Module 3: chapter 7 periodicity
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
How did Mendeleev create the periodic table
Arranged 60 known elements in order of atomic mass
Lined up elements with similar properties.
Swapped any elements that don't the properties ( e.g. Te, I)
Left gaps for undiscovered elements + predicted properties of them
How is the periodic table arranged now
• 114 elements arranged in order of atomic number
Groups are columns going down (no. Of e- in outer shell)
Periods are rows that go across (no. Of e- shells)
What is periodicity
Across each period there is a repeating trend in properties
Examples of periodicity
Metals → non metals, election configuration, ionisation energy, structure, melting point,
What is the trend in electron configuration across a period
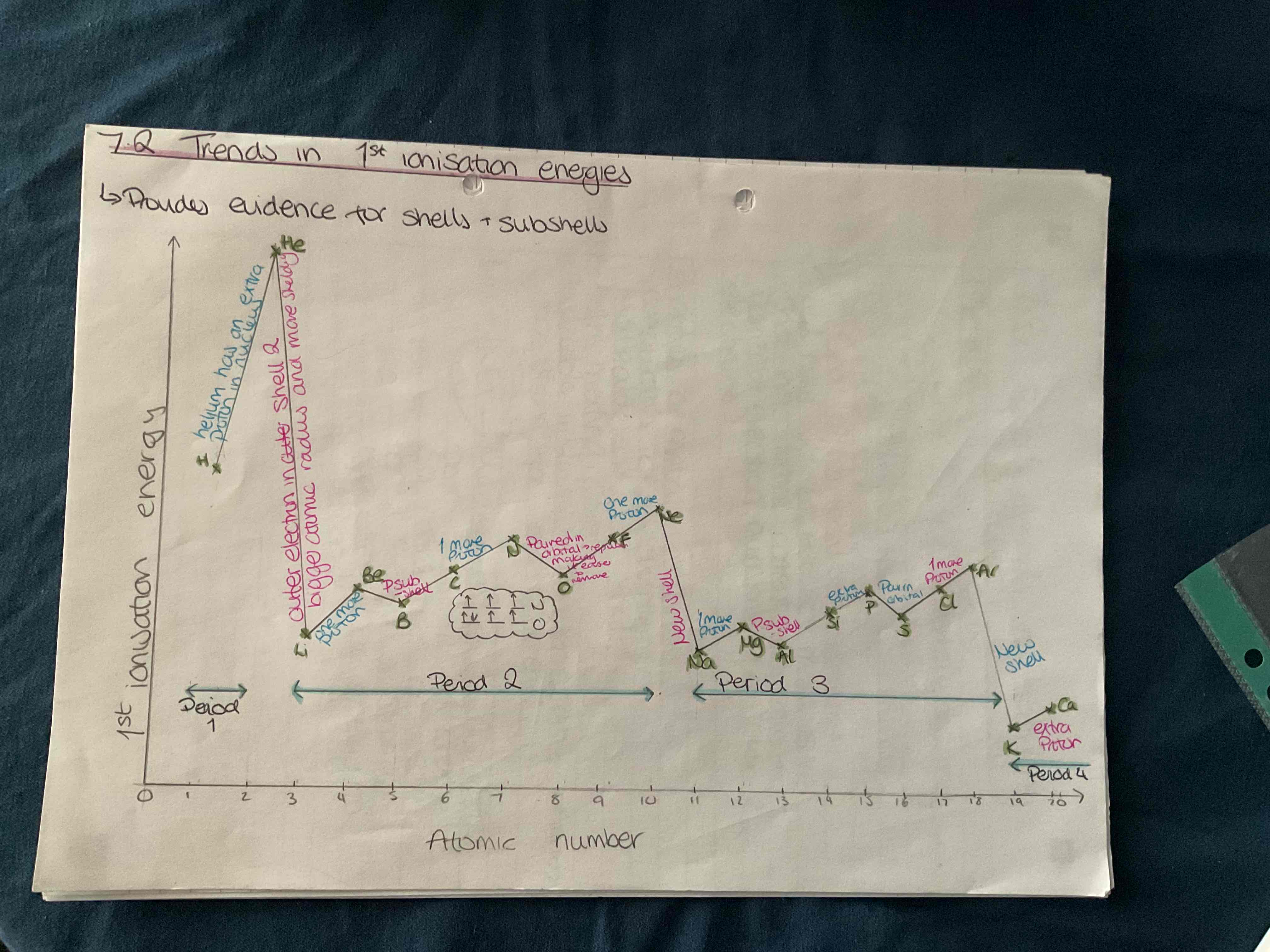
Each period starts with an electron in a new higher energy shell
What is the trend in electron configuration across period 2
Fill s subshell then P subshell
What is the trend in electron configuration across period 3
Fill s subshell then p subshell
What is the trend in electron configuration across period 4
Fill s subshell then 3D subshell then P subshell
How is the periodic table divided into blocks
Matching their highest energy level ( s PDF)
What is ionisation energy
Measures how easily an atom loses elections to form a positive ion
First ionisation energy
The energy required to remove one election from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms of an element to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions
What are the factors affecting ionisation energy
Atomic radius
Nuclear charge (number of protons)
Electron shielding
Now many ionisation energies will an element have
As many as there are electrons
Do successive ionisation energies increase or decrease
Increase
What do successive ionisation energies provide evidence about
For the different election energy levels. Can make predictions about the number of electrons in the outer shell the group of the element and the identity of the element
Graph for trends in 1st ionisation energies
Structure of metals
Layers of positively charged ions in a sea of delocalised electrons
What are the properties of metals
Conductors of electricity
Malleable
High melting point
Insoluble in water → electrostatic attraction too strong for water to break
Why does magnesium have a higher melting point than sodium
Mg has a 2 + charge so attraction between ion and election is stronger and requires more energy to break
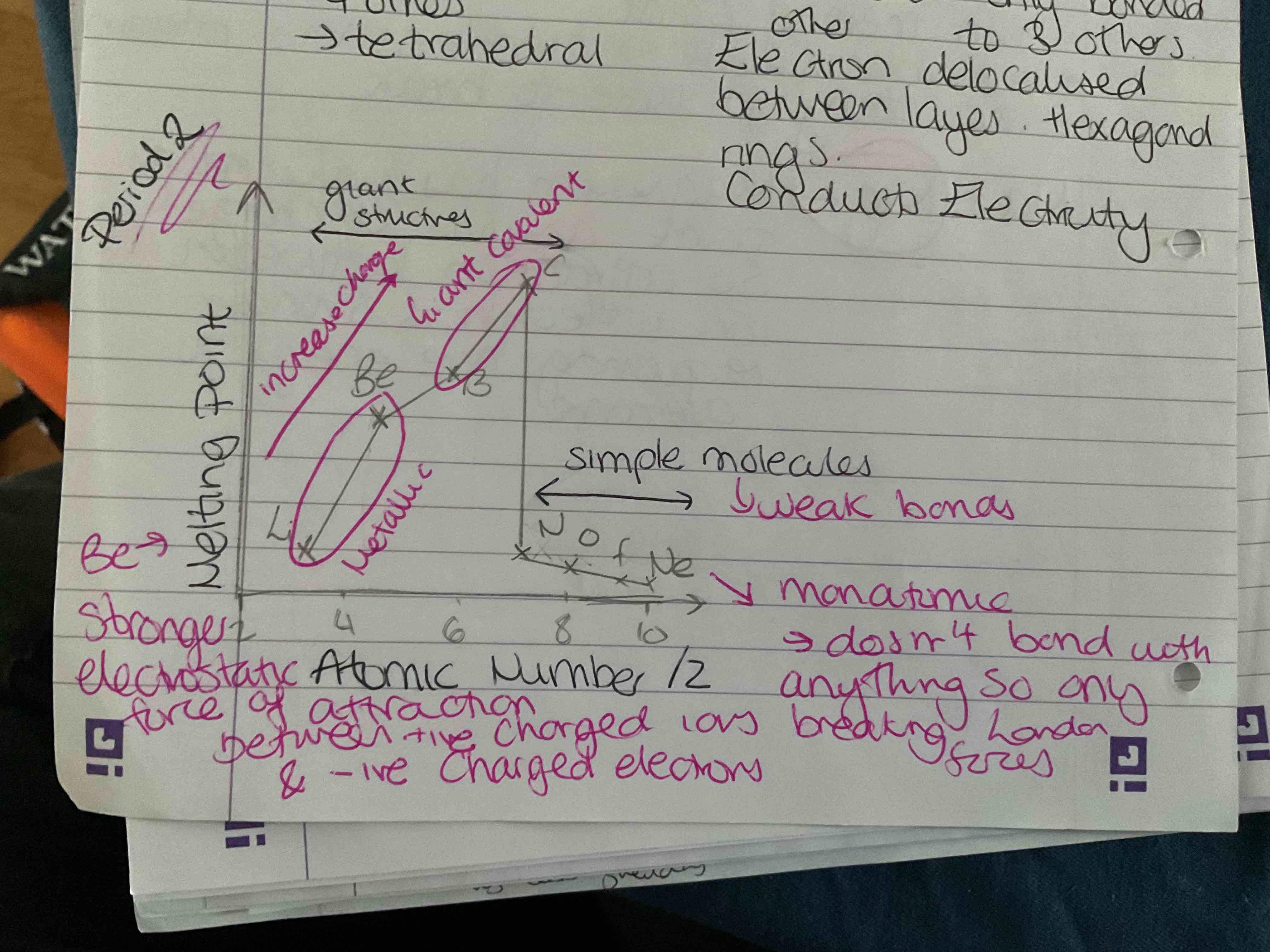
Which elements are giant covalent lattices in elemental form
Boron, Carbon, silicon
What are the properties of giant covalent structures
High melting and boiling point
Insoluble in water (bonds too strong for water to break)
Generally don't conduct electricity except graphene / graphite
What are some carbon allotropes
Diamonds → each carbon is bonded to 4 others ( tetrahedral )
Graphite → each carbon only bonded to 3 others electron delocalised between layers hexagonal rings

What does the trend in melting points for period 2 look like
Increases from lithium to Carbon as giant covalent and increase in charge
Then drops as simple molecules so weaker bonds and monatomic so only breaking London forces
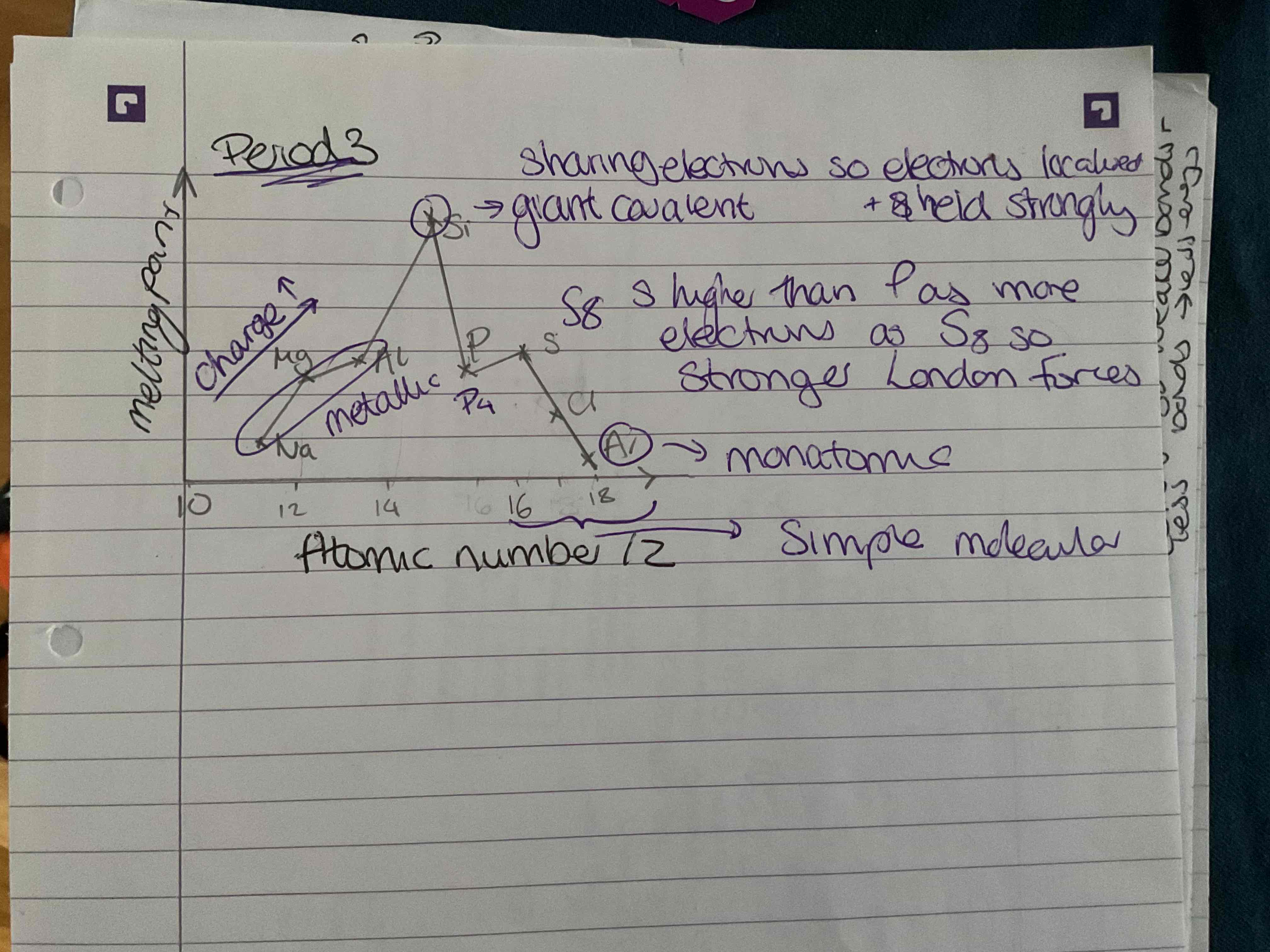
What does the trend in boiling points across period 3 look like
Increases from sodium until silicon as charge increases
Silicone has highest as giant covalent and sharing electrons so elections localised and held strongly
Then decreases except s is higher than P as There are more electrons in S8 so stronger London forces