Human Physiology Lab Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:41 AM on 3/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
1
New cards
4 Primary Tissues
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous
2
New cards
Epithelial Tissue
sheets of tightly packed cells (membranes and glands); in charge of protection, secretion, excretion, absorption
3
New cards

Which epithelial tissue is this?
Simple

4
New cards
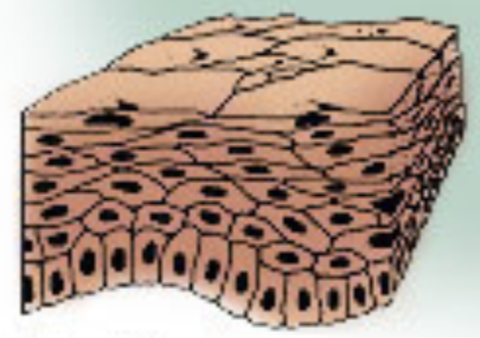
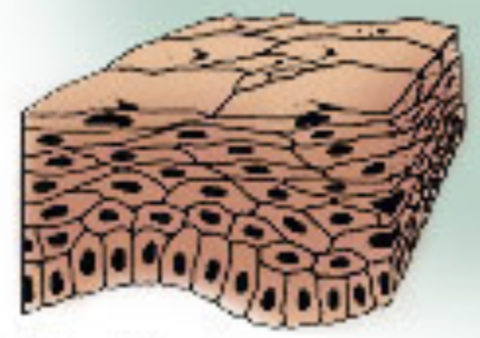
Which epithelial tissue is this?
Stratified
5
New cards

Which epithelial tissue is this by cell shape?
Squamous (flat)

6
New cards
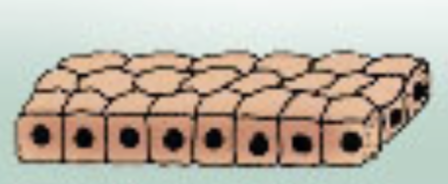
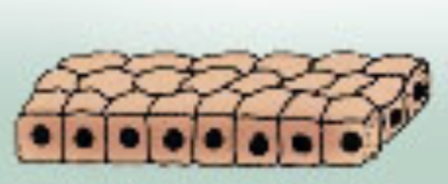
Which epithelial tissue is this?
Cuboidal (cube)
7
New cards
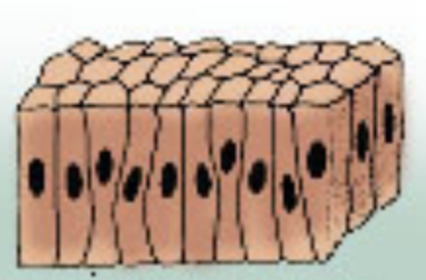
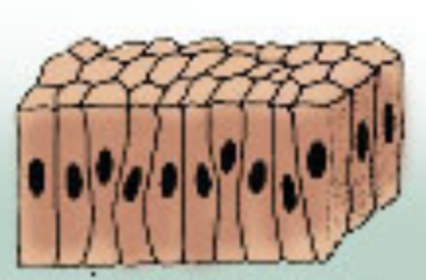
Which epithelial tissue is this?
Columnar
8
New cards
Exocrine Glands
Part of epithelial tissue; have ducts, secrete chemicals out of body or into digestive tract
example: sweat glands, majority of pancreas
example: sweat glands, majority of pancreas
9
New cards
Endocrine Glands
Part of epithelial tissue, no ducts, secrete chemicals (hormones) into blood
example: adrenal gland, certain cells of pancreas
example: adrenal gland, certain cells of pancreas
10
New cards
Connective Tissue
Sparse scattering of cells in extracellular matrix that bind/support
11
New cards
4 Types of Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue Proper, Cartilage, Bone, Blood
12
New cards
Connective Tissue Proper
binds, fills spaces, etc
example: tendons, ligaments, dermal of skin
example: tendons, ligaments, dermal of skin
13
New cards
Adipose (fat)
type of connective tissue found throughout the body that store energy and act as insulation
14
New cards
Cartilage
Support and protect; prevent bone-on-bone
example: joint surfaces, nose, ear
example: joint surfaces, nose, ear
15
New cards
Bone
Structure, support, and protection
example: skeleton
example: skeleton
16
New cards
Blood
found in blood vessels, transport materials (oxygen, nutrients, etc)
extracellular matrix is plasma
extracellular matrix is plasma
17
New cards
Muscle Tissue
Specialized for contraction; contraction leads to movement of skeleton or internal organs
18
New cards
What are the types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
19
New cards
Skeletal Muscle
attaches to bone, causes movement of skeleton
characteristics:
\-long, unbranched, tightly packed cells
\-multi-nucleated
\-striated (striped)
\-voluntary (conscious control)
characteristics:
\-long, unbranched, tightly packed cells
\-multi-nucleated
\-striated (striped)
\-voluntary (conscious control)
20
New cards
Cardiac Muscle
heart muscle, contraction leads to blood pumping
characteristics:
\-branched, interconnected cells
\-1 nucleus/cell
\-striated
\-involuntary
characteristics:
\-branched, interconnected cells
\-1 nucleus/cell
\-striated
\-involuntary
21
New cards
Smooth Muscle
contraction leads to movement within internal organs (except heart)
characteristics:
\-tapered cells
\-1 nucleus/cell
\-no striations
\-involuntary
characteristics:
\-tapered cells
\-1 nucleus/cell
\-no striations
\-involuntary
22
New cards
Nervous Tissue
composed of cells that generate and conduct electrical impulses and some are supporting cells; fast coordination of body
types:
\-neuron: conducts electrical impulses
\-glial (support) cells: various functions and structural support of neurons
\
types:
\-neuron: conducts electrical impulses
\-glial (support) cells: various functions and structural support of neurons
\
23
New cards
homeostasis
maintenance of relatively stable internal environment
24
New cards
normal range
variability around allowed or acceptable variability around set points
highest and lowest acceptable values
highest and lowest acceptable values
25
New cards
set point
targeted value
1/2(min +max)
1/2(min +max)
26
New cards
negative feedback
response mechanism that maintains homeostasis by counteracting change; drives variable back to set point
stimulus (changes that evoke response) → sensor (detects stimulus) → integrating center (receives input, controls effector tissue) → effector (generates response)
stimulus (changes that evoke response) → sensor (detects stimulus) → integrating center (receives input, controls effector tissue) → effector (generates response)
27
New cards
response in negative feedback
action that brings back to set point
28
New cards
solutions
homogeneous mixture of 2 or more components
29
New cards
solute
substances present in smaller amounts
30
New cards
solvent
substance present in largest amount
31
New cards
mg/dL
weight per volume
32
New cards
grams solute/mL solvent x 100
percentage (%) solutions
33
New cards
molarity (M)
mol solute/L solution
34
New cards
molality (m)
mol solute/kg of solvent
35
New cards
osmolality (osm)
molality \* # of particles in H2O
36
New cards
What is solubility of different molecules?
like dissolves like
hydrophilic molecules like polar and ionic solutes
hydrophobic molecules like non-polar solutes
hydrophilic molecules like polar and ionic solutes
hydrophobic molecules like non-polar solutes
37
New cards
plasma membrane is largely non polar “solvent”
hydrophobic molecules easily pass through
hydrophilic molecules (ions and large polar molecules) need channels, carriers, or transporters to cross
hydrophobic molecules easily pass through
hydrophilic molecules (ions and large polar molecules) need channels, carriers, or transporters to cross
What is the solubility of the plasma membrane?
38
New cards
diffusion
net movement of atoms or molecules from area of high concentration to low concentration
39
New cards
osmosis
movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane; H2O cross through aquaporins
solutes that are unable to move are “osmotically active'“
solutes that are unable to move are “osmotically active'“
40
New cards
osmotic pressure
how strongly solution draws H2O to it; greater concentration of osmotically active solute → greater osmotic pressure
41
New cards
osmolality
ionic molecules split apart in H2O, covalently bonded molecules don’t split
42
New cards
isotonic
equal inside and out
43
New cards
hypertonic
more outside than inside cell; leads to crenate
44
New cards
hypotonic
less outside than inside cell; leads to lysis
45
New cards
purpose of concentration
tells us normal ranges
46
New cards
What happens when there’s excessive glucose?
pancreas release insulin → insulin sends signal to live → liver takes glucose from blood → glucose turned into glycogen during glycogen synthesis
47
New cards
glycogen synthesis
dehydration/condensation reaction; removes OH- and H+ from two glucose molecules to make H2O and glycogen
48
New cards
What happens when there’s low glucose?
pancreas releases glucagon → glucagon sends signal to live → liver breaks glycogen during glycogen breakdown → glucose enters blood
49
New cards
glycogen breakdown
hydrolysis reaction with glycogen, addition of H2O to break bond
50
New cards
Type 1 Diabetes
pancreas can’t make insulin
treatment: more insulin
treatment: more insulin
51
New cards
Type 2 Diabetes
liver tissue loses sensitivity to insulin
treatment: metformin
treatment: metformin
52
New cards
lipids
non polar compounds that are insoluble in polar solvents (hydrophobic)
tend to big and bulky with lots of carbon, usually a double bond somewhere
example: triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol, steroid hormones, prostaglandins
tend to big and bulky with lots of carbon, usually a double bond somewhere
example: triglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol, steroid hormones, prostaglandins
53
New cards
phospholipids
head is hydrophilic (oriented on outside of cells)
tail is hydrophobic (oriented on inside of cells)
tail is hydrophobic (oriented on inside of cells)
54
New cards
What is a blank comprised of in a colorimeter or spectrophotometer?
cuvette, reagent, and water
55
New cards
Beer’s Law
Concentration is proportional to amount of light absorbed by solution
Low concentration → low absorbance
conc soln 1/conc soln 2 = abs sol 1/abs sol 2
Low concentration → low absorbance
conc soln 1/conc soln 2 = abs sol 1/abs sol 2
56
New cards
enzymes
allow reactions to go faster by lowering the necessary activation energy
biological catalysts, typically proteins, end in “-ase”
doesn’t change during the reaction
biological catalysts, typically proteins, end in “-ase”
doesn’t change during the reaction
57
New cards
characteristics of enzymes
very specific to substrates they bind (lock and key model at active site)
require optimal conditions (temperature, pH, etc)
require optimal conditions (temperature, pH, etc)
58
New cards
active site
place where substrate binds and where reaction takes place
59
New cards
How does pH affect enzyme reactions?
optimum depends on enzyme location in body or cell
60
New cards
How does temperature affect enzyme reactions?
optimized for each enzyme and where reaction occurs
at extreme temperatures enzymes denature
at extreme temperatures enzymes denature
61
New cards
How does substrate concentration affect enzyme reactions?
Reaction rate increases as this concentration increases until reach saturation
62
New cards
Saturation
all or most enzymes are bound to substrate
63
New cards
Enzyme Concentration
increasing this concentration increases reaction rate so long as there’s enough substrates
64
New cards
Iodine Test
tested starch presence
changed lighter if no/less starch
changed lighter if no/less starch
65
New cards
Benedict’s Test
detected presence of maltose
blue (none) → rusty red (a lot)
blue (none) → rusty red (a lot)
66
New cards
Neuron
electrical conducting cells of nervous system
67
New cards
Synapse
functional connection between neuron and second cell (another neuron, effector cell)
68
New cards
Central Nervous System
brain and spinal cord, integration and interpretation of information
69
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
sensory and motor neurons; transmits information to and from CNS
70
New cards
Reflexes
involuntary motor response to stimulus without involvement of higher brain tissue
prevents potential tissue damage
prevents potential tissue damage
71
New cards
Where is the reflex action processed?
processed by spinal cord
72
New cards
Where is the reflex sensation processed?
processed by brain
73
New cards
Reflex Arc
nerve impulse pathway of reflex
Stimulus → sensory neuron (afferent: sends message to central nervous system) → interneuron → motor neuron (efferent: sends message from central nervous system to effector) → effector
Stimulus → sensory neuron (afferent: sends message to central nervous system) → interneuron → motor neuron (efferent: sends message from central nervous system to effector) → effector
74
New cards
Monosynaptic Reflex
only 2 neurons and 1 neuron-neuron synapse
stimulus → sensory neuron → motor neuron → effector
stimulus → sensory neuron → motor neuron → effector
75
New cards
Muscle Spindle Apparatus
clusters of special cells (spindle fibers) in muscle
76
New cards
Knee-Jerk
first: hit patellar ligament or tendon stretches; quadriceps also stretch because attached to tendon
second: spindle fiber stretched (neuron activated and send info to central nervous system)
third: synapse between sensory and motor neurons in spinal cord
fourth: activated motor (efferent) neuron signals quadriceps muscle (effector) to contract
second: spindle fiber stretched (neuron activated and send info to central nervous system)
third: synapse between sensory and motor neurons in spinal cord
fourth: activated motor (efferent) neuron signals quadriceps muscle (effector) to contract
77
New cards
Chemoreceptors
perceives taste, smell, pH
78
New cards
Mechanoreceptors
perceives touch, pressure, stretch, sound, and balance
79
New cards
Photoreceptrs
perceive sight
80
New cards
Thermoreceptors
perceive an increase or decrease in temperature
81
New cards
Perception
Limited by limited ability to detect various forms of energy
brain manipulating incoming data comparing to other info and memories
brain manipulating incoming data comparing to other info and memories
82
New cards
Receptive Fields
area of skin that can activate single neuron
big area → few receptors
small area → more receptors
high density of sensory neurons → large portion of brain (sensory cortex) associated with generating perception for body part
big area → few receptors
small area → more receptors
high density of sensory neurons → large portion of brain (sensory cortex) associated with generating perception for body part
83
New cards
What happens when there is a constant stimulus?
Our receptors decrease firing rate (phasic receptors); our brain stop paying attention to certain constant stimuli
84
New cards
What is the exception to sensory adaptation?
Most pain receptors; maintain firing rate (tonic receptor)
85
New cards
photoreceptors
sensory cells that transduce light energy into electrical impulses; located in retina of eye
86
New cards
What spectrum is visible light?
400-700 nm
87
New cards
How does light travel through eyes?
cornea → pupil → lens → retina
88
New cards
lens
concentrate and amplifies light in eye; works like a light house
89
New cards
retina
innermost layer of eye; has two structures: fovea and optic disk
90
New cards
fovea
pinhead sized pit; only contains cones; visual acuity highest; 1 ganglion per cone → highest resolution
91
New cards
optic disk
fibers and neural fibers exit here; doesn’t contain photoreceptors; blind spot
92
New cards
refraction
bending of light as passes through different materials
93
New cards
How does refraction work in the eye?
light bends as it passes through the lens and cornea; the light is then focused on the fovea
94
New cards
myopic
near sighted; poor distance vision
usually eyeball too long or lens too strong so light is focused in front of the fovea/retina
corrected with concave lens
negative dioptric value for concave lenses
usually eyeball too long or lens too strong so light is focused in front of the fovea/retina
corrected with concave lens
negative dioptric value for concave lenses
95
New cards
hyperopic
far sighted; poor near vision
usually eyeball too short or lens too weak so light is focused behind the fovea/retina
correct with convex lens
positive dioptric value for convex lens
usually eyeball too short or lens too weak so light is focused behind the fovea/retina
correct with convex lens
positive dioptric value for convex lens
96
New cards
visual acuity
sharpness of vision; measured with snellen chart
97
New cards
What does 20/70 vision mean?
What that person can see at 20 feet is what “normal” people can see at 70
98
New cards
astigmatism
irregularities in curvature of cornea or lens causes light not to focus
99
New cards
diopter
1/focal length in m
as focal length increases, diopter decreases
as focal length increases, diopter decreases
100
New cards
When a lens has a power of 3 diopters, what does this mean?
The lens focuses light in 1/3 of a meter.