nurs320 final - cardiac disorders
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
central perfusion
force of blood movement by CO (SV*HR, need good function, BP + vol)
decreased SV indicates
increased CO
increased SV indicates
decreases HR
peripheral perfusion
vol of blood to target tissue (impaired can lead to ischemia/necrosis/shock)
preload
vol in LV after diastole (ventric. relax)
good/high preload means
high SV (more stretch = good contract/perfuse)
afterload
resistance ventricles have to contract against (SVR, blood vol, vessel diam.)
increased afterload means
low SV (more resistance = plaque from smoke, etc.)
7 approaches to stay heart healthy
active (healthy weight, know abt choles./BS/diabetes), no smoke, diet, BP
patient history assessment - 6 P's of perfusion
(OLDCART) polar (cold), pale, pulseless (+1/weak, SOB/dizzy), paresthesia (numb/tingle), paralysis, pain
keep BP below
<140/90
cardiac meds
vasopressor, cardioglyco (dig, increase contract) diuretic, antidysrhyth, anticoag/PLT (prevent more clot), thrombolytic (breakdown clot), statin
peripheral arterial disorder (PAD)
poor perfuse + O2
PAD - atherosclerosis
(main cause) plaque/choles in arteries (can occur anywhere unknown, narrow + obstruct lumen, ulcer/rupture)
s/s of PAD
6 P (pt w CAD def has PAD, blood to central first)
periph perfusion testing - treadmill
pain in calf when walk (no O2 to muscle = intermittent claudication/PAD/CAD)
intermittent claudification
muscle pain (cramp/weak) in legs during exercise (relieved by rest)
periph perfusion testing - ultrasound
velocity of blood flow
periph perfusion testing - CT scan/MRI
see vessels (may need dye, know cautions!!)
periph perfusion testing - angiography
see vessel narrow diam. (may need dye)
periph perfusion testing - ankle brachial index (ABI)
check BP of lower/brachial
does lower or upper extremities have a higher BP
lower
altered peripheral perfusion s/s
intermittent claud, shiny/thin skin (tight), leg hair loss, low (absent) pulse, poor wound heal (+ulcer on toes, 6P)
dependant rubor
(red) feet dangle = red + perfuse (based on gravity)
elevation pallor
lift legs = white (blood cant reach heart against gravity, ONLY FOR PAD not PVD)
altered periph perfusion - pain at rest
in foot/toes by elevate (limbs)
how to position w altered periph perfuse
put affected area below heart, if edema = higher but below heart (isotonic/walk exercise for circulate)
peripheral artery bypass surgery
bypass vein to carry blood around occlude
how often to check pedal pulses
q15 mins (assess for 6 P, bedrest 18-24 hrs, pulse/cap refill, notify surgeon ASAP of ABN)
carotid artery disease
(similar to arterial) decrease blood to brain
carotid artery disease s/s
(neuro) change LOC, stroke
carotid artery disease caused by
(main cause, like PAD) atherosclerosis
carotid artery disease treatment
lower BP (carotid artery stent = assess VS + neuro)
carotid endarterectomy
scrape plaque in carotid (check CN status + meds post op)
PAD - raynaud's phenomenon
pallor/cold (vasoconstrict) in hands/feet
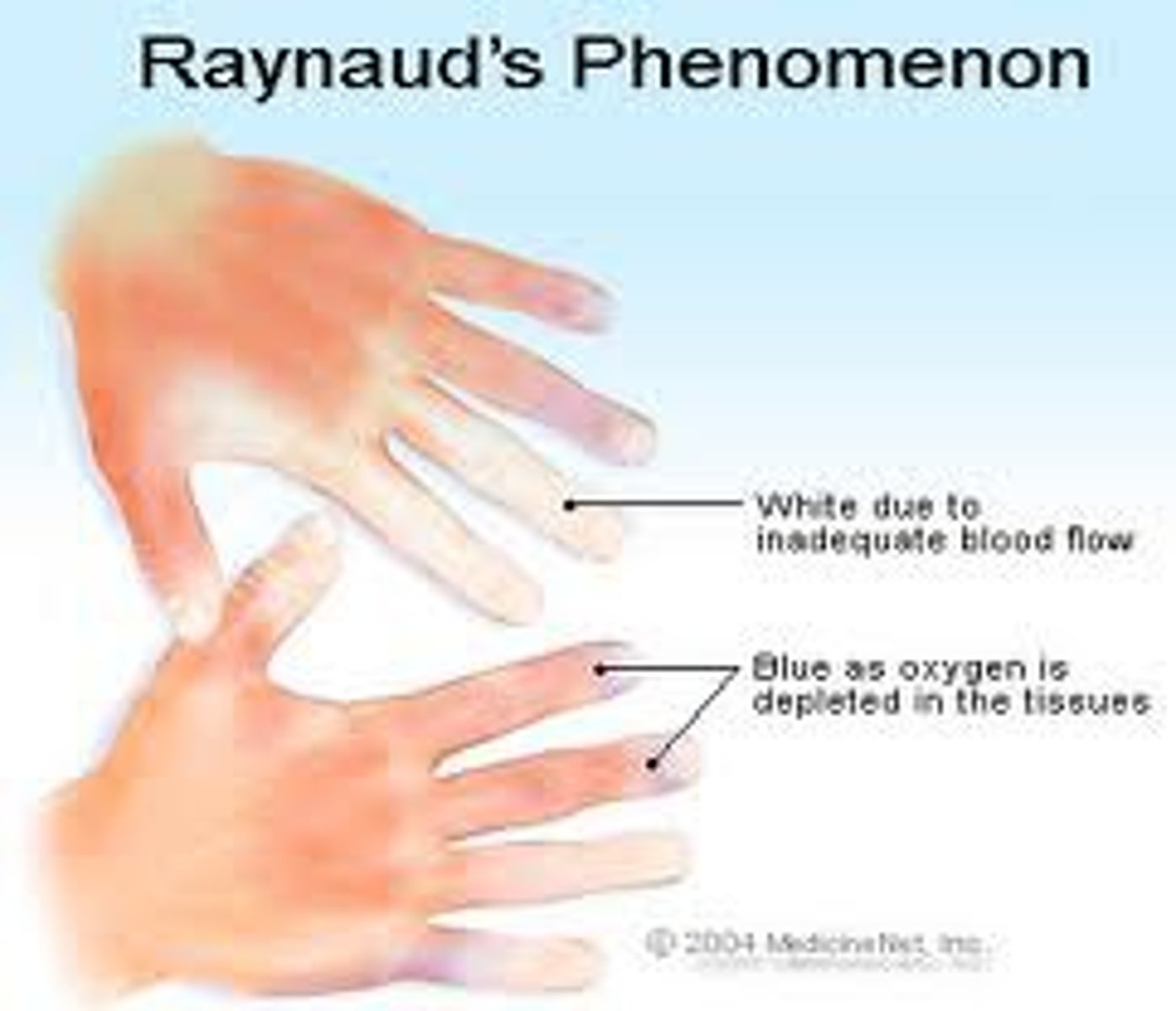
raynaud's phenomenon triggered by
(go to warm area) cold, nic, emotion (stress/anxious)
PAD - thromboangiitis obliterans/buerger's disease
(reccurrent) inflamm vaso-occlude = thrombi in upper/lower vessels
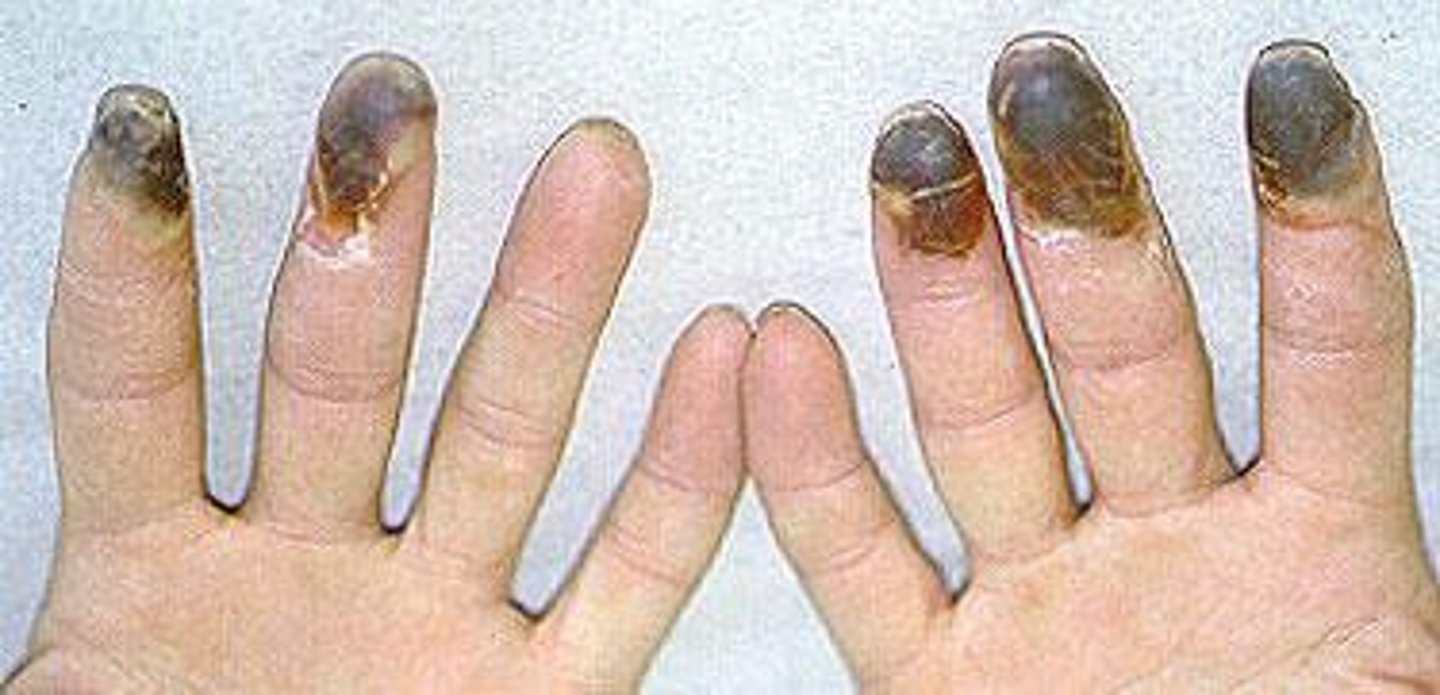
PAD - buerger's disease caused by
smoke (tobacco/marijuana) = inflamm/6 P/necrosis) = STOP
PAD - both raynaud's + buerger's is not caused by
atherosclerosis
how to help PAD
no tight clothes/cross legs, no stimulants (caffeine/chocolate + no smoke/stress, stay warm)
venous thrombosis
clot in vein from inflamm (stagnant/stasis = still blood)
superficial vein thrombosis (SVT)
(clot in superficial vein, benign) dont need dr help to break (put on anticoag)
deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
(illiac/femoral vein) decrease perfuse + travel (to diff organs)
DVT treatment
anticoag
high D-DImer indicates
(check for PE too!!) clot
venous thromboembolisms s/s
(asymptomatic) pain, swell (edema), tender, red (warm)
how to prevent venous thromboembolisms
(ambulate, fluids) elevate leg (NOT FOR PAD), compression socks (BAD when clot already present = travel), anticoag/PLT (subQ hep)
venous insufficiency disorders (PVD) s/s
ulcer (hard to heal) norm pulse (may need doppler but present), heavy legs (swell)
what is intermittent claudication typically seen in
PAD, not PVD
PVD treatment/care
no prolong sit/stand, elevate legs, wound therapy (diet/exercise)
BP is considered
(CO*SVR) amnt of force by blood against vessels
HTN is considered
>140/90 (pre = 120-139/80-89)
HTN diagnosis based on
>3 elevated readings (over wk or more), check both arms + use highest (120/130 = ok)
HTN emergency (crisis)
(hrs-days) >180/120 + acute organ dmg (MI, retinopathy, renal fail, etc.)
HTN urgency
(days-wks) >180/120, NO organ dmg
HTN treatment
(assess dmg organ) dash diet (healthy food, no smoke/alc/stress)
heart failure (HF)
impair contract/fill = low CO (HR*SV)
heart failure (HF) s/s
(fluid overload in heart) back flow, SOB
heart failure (HF) typically caused by
atherosclerosis (high afterload = pump hard thru plaque + work harder)
chronic HF indicates
lifestyle changes
does left or right fail first in HF
left (backflow then to lungs)
acute decompensated heart fail (ADHF/CHF exacerbate)
rapid backup to lungs = PE (pulm edema, increase in pulm venous pressure)
left side HF s/s
(resp s/s) cyanosis, crackle (cough, wheeze), high RR + HR (poor perfuse to brain/lungs)
right side HF commonly caused by
COPD (underlying resp disorder)
right side HF s/s
(by itself) distended JV (/organs), weight gain, edema, enlarge organs (splenomegaly)
how to help/manage HF
less salt/choles/fluids, weight self daily (no smoke/metabolic syndrome)
HF + weight gain
3 lbs in 2 days, 5 lbs in 1 wk (productive cough = retain fluid)
HF diagnosis - echo ejection fraction (EF)
(low = contract/CO problem) <55% (55% = norm)
HF diagnosis - elevated BNP indicates
(HF) heart stressed + release BNP to notify (when overstretch/bad contract)
meds for HF
diuretic, ACE/ARB, beta block, dig
coronary artery disease (CAD) - ischemia
lack of O2 to heart (angina from athersclerosis)
CAD - stable angina triggered by
(predictable, temporary) exertion (going up steps)
how to treat stable angina
PRN nitrate
CAD - unstable angina (acute coronary syndrome)
heart supply + demand issue (occur at rest, MI)
how to treat unstable angina
daily nitrate (patch/cardiac cath)
myocardial infarction (MI)
(emergency!!) no blood/O2 (cell death)
how to treat MI
(rapid response) 2L max O2 PRN, semi fowler, MONA (morph, O2, nitro SL, ASA CHEW, small amnt) (PCI or fibrinolytics if not PCI)
silent ischemia
no blood/O2 (to heart) w no s/s, seen on EKG
variant (prinzmetal) angina caused by
coronary artery spasm (occur at rest, tone not fat)
microvascular angina
bad function of small coronary arteries
CAD treatment
(ABCDEF), antiPLT(aspirin/NSAID)/coag/angina (nitrate)/HTN(ACE/ARB), beta block, cig smoke/choles (STOP), exercise (education, no overexert), flu vaccine
percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PCTA)
thru artery, open w balloon + place stent (for more blood/O2 flow)
infective endocarditis (IE)
valve infection of heart endothelial
infective endocarditis (IE) caused by
bacteria (valve deformity)
infective endocarditis (IE) treatment
IV antibiotics (PICC + before surgery), rest (replace valve PRN)
labs for infective endocarditis (IE)
echo, CRP, CBC
infective endocarditis (IE) s/s
(immunosuppressed) fever, anorexia, abd/back pain (arthralgia, decrease CO, high HR, low RR)
big sign of infective endocarditis (IE)
(vasc.) osler node (red spot, janeway leision, roth spot)
myocarditis
inflamm of myocardium (can possible resolve on its own or lead to HF, 3rd leading cause of death in young athletes)
myocarditis can be trigered by
virus (bacteria, parasite, fungi, auto immune = treat based on cause)
myocarditis s/s
angina, dysrhyth, SOB, syncope (fever/infection)
myocarditis diagnostic tests
CRP, troponin, EKG, echo, biopsy (more definitive, but only acute)
pericarditis
outer layer of heart fill w fluid (effusion) = peri friction rub (from heart compress/tamponade)
pericarditis can be caused by
(unknown) infection, autoimmune, MI
pericarditis s/s
friction rub, SOB, angina (worse when lay flat), JVD (low BP)
pericarditis diagnostic test
echo, CT, EKG, CRP (CXR)
pericarditis treatment
increase HOB to 45, antiinflamm/biotic (rest, no strenuous activity, sentesis to aspirate fluid in effusion)
cardiac rehab
slow + gradual (relax, increase MET>1 is min.)
cardiac rehab - exercise
increase CO/blood flow, decrease BP (+lipid)
static exercise
lift, heavy, strain (limited, increase HR + BP fast)