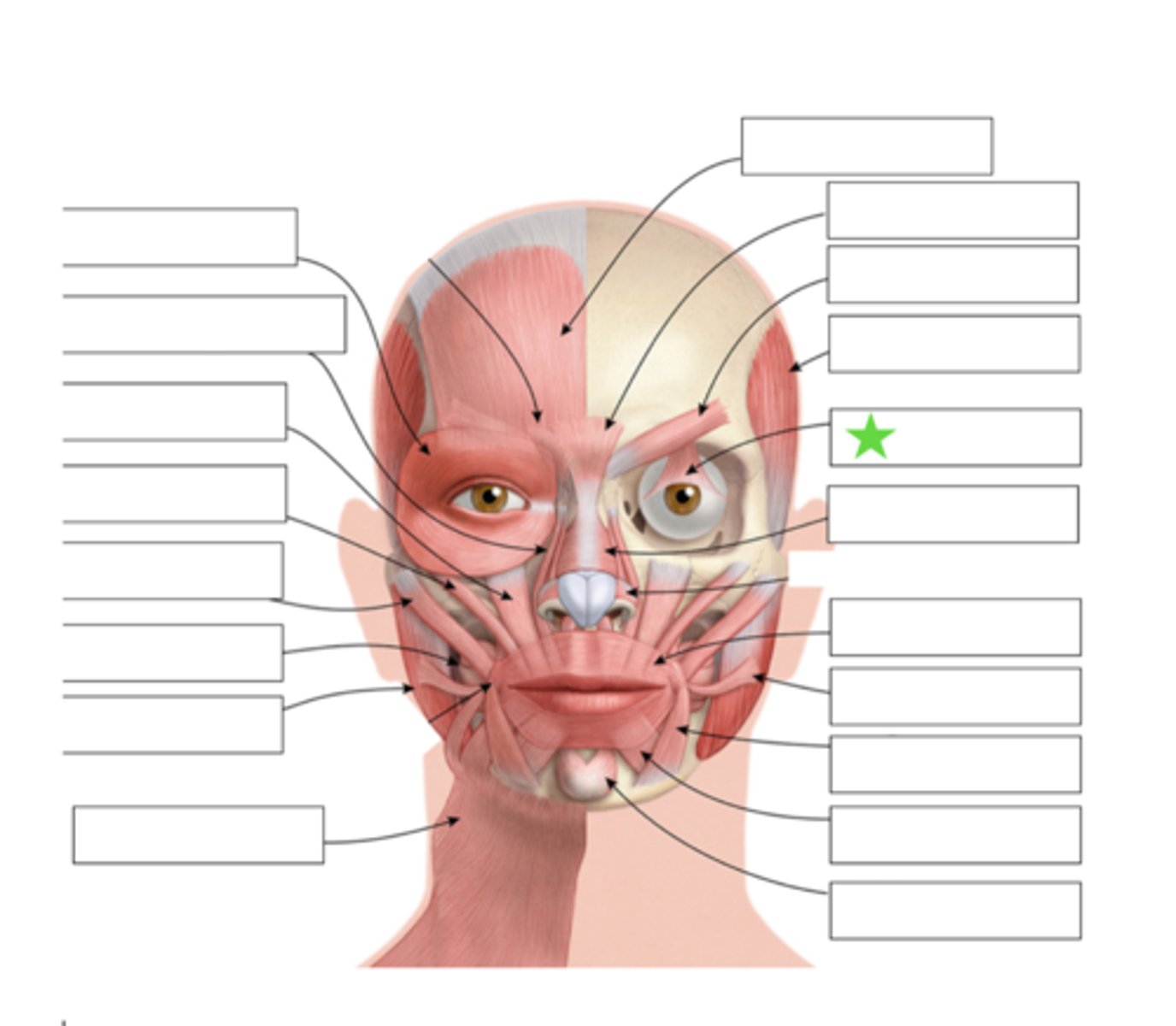
Orbicularis Oculi
What is this?
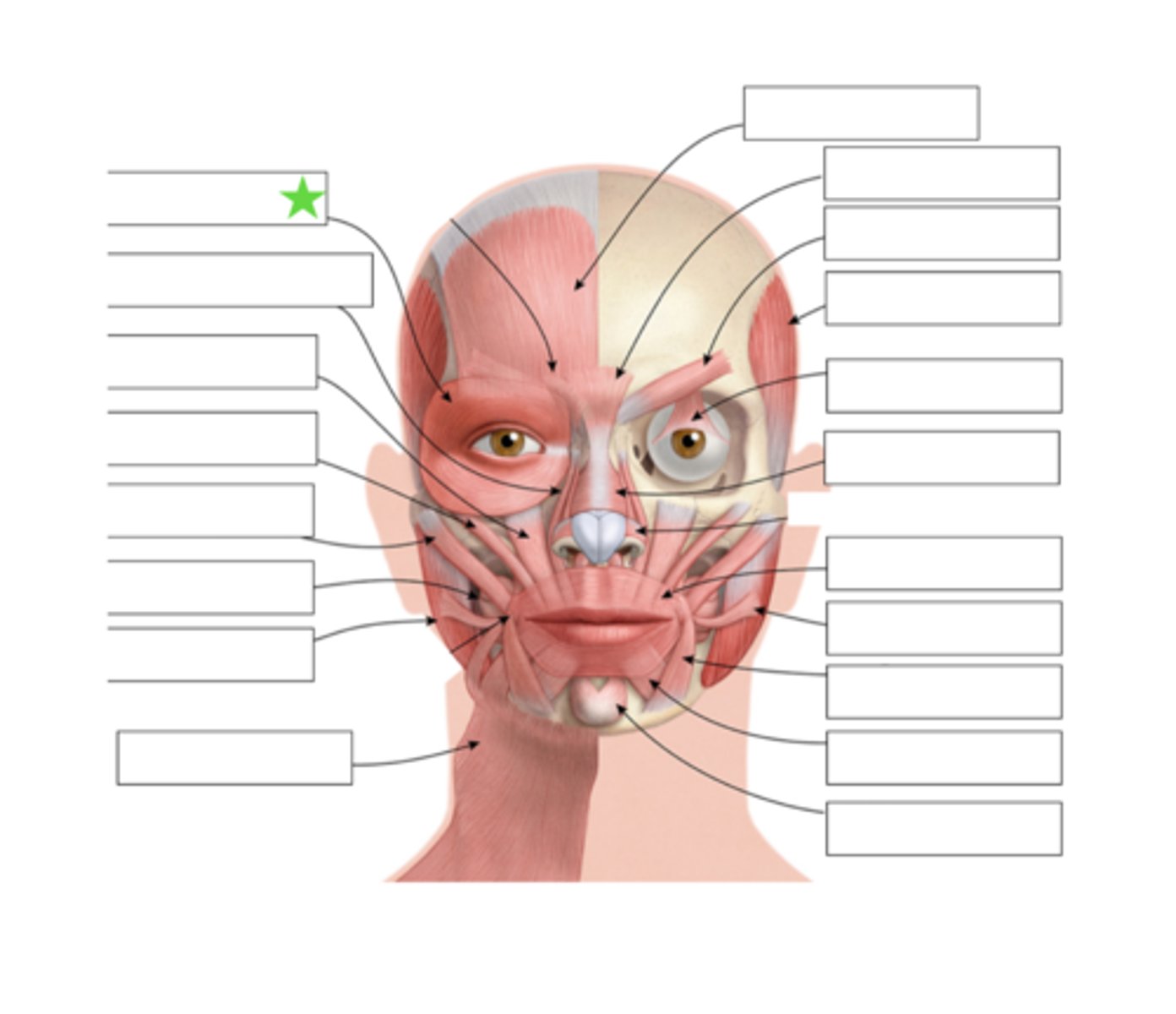
Nasalis
What is this?
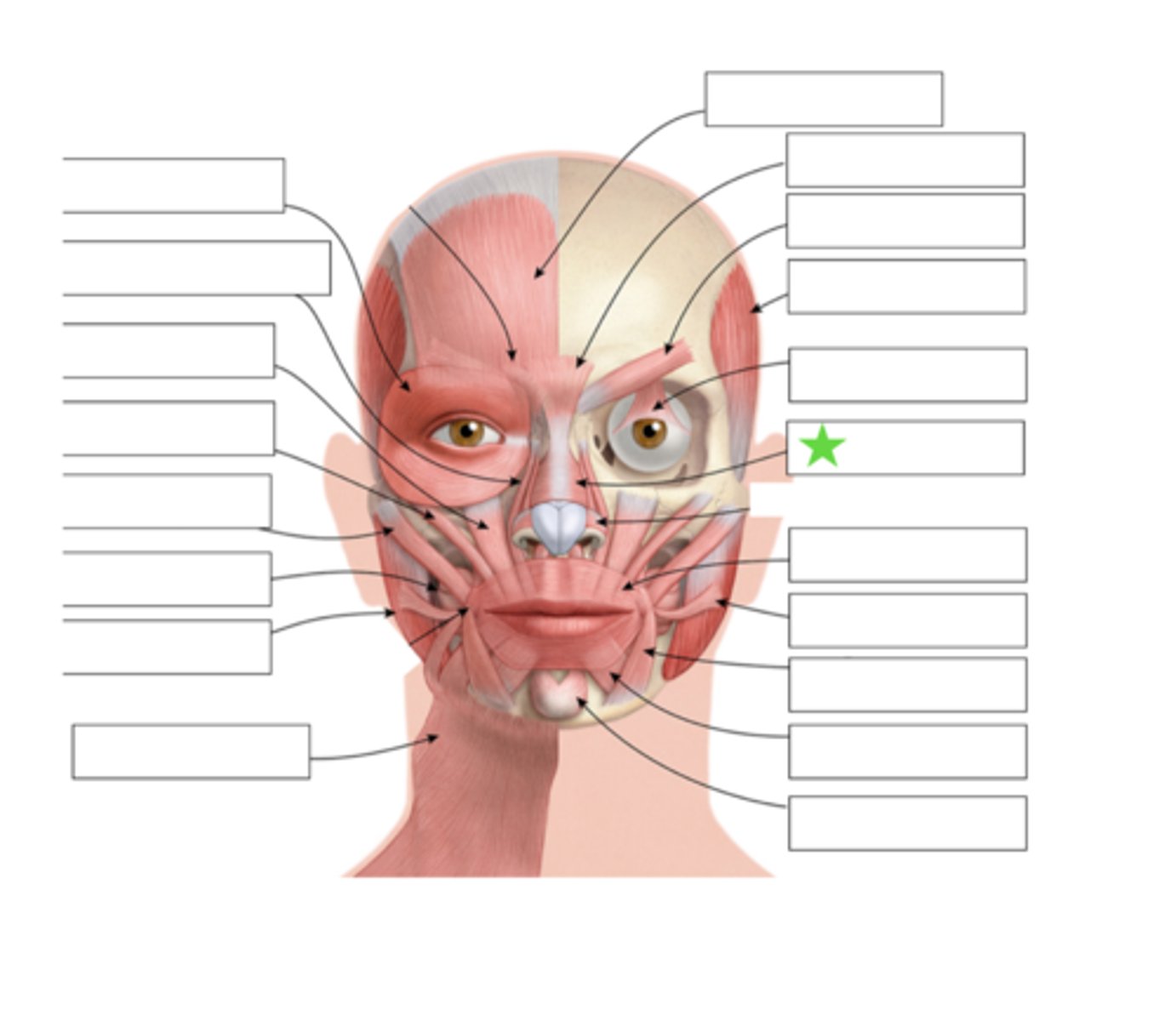
Risoris
What is this?
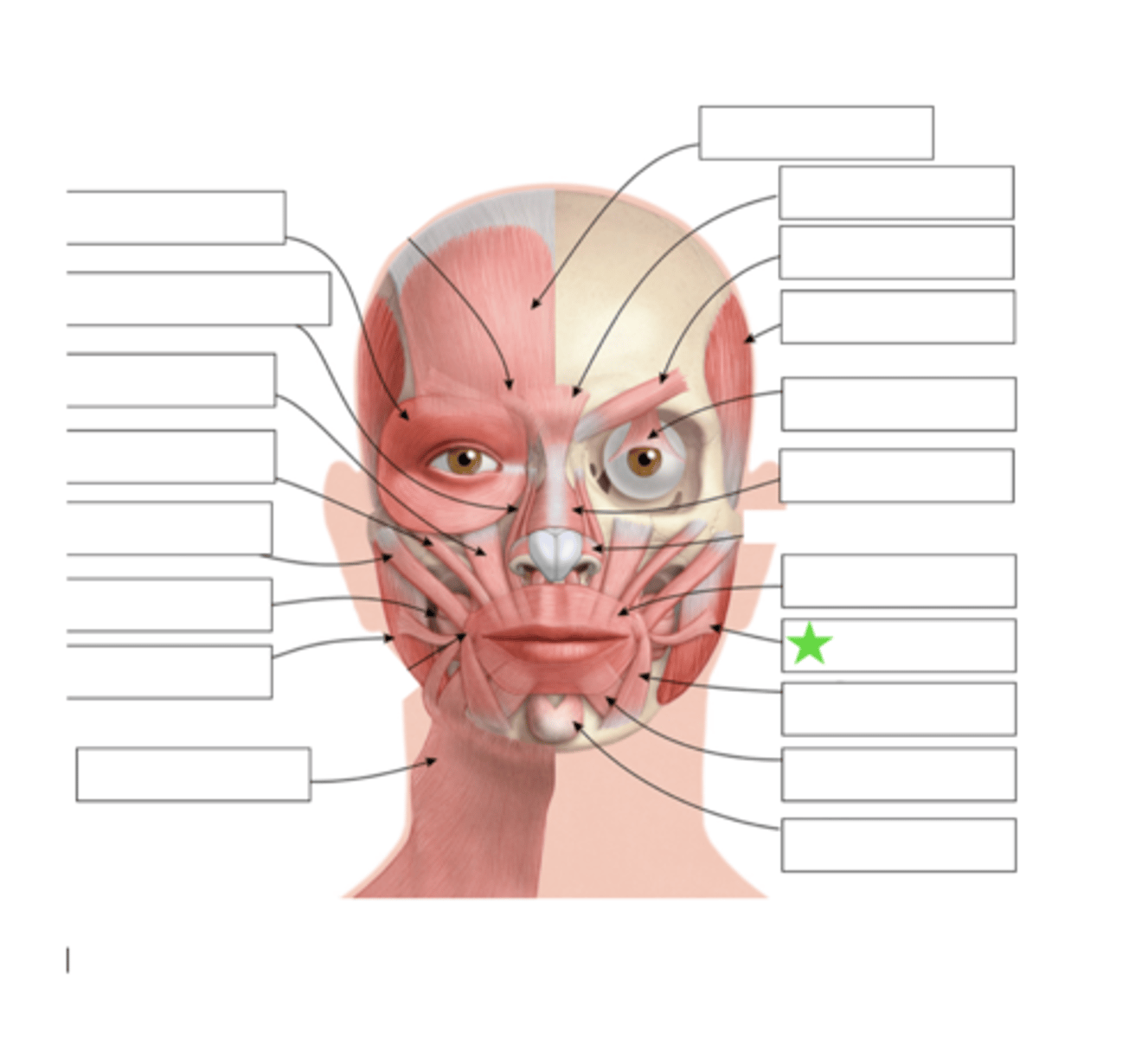
Depressor Anguli Oris
What is this?

Depressor Labii Inferioris
What is this?
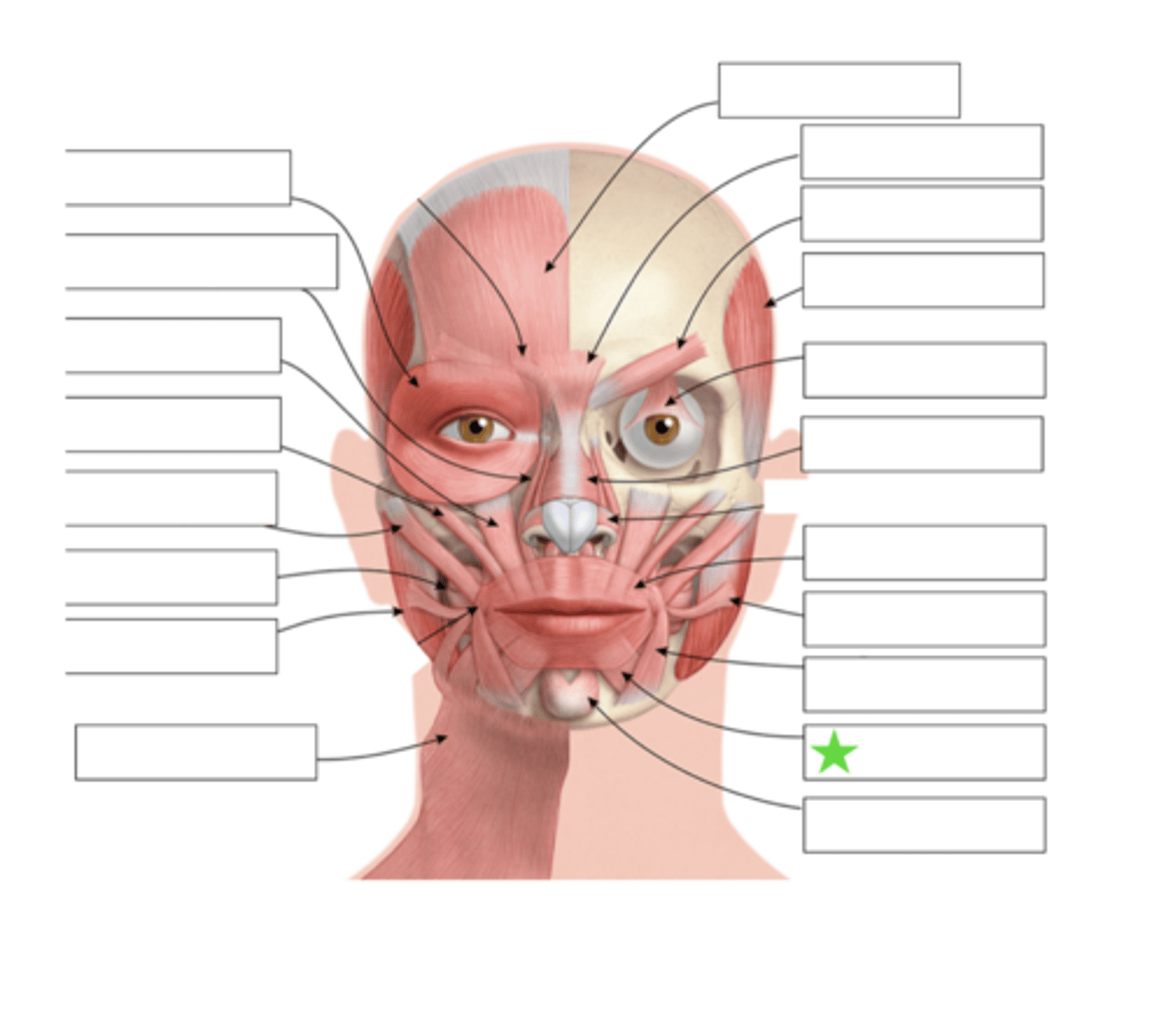
Mentalis
What is this?
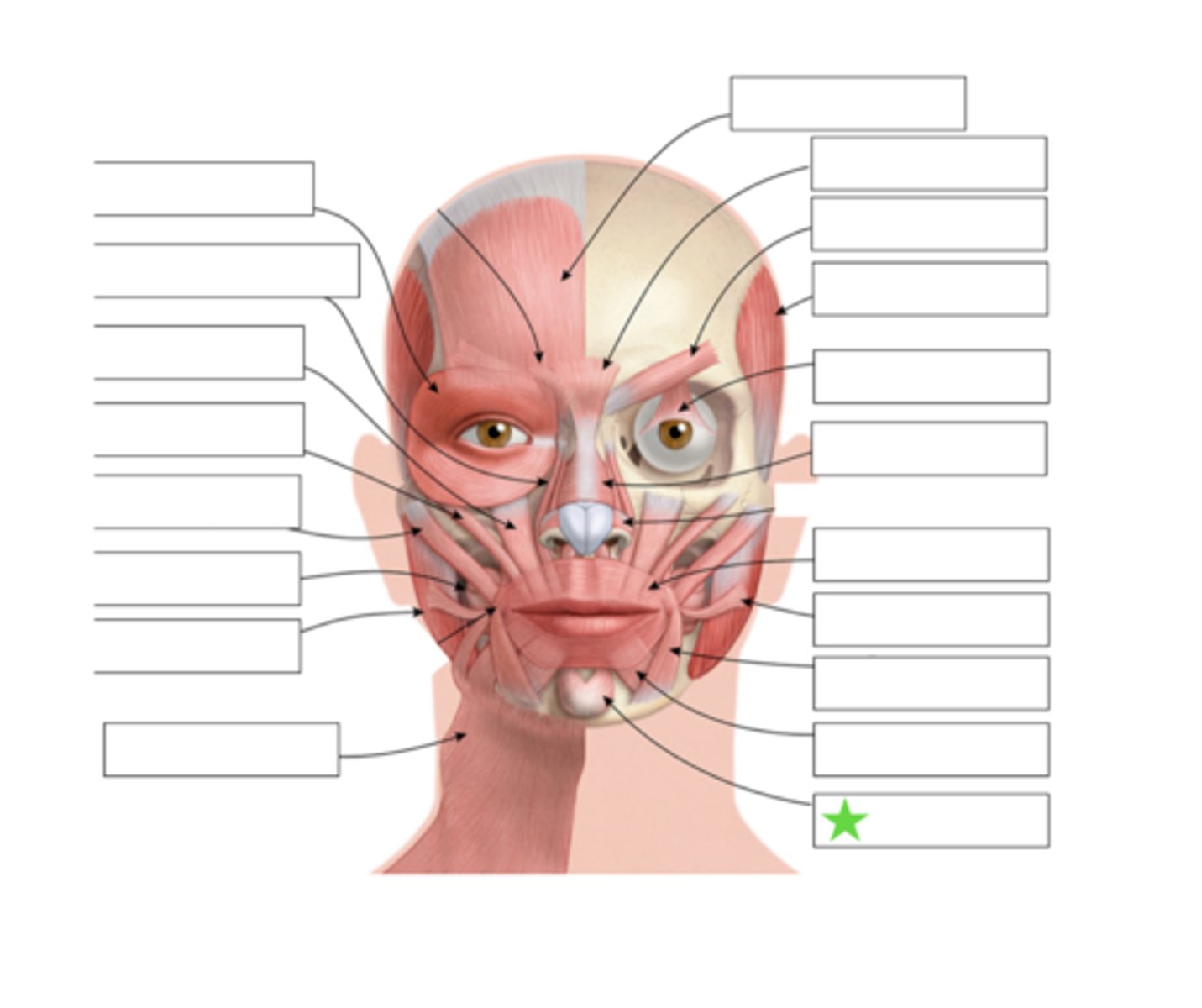
Orbicularis Oris
What is this?
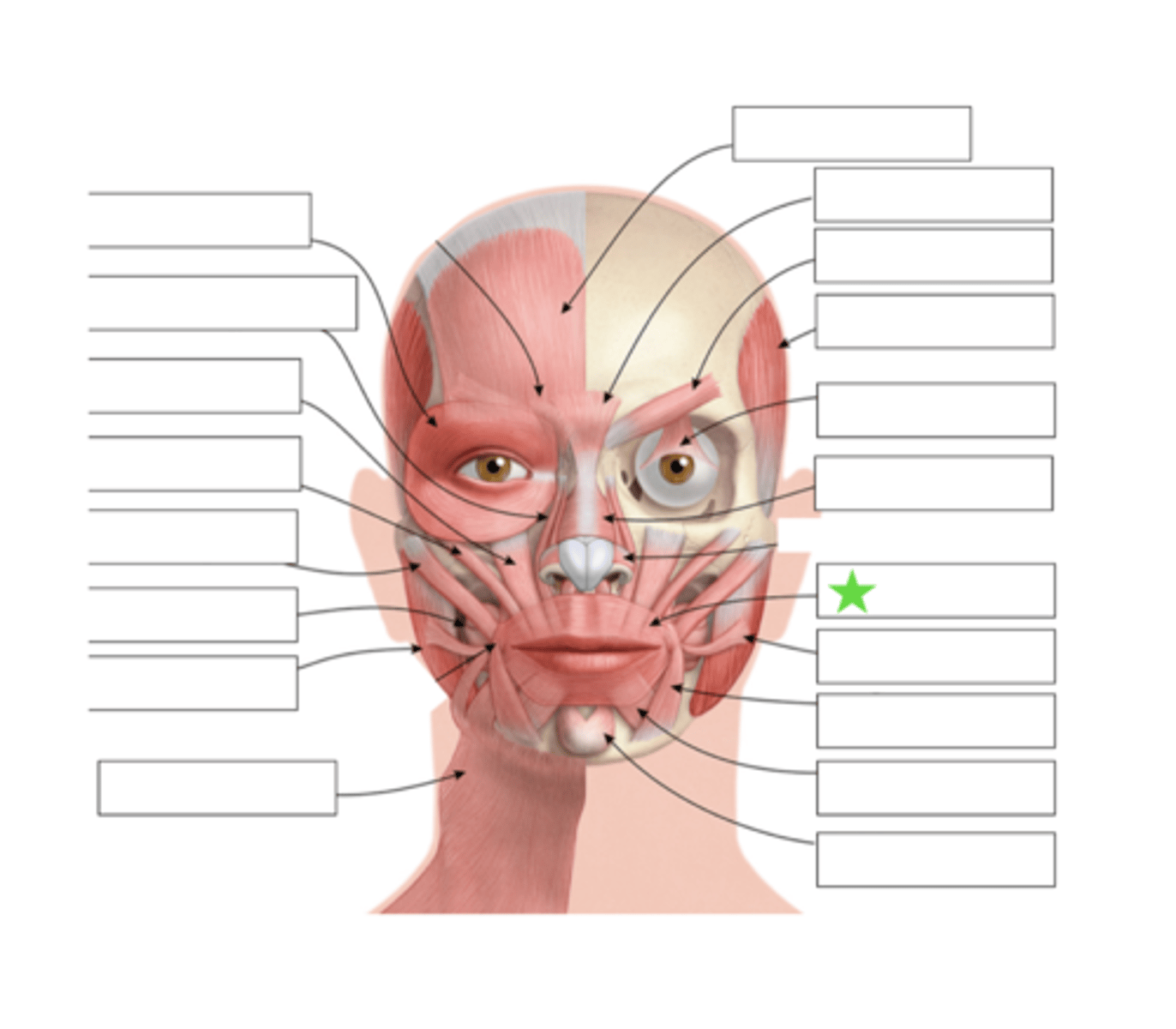
Levator Labii Superioris Alaque Nasi
What is this?
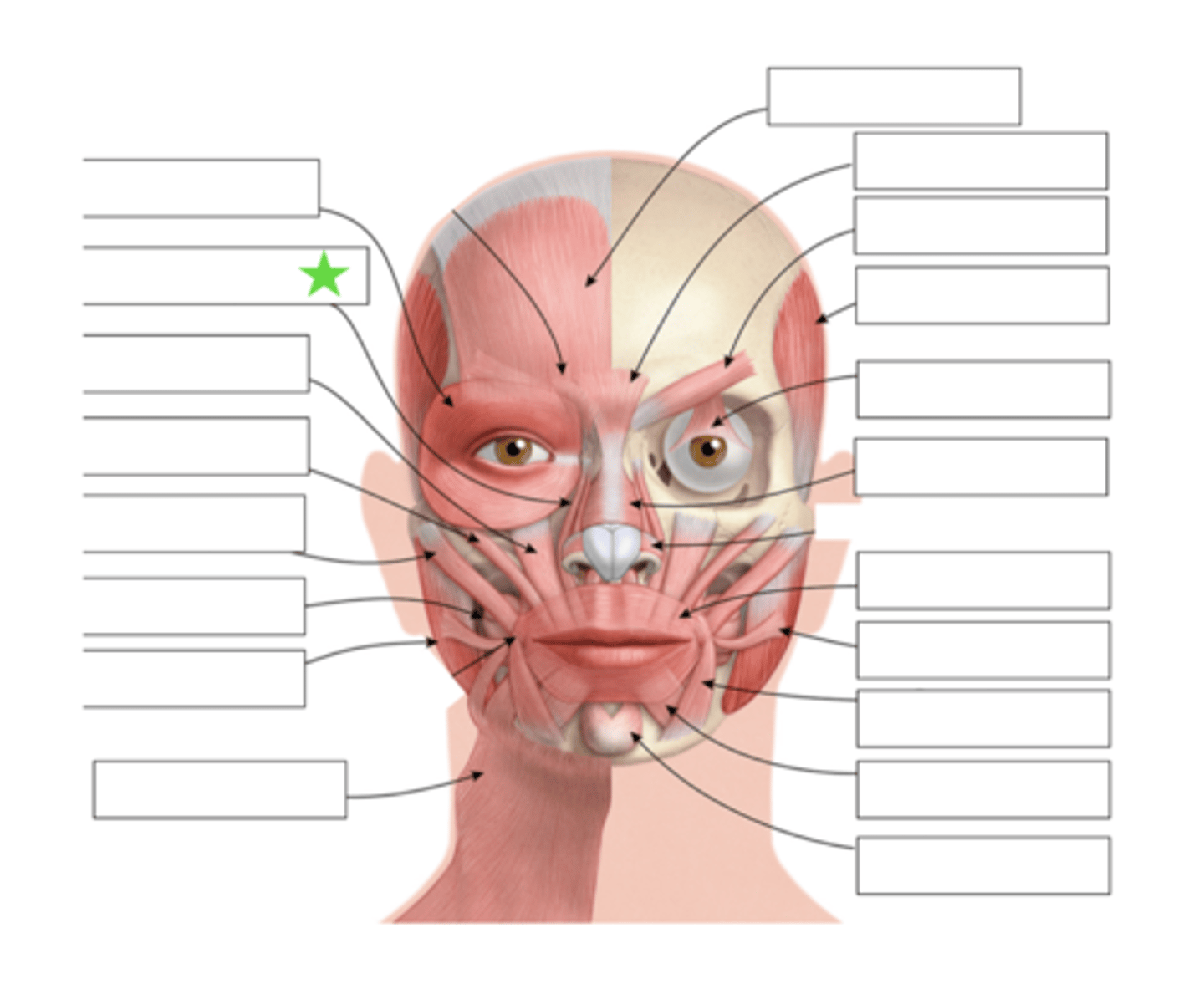
Levator Labii Superioris
What is this?
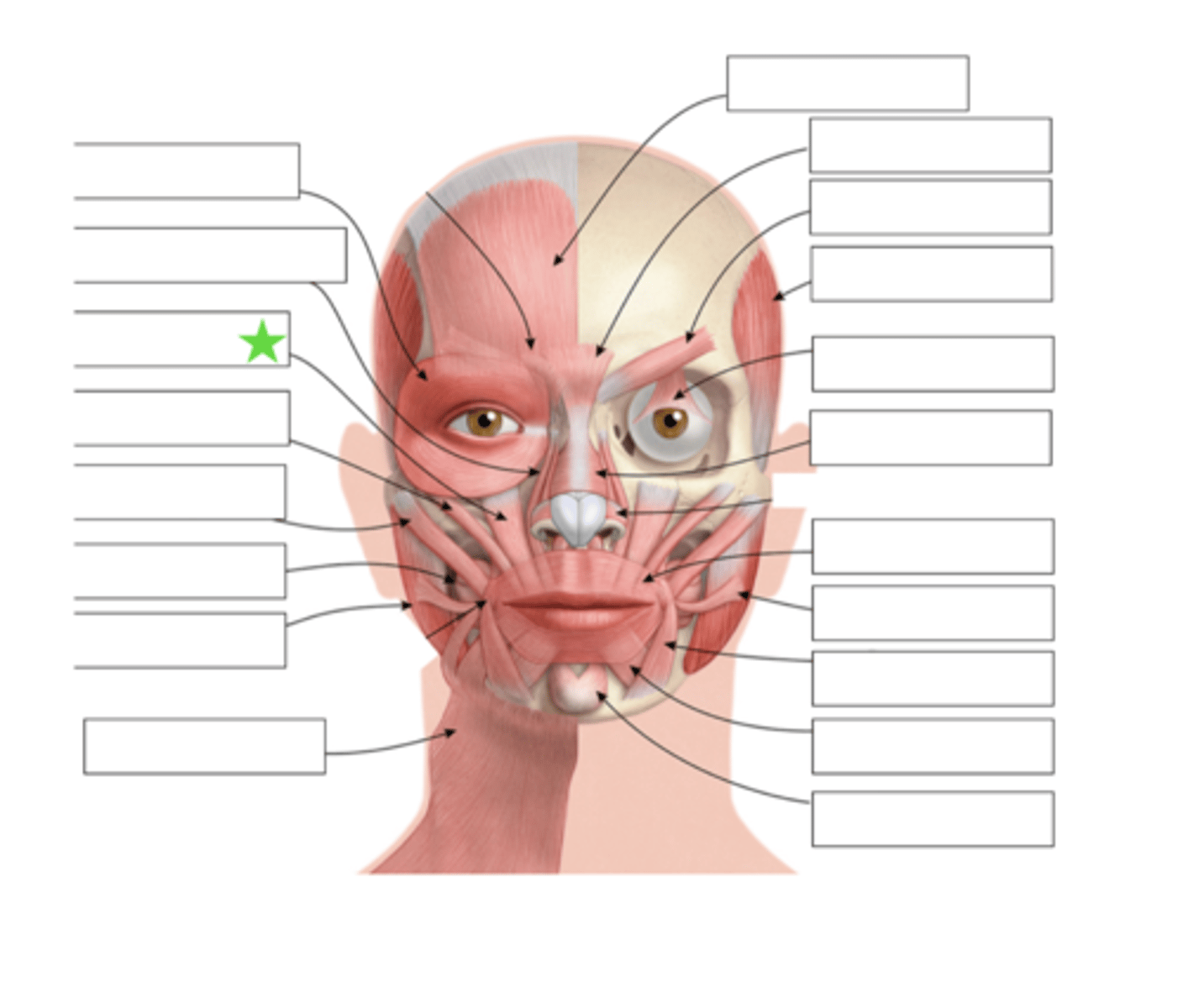
Zygomatic Minor
What is this?
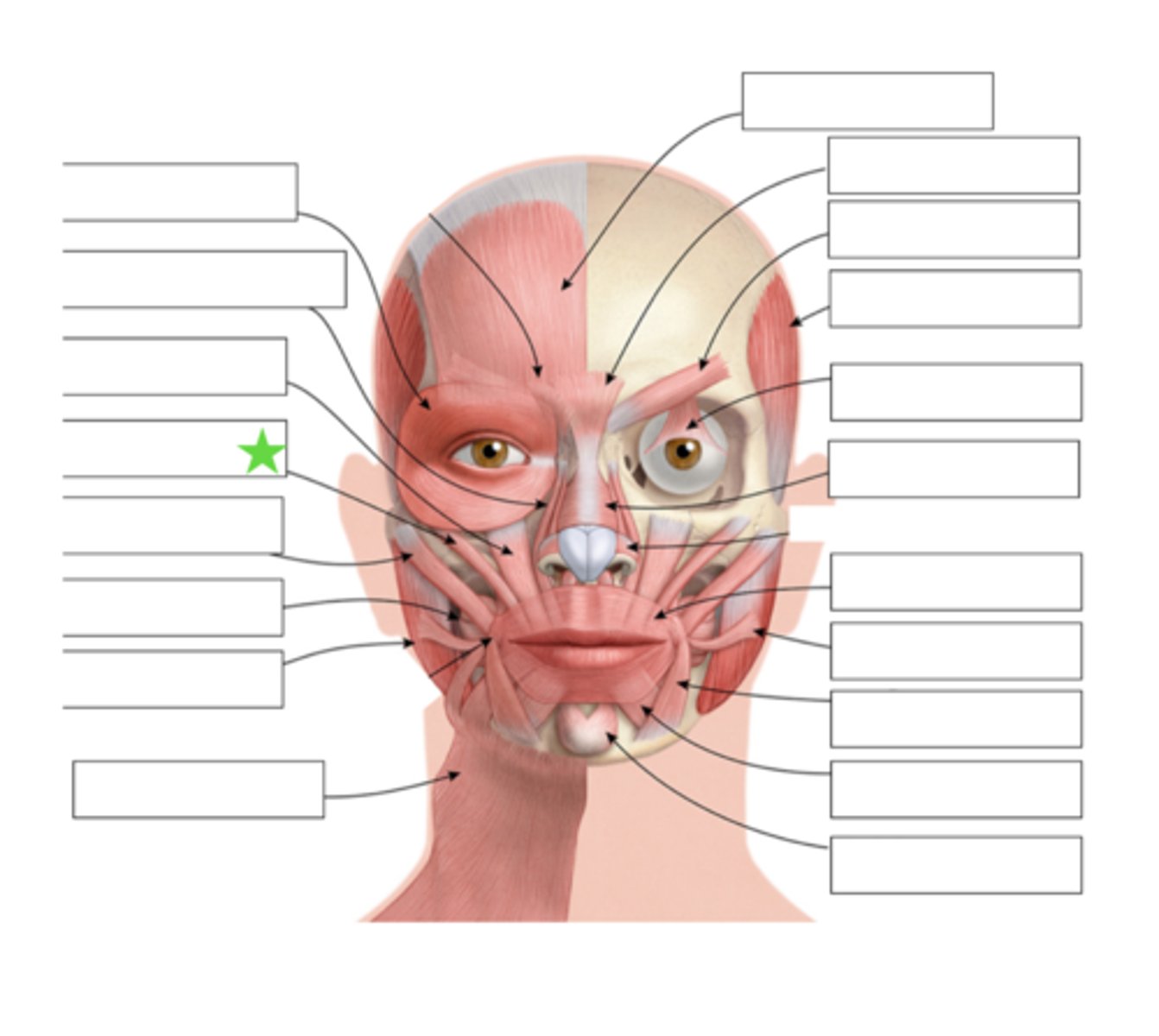
Zygomatic Major
What is this?
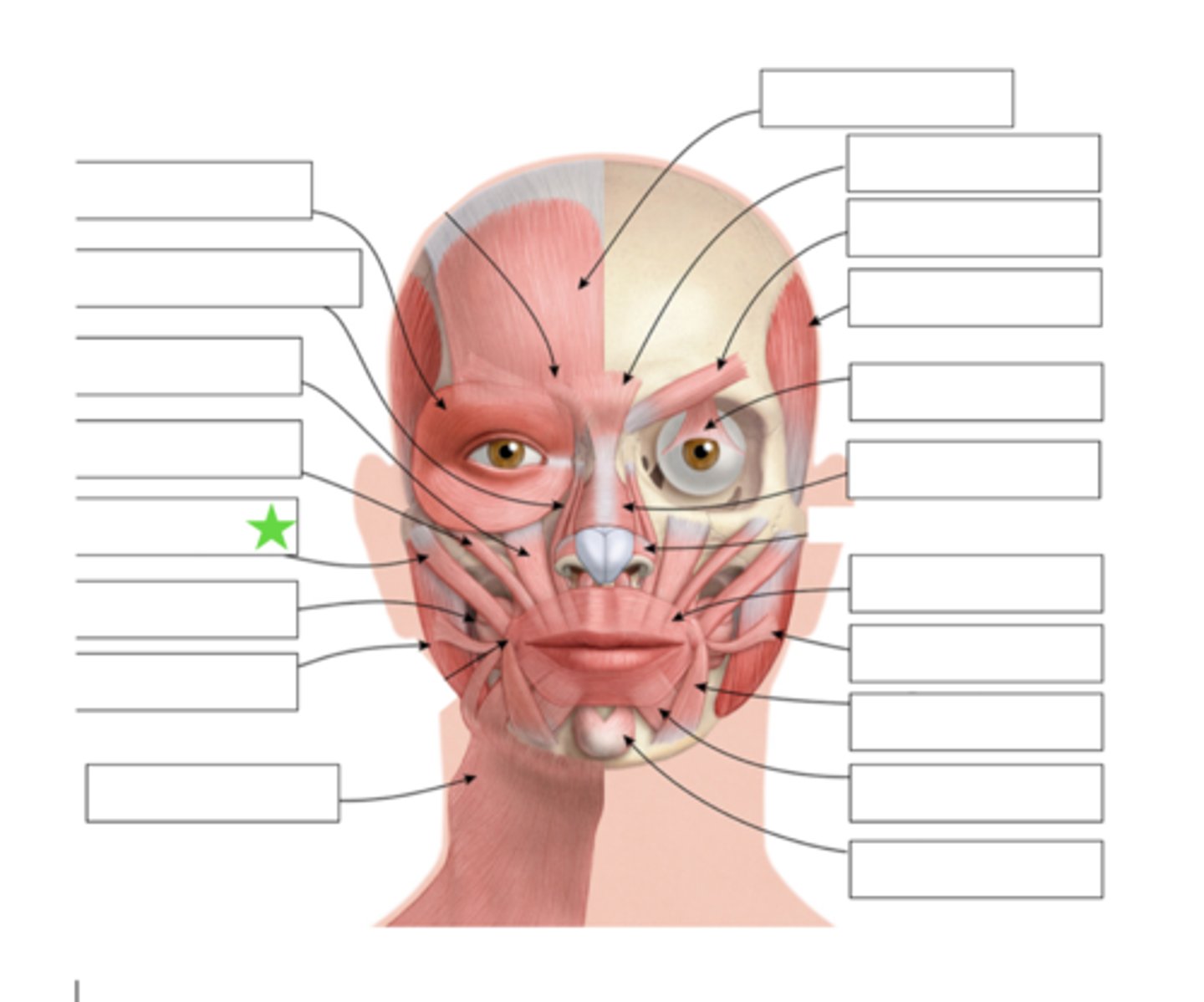
Buccinator
What is this?
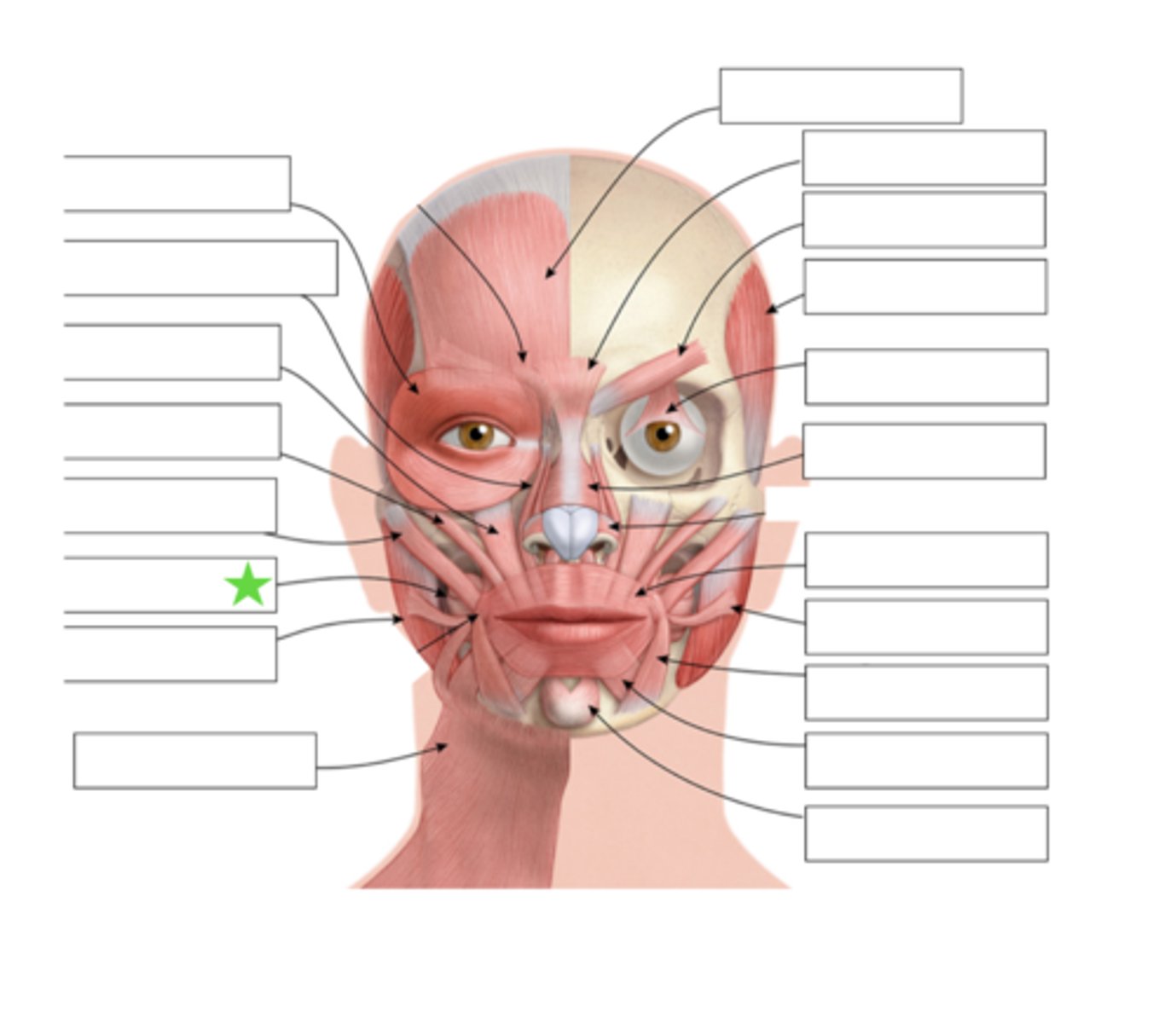
Masseter
What is this?
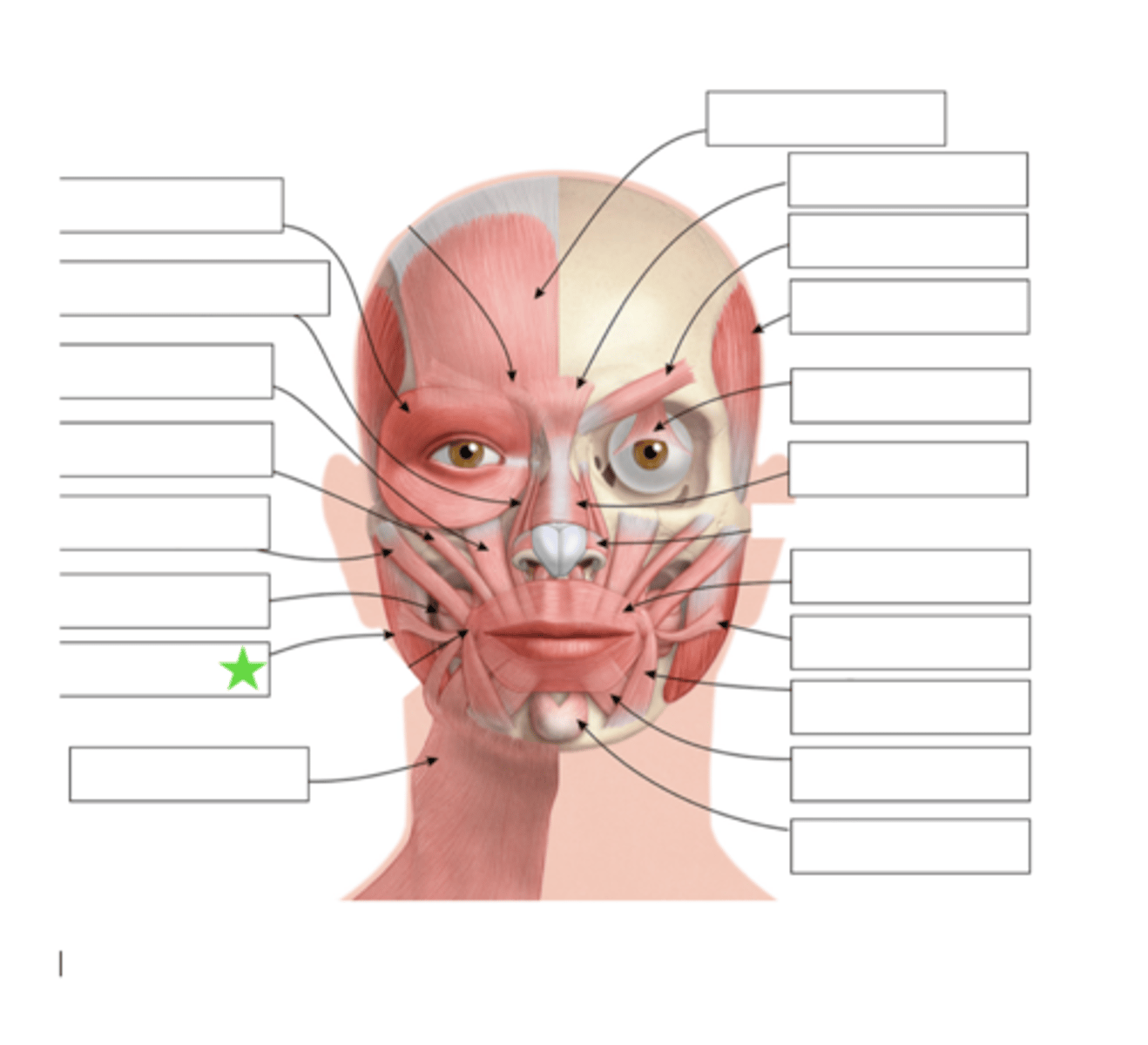
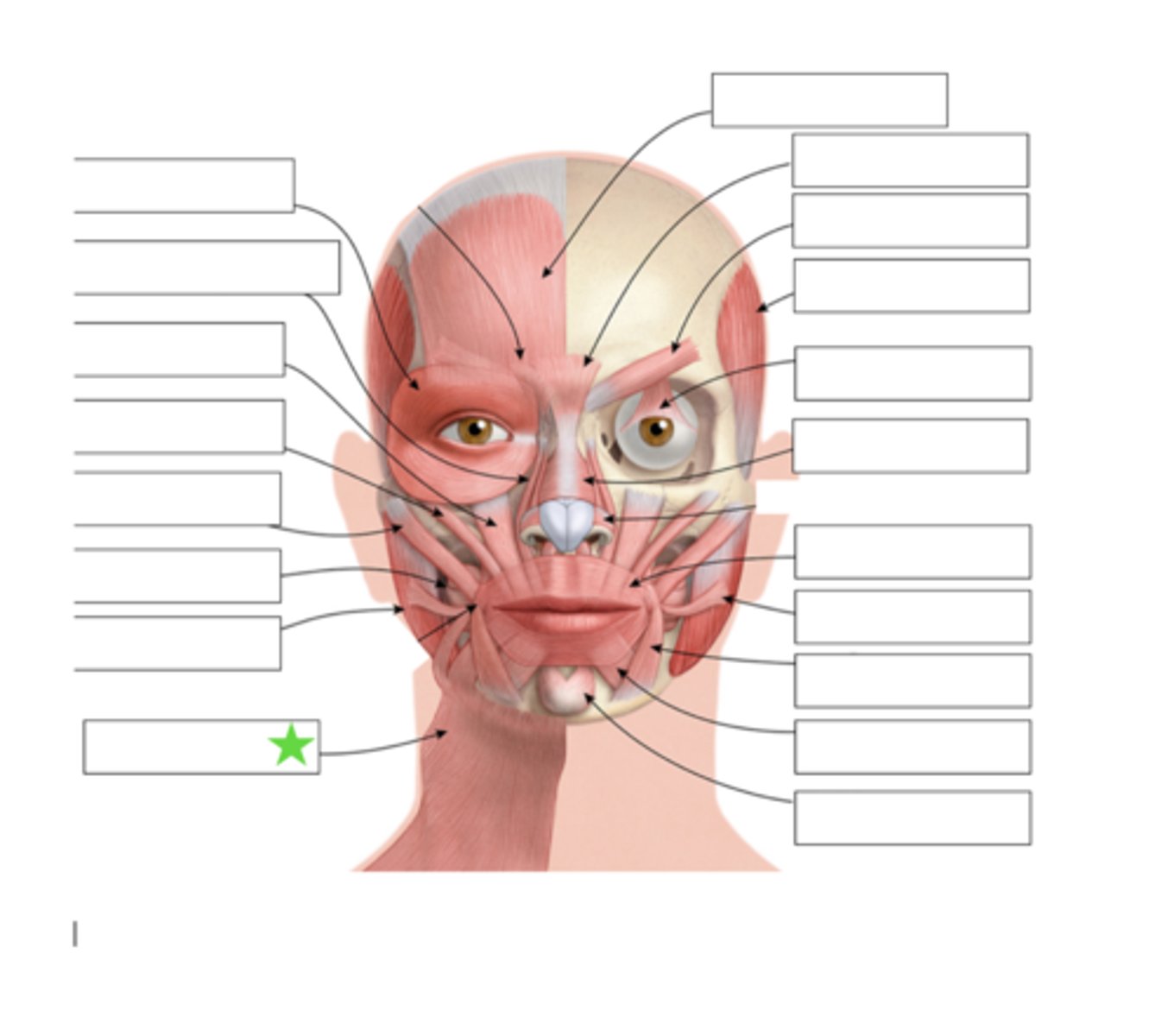
Platysma
What is this?
Parietal
What is this?
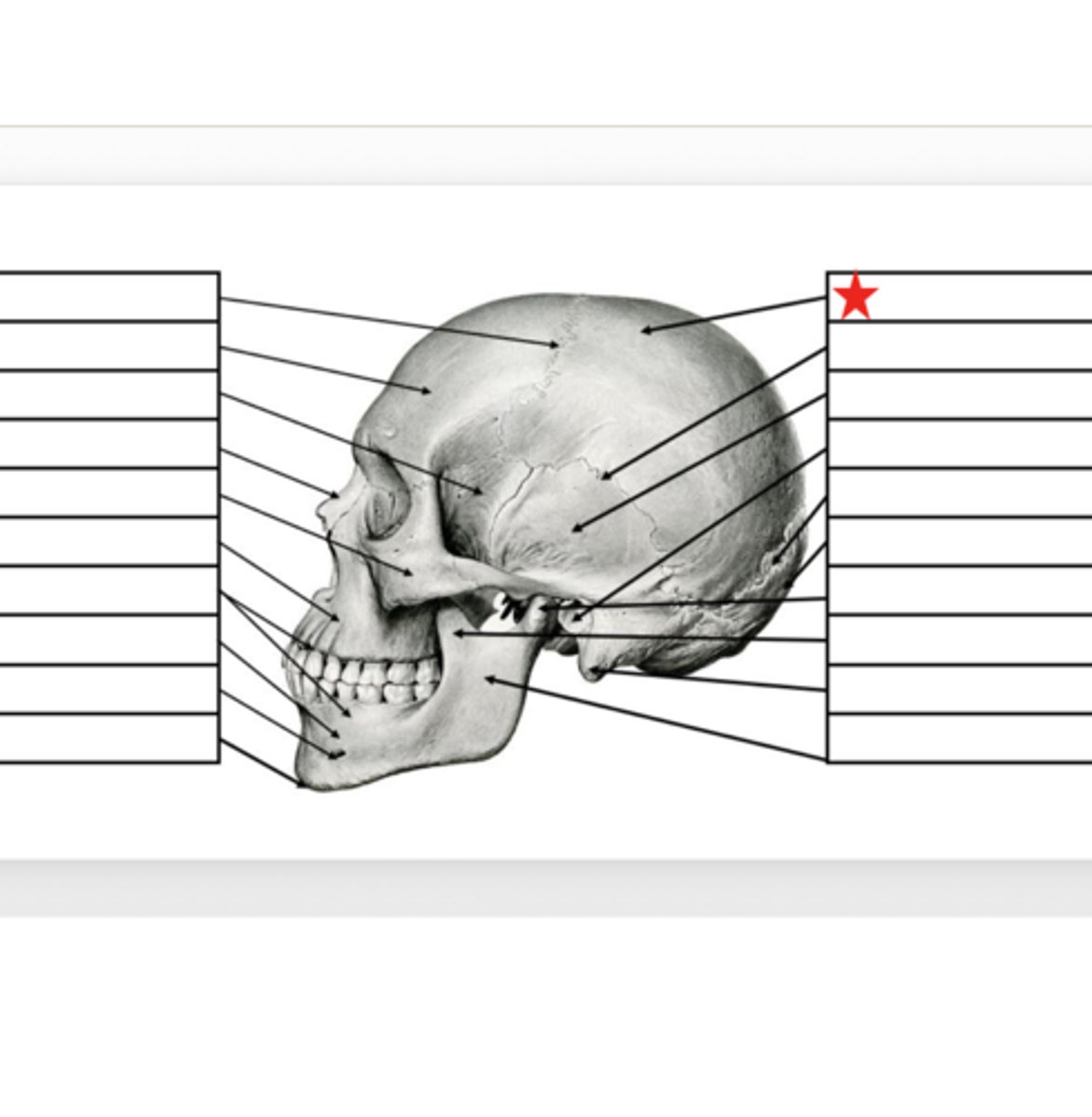
Squamosal Suture
What is this?
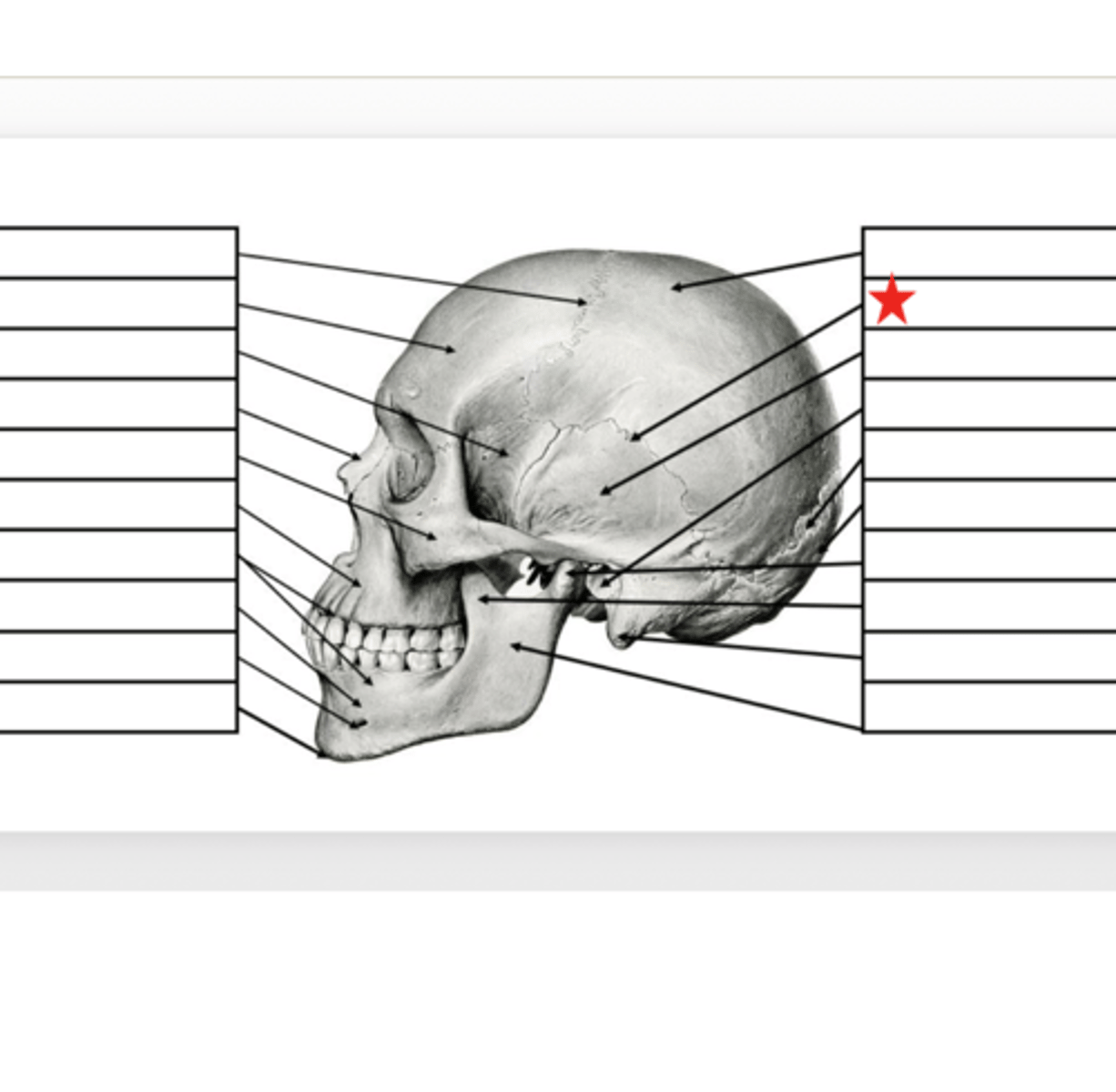
Temporal
What is this?
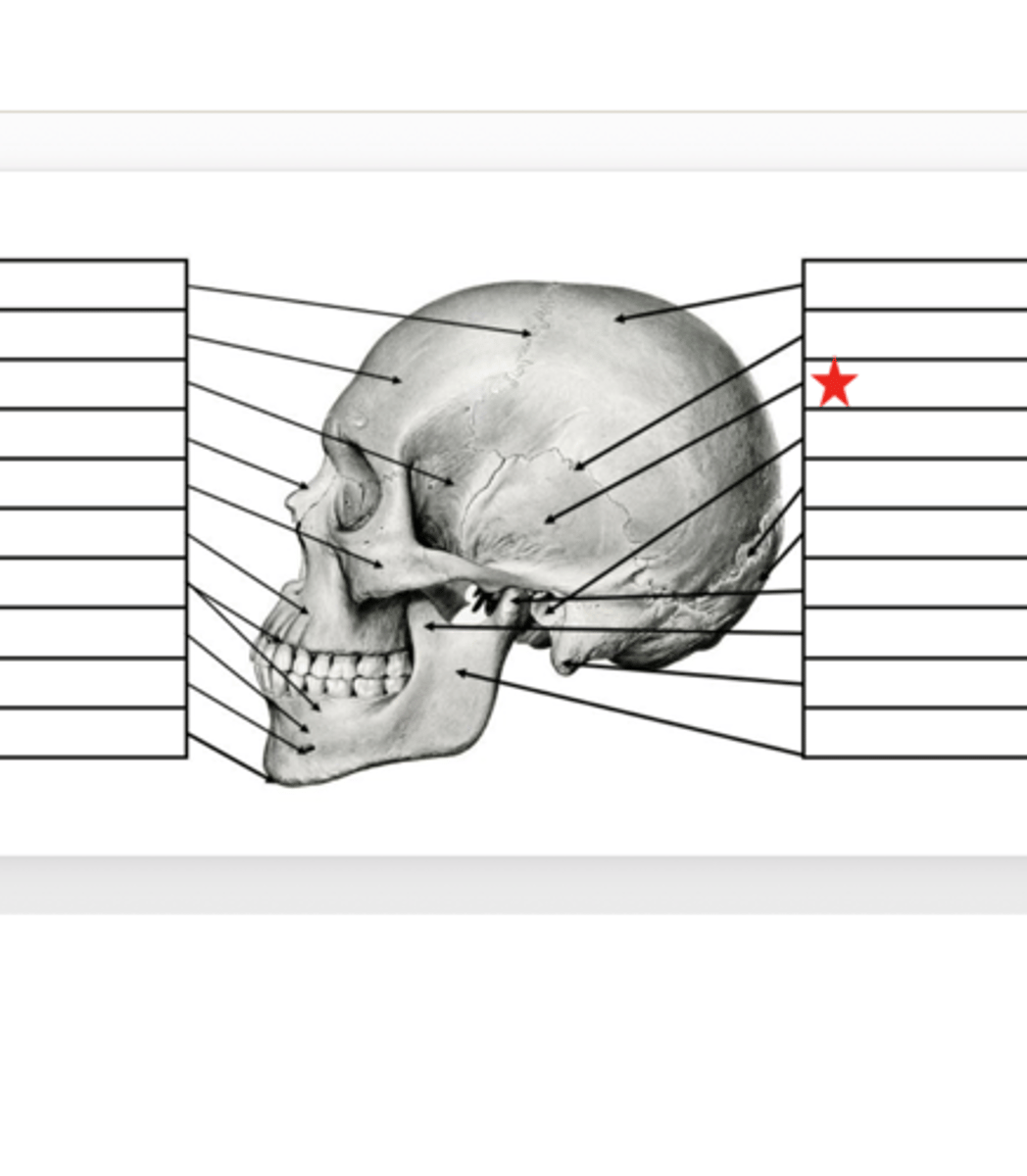
External Auditory Meatus
What is this?
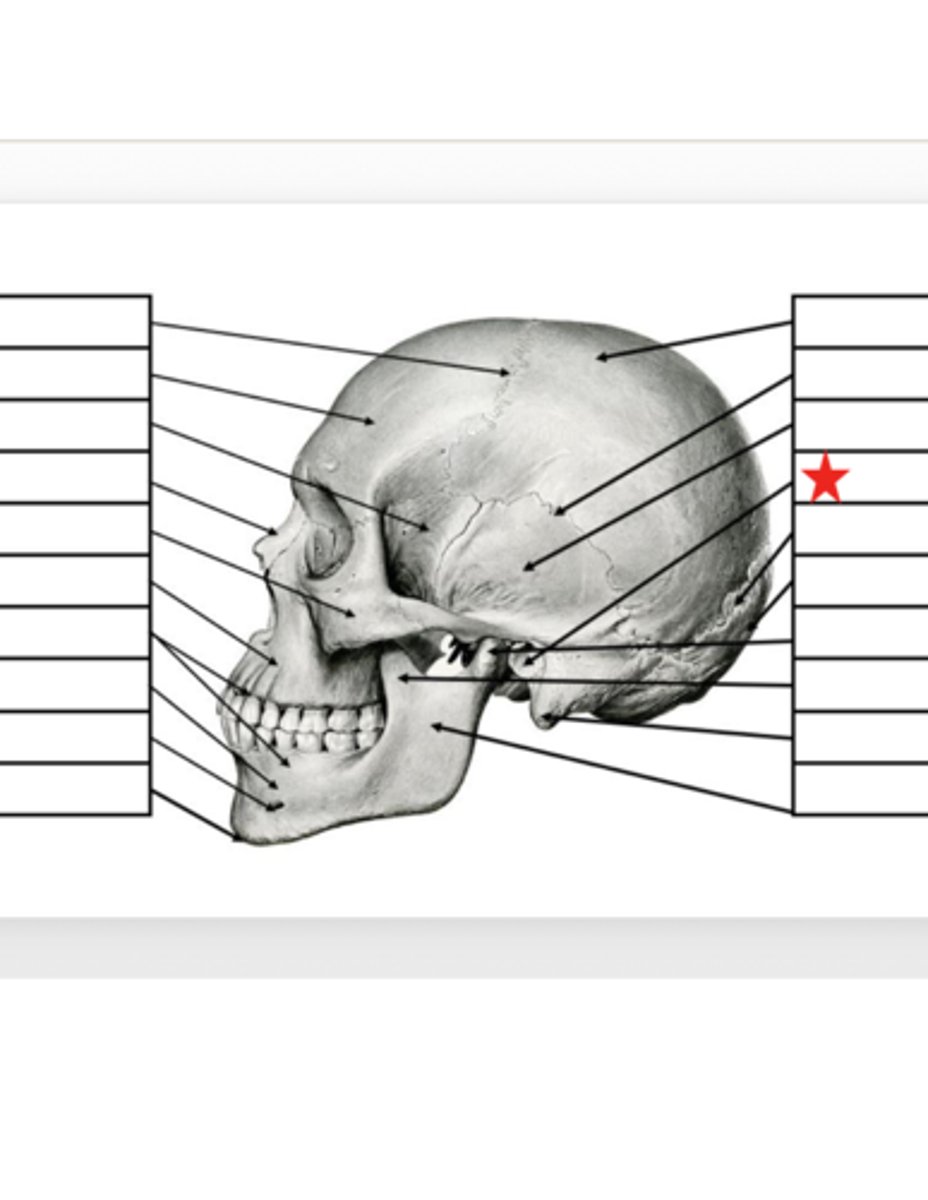
Lambdiodal Suture
What is this?
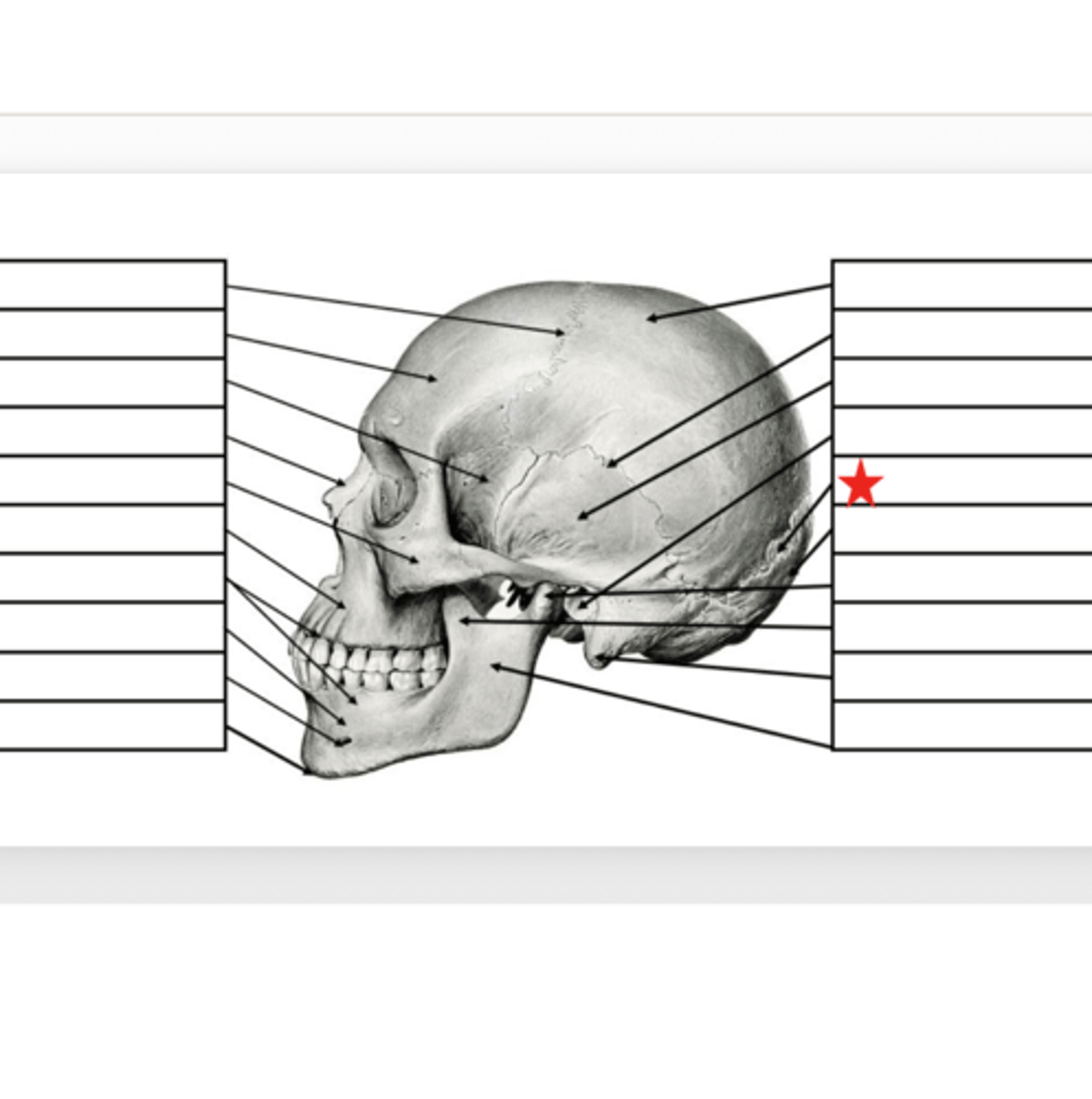
Occipital
What is this?
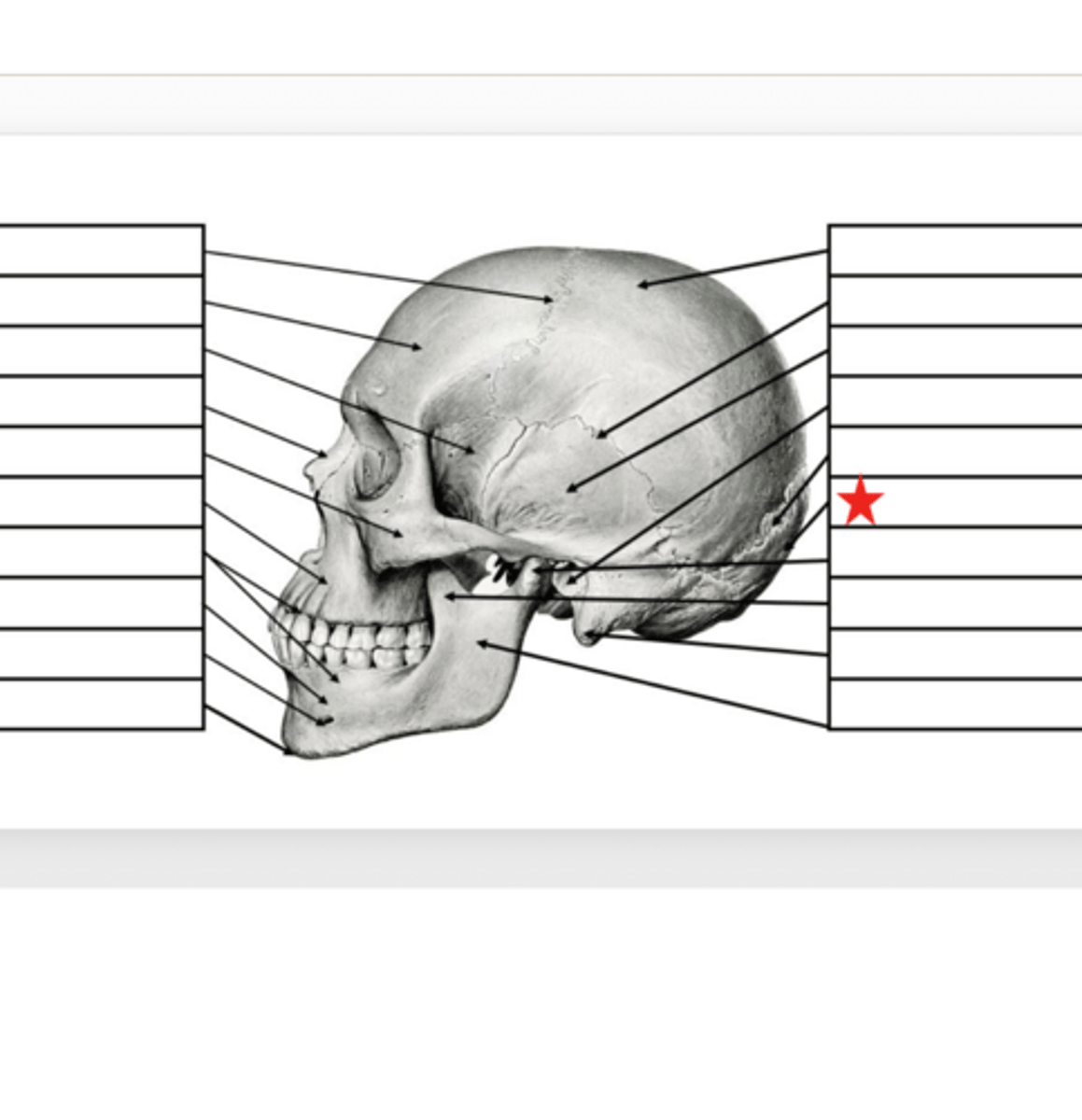
Mandibular Condyle
What is this?
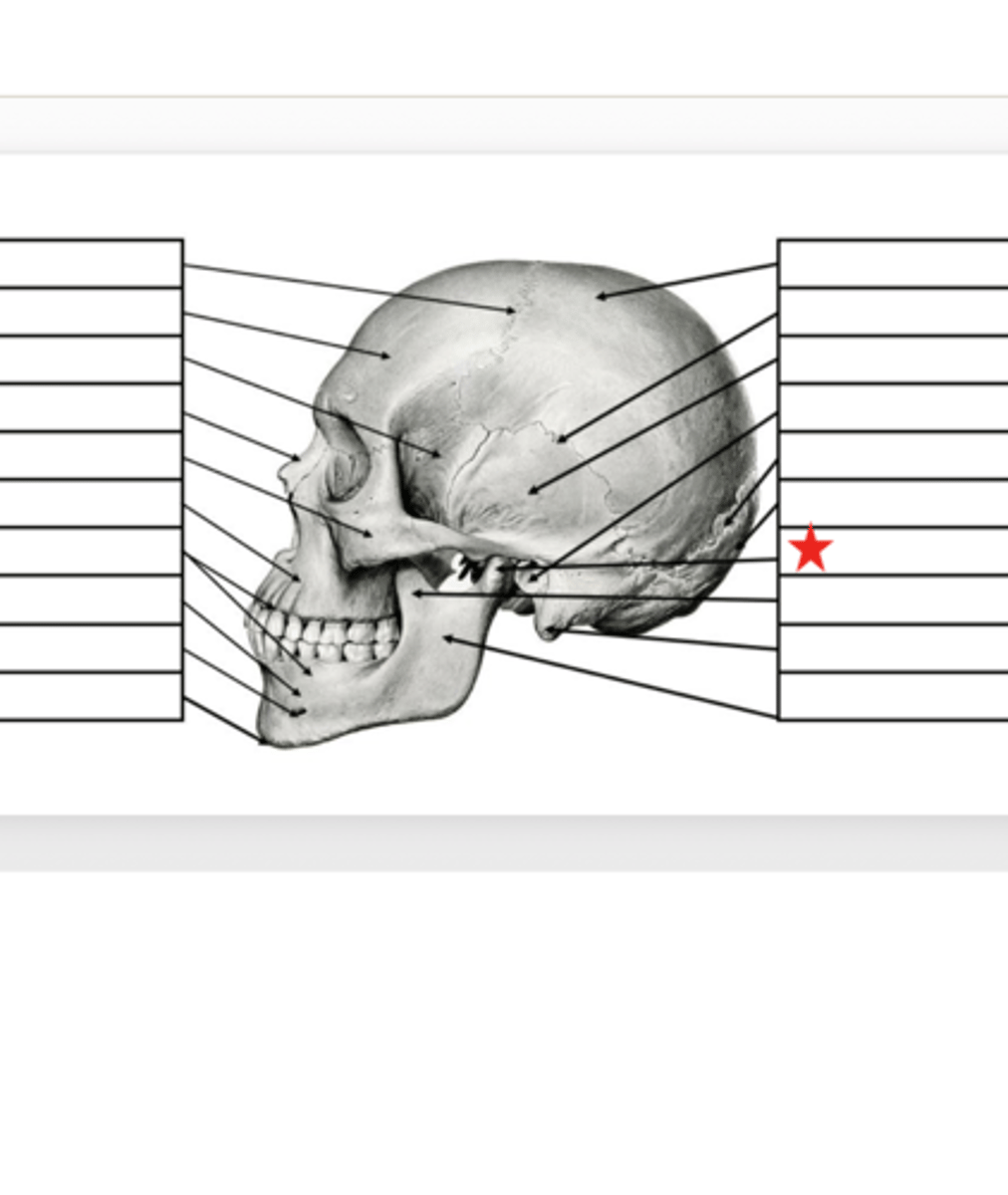
Coronoid Process
What is this?
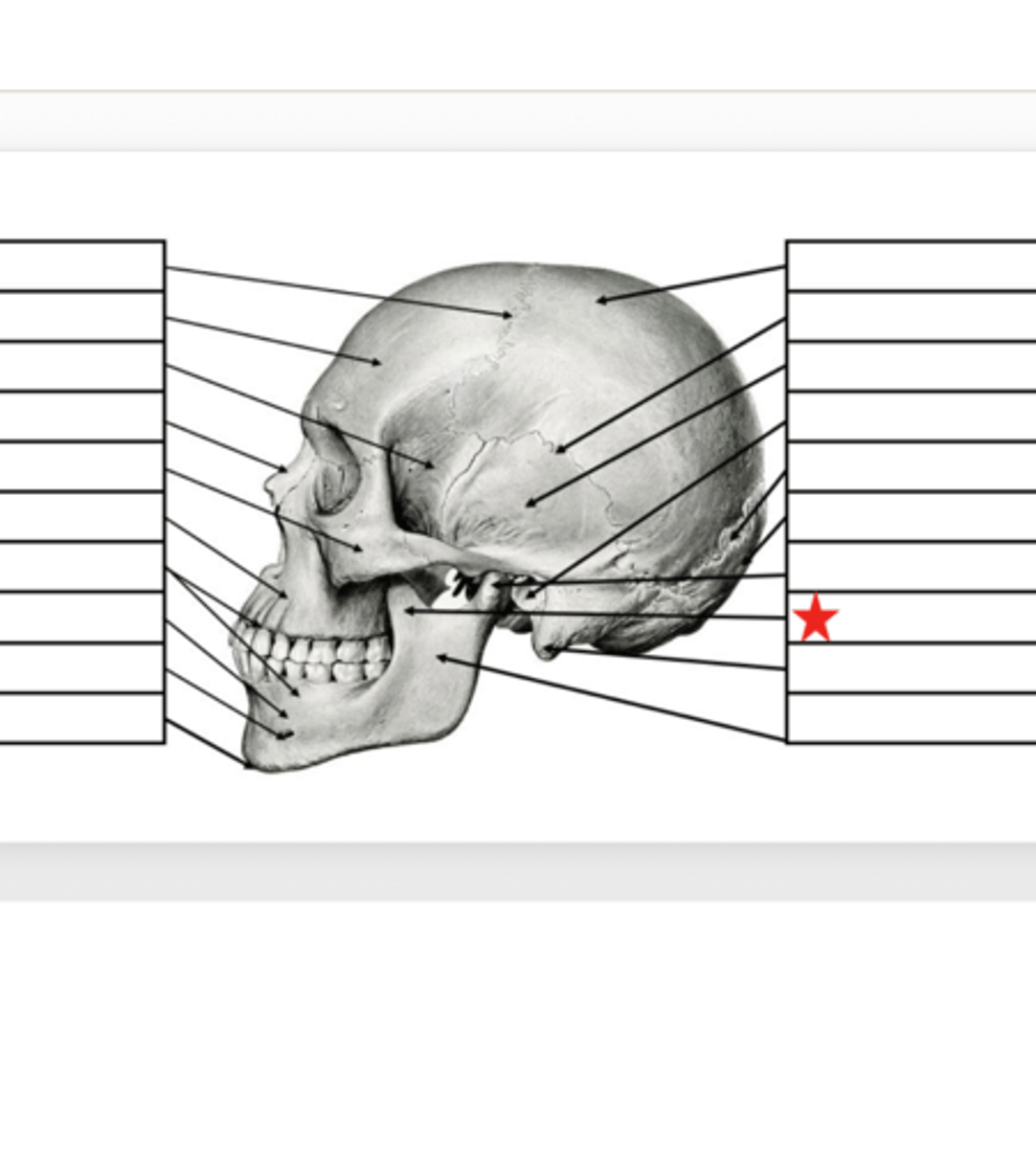
Mastoid Process
What is this?
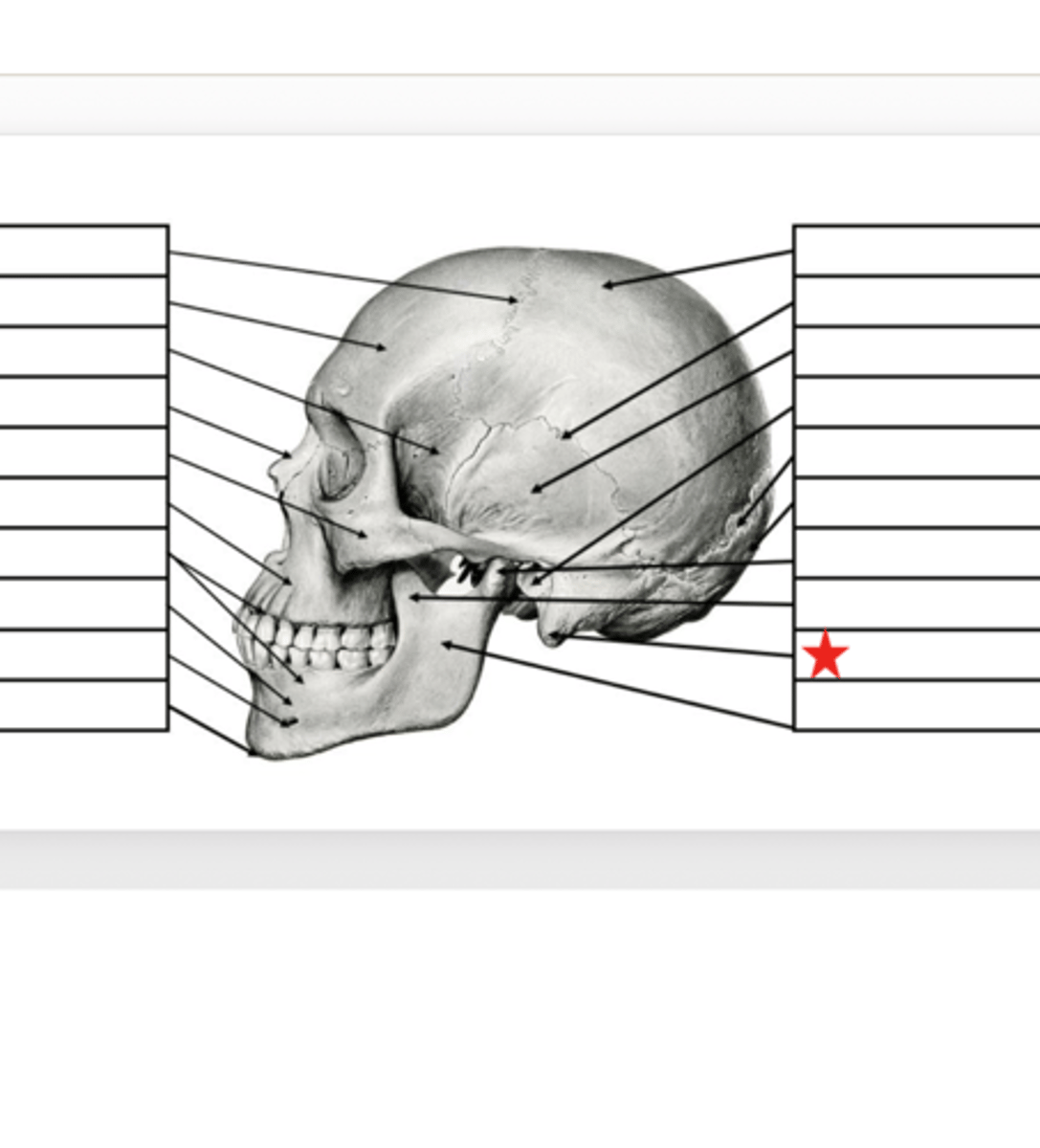
Mandibular Ramus
What is this?
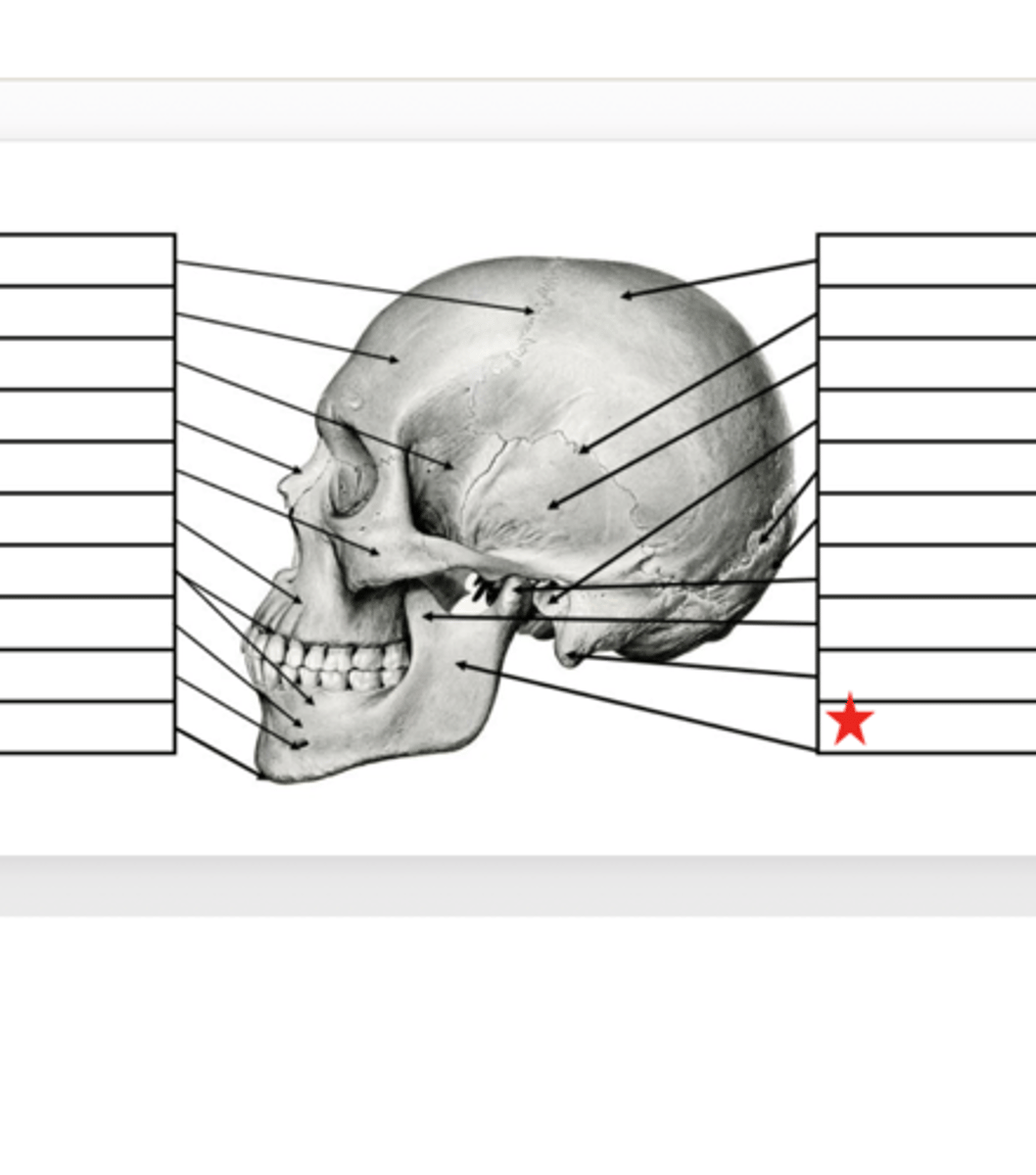
Mental Eminence
What is this?
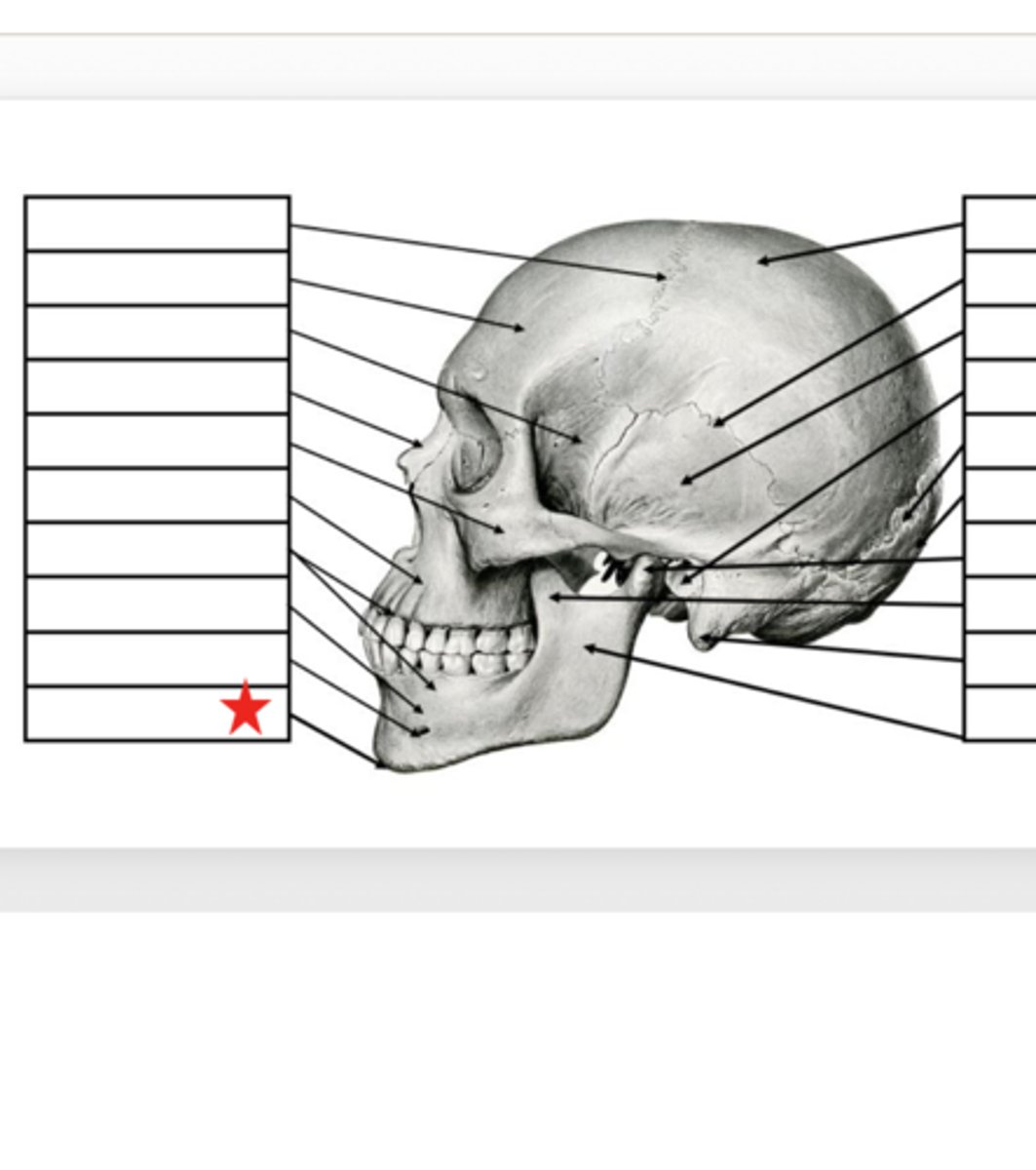
Mental Foramen
What is this?
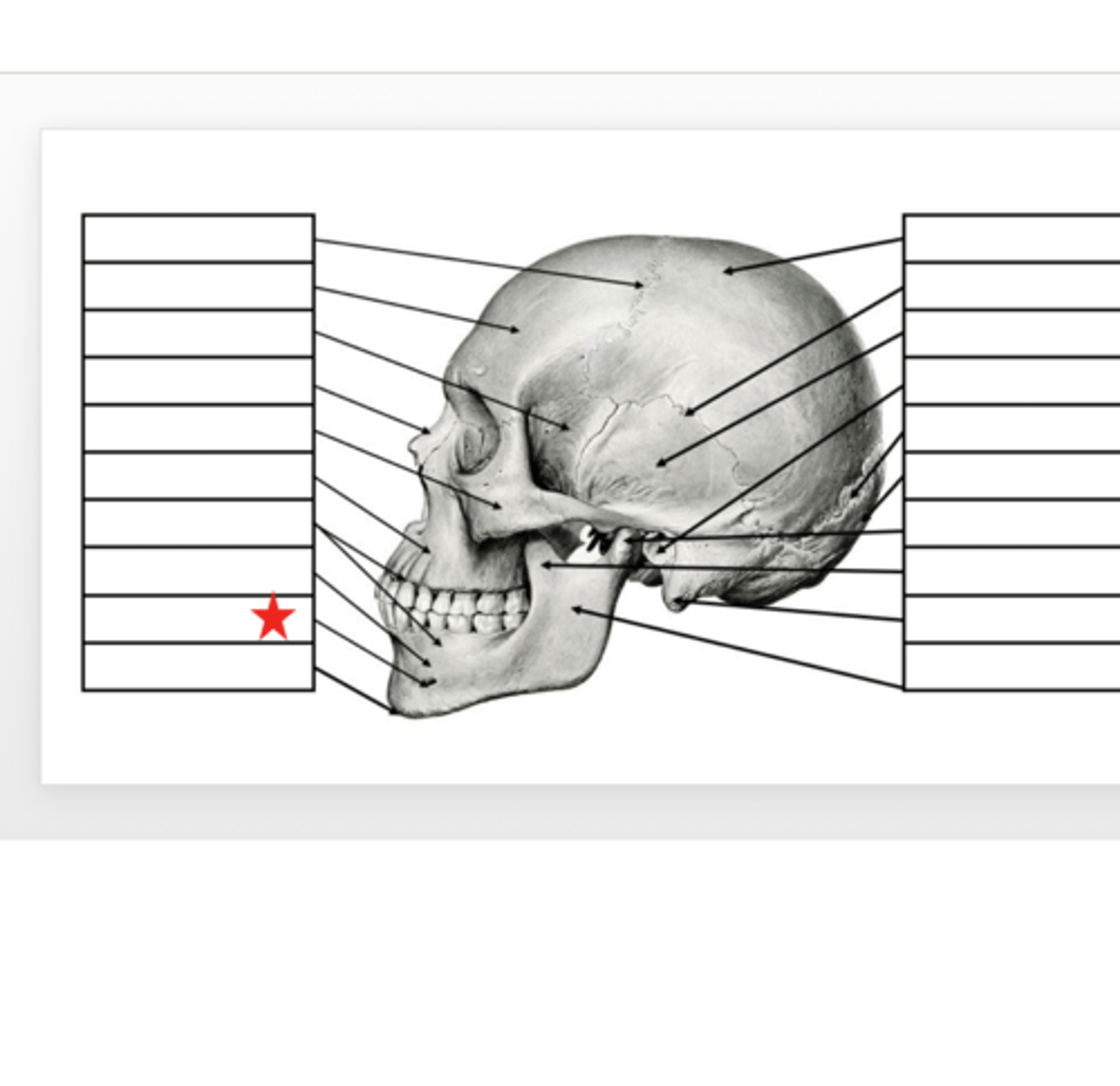
Mandible
What is this?
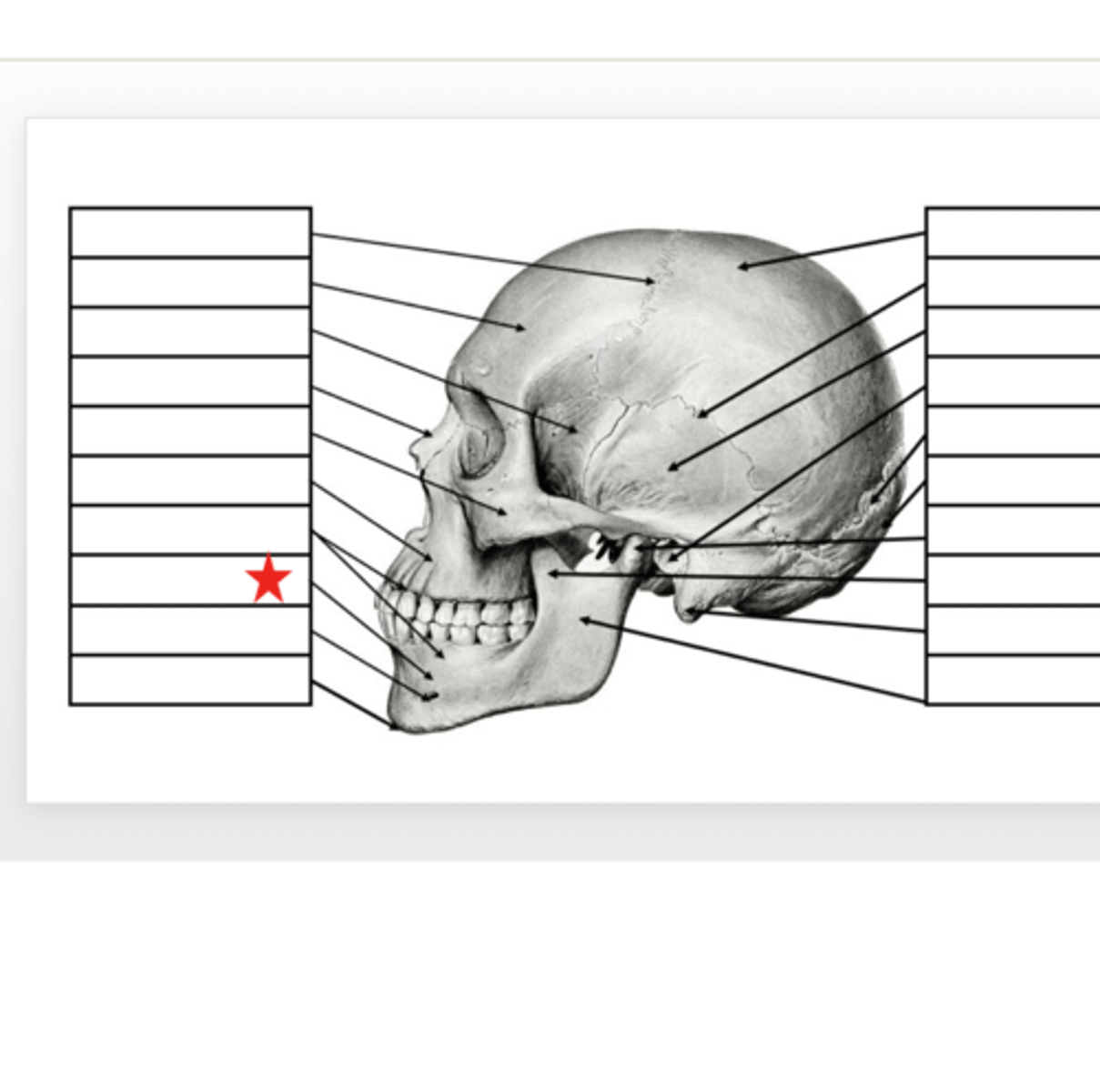
Alveolar Margins
What is this?
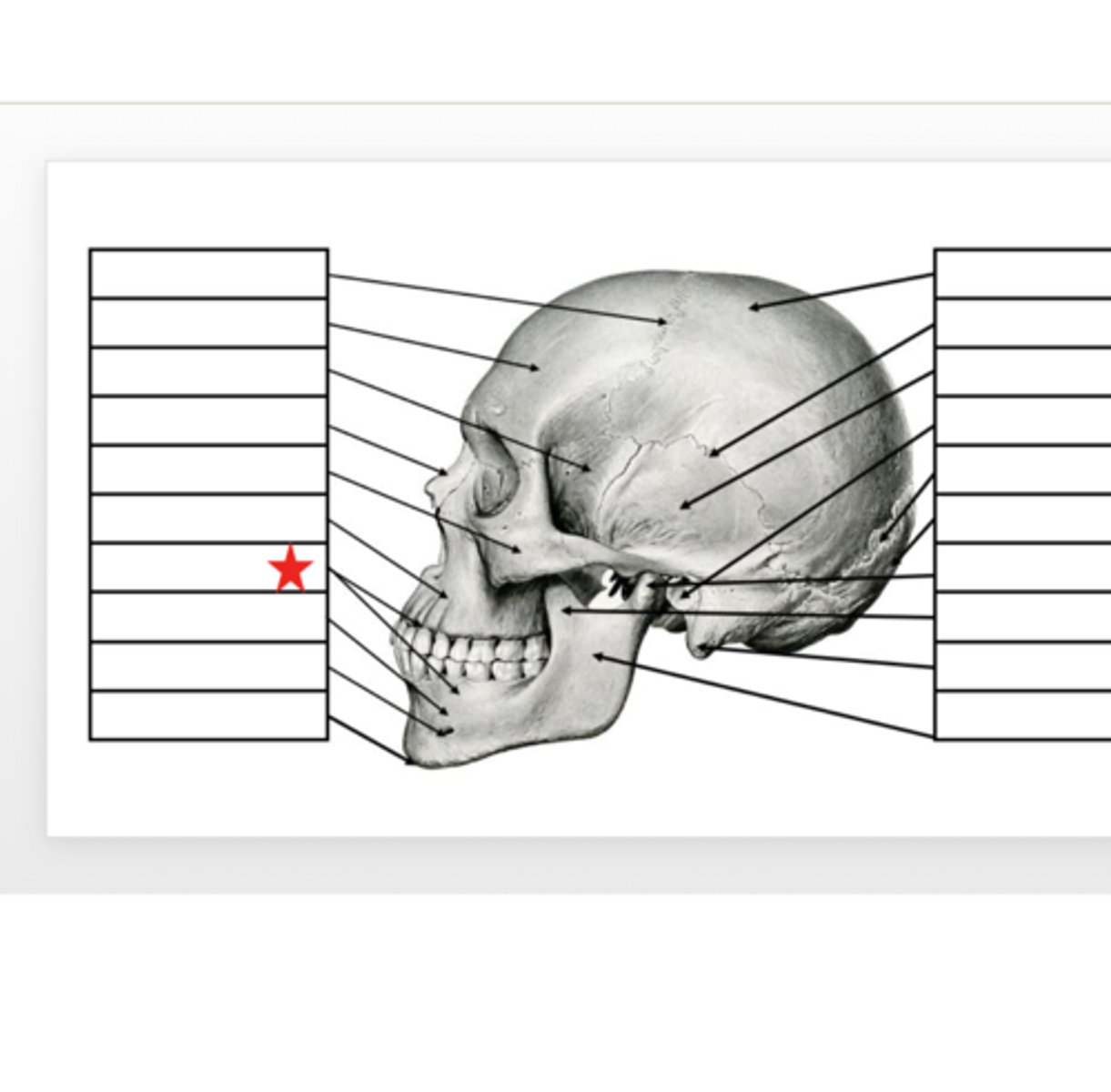
Maxilla
What is this?
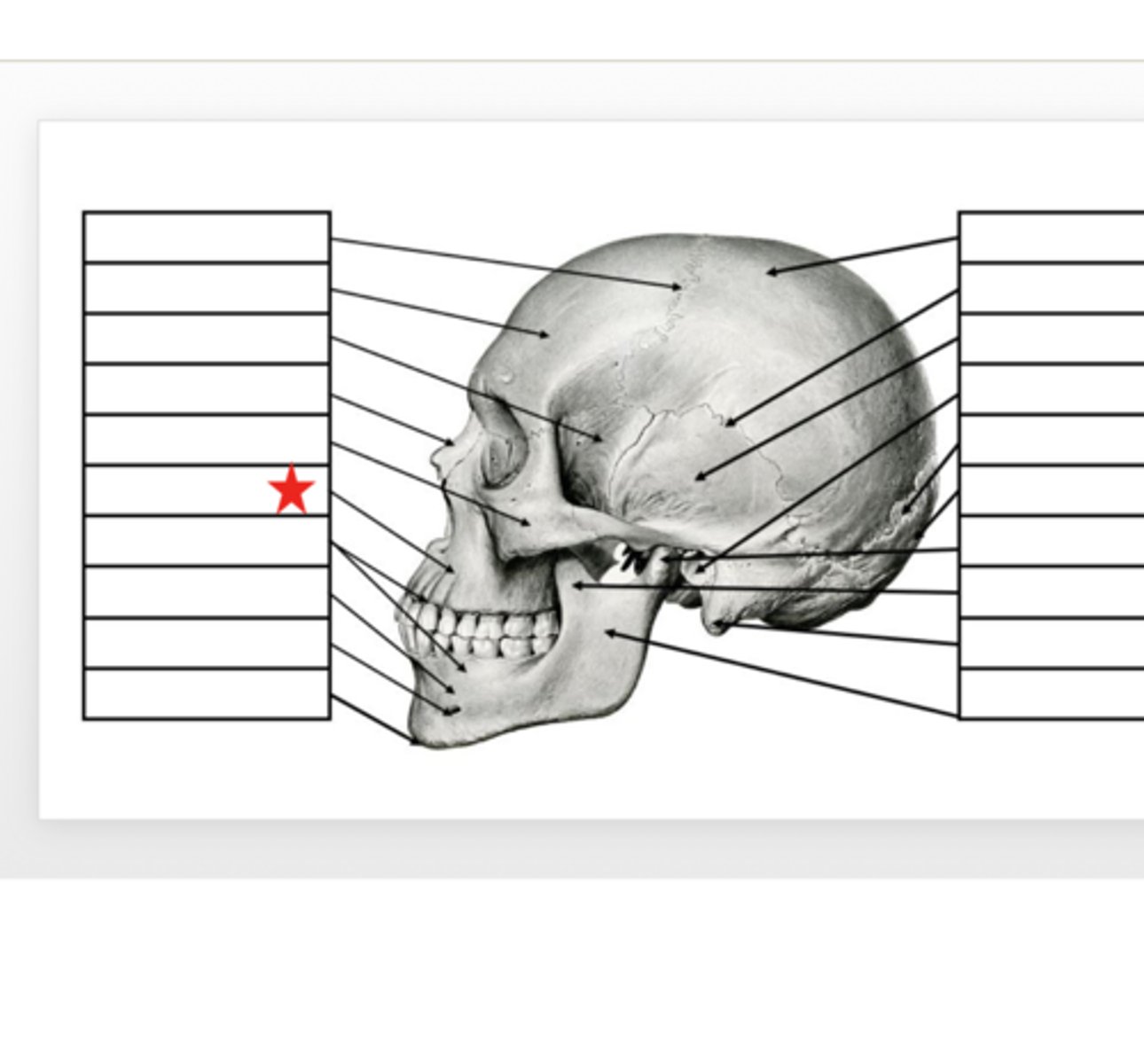
Zygomatic
What is this?
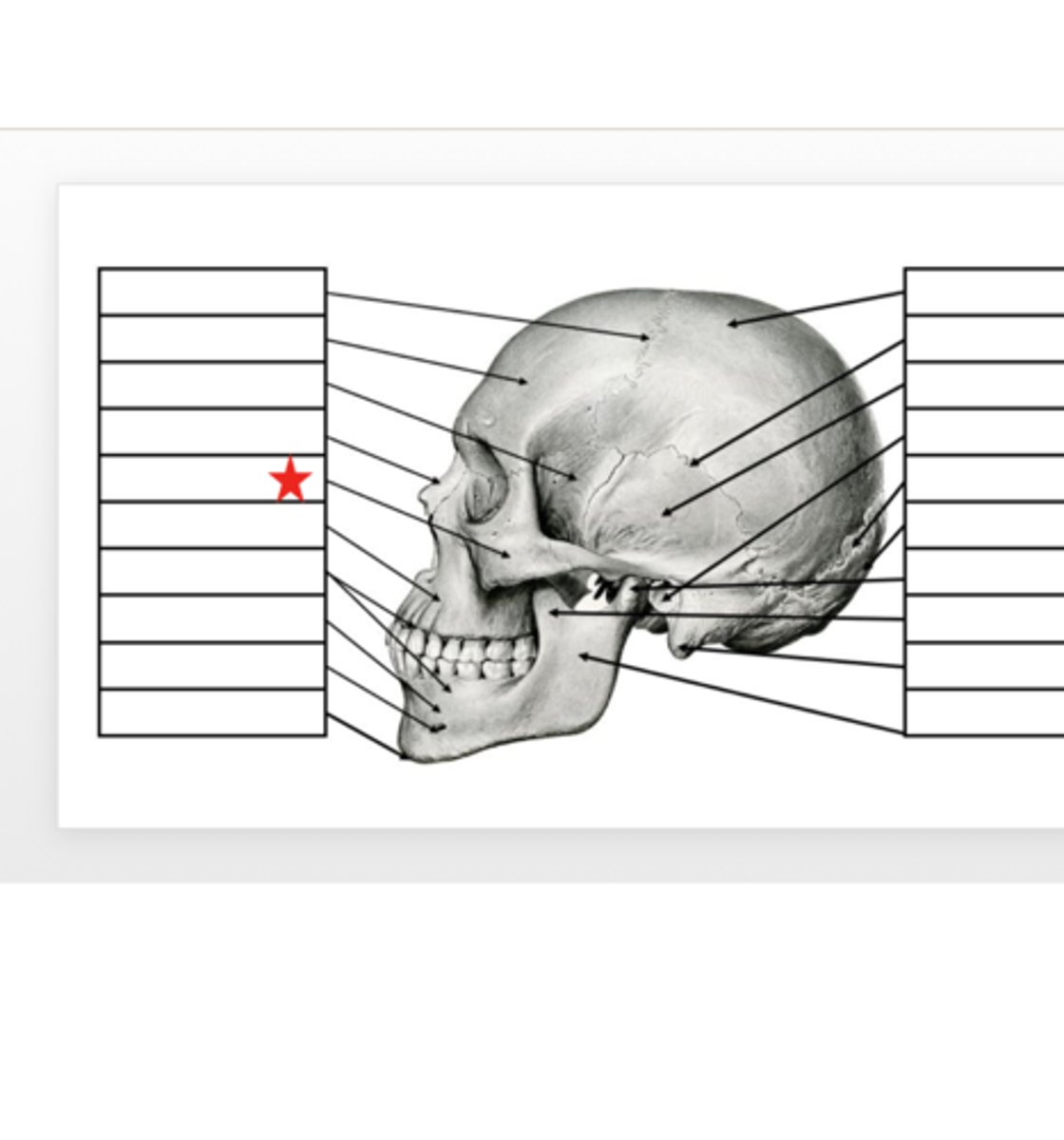
Nasal
What is this?
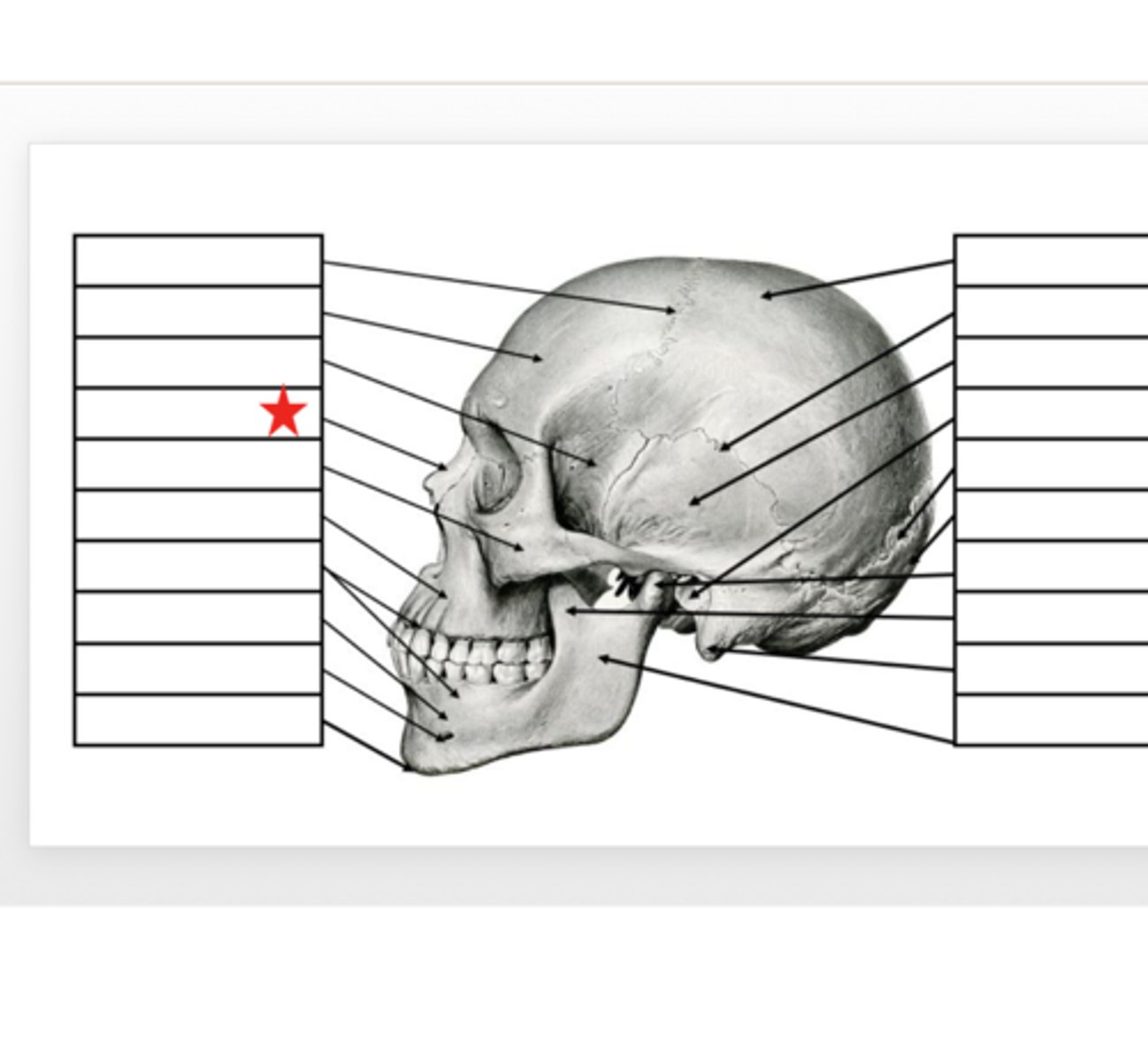
Sphenoid
What is this?
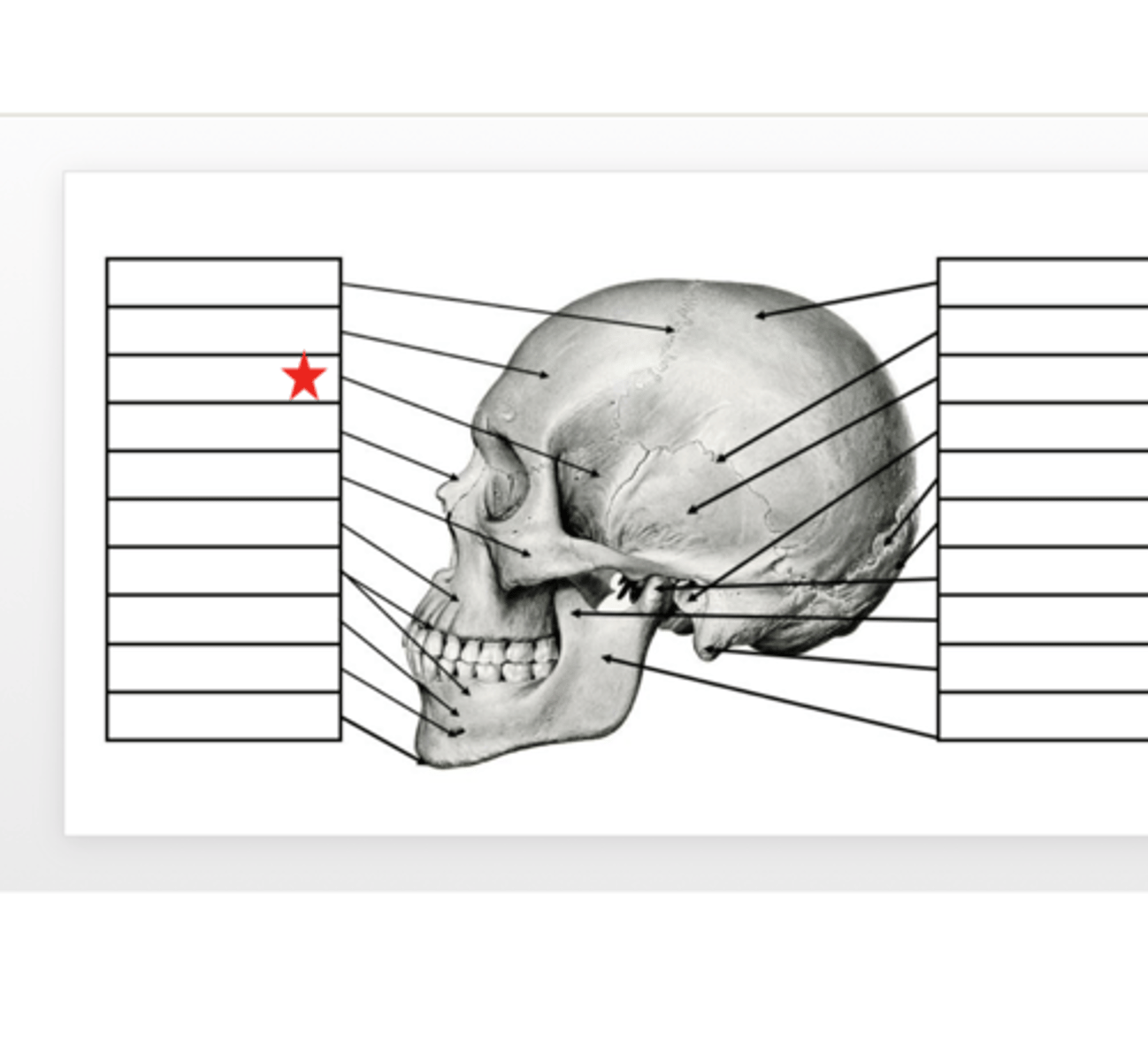
Frontal
What is this?
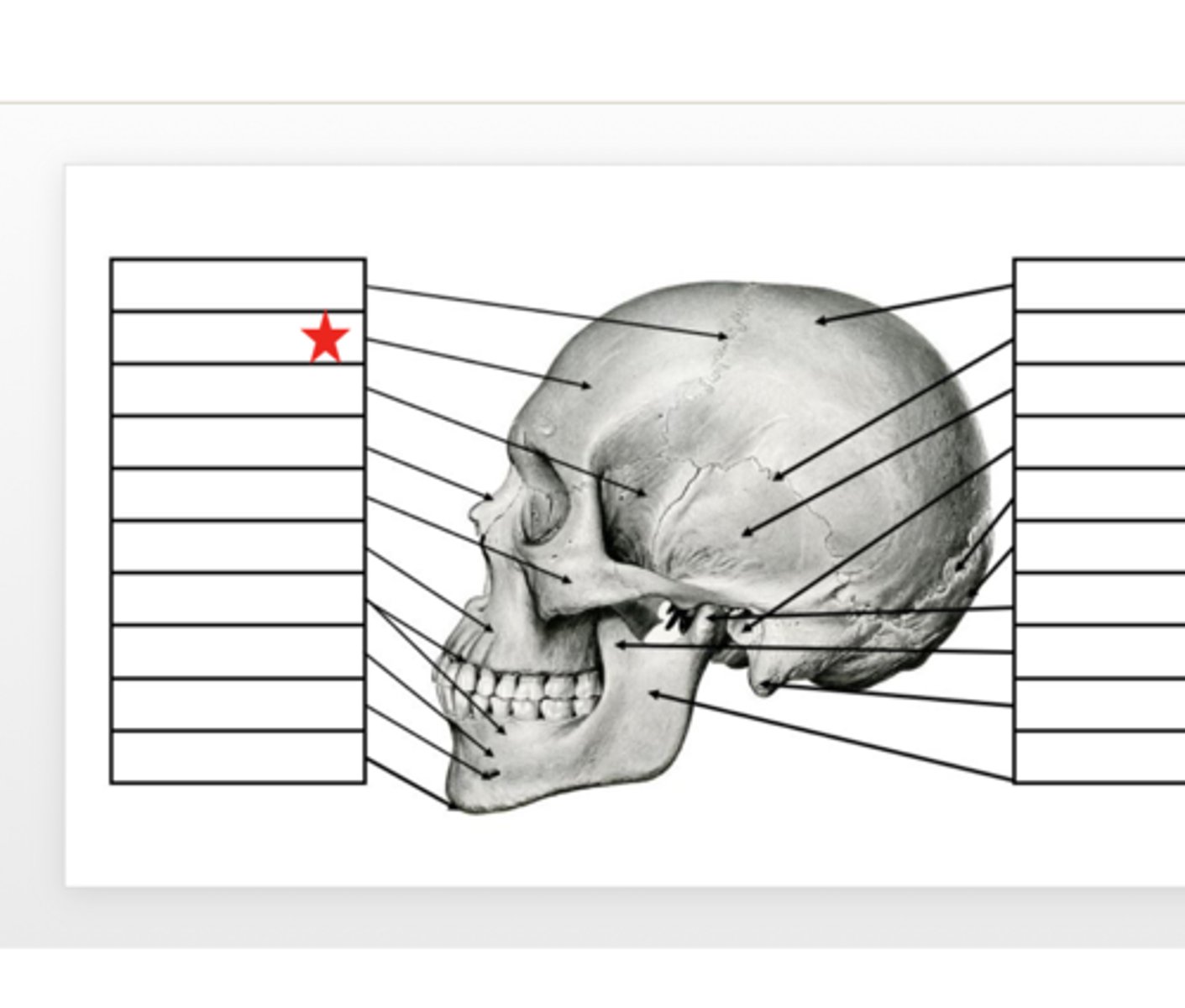
Coronal Suture
What is this?
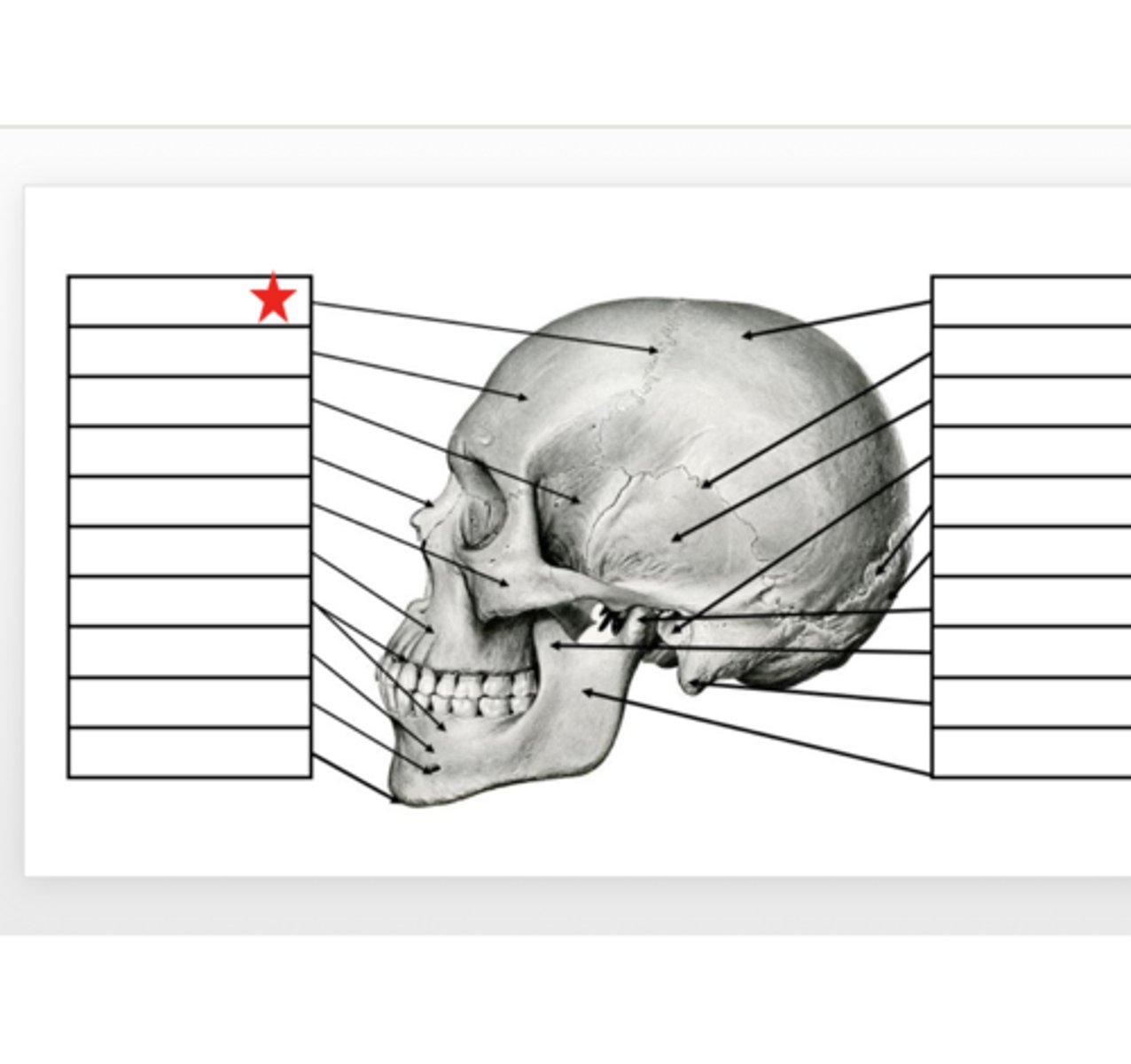
Occipital
Lowest part of the back of the base of the cranium, forming the cradle of the brain.Articulates with the parietal bone at the lambdoidal suture and the temporal bone at the squamosal suture
Foramen magnum
an opening in the occipital bone through which the spinal cord, spinal arteries and nerves pass.
Parietal
These bones create the superior portion of the sides and back of the cranium as well as the posterior 2/3 of the roof of the cranium. Articulates with the occipital bone at the lambdoidal suture, frontal bone at the coronal suture, and the opposite side parietal with the sagittal suture
Temporal
Comprises the inferior portion of the sides and base of the cranium. They are located inferior to the parietal bones and anterior to the occipital bone. Articulates with the parietal bone at the squamosal suture, occipital bone at the lambdoidal suture, and the greater wing of the sphenoid bone.
Squama
Thin superior part of the temporal bone
External auditory meatus
Opening of the ear passage in front of the mastoid process
Zygomatic arch
A long thin arched process extending anteriorly from the squama to the zygomatic bone. Determines the widest part of the face
Mastoid process
Rounded projection of the inferior portion of the temporal bone just medial to the lobe of the ear
Mandibular fossa
Small oval depression or socket on the underside of the temporal bone
Frontal
The anterior 1/3 of the cranium forming the forehead and part of the eye sockets and the most anterior of the cranial floor. It makes up the vertical plane of the forehead and the horizontal plane of the crown. It articulates with the parietal bones at the coronal suture
Frontal eminence
Rounded prominences on either side of the median line and a little inferior to the center of the frontal bone. A warm area of the face
Supraorbital Margin
The superior rim of the eye socket
Supraciliary Arches
The inferior part of the forehead just superior to the medial ends of the eyebrows
Nasal
These bones lie directly inferior to the glabella. They form the bridge of the nose and the dome over the superior portion of the nasal cavity. They articulate with each other and the frontal bone to form the root of the nose
Glabella
An elevation between the supraciliary arches on the inferior part of the frontal bone immediately above the root of the nose
Zygomatic
The diamond shaped bones that form the cheekbones. They are located on the frontal and lateral planes of the face. The bones form part of the inferior and lateral surfaces of the orbital cavity. Articulates with the zygomatic process of the temporal bone.
Maxilla
The bones of the upper jaw. The skeletal base for most of the superior portion of the face, anterior portion of the mouth, sides and floor of the nasal cavity, and the floor of the eye orbits. Articulate with each other, forming the nasal spine, a small bony process at the base of the nose
Nasal spine
The sharp bony projection located medially at the inferior margin of the nasal cavity
Alveolar process
Bony ridge found on the inferior surface of the maxilla and the superior surface of the mandible which contains the sockets for the teeth
Frontal process
The ascending part of the upper jaw which gradually protrudes as it rises to meet the frontal bone
Mandible
Horseshoe shaped bone forming the lower jaw, it consists of the body and ramus
Mental eminence
A triangular projection on the inferior of the anterior mandible
Coronoid process
Thin flat process projecting from the anterior portion of the upper ramus
Mandibular condyle
Round prominence that articulates with the temporal bone
Concave
The forehead protrudes beyond the eyebrows, the chin protrudes beyond the plane of the upper lip
Convex
The forehead recedes posteriorly from the eyebrows, while the chin recedes from the plane of the upper lip.
Vertical
The chin, forehead, and upper lip all project to an imaginary vertical line. Not any one feature protrudes or recedes more than another
Vertical Convex
The forehead and eyebrows project equally to an imaginary line and the chin recedes less than the upper lip
Convex Concave
The forehead recedes from the eyebrows and the chin protrudes beyond the plane of the upper lip
Concave Convex
The forehead protrudes beyond the eyebrows and the chin recedes from the plane of the upper lip
Convex Vertical
The forehead recedes from the eyebrows while the chin and upper lip project equally to an imaginary line.
Concave Vertical
The forehead protrudes beyond the eyebrows while the upper lip and chin project equally to n imaginary line
Vertical Concave
The forehead and eyebrows project to an imaginary line and the chin protrudes more than the upper lip
Bi-Parietal Width
The widest part of the cranium and skull - measured by a straight line across the parietal eminences
Bi-Zygomatic Width
The widest part of the face (5 eye widths) - measured by a straight line from the peak of one zygomatic arch to the peak of the other zygomatic arch
Bi-Mandibular Width
The widest part of the jaw - measured by a straight line across the angles of the jaw
Oval
This is the ideal shape and the most common shape. Cheekbones are wider than the cranium and the cranium is slightly wider than the lower jaw
Round
Short with round cheeks and a rounded, fuller jawline and a rounded cranium
Square
Appears to be short and composed of straight lines. The forehead, jawline, and cheeks are approximately the same width. The hairline is often straight
Triangle
Appears significantly wider at the jawline than the cheekbone and forehead. The forehead is the narrowest feature. Eyes are close-set. This is the least common head shape
Inverted Triangle
Characterized by a jawline that is narrower than the cheekbone or forehead. The forehead is the widest feature of the face. Eyes are wide set
Diamond
Characterized by wide cheekbones and a narrow forehead and jawline. Greatest width is across the cheekbone
Oblong
Long and narrow. The forehead and chin may be rounded or square. The nose is usually long