Ch.17 The Cardiovascular System
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
where is the heart located?
5th intercostal space at midclavicular line
**what are the 3 parts of the circulatory system?
blood, blood vessels ( vascular system), heart
what does the cardiac conduction system innervate?
• sympathetic receptors = (B1)
• parasympathetic = SA node & AV node
what does conduction of the heart consist of?
SA node
AV node
AV bundle (of his)
bundle branches
purkinje fibers
**what is the composition of whole blood?
• proteins (7%)
• other solutes (2%)
• platelets (140-340K)
• leukocytes (5-9K)
• erythrocytes (4.2-6.2 MM)
•91% water
what is the percentage of proteins in the blood?
7%
albumin (57%) → nutrition
globulins (38%)
fibrinogens (4%)
prothrombin (1%)
what is the percentage of other solutes in the blood?
2%
ions
nutrients
waste products
gases
regulatory substances
what is the percentage of leukocytes in the blood?
5-9K
neutrophils
lymphocytes
monocytes
eosinophils
basophiles
**how much percent of blood does the body make up?
8% of total body weight
**what percent of formed elements make up total blood vol?
45%
•RBCS
•WBC
•platelets
**how much plasma makes up % of total blood vol?
55%
**what is the average blood in males & females?
5L
***what are the 3 formed elements?
•WBC
•RBC
•platelets
**what is the function of RBCs?
• transports O2 from lungs to tissues
• transports CO2 from tissue cells to lungs
RBC number: (4.2-6.2 mil per each m of blood)
adult male → 5.8mil
adult female → 4.8 mil
percent of Hb in relation to total blood vol?
adult male→45%
adult female →40%
newborn→ 46-60%
**what is the function of WBCs?
protects body against invading microoganisms
consider complete blood cell count (CBC)
**what is the function of platelets?
instrumental in blood clotting
**what are the basic structures of the heart?
• layers
• chambers
• valves
• blood vessels
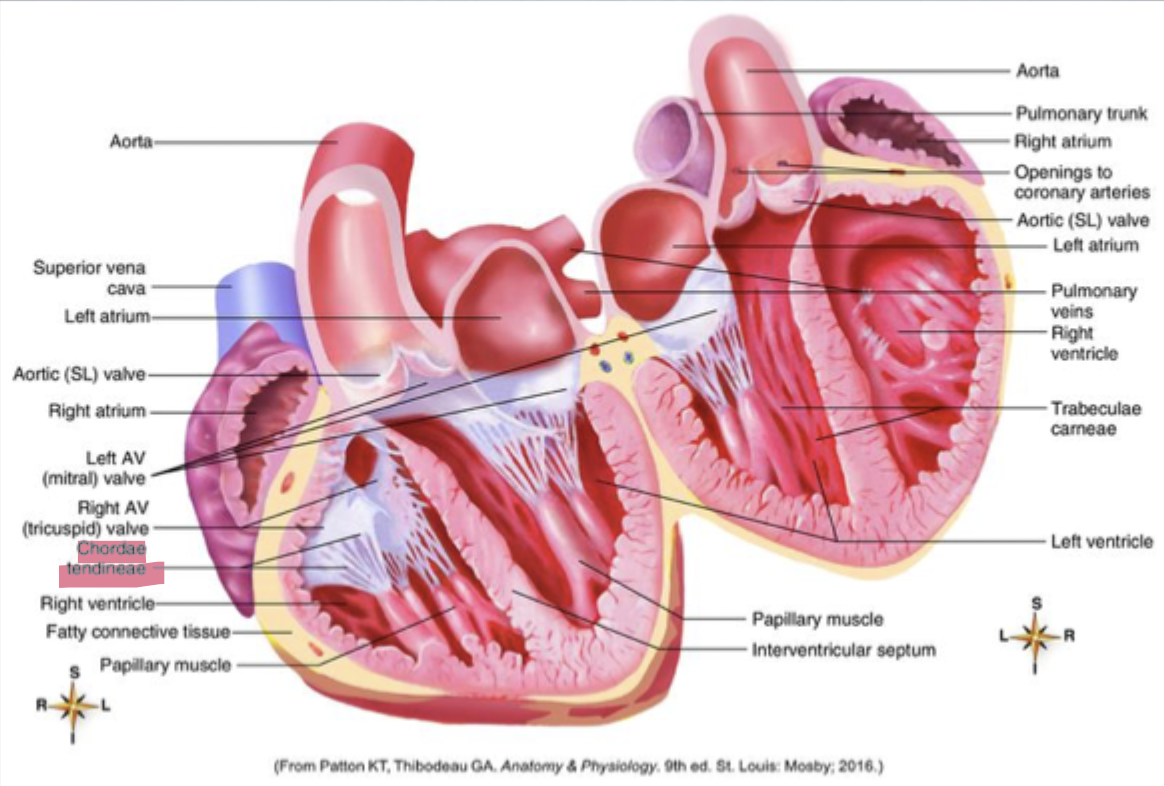
what is the order of the layers of the heart from external to internal?
Fibrous Pericardium → surrounds heart & attaches to surface of diaphragm; tough loose-fitting, inelastic sac surrounding heart
Parietal pericardium
Pericardial space → space between parietal & visceral layer
Epicardium (visceral pericardium) → adheres to heart’s outer surface
Myocardium → heart muscle proper that forms bulk of heart walls
Endocardium → lines inner surface of heart’s chambers
what makes up the serous epicardium?
• parietal layer (inner lining of fibrous pericardium)
• pericardial space
• visceral layer (covers outer surf of heart and great vessels)
what is the order of blood flow through the heart
SVC/IVC/coronary sinus ->
RA ->
tricuspid valve -(right AV valve)->
RV-> pulmonary circulation (R side )
Pulmonary semilunar Valve->
pulmonary trunk ->
pulmonary arteries->
L&r lung (pulmonary capillaries). ->
Pulmonary veins ->
LA ->
Bicuspid/mitral valve (left AV valve) ->
LV->
Aortic semilunar valve ->
Aorta->systemic circulation (L side)
Systemic arteries->
To the body(systemic capillaries)->
Systemic veins
what side of the heart pumps blood through pulmonary circulation?
R side of heart
what side of the heart pumps blood through systemic circulation
L side heart
what side of the blood receives deoxygenated blood from SVC, IVC, coronary arteries?
R side of heart
what side of the heart has greater muscle mass?
L side of heart
what is myocardial infarction?
myocardial tissue death
what do semilunar valves separate?
ventricles from arterial outflow tracts
what is cardiac output?
HR x SV
leukocytosis vs leukopenia?
overall ↑ # WBC
vs
overall ↓ # WBC