8.0 Anaemia iron deficiency anaemia IDA
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
anaemia
either the number of circulating erythrocytes (RBC) or haemoglobin (HB) conc contained within them are below reference range leading to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity
IDA means there is insufficient iron to meet the body’s demand for haemoglobin production
leading to reduced RBC formation an dimpaired oxygen transprot
iron is a crucial component of haemoglobin and without enough
the body can’t produce enough functional RBC resulting in anaemia
iron is stored in the liver + bone marrow as
ferritin
ferritin is a compound composed of iron molecules bound to apoferritin, a protein shell
the stored iron represents 25% of total iron in the body and most of this iron is stored as ferritin
ferritin is found in many body cells
but especially those in the liver/ spleen/ bone marrow and reticuloendothelial cells
when ferritin stores are depleted
haemoglobin synthesis is impaired
without sufficient iron the bone marrow cant produce healthy RBC
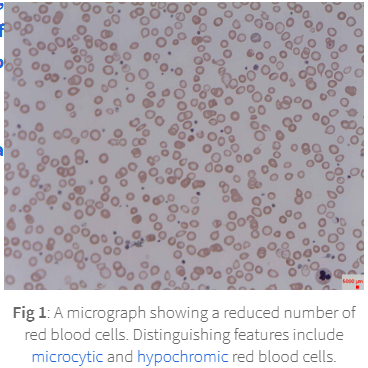
leading to small (microcytic) pale (hypochromic) RBC less capable of carrying oxygen
typical western diet contains daily intake of 15mg of iron
of which 10% is absorbed
approximately 20-25 mg iron is reuqired daily for RBC production
obtained from iron stores + recycled from old RBC after 120 within the ciruclation
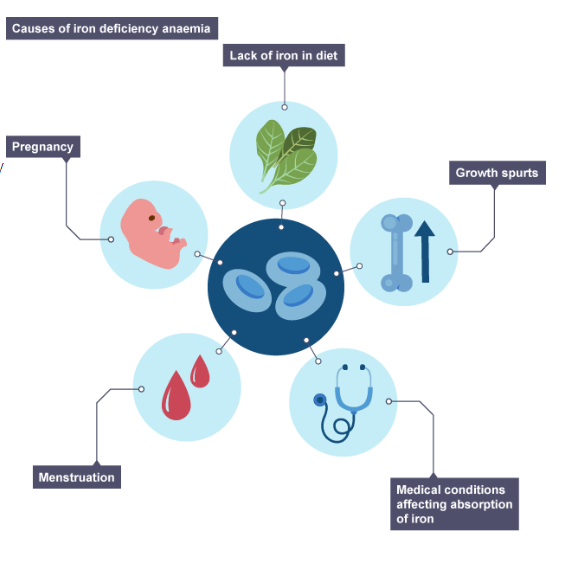
causes of IDA
inadequate dietary intake
increase iron requirements
blood loss
malabsorption of iron
chronic diseases
medicines
inadequate dietary intake
insufficient iron in diet fails to meet daily requirement
increased iron requirements
pregnancy + lactation increases maternal blood volume creating a higher demand for iron
growth spurts during infancy + hcildhood + adolescence also increase iron demand
blood loss
from heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
gastric ulcers
colon + gastric cancer
haemorrhoids
surgery
haemorrhage or frquent bood donations
malabsorption of iron
coeliac disease / after GI surgery (gastric bypass)
iron absorption primarily done in the duodenum and proximal jejunum
chronic diseases
chronic kidney diease / chronic inflammatory disease
medicine
NSAIDs- due to potential GI bleeding
PPI- due to impact on iron absorption