midterm practical lab
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is the total magnification when using a 100x objective lens and a 10x ocular lens?
1000x

What is the purpose of immersion oil when using the 100x objective?
It reduces refraction and increases resolution.
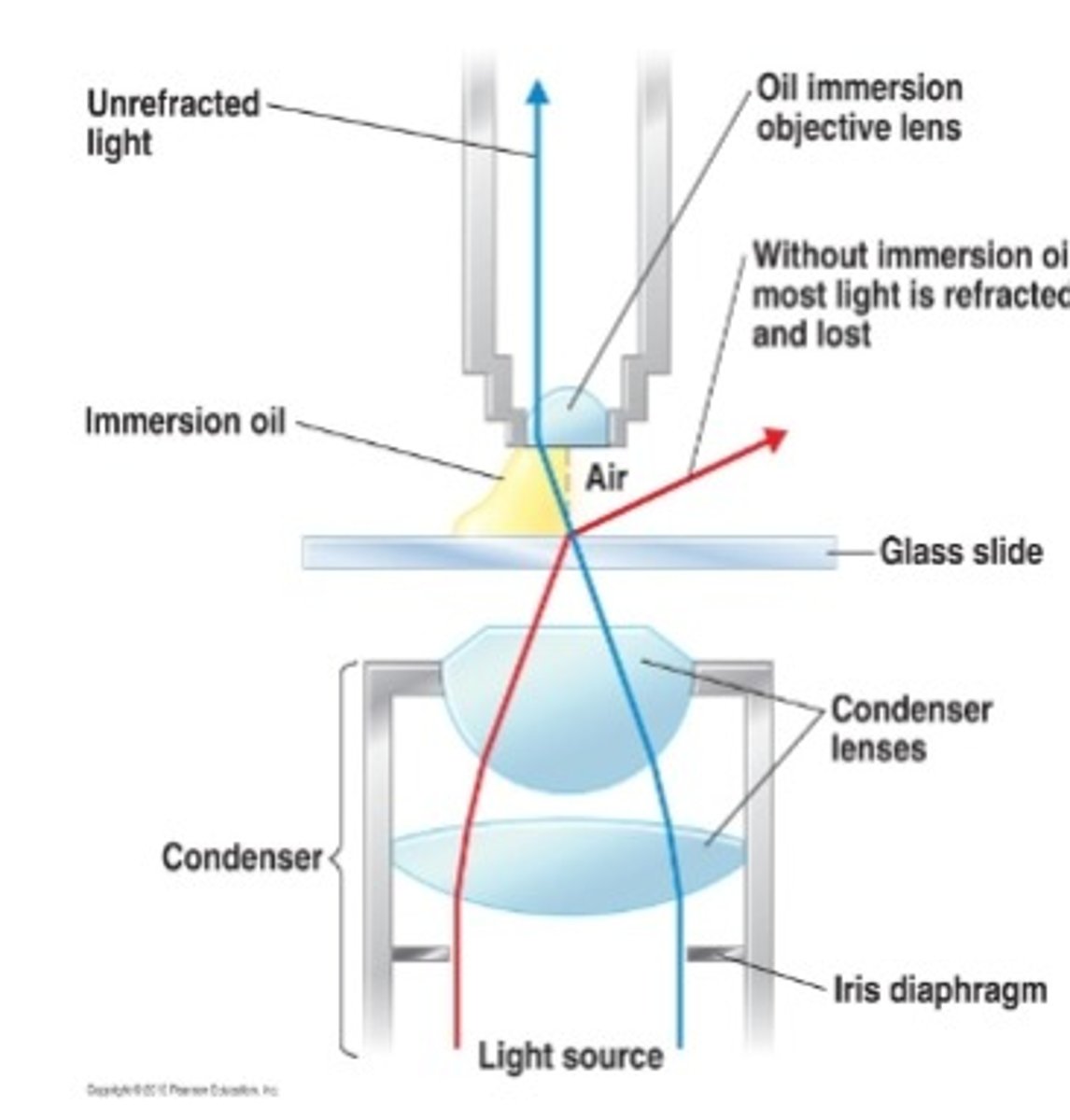
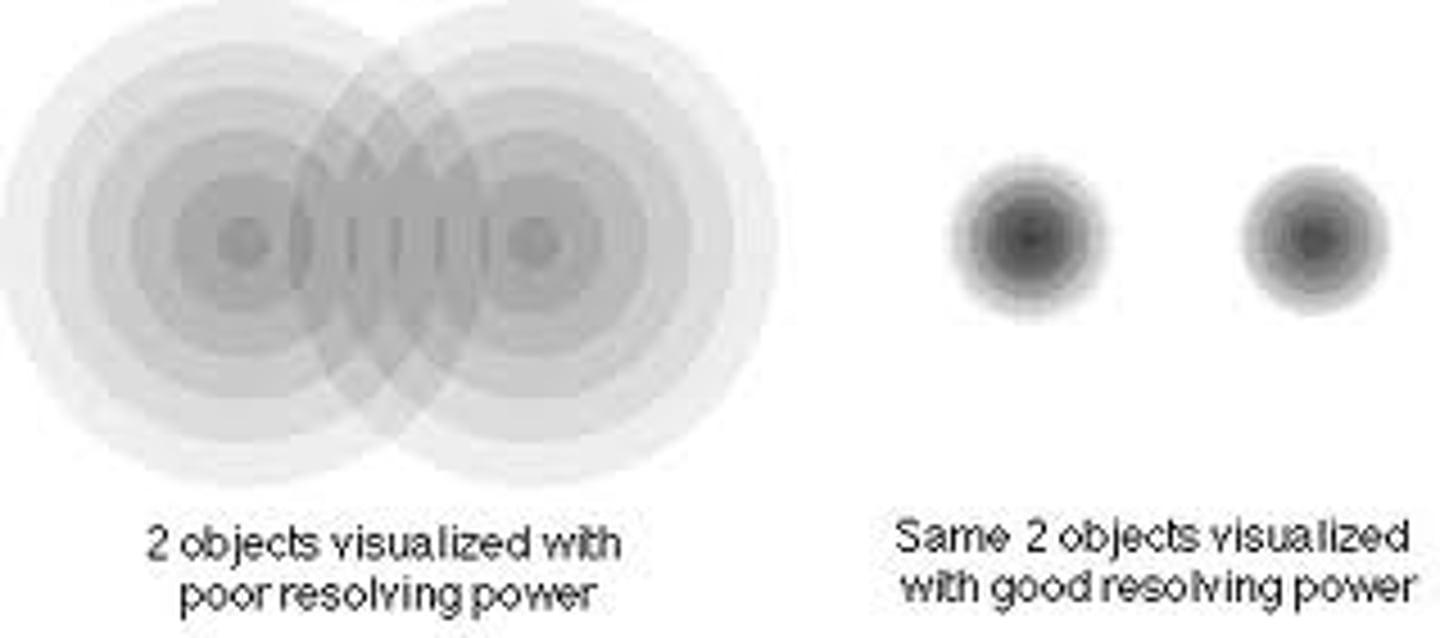
what is resolving power in a microscope?
The ability to distinguish two closely spaced points as separate.
What does "depth of field" describe in microscopy?
The vertical range that stays in focus under magnification.
Why do we use aseptic technique in microbiology labs?
To avoid contamination of cultures, tools, and self.
What result is expected when a sterile disc is transferred to sterile media correctly?
No microbial growth.
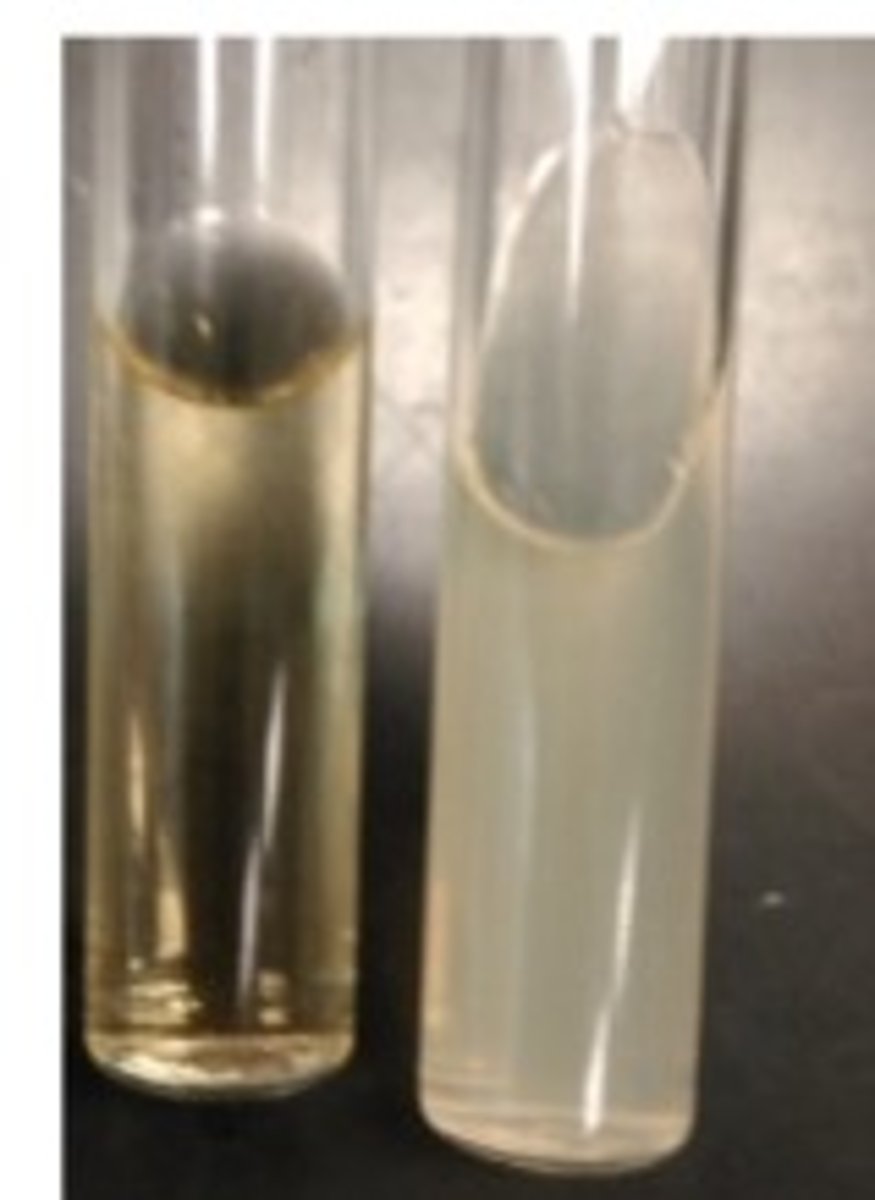

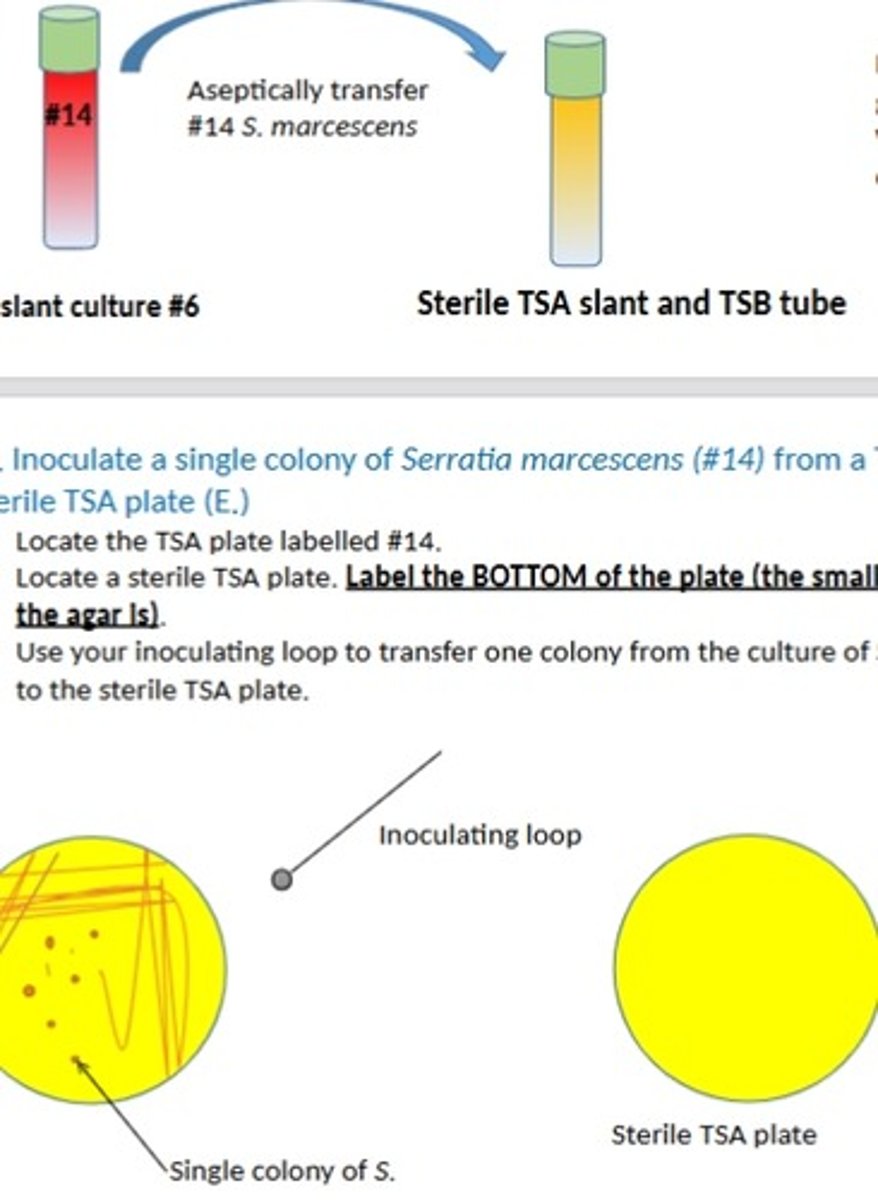
What is the purpose of TSA slants, TSA plates, and TSB tubes?
TSA = solid growth; TSB = broth; plate = colony isolation
Why are plates incubated upside down?
To prevent condensation from dripping on the agar.
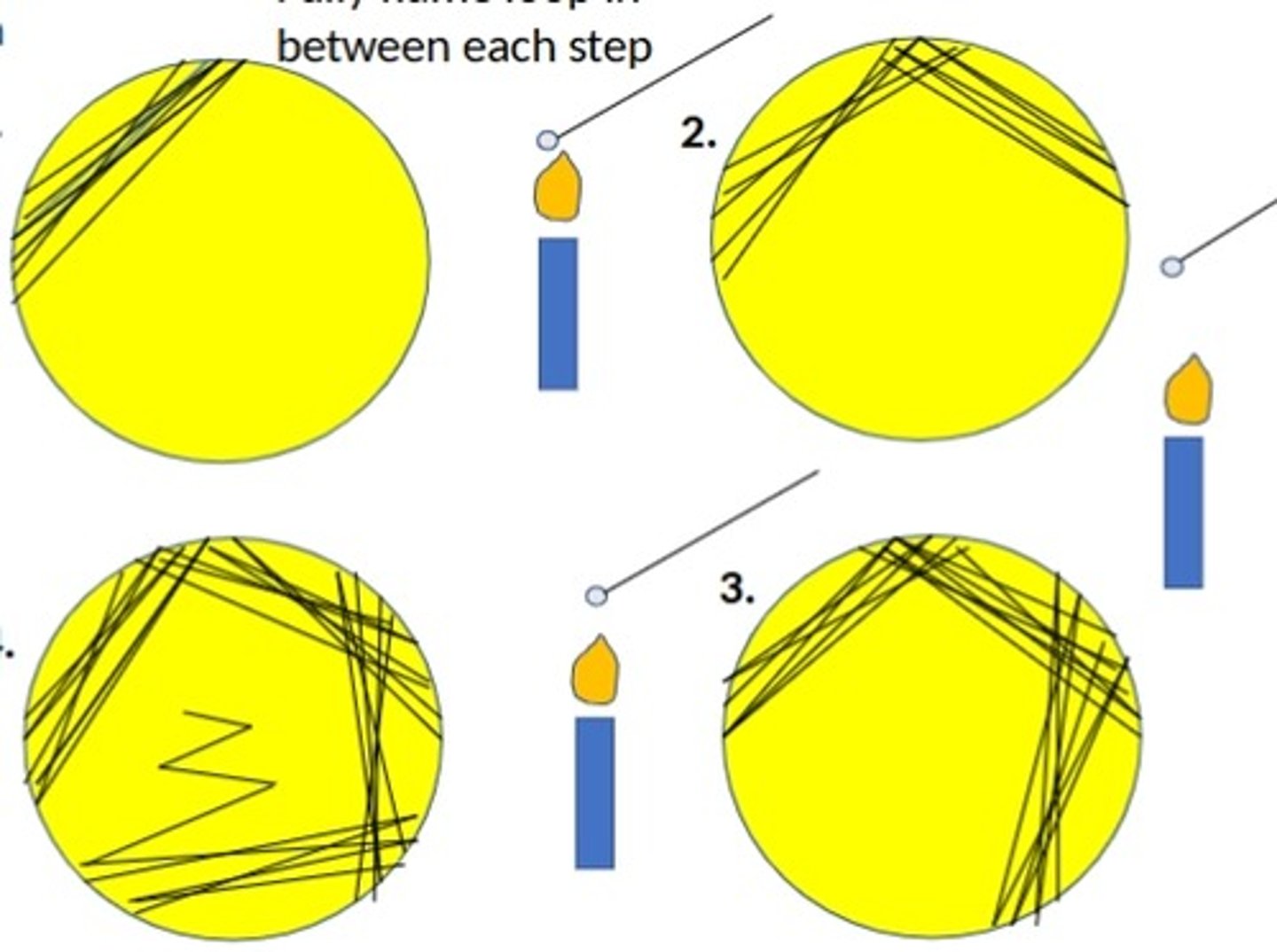
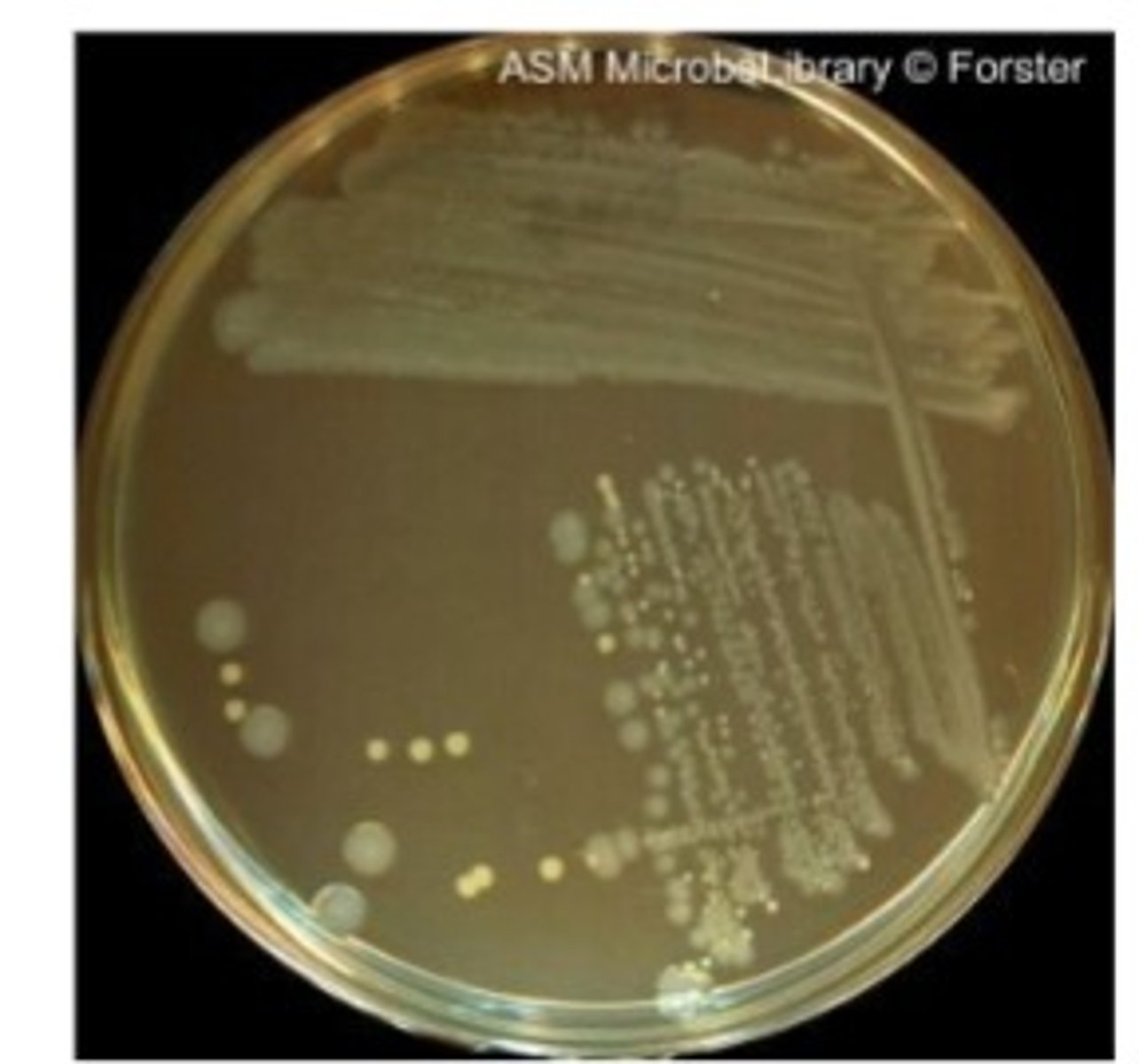
What is the purpose of a 4-phase streak plate?
To isolate individual colonies.
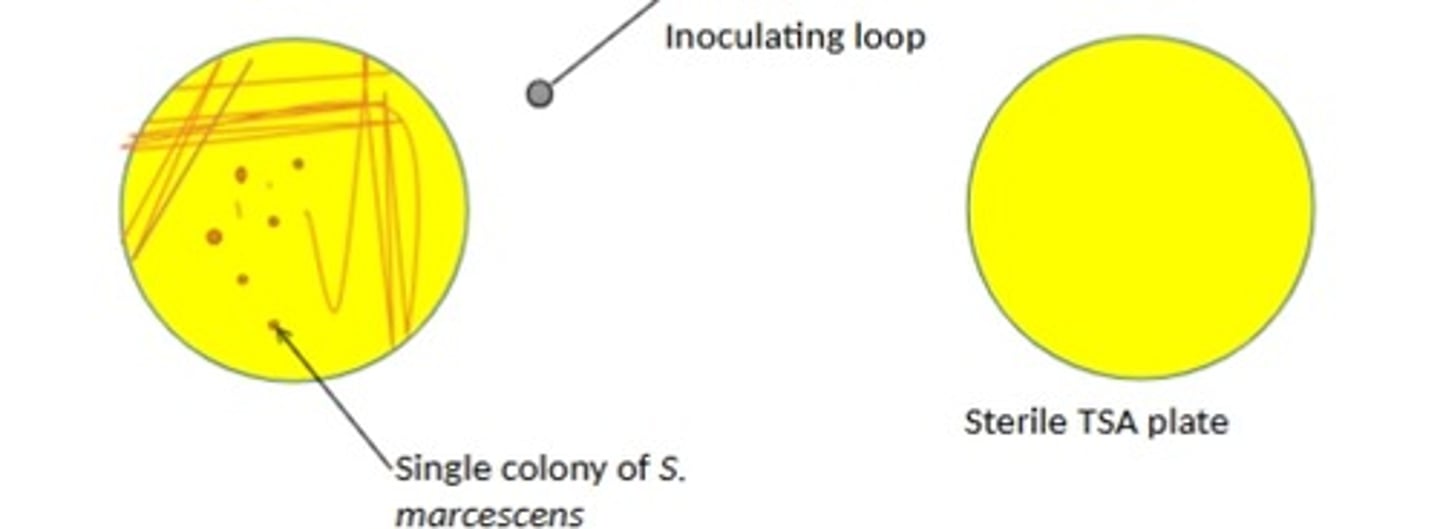
What does a single colony on a plate represent?
A pure culture derived from one bacterial cell.
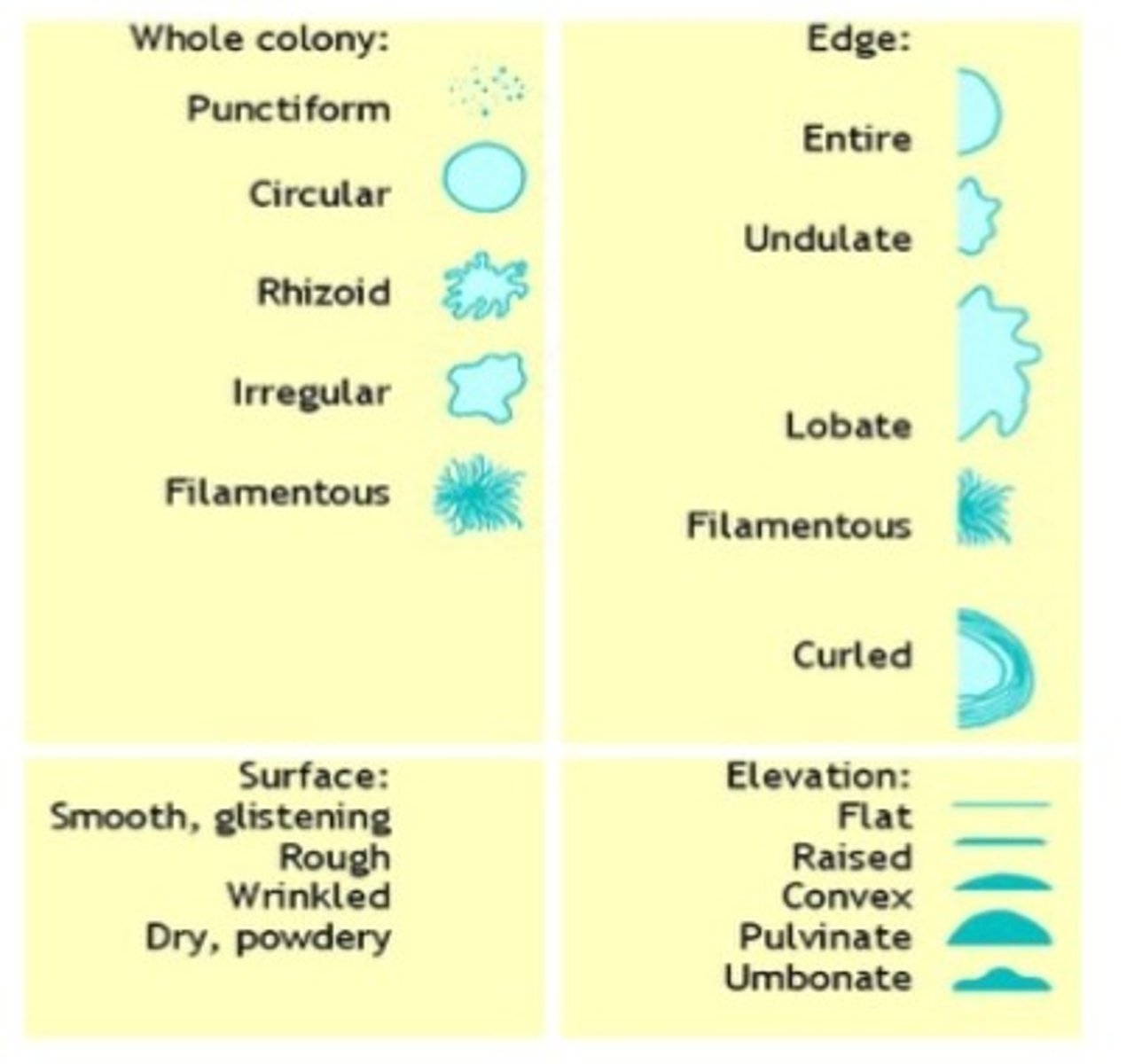
What are common colony edge descriptions?
Entire, undulate, lobate, filamentous
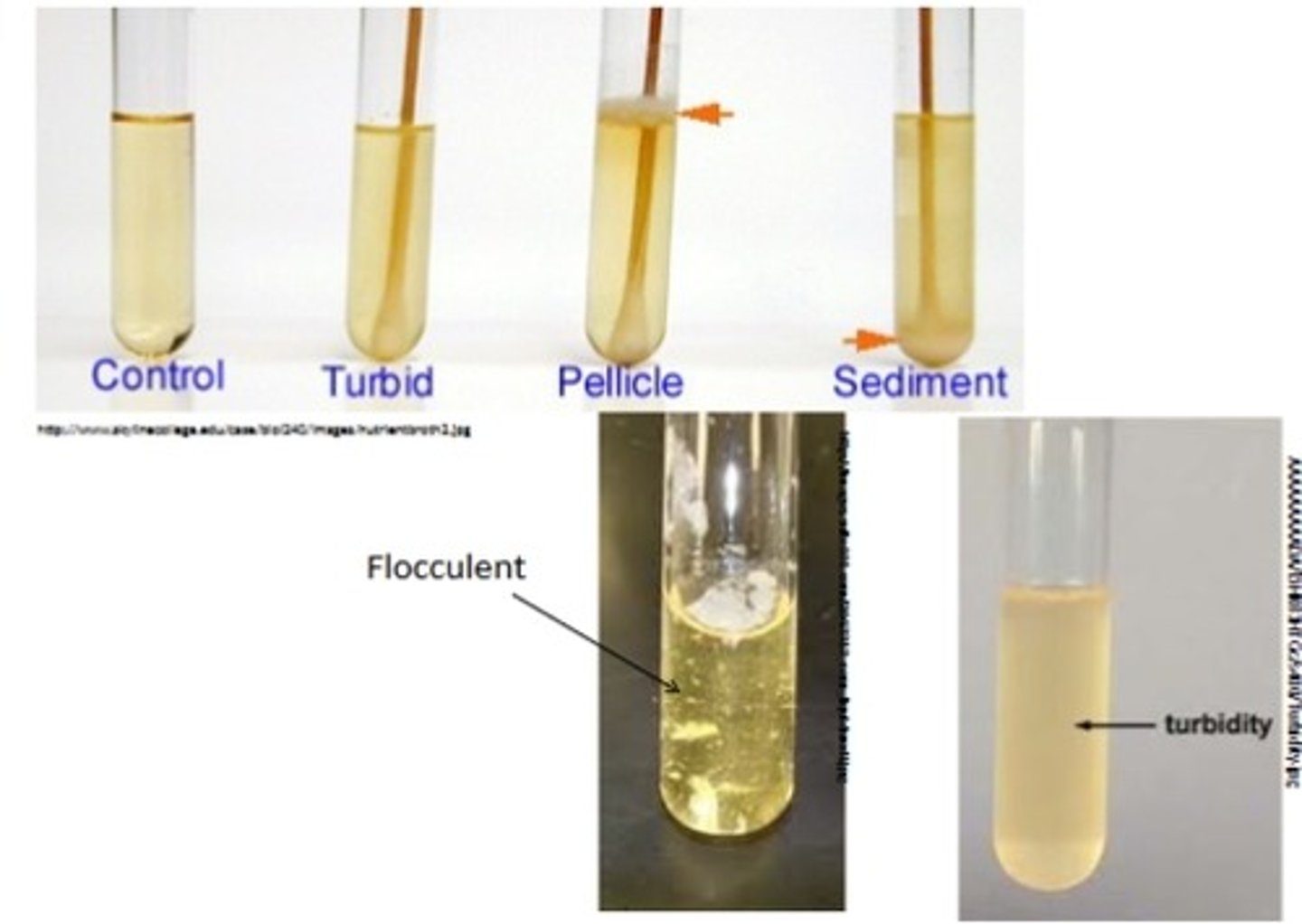
What are common broth growth patterns?
Turbidity, pellicle, sediment, ring

What are the steps of smear prep?
Water drop → bacteria → air dry → heat fix
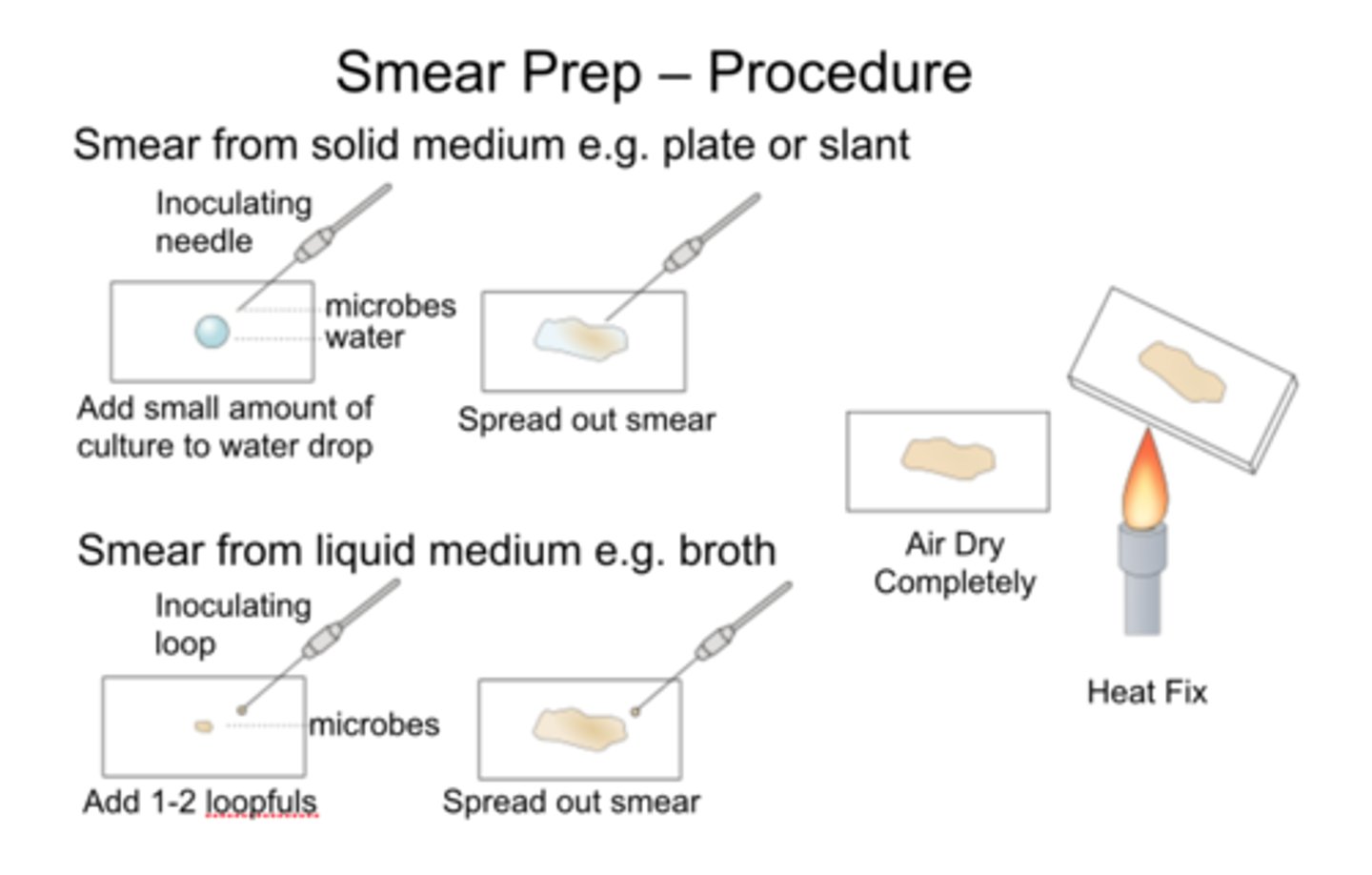
Why do we heat fix a slide before staining?
To adhere cells and kill them.
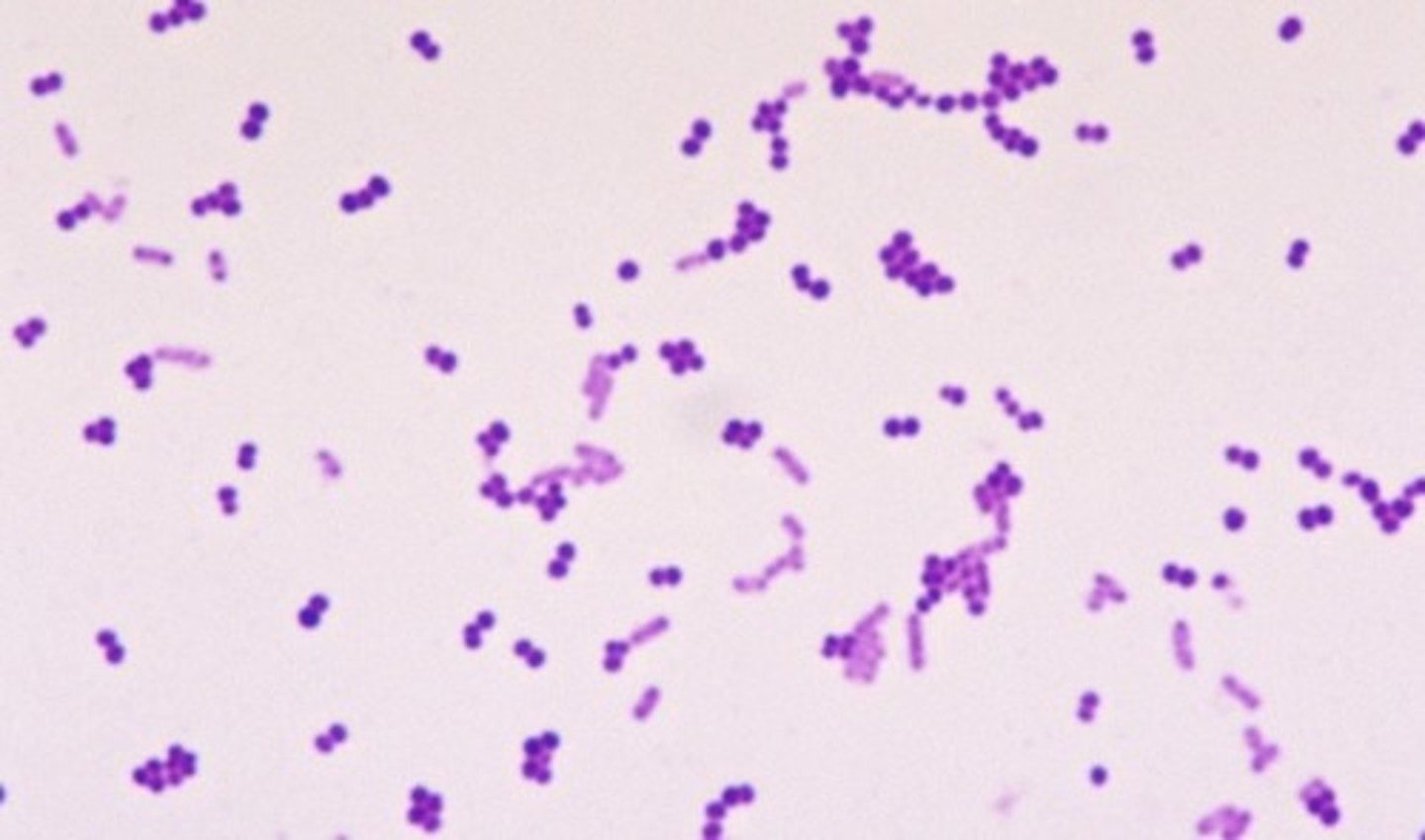
What shape and arrangement does E. coli have?
Rod-shaped bacillus, single or pairs
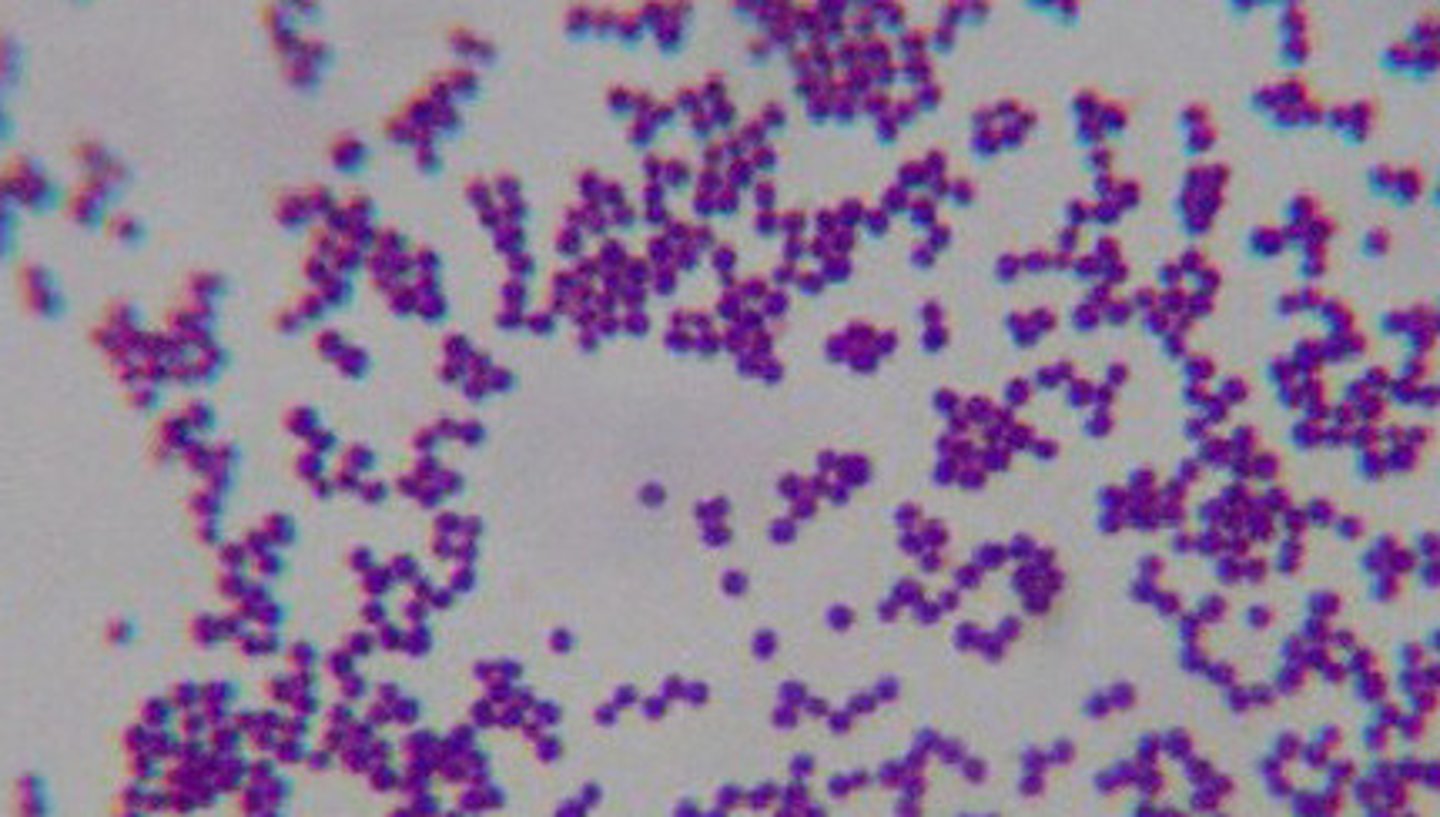
What is the morphology of Staphylococcus epidermidis?
Cocci in clusters (grape-like)
What are the steps of Gram staining?
Crystal violet → iodine → alcohol → safranin
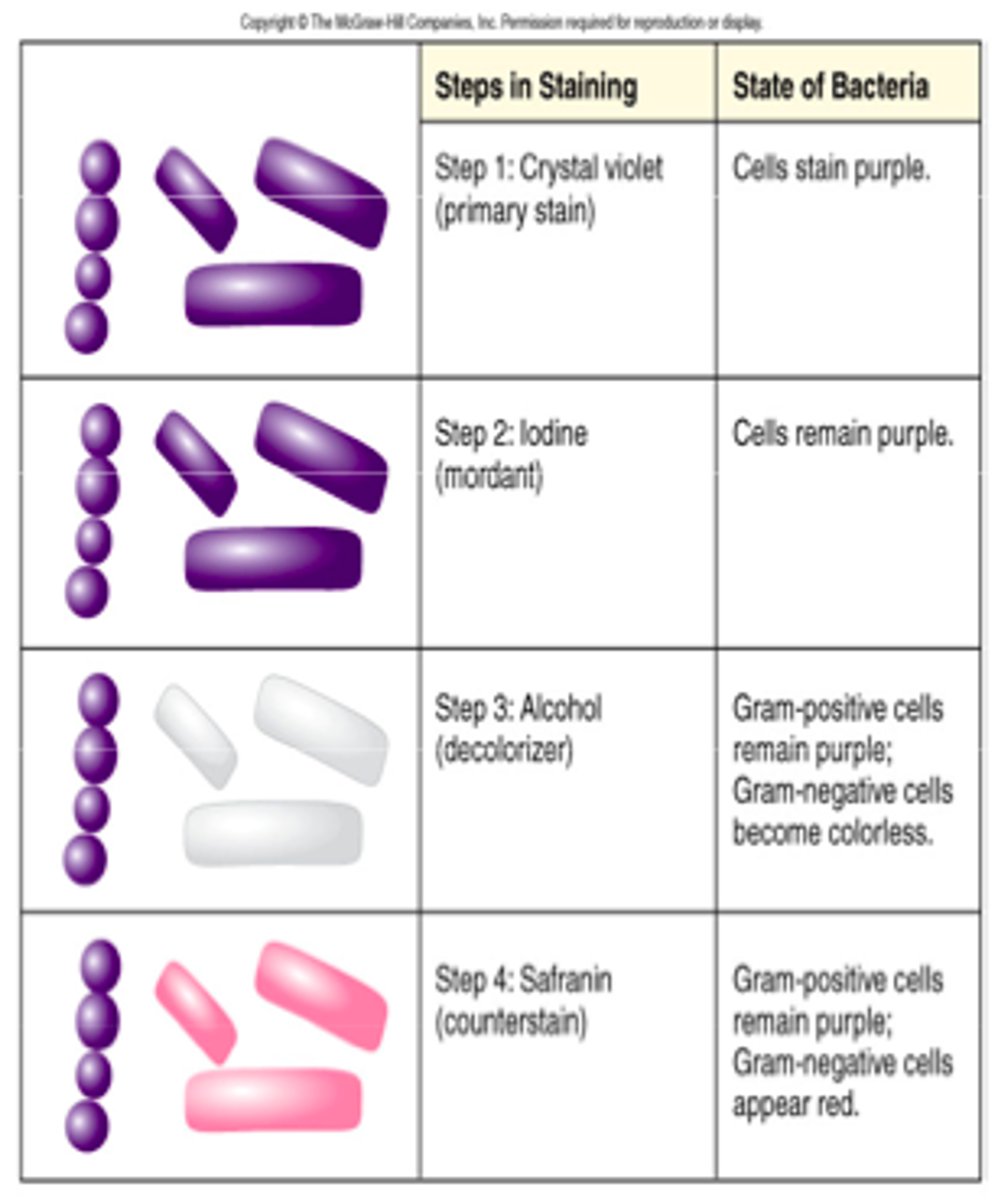
What color does a Gram-positive bacterium stain?
Purple
What color does a Gram-negative bacterium stain?
Pink/red
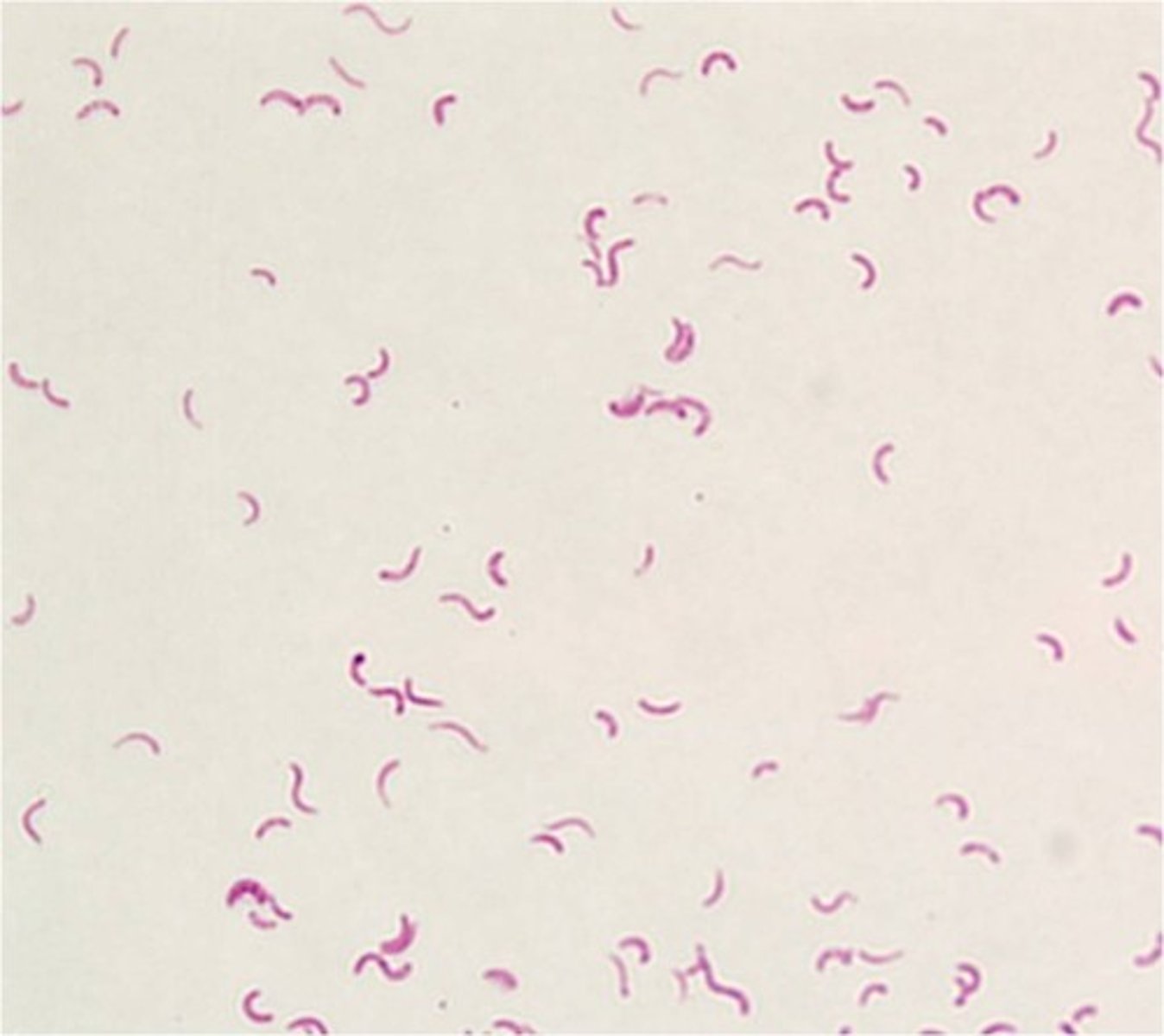
What are the Gram stain results for E. coli and S. epidermidis?
E. coli = Gram-negative rods; S. epidermidis = Gram-positive cocci
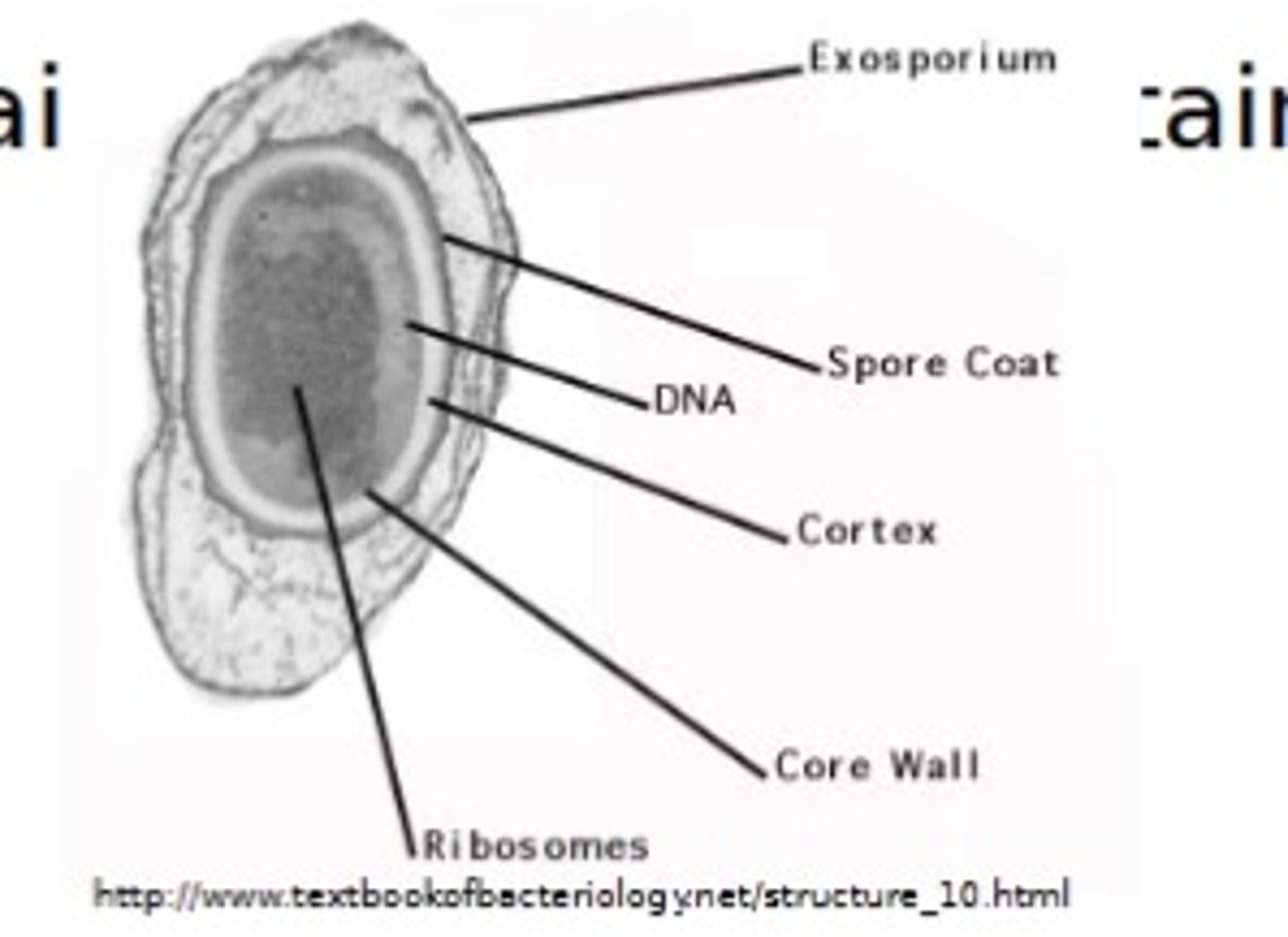
What bacteria form endospores?
Bacillus and Clostridium
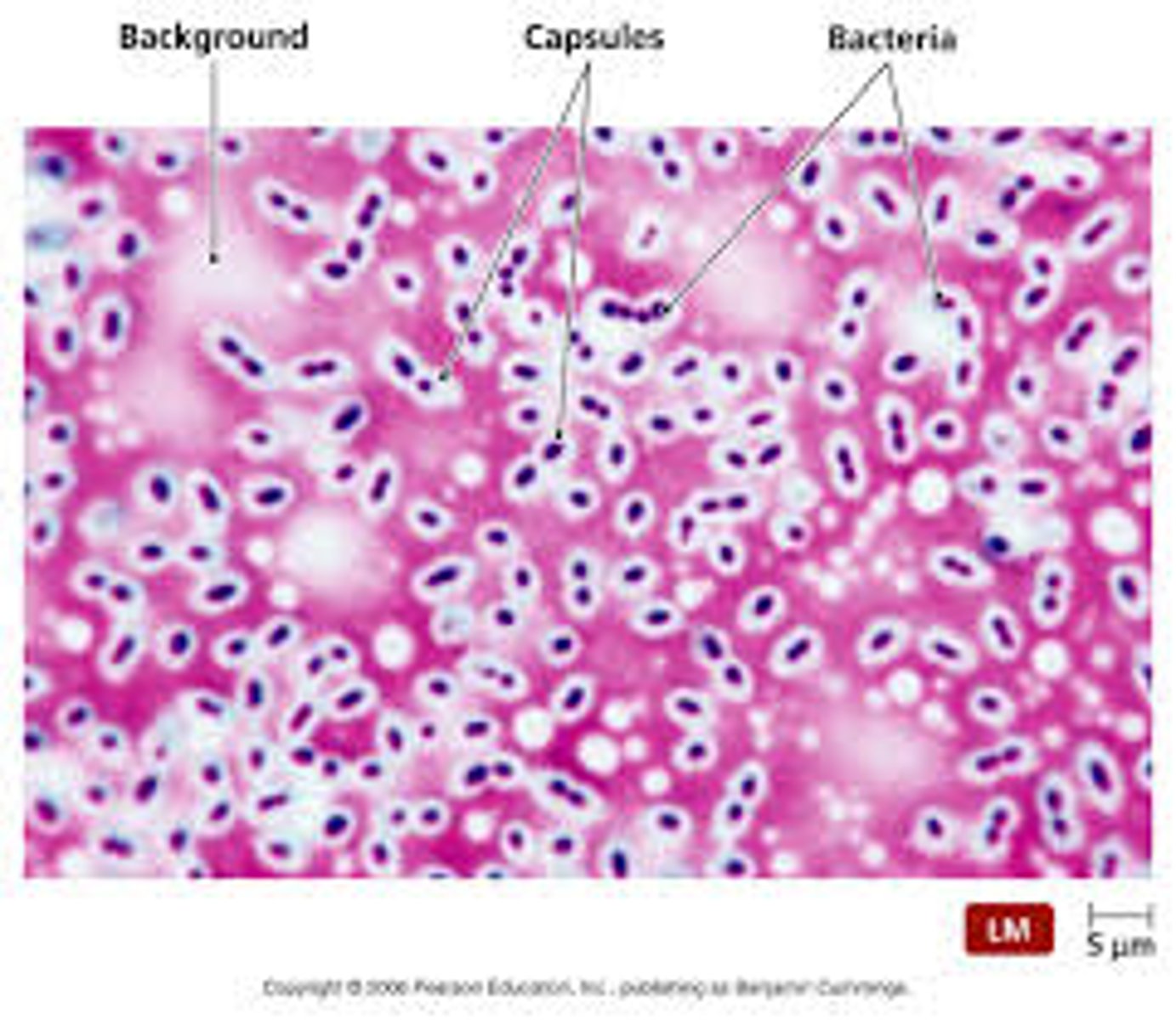
What stain is used for capsules?
Negative stain (India ink or Congo red)
Why don't we heat fix during capsule staining?
Heat destroys or distorts capsules
What is the appearance of acid-fast bacteria?
Bright pink (non-acid-fast = blue)
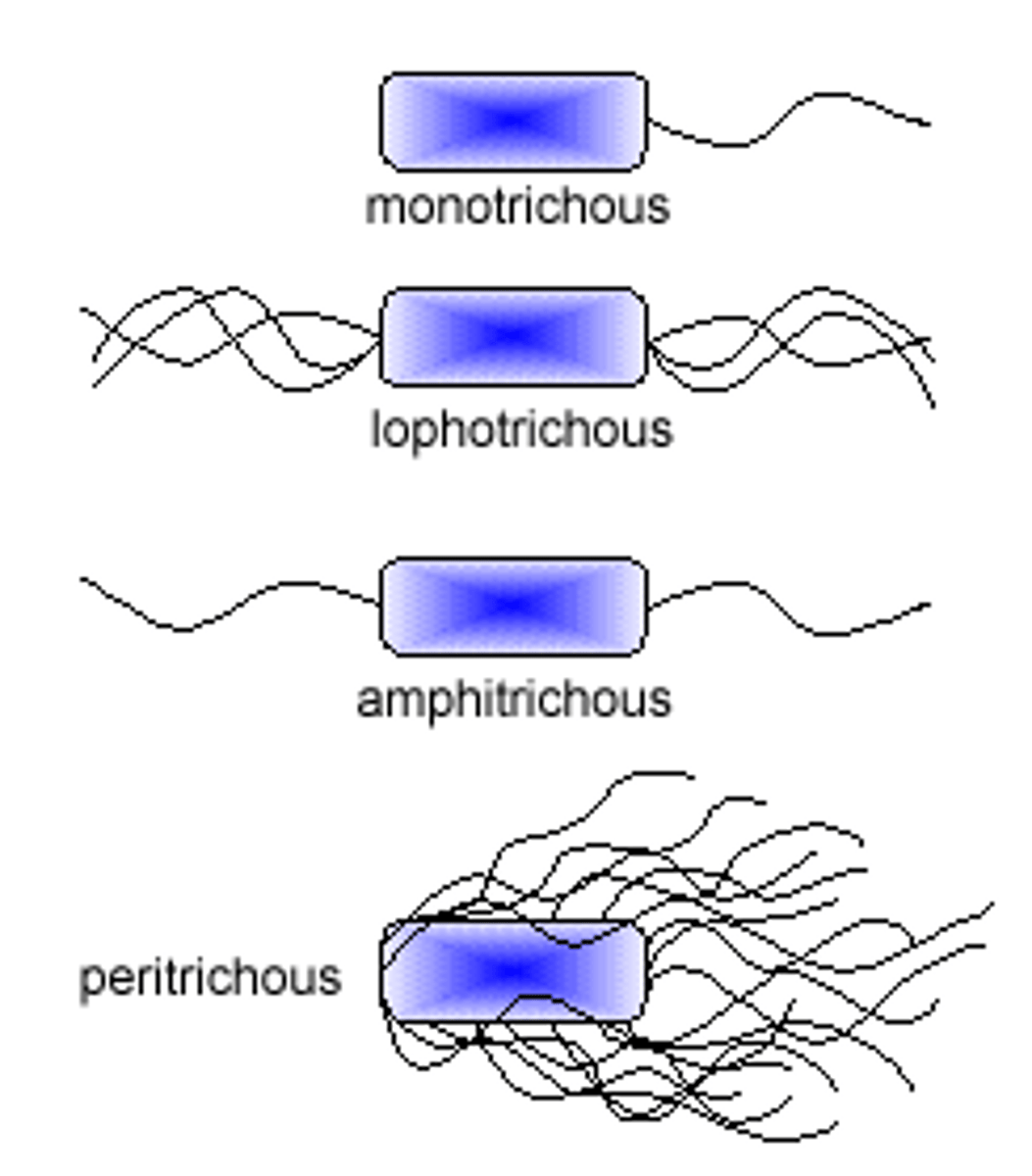
What is monotrichous flagella?
A single flagellum at one end
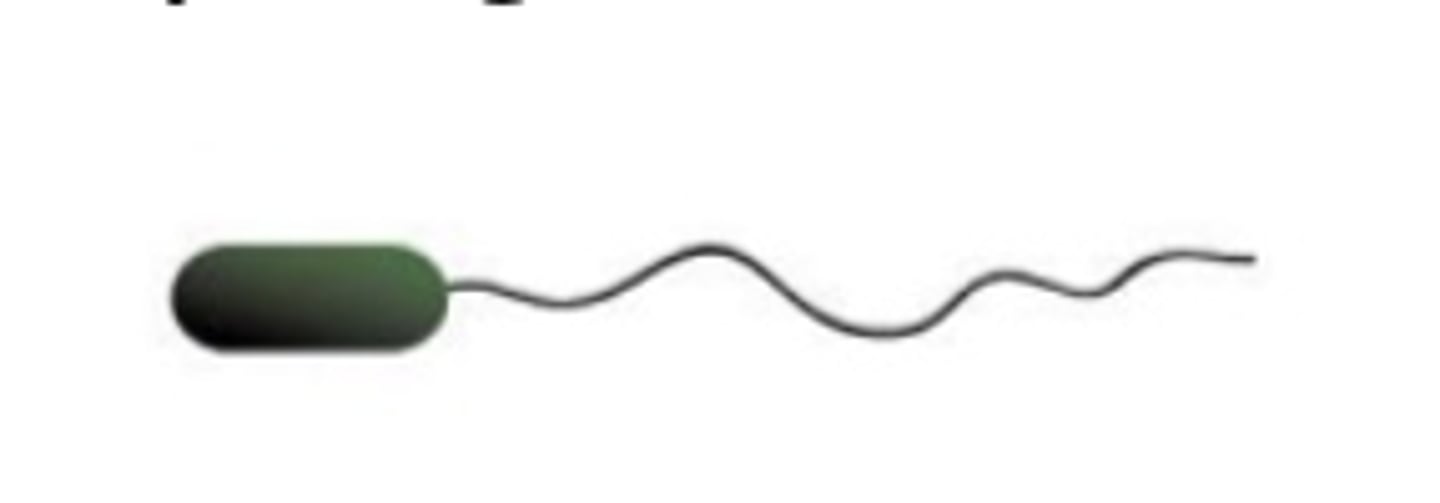

What is peritrichous flagella?
Flagella covering the entire surface
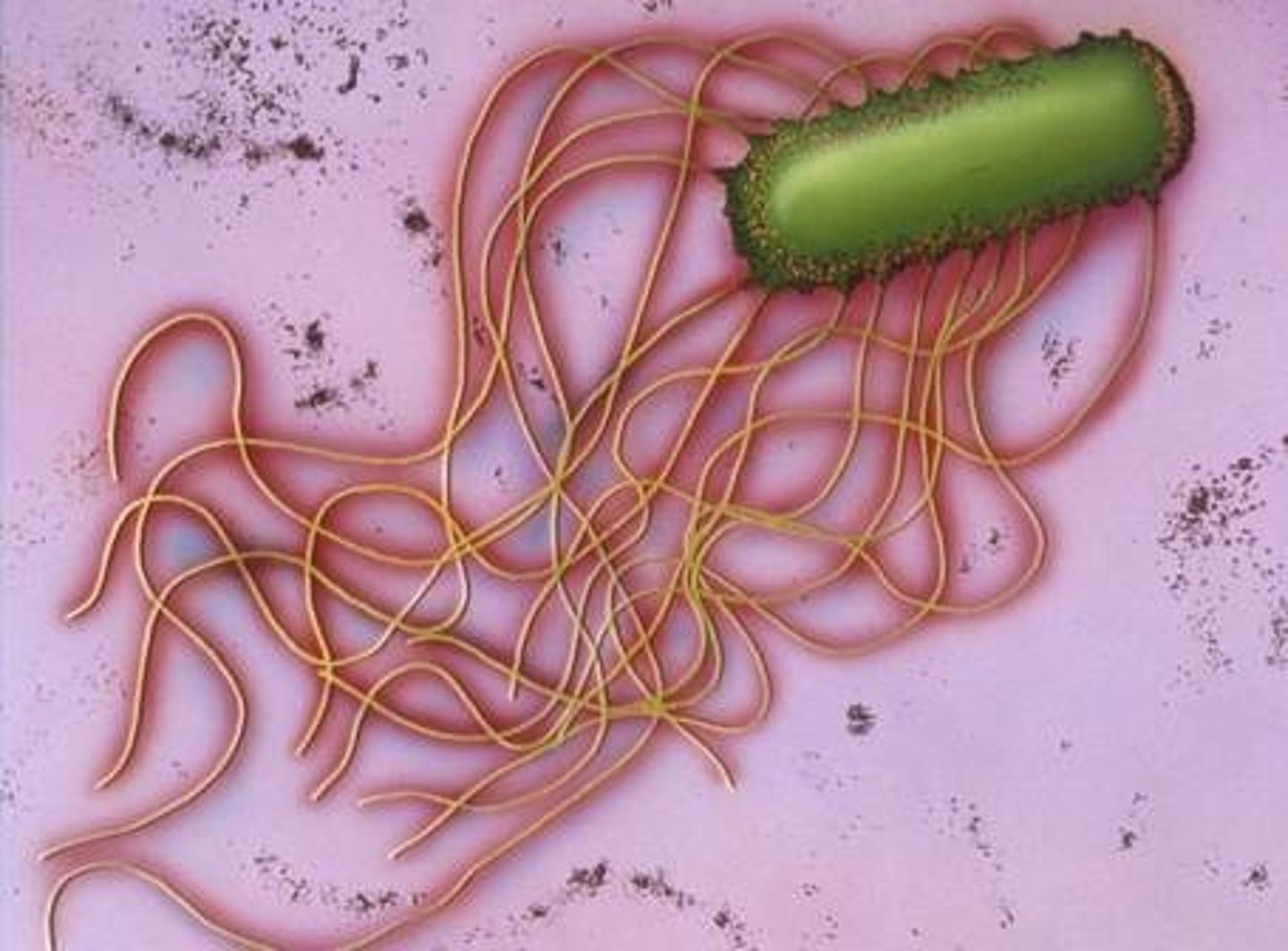
Why are flagella important?
They help bacteria move toward nutrients and away from harm.
What is an obligate aerobe?
Bacteria that require oxygen to grow.
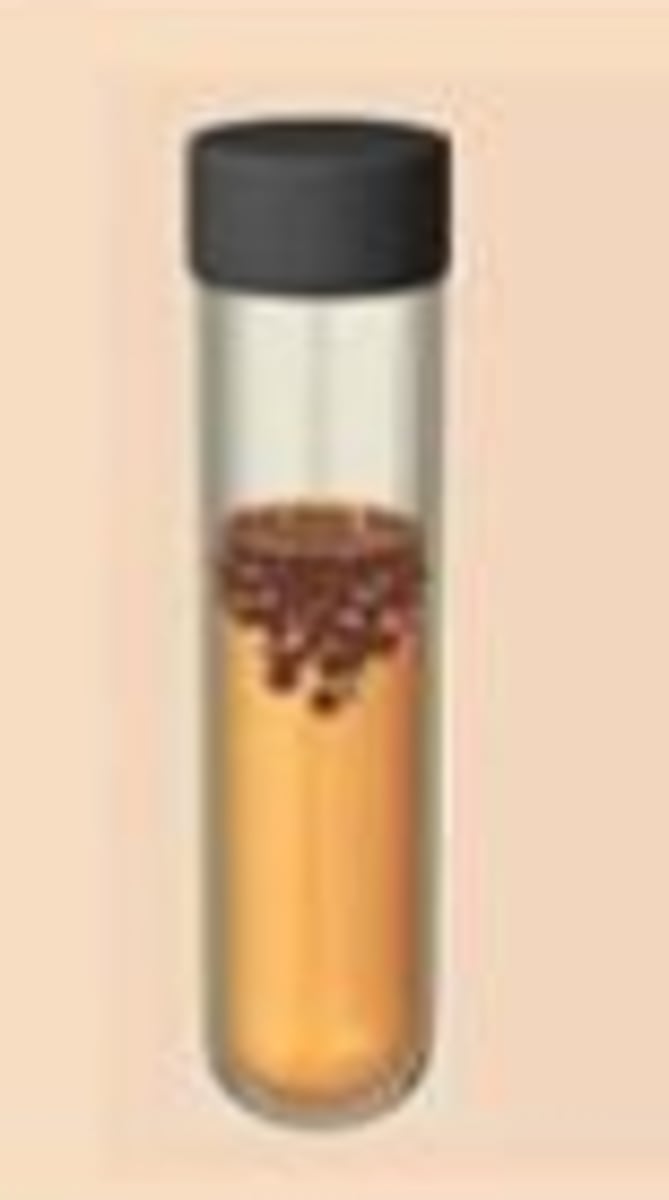

What does thioglycollate broth test?
Oxygen tolerance

What does resazurin indicate?
Pink = oxygen present; colorless = no oxygen

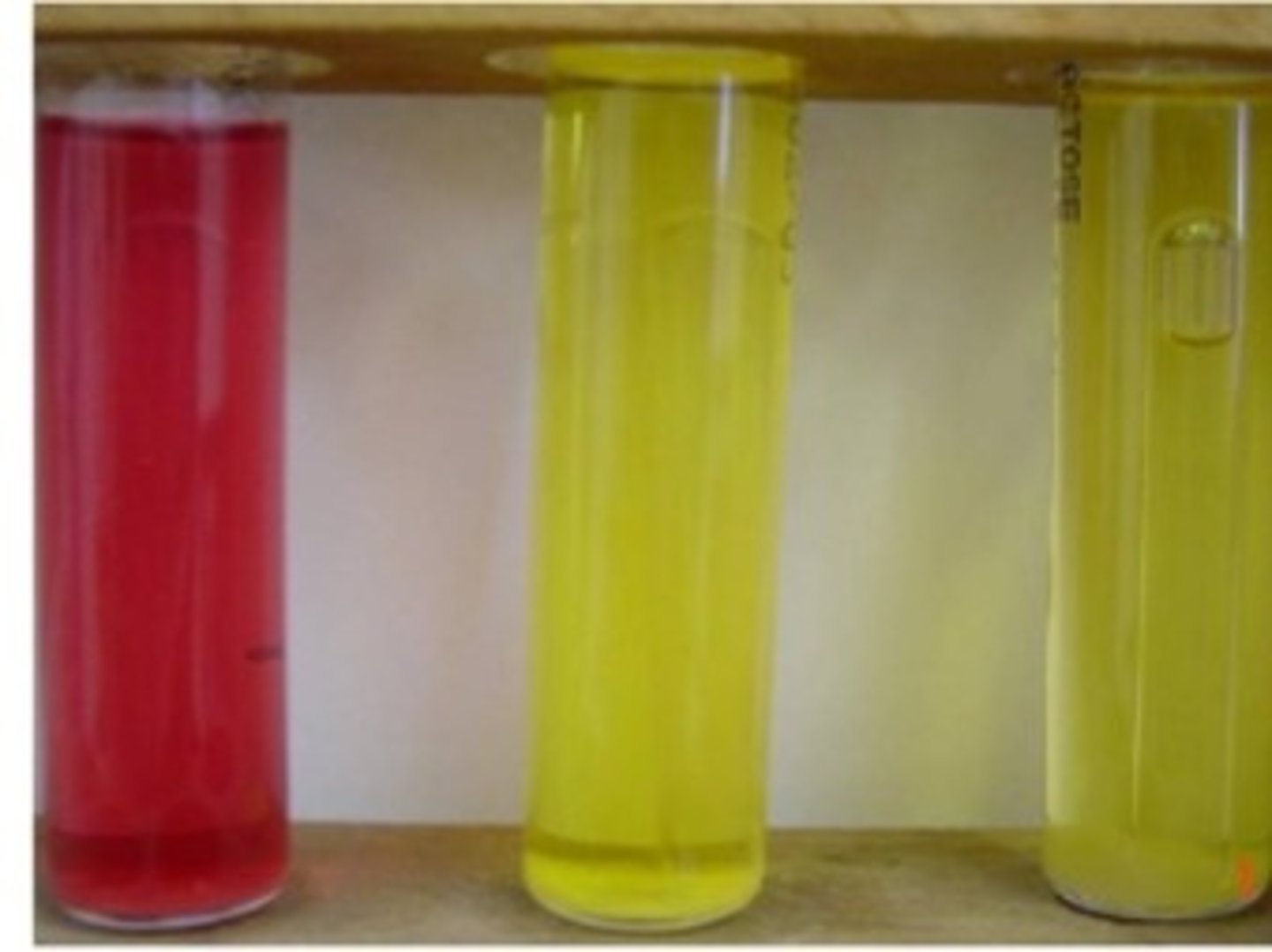
What does yellow phenol red broth indicate?
Acid production from fermentation

What does a bubble in a Durham tube mean?
Gas was produced
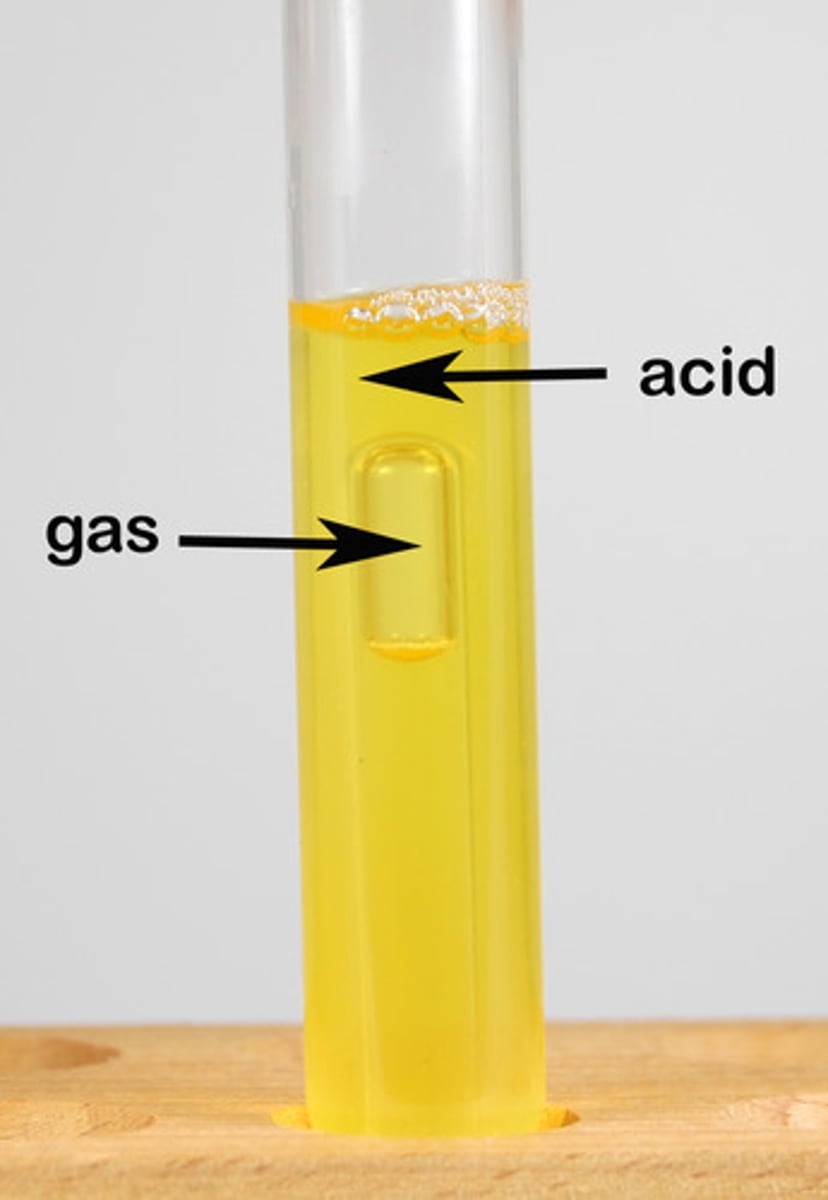

What is the result for E. coli in glucose phenol red?
Yellow with gas (A/G)
What does A/A in a TSI slant mean?
Fermentation of glucose and lactose/sucrose
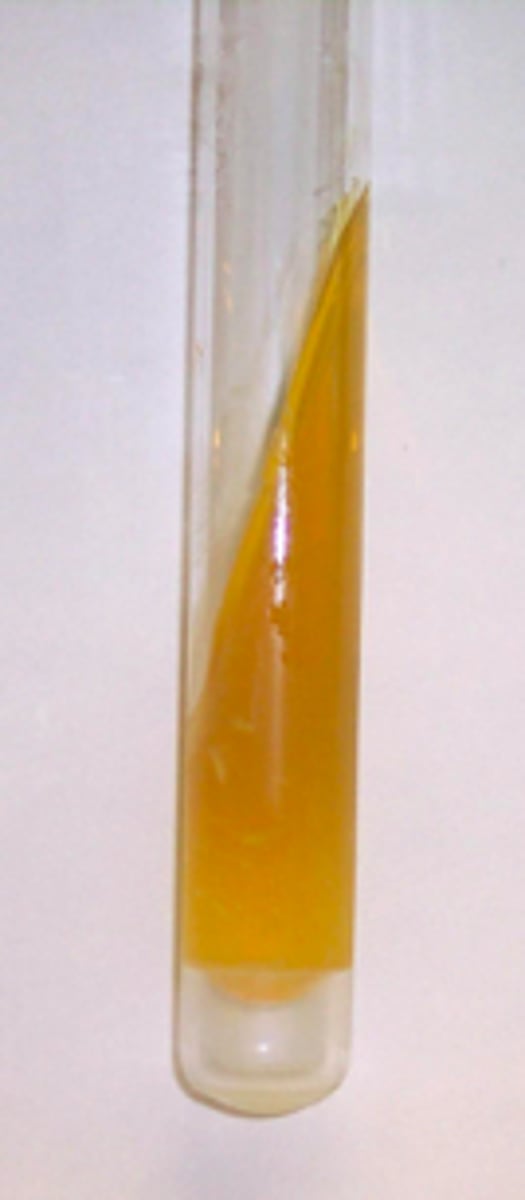

What does K/A in a TSI slant mean?
Glucose fermentation only (red slant, yellow butt)

What causes black precipitate in a TSI tube?
H₂S production reacts with iron salt

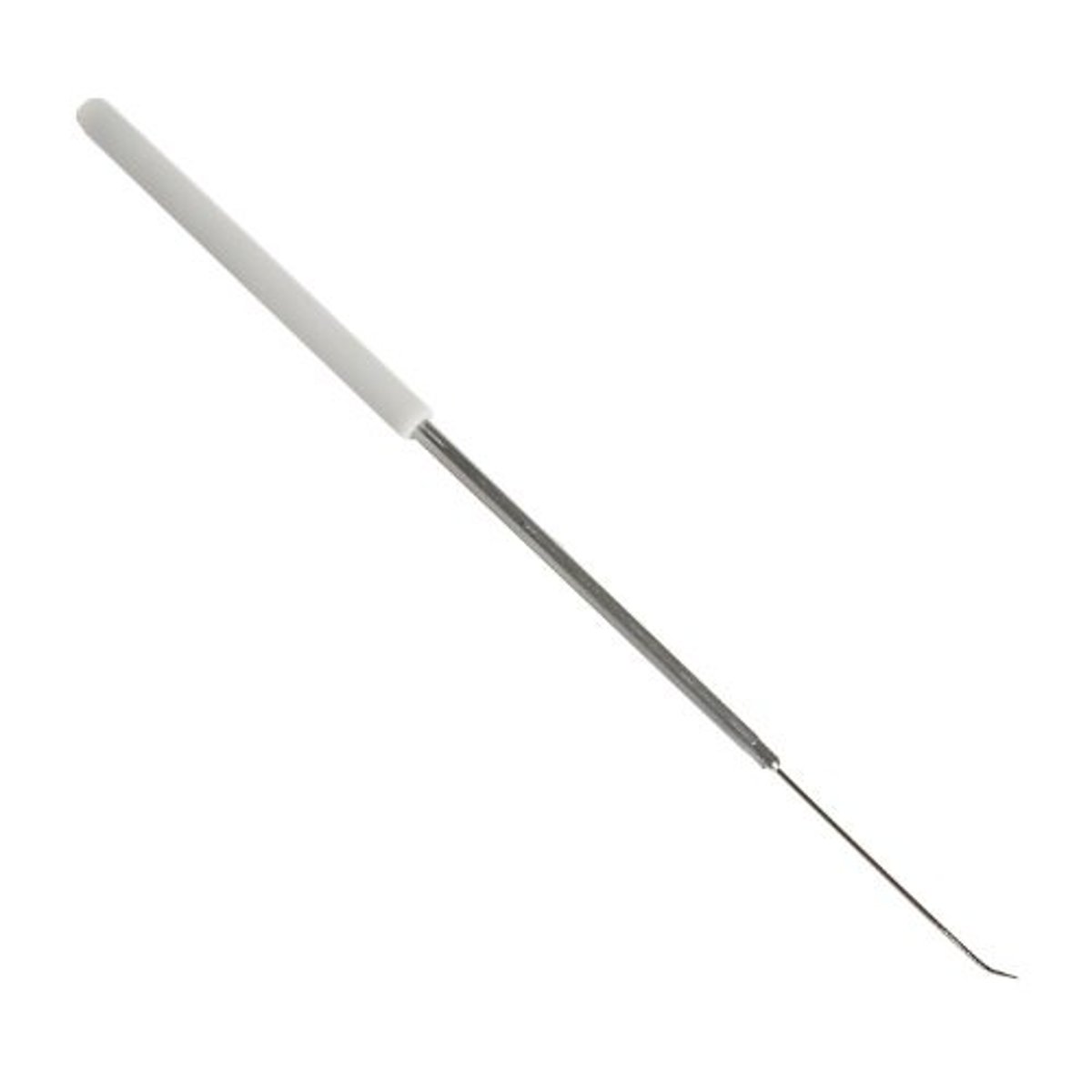
What tool do we use to inoculate a TSI slant?
Inoculating needle

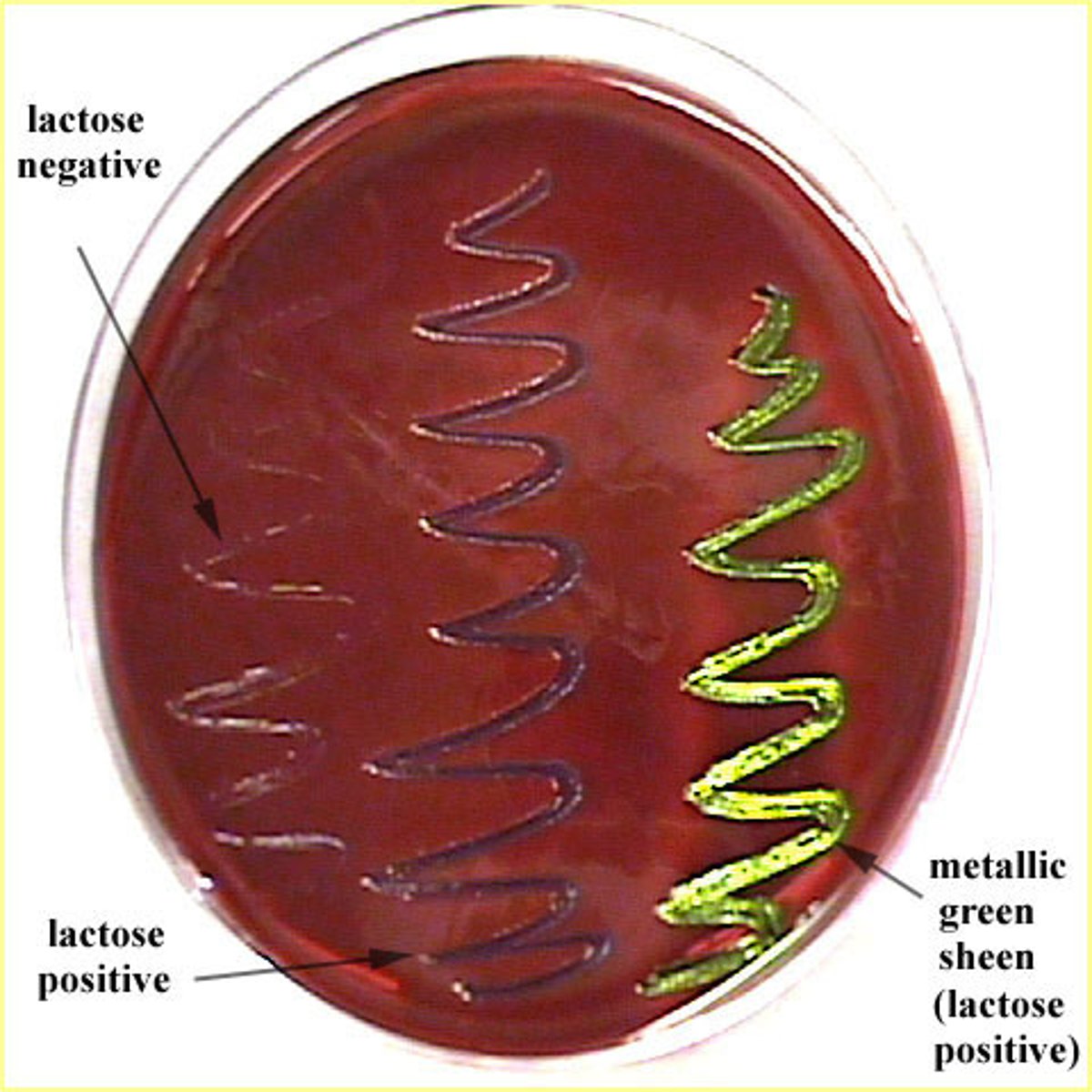
What does EMB select for and differentiate?
Gram-negatives; strong lactose fermenters = green sheen
What does MAC agar indicate?
Pink colonies = lactose fermentation
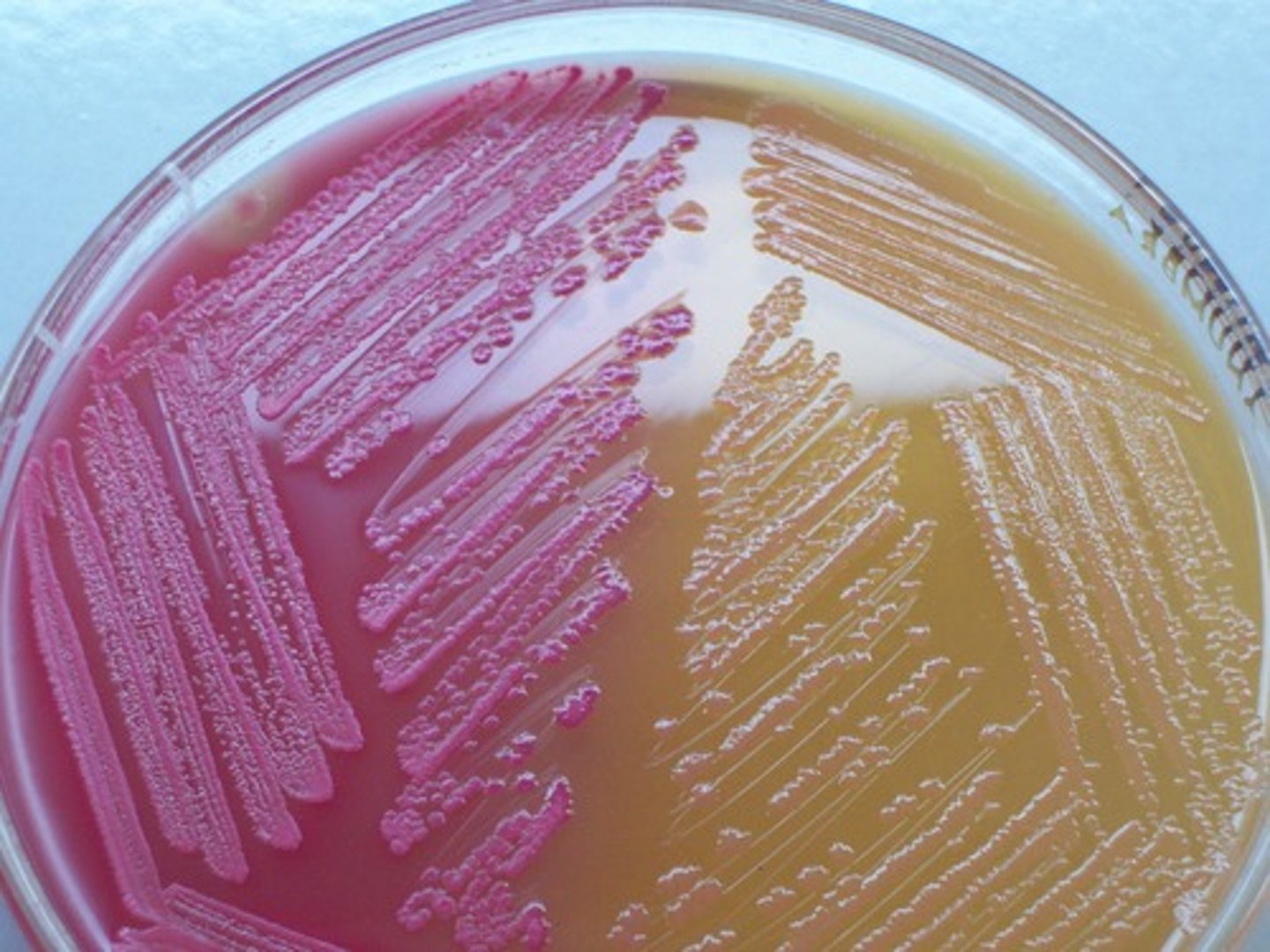
What does MSA test for?
Staphylococcus and mannitol fermentation (yellow = positive)
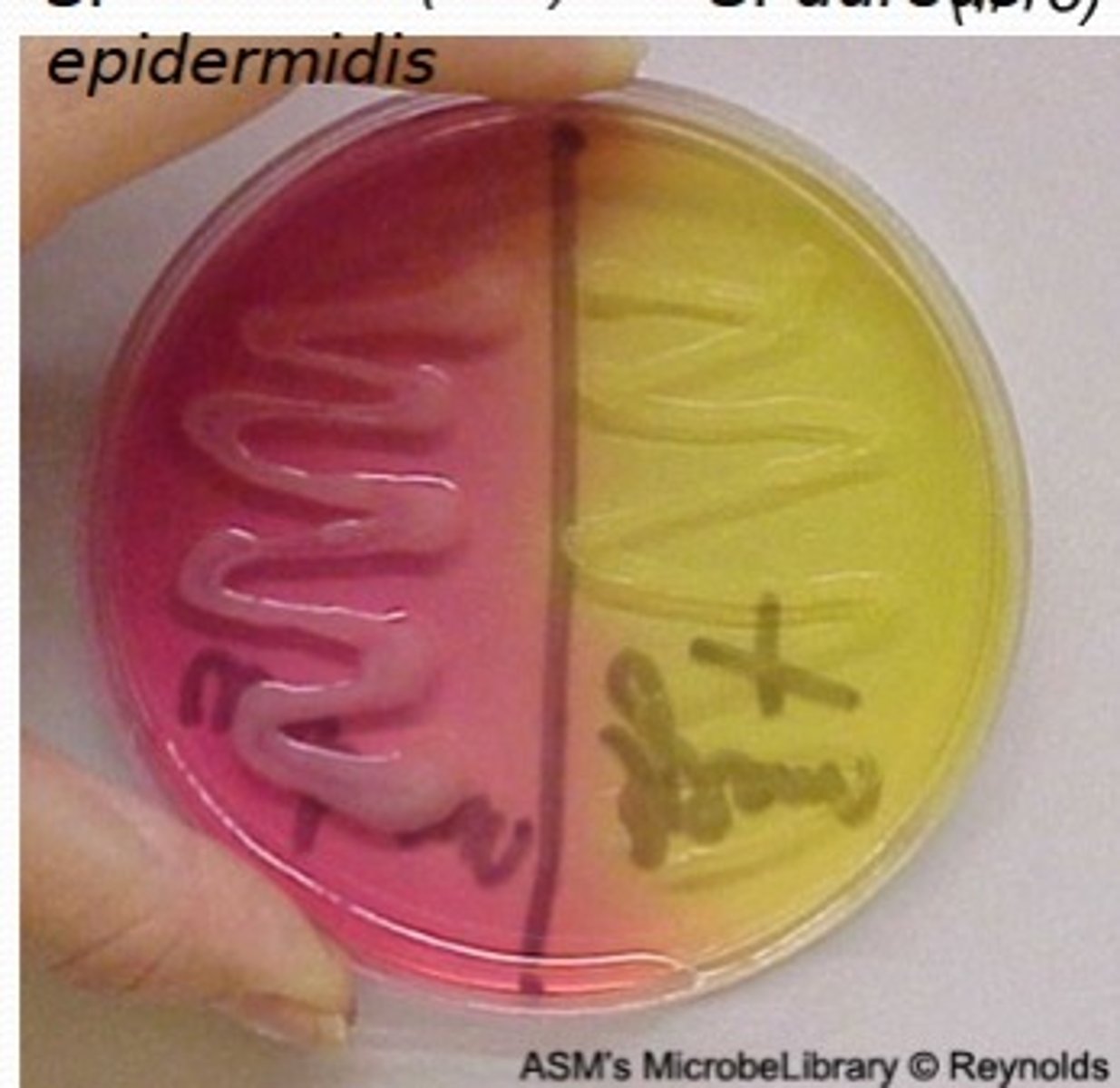
What does PEA select for?
Gram-positive bacteria
What does CNA media select for?
Gram-positive organisms; inhibits Gram-negative
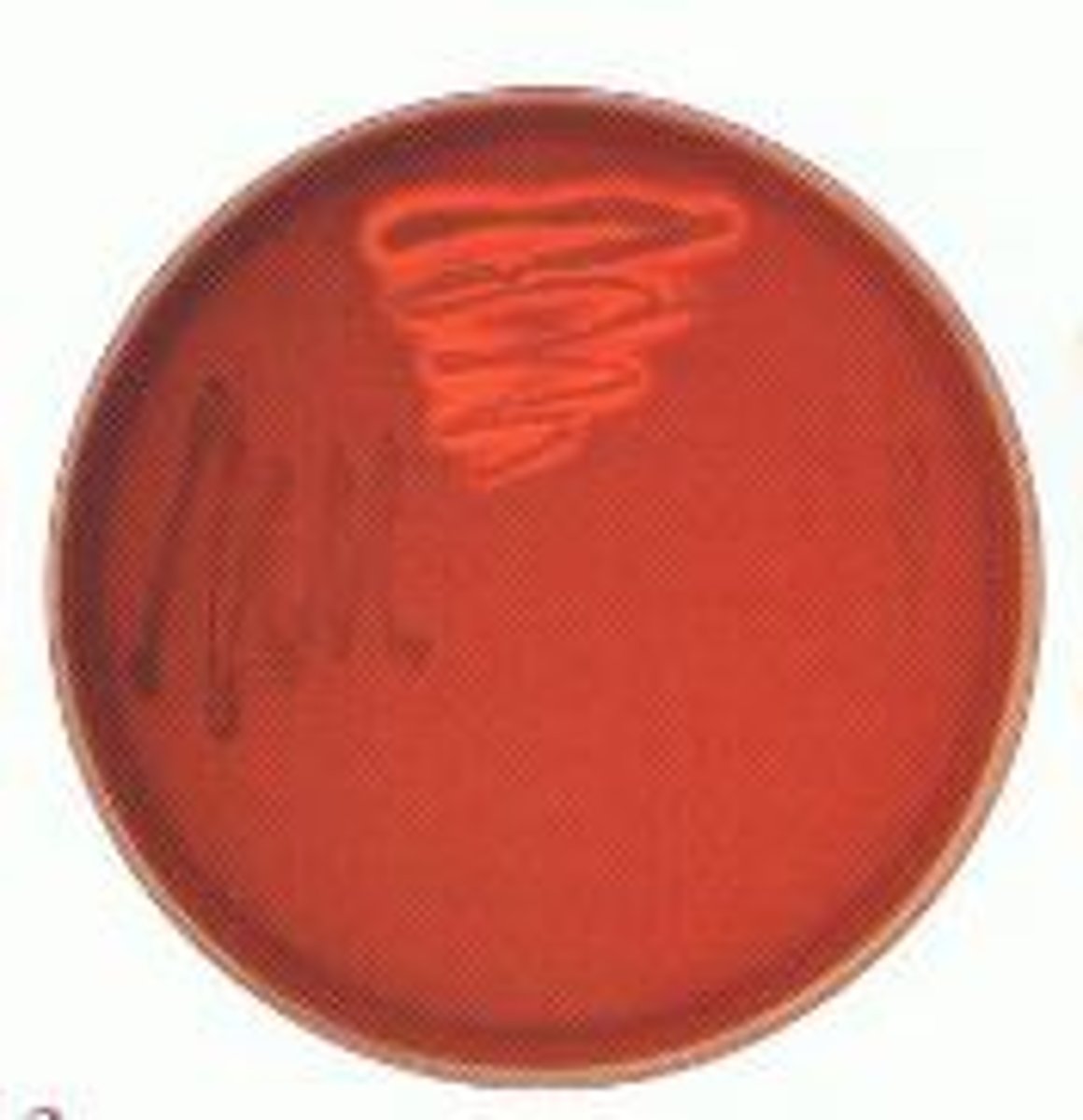
What is beta hemolysis?
Complete RBC lysis; clear zone
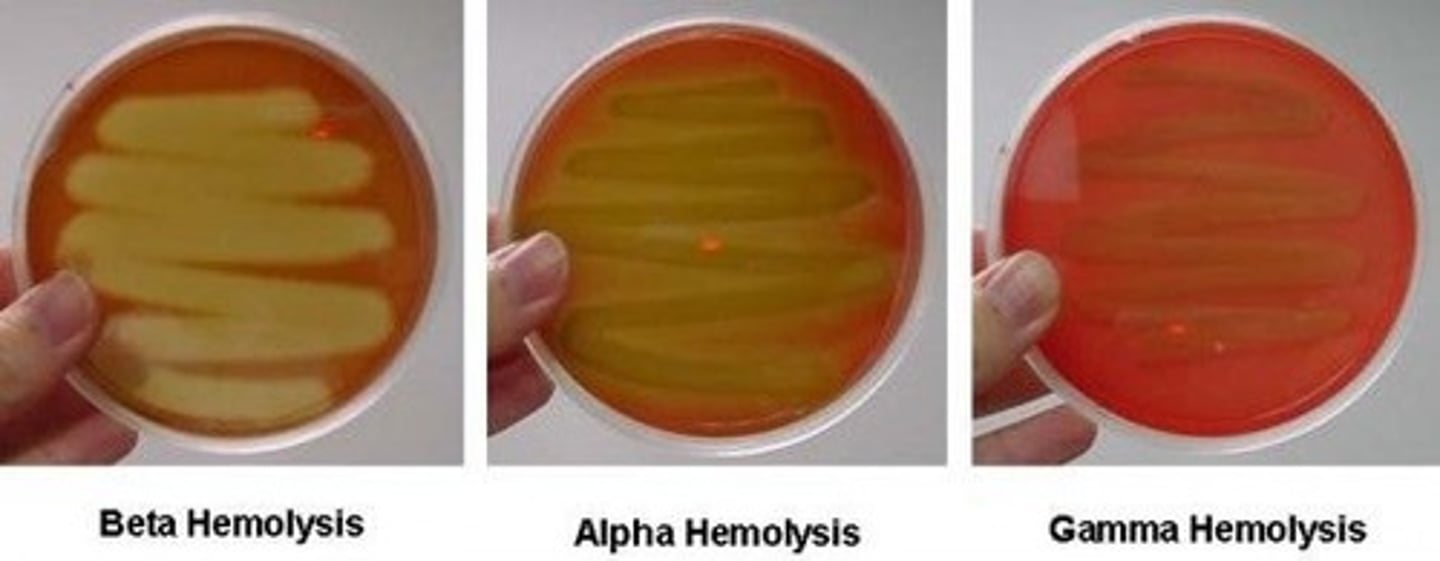
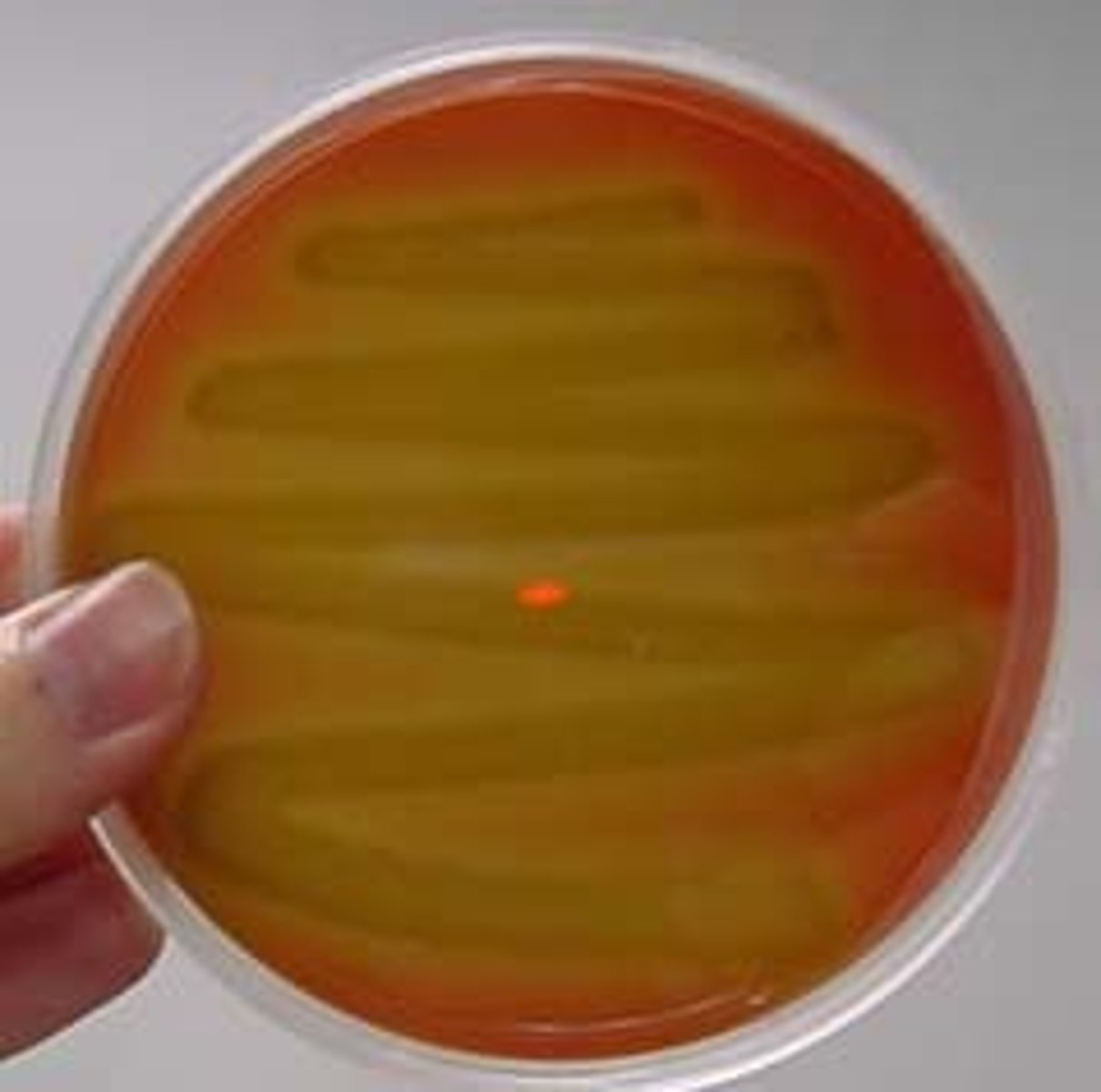
What is alpha hemolysis?
Partial lysis; greenish discoloration
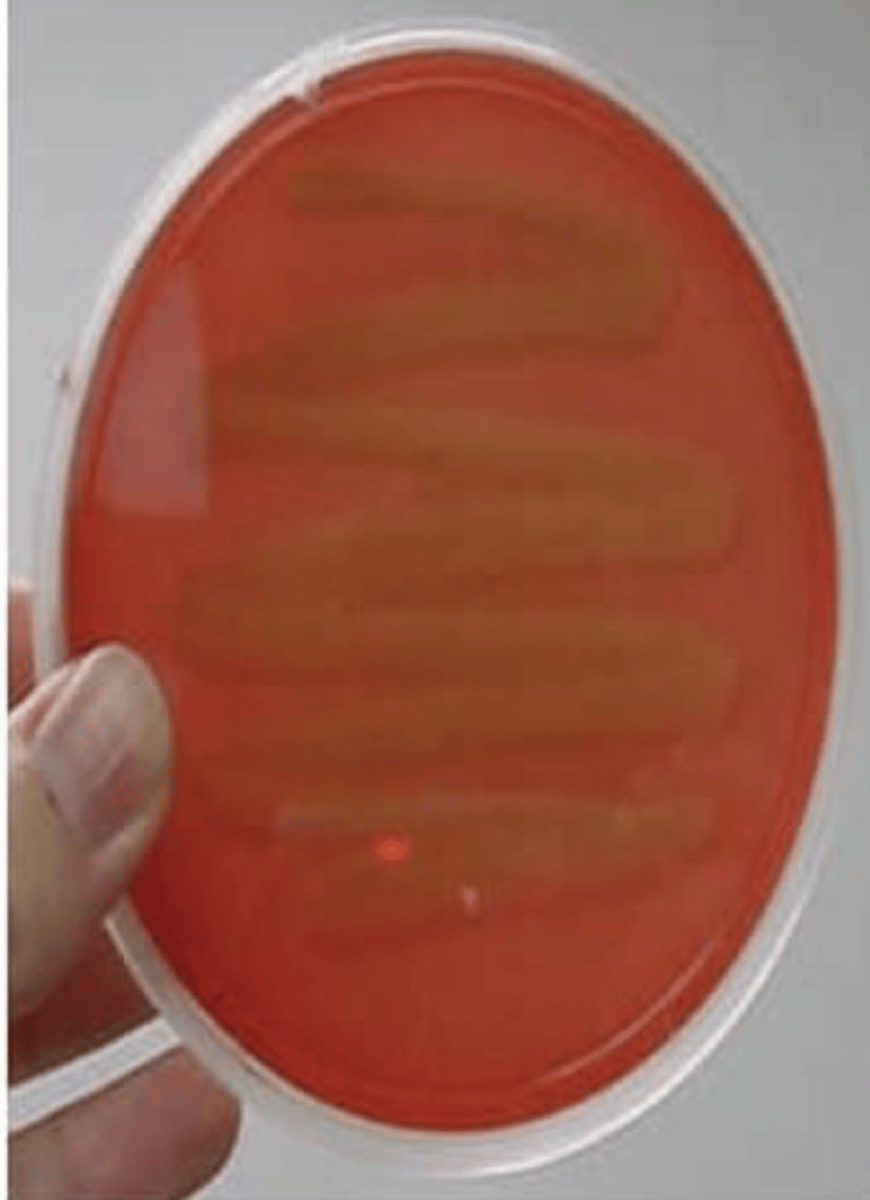
What is gamma hemolysis?
No hemolysis; red unchanged
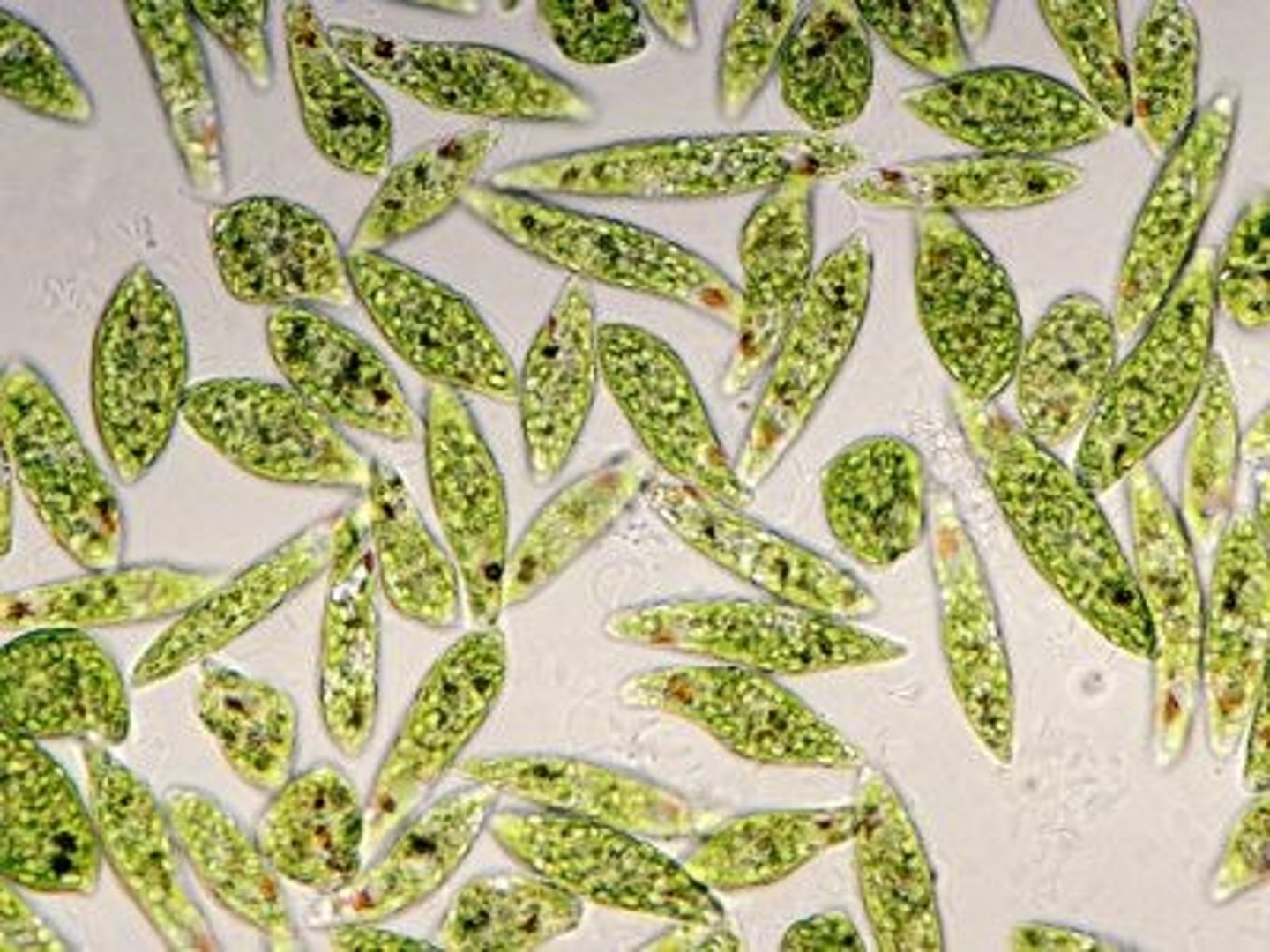
What does Euglena look like under a microscope?
Green, flagellated, has red eyespot
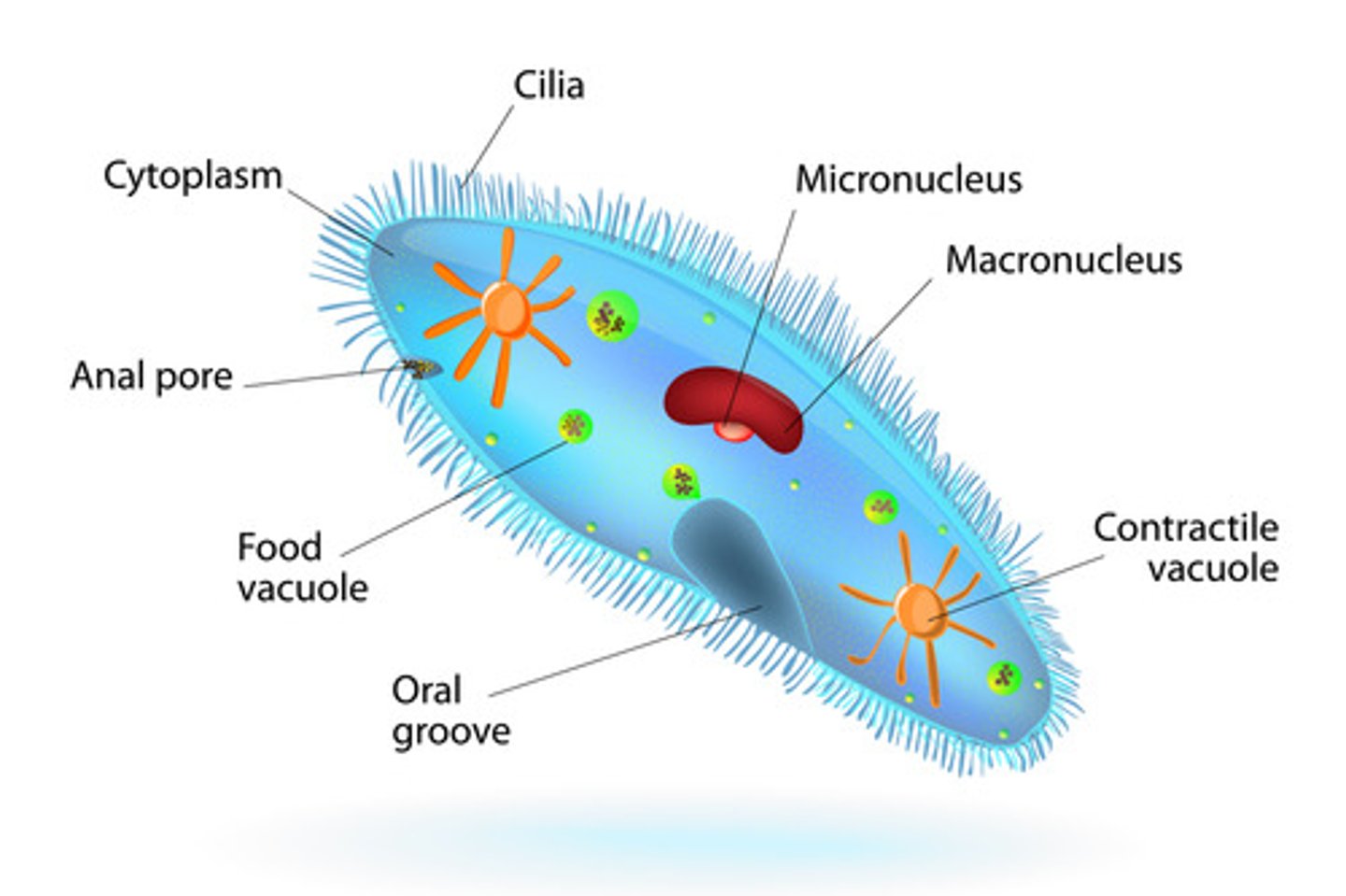
How does Paramecium move and feed?
Uses cilia; has an oral groove
What is characteristic of Amoeba proteus?
Irregular shape, pseudopods for movement
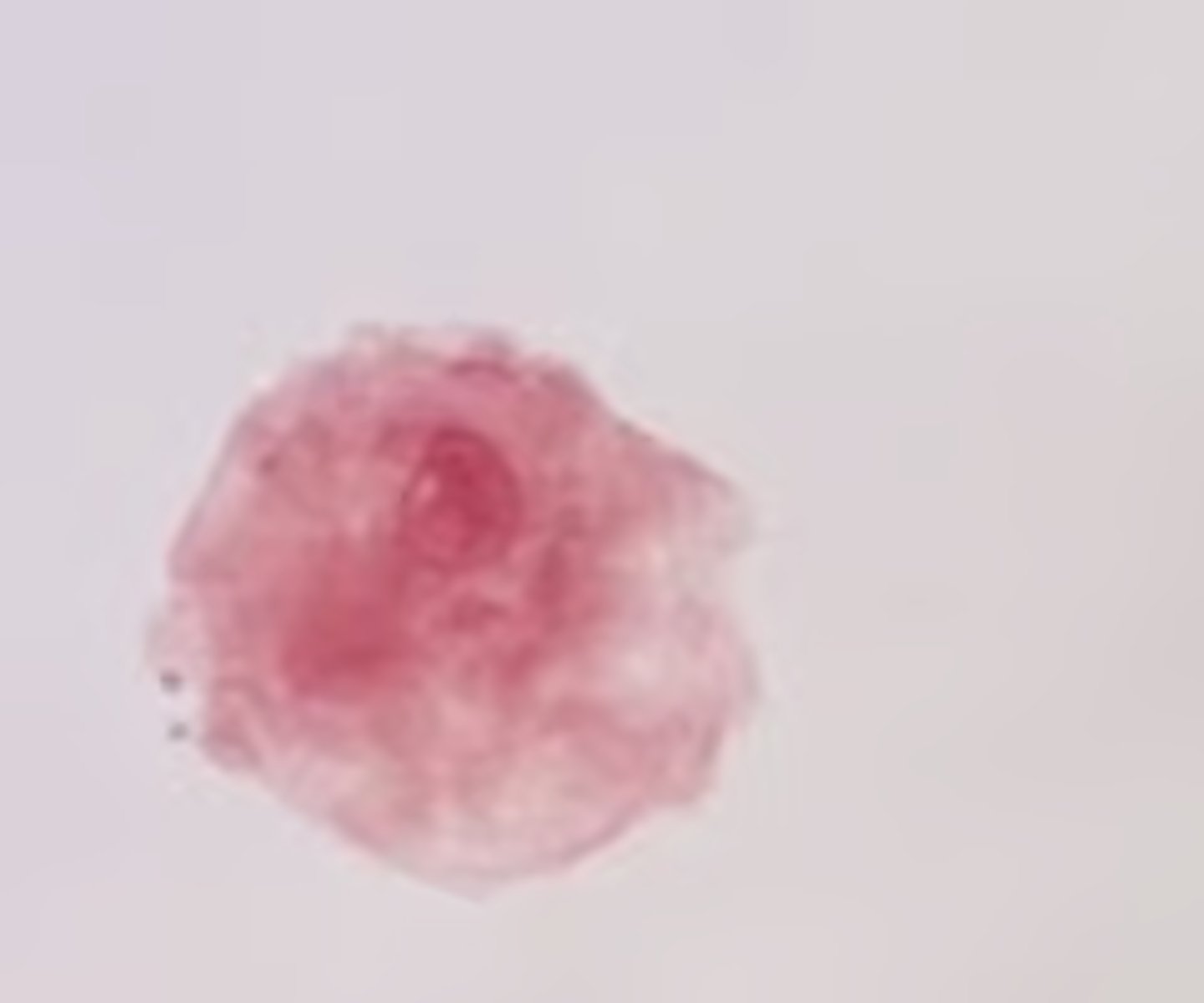

What feature helps Stentor anchor itself?
A hold-fast and trumpet shape
What makes protozoa hard to treat medically?
They are eukaryotic and similar to human cells
what are facultative anaerobes
Organisms that can survive with or without oxygen.
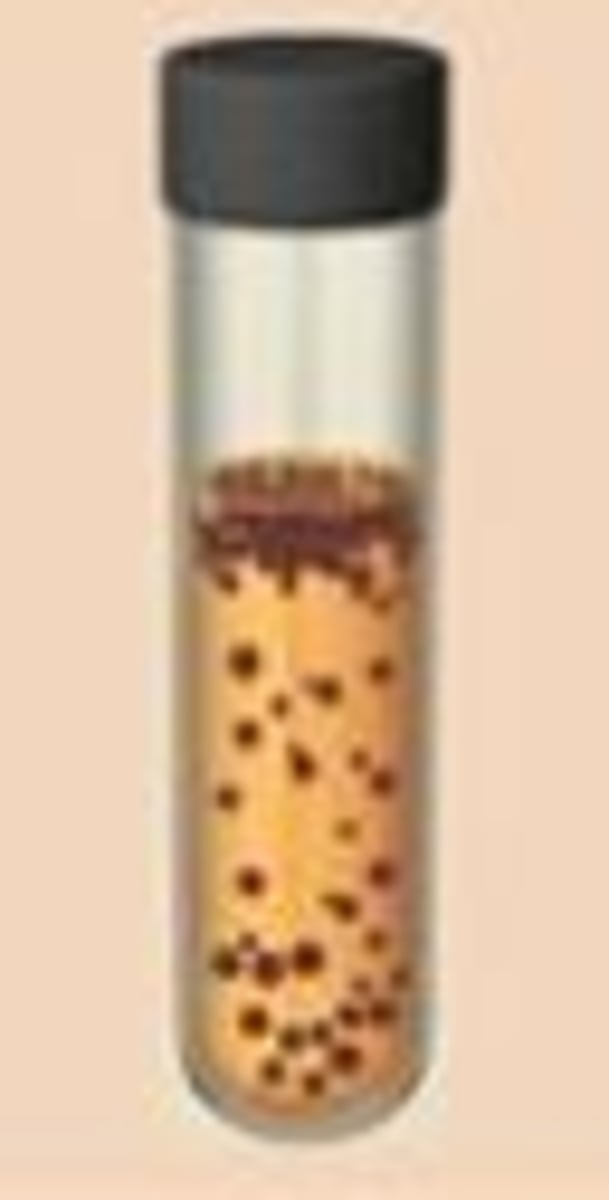

what are obligated anaerobes
organisms that cannot use oxygen as an electron acceptor
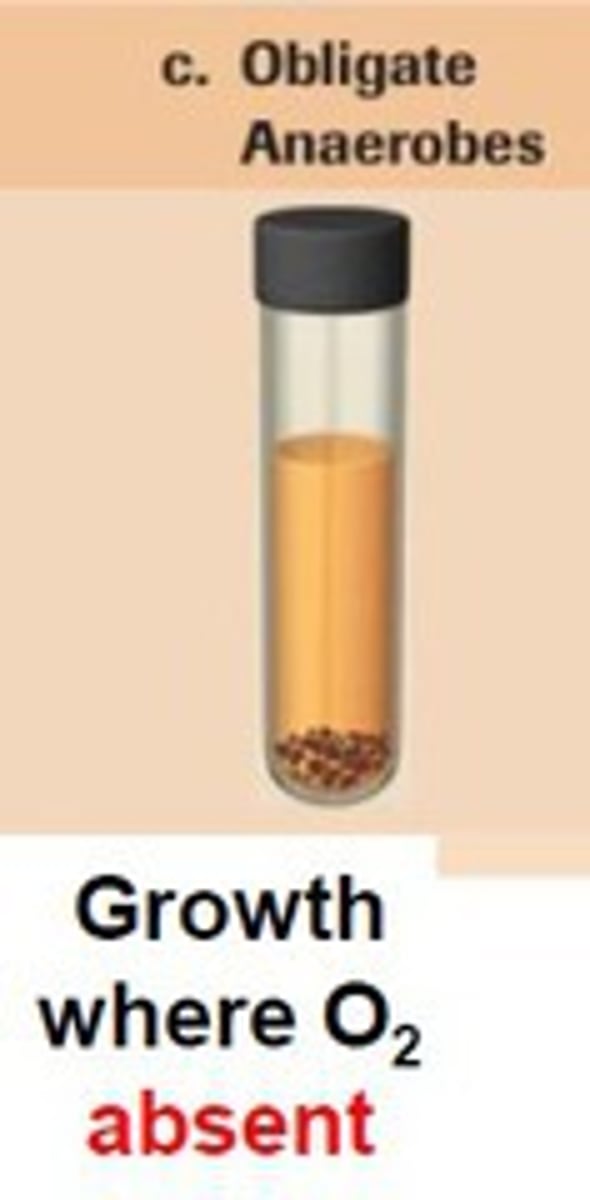

What are aerotolerant anaerobes?
only anaerobic growth; but continues in presence of oxygen
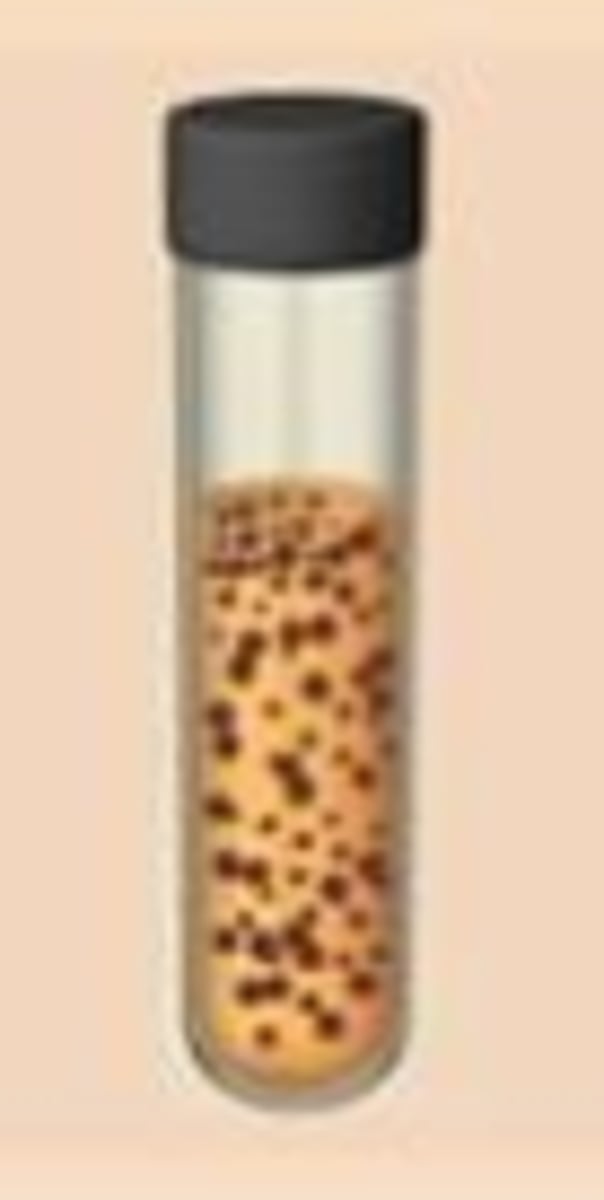

What are microaerophiles?
only aerobic growth; oxygen required in low concentration
