Forensic Toxicology - Exam 1
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
pharmacology
the study of drugs
toxicology
the study of poisons
forensic toxicology
applying toxicology to aspects of the law
“poison” hemlock
neurotoxin, blocks neuromuscular transmission, 6-8 leaves is a toxic dose
tetrodotoxin
found in puffer fish and blue-ringed octopus
botulinum toxin
most lethal toxin known to man, produced by bacteria
arsenic
king of poisons, silent, deadly, virtually undetectable
paracelsus
everything is a poison at the right dose
hyponatremia
over-hydration (water toxicity), skull pressure squeezes brain and spinal cord, swollen brain cells
marijuana, cocaine, amphetamines, opiates, pcp
NIDA-5 tests for
receipt of evidence, conduct analyses, review data, prepare a report, review a report
forensic lab workflow
pharmacokinetics
what the body does to the drug
pharmacodynamics
what the drug does to the body
dose-response effect
dose determines blood concentration determines effect
absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination
movement of a drug over time through the body
bioavailability
the fraction of drug that reaches the systemic circulation after oral ingestion
intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, oral, rectal, inhalation, transdermal
routes of administration in order of bioavailability
dosage form, additives, delayed response preparations
rate of dissolution and release of drug from pharmaceutical preparation are determined by _____________
uncharged
permeability favors small _____ solutes
low pH
acidic drugs are better absorbed at _______
high pH
basic drugs are better absorbed at __________
one compartment model of distribution
instantaneous distribution after administration, even distribution throughout body (blood)
two compartment model of distribution
different distribution rates, more rapid distribution into high perfused tissues, followed by a slower distribution into less well-perfused tissues (blood and fat)
blood brain barrier
lipid membrane located between the plasma and extracellular space in the brain, limited to small and highly lipophilic drugs
volume of distribution
theoretical volume of fluid into which the total drug administered would have to be diluted to produce the concentration in plasma
dose (mg)/ plasma concentration (mg/L)
volume of distribution equation
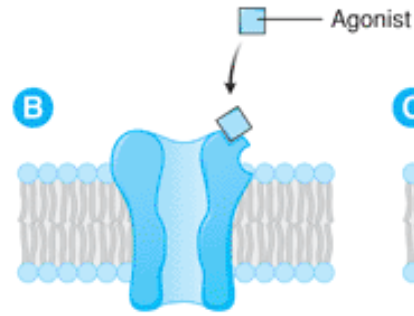
agonist
drug binds to and activates a target, maximal response when used at high enough concentrations
partial agonist
drug produces less than maximal response even at high enough concentrations to cause maximal response
antagonist
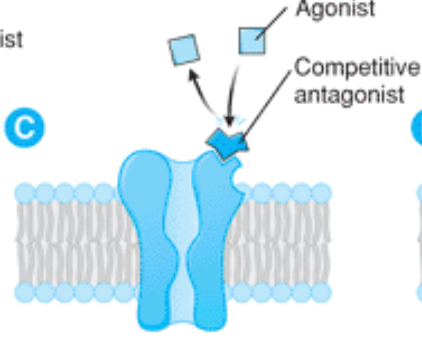
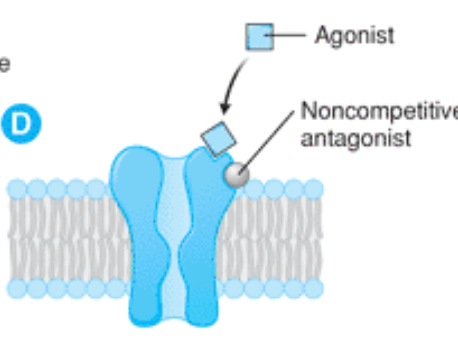
inhibit the ability of targets to be activated by physiologic or pharmacologic agonists
competitive antagonist
key that fits in lock, does not open door, usually reversible
non-competitive antagonist
dead-bolt lock, door will never open, even if key is put into lock
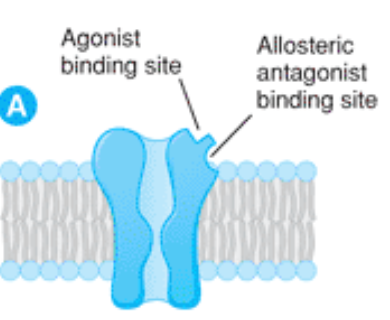
unbound receptor
agonist binding
competitive antagonist binding
noncompetitive antagonist binding
metabolism
biotransformation of chemicals into water soluble compounds to be eliminated in urine/bile
first pass metabolism
phenomenon of drug metabolism whereby the concentration of a drug is greatly reduced before it reaches the bloodstream
cytochrome P450 enzymes
75% of metabolism of drugs
inducers
speed up CYP, lower drug blood concentrations
inhibitors
slow down the CYP, increase drug blood concentrations
elimination
elimination of unchanged drug or metabolite from the body
glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion
mechanisms of the kidney
glomerular filtration
small molecules/drugs filtered through the glomerulus, drugs bound to plasma proteins are too large
tubular reabsorption
lipid soluble drugs are reabsorbed from the lumen of the nephron back into the systemic circulation
tubular secretion
carrier-mediated active transport system that requires energy, shows competition effects
acidify the urine
to increase the renal clearance of a drug that is a weak base you should ____________
first-order
a constant fraction of drug is eliminated with time (exponentially)
zero-order
a constant amount of drug is eliminated with time (linear)
cyanide
________ inhibits Cyt C (electron transport chain)
LC/MS
gold standard for instruments
albumin
most common protein that binds to drugs
glucuronidation
a metabolic process that attaches glucuronic acid to a drug, increasing its solubility, making it easier for the body to eliminate
sulfation
a metabolic process were a sulfate group is added to a molecule to facilitate its excretion
intravenously
drugs administered ____________ do not go through first pass metabolism
cmax
maximum concentration
tmax
time at cmax
cocaine, sympathomimetic amines, methylxanthines, nicotine
types of CNS stimulants
pupils dilated, HGN and VGN absent, pulse and blood pressure elevated, hot, rigid muscles, injection sites
DRE assessment for stimulants
paranoia, psychosis, impaired task performance, euphoria, violence
characteristics of stimulant symptoms
schedule II, ENT surgeries
cocaine schedule
cocaine hydrochloride
powder form, cut with things like caffeine or benzocaine
inhaled, smoking, intravenous, orally
routes of administration of cocaine
mechanism of action of cocaine
blocks Na channel conductance (anesthetic), blocks reuptake of neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin
metabolism of cocaine
metabolizes to benzoylecgonine and methylecgonine, becomes cocaethylene in presence of EtOH, long term storage of samples convert to BZE
0.5-1 hour
half-life of cocaine
3-5 hours after formed
half-life of BZE
2 hours after formed
half-life of cocaethylene
analysis of cocaine
GC/MS, filtration/extraction then LC/MS
methamphetamine, amphetamine, MDMA, ephedrine
types of sympathomimetic amines
schedule II, narcolepsy or ADD
sympathomimetic amine schedule
meth/amphetamine mechanism of action
stimulates neurotransmitter release and then inhibits metabolism
10-12 hours
methamphetamine half-life
11-12 hours
amphetamine half-life
elimination of sympathomimetic amines
eliminated via kidney, unchanged
teeth grinding, desire to move
MDMA symptoms
theophylline, theobromine, caffeine
types of methylxanthines
cardiac arrhythmia
symptom of cocaine
vasoconstriction
decreasing surface area of a blood vessel
D
__-methamphetamine is deadly
schedule IV
phentermine schedule
schedule I
MDMA schedule
opiate
used to describe drugs that are derived from opium
opioid
synthetic and semi-synthetic entities that have morphine-like actions
narcotic
applied to any drug that induces sleep
analgesic
a drug used to relieve pain without loss of consciousness
brainstem
mediate respiration, cough, maintenance of BP, pupillary diameter, and control of stomach contents, nausea, vomiting
medial thalamus
mediate deep pain that is poorly localized and emotionally influenced
spinal cord
involved with the receipt and integration of incoming sensory information, leading to the attenuation of painful stimuli
hypothalamus
affect neuroendocrine secretion
limbic system
may influence emotional behavior
periphery
bind to peripheral sensory nerve fibers and their terminals and inhibit release of pro inflammatory substances
immune cells
receptors have been found on immune cells, but the role in response to painful stimuli has not been determined
mu, kappa, delta, sigma
receptor subtypes
morphine, fentanyl, heroin, meperidine, methadone
full agonist opioids
naloxone, naltrexone
antagonist opioids, do not activate the receptor-mediated response
opioid uses
chronic pain, trauma, burns, cough suppression, diarrhea, detoxification of opioid use
opioid disadvantages
respiratory depression, addiction potential, tolerance, sedation
opioid mechanism of action
at spinal site they inhibit neurons that transmit pain transmission, at brainstem they activate neurons that send impulses to the spinal cord to inhibit pain transmission
pupils constricted, HGN and VGN absent, pulse and blood pressure lowered, cold, droopy eyelids, on the nod, raspy speech
DRE assessment for opioids
insufflation, smoked, injected, oral
opioid ingestion methods