COMSCI 1100 UNIT 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:18 AM on 10/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
1
New cards
IBM System/360 series
Family of computers and their peripherals which are mutually compatible and all worked together.
2
New cards
John von Neumann machine
Developed a concept of storing a program in memory.
3
New cards
Main Memory (RAM)
where data and numerous programs are currently being executed by the CPU are stored.
4
New cards
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
A series of related technologies that tries to simulate and reproduce human behavior including thinking, speaking, reasoning.
5
New cards
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
Developed for calculating artillery firing tables.
6
New cards
EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)
First electronic computer to use stored program concept.
7
New cards
Napier Bones
small instrument made of 10 rods on which multiplication table was engraved.
8
New cards
Joseph Marie Jacquard
He invented a loom that used punch cards to control patterns into woven cloth (1801)
9
New cards
Abacus
derived from the Arabic word ‘ abaq which means ‘ dust.
10
New cards
Blaise Pascal
He invented the first mechanical adding machine called Pascaline (1642)
11
New cards
Secondary Memory
It provides stable storage for both programs and data in a longer period of time.
12
New cards
Microprocessor
Built onto a single piece of silicon, known as chip; about 0.5 cm long and not more than 0.05cm thick.
13
New cards
EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer)
It is a machine to run the first successful program.
14
New cards
Colossus
Worlds first electronic digital computer used to decode intercepted message.
15
New cards
Second generation computers
What computer generation moved from cryptic binary machine language to symbolic or assembly language which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words?
16
New cards
Apple II
One of the first highly successful mass- produced microcomputer products.
17
New cards
Sand Tables
It is known to be the earliest device for computation that consists of three groves in the sand with a maximum of 10 pebbles in each groove.
18
New cards
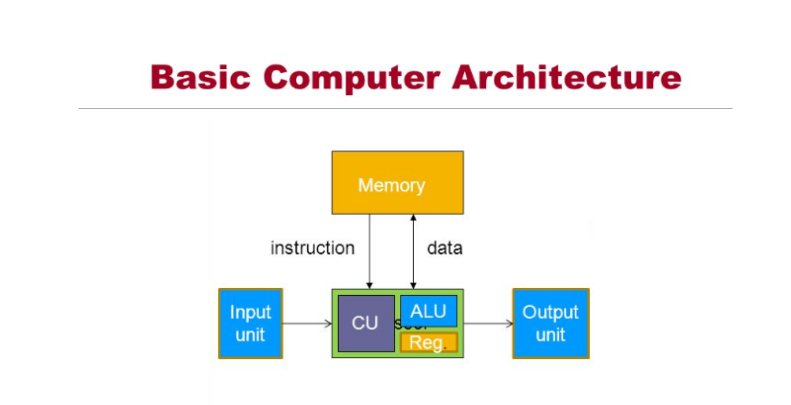
Howard Aiken
He led the designing of MARK I (1937). He also improved Babbages machine and his machine was considered the first electronic machine using thousands of relays.
19
New cards
Apple Lisa (1983)
First commercial personal computer to use graphical user interface with 1MB RAM, 12 inch black monitor, 2 5 ¼ floppy disk driver, 5MB of profile hard drive and used Motorola 680000 microprocessor.
20
New cards
electronic circuits
Consist of the ________ which are necessary to perform a variety of operations on the data.
21
New cards
Difference Engine
It is used to computer table of numbers using naval navigation and can only add & subtract.
22
New cards
Disk drives
They are also known as mass storage devices because of their capacity to store relatively large amounts of data and many programs.
23
New cards
Transistor
It was invented at Bell Labs in 1947 but did not see widespread use in computers until the late 1950s.
24
New cards
CRAY I
A supercomputer designed, manufactured and marketed by Cray Research.
25
New cards
Third generation of computers
Integrated Circuits was the hallmark of what generation of computers?
26
New cards
Mega Chips
Computers will use Super Large- Scale Integrated chips.
27
New cards
Input Output Devices
used in getting and displaying information.
28
New cards
Parallel Processing
Computers will use multiple processors and perform ________ thereby accessing several instructions at one time and working at the same time.
29
New cards
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
defined as the major component of a computer.
30
New cards
UNIT 2.1
Computer History
31
New cards
Sand Tables
It is known to be the earliest device for computation, it consists of three groves in the sand with a maximum of 10 pebbles in each groove
32
New cards
Abacus
derived from the Arabic word ‘abaq which means ‘dust. It consists of sliding beads arranged on a rack.
33
New cards
Upper and lower part
Abacus consists of sliding beads arranged on a rack which has two parts.
34
New cards
Napier Bones
A small instrument made of 10 rods on which multiplication table was engraved
35
New cards
Slide Ruler
jointly devised by Edmund Gunter & William Oughtred
36
New cards
Blaise Pascal
He invented the first mechanical adding machine called Pascaline (1642)
37
New cards
Baron Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz
He improved Pascals machine
38
New cards
Joseph Marie Jacquard
He invented a loom that used punch cards to control patterns into woven cloth (1801)
39
New cards
Charles Babbage
Father of Modern Computer
40
New cards
Difference Engine
used to computer table of numbers using naval navigation and can only add & subtract
41
New cards
Analytical Engine
general purpose machine
42
New cards
Herman Hollerith
Invented one of the first commercial machine which used punch card to tabulate and process the data collected
43
New cards
AB Computer (Atasoft Berry Computer)
First electronic computing machine, which introduced the idea of binary arithmetic, regenerative memory and logic circuits
44
New cards
Colossus
Worlds first electronic digital computer used to decode intercepted message
45
New cards
John von Neumann machine
Developed a concept of storing a program in memory
46
New cards
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
Developed for calculating artillery firing tables
47
New cards
EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)
First electronic computer to use stored program concept
48
New cards
EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer)
Machine to run the first successful program
49
New cards
UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer)
First commercially available computer
50
New cards
Transistor
it was invented at Bell Labs in 1947 but did not see widespread use in computers until the late 1950s
51
New cards
Integrated Circuits
it was the hallmark of the third generation of computers
52
New cards
IBM System/360 series
Family of computers and their peripherals which are mutually compatible and all worked together
53
New cards
PDP 8
Developed by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC)
54
New cards
Microprocessor
Built onto a single piece of silicon, known as chip; about 0.5 cm long and not more than 0.05cm thick
55
New cards
Large Scale Integration (LSI)
Approximately 180 transistors
56
New cards
Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI)
Approximately 275,000 transistors
57
New cards
Altair 8800 (1975)
Developed by MITS (Mirco Instrumentation Telemetry Systems)
58
New cards
Apple II
One of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products
59
New cards
CRAY I
A supercomputer designed, manufactured and marketed by Cray Research
60
New cards
Apple Lisa (1983)
First commercial personal computer to use graphical user interface with 1MB RAM, 12 inch black monitor, 2 5 ¼ floppy disk driver, 5MB of profile hard drive and used Motorola 680000 microprocessor
61
New cards
‘Lisa
stood for ‘Local Integrated Software Architecture
62
New cards
Fifth Generation
Artificial Intelligence (Present and Beyond)
63
New cards
Mega Chips
Computers will use Super Large-Scale Integrated chips
64
New cards
Parallel Processing
Computers will use multiple processors and perform parallel processing thereby accessing several instructions at one time and working at the same time
65
New cards
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
A series of related technologies that tries to simulate and reproduce human behavior including thinking, speaking, reasoning
66
New cards
UNIT 2.2
Computer System and its Components
67
New cards
Computer System
defined as general purpose information processing machine
68
New cards
Hardware
tangible parts
69
New cards
Software
intangible parts; data and programs
70
New cards
Computer Hardware
physical machine, consisting of mechanical parts and electronic circuits
71
New cards
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
defined as the major component of a computer. also known as the processor or the electronic brain
72
New cards
Main Memory (RAM)
where data and numerous programs are currently being executed by the CPU are stored
73
New cards
Secondary Memory
provides stable storage for both programs and data in a longer period of time
74
New cards
Disk drives
are also known as mass storage devices because of their capacity to store relatively large amounts of data and many programs
75
New cards
Input/Output Devices
used in getting and displaying information
76
New cards
Input unit
inputs the data and programs for computer processing
77
New cards
Storage unit
stores the input data and programs
78
New cards
Processing unit
conducts calculations on the input data and controls input
79
New cards
Output unit
output the result of computer processing in a certain format
80
New cards
Computer Software
set of computer programs and algorithms that tells the
computer what to do and how to do it.
computer what to do and how to do it.
81
New cards
1. System Software
2. Programming Software
3. Application Software
2. Programming Software
3. Application Software
What are the three categories of Computer Software?
82
New cards
Control Unit, Arithmetic Logic Unit and Registers
What are the major components of CPU?
83
New cards
1. Central Processing Unit
2. Main Memory (RAM)
3. Secondary Memory (HDD, SDD)
4. Peripherals (I/O devices)
2. Main Memory (RAM)
3. Secondary Memory (HDD, SDD)
4. Peripherals (I/O devices)
What are the major units of Computer Hardware?
84
New cards
1. Keyboards
2. Pointing Devices
3. Sensors
4. Remote Control
5. Card Readers
2. Pointing Devices
3. Sensors
4. Remote Control
5. Card Readers
Examples of input devices
85
New cards
1. Printers/Plotters
2. Monitors
2. Monitors
Examples of output devices
86
New cards
Input data
CPU
Main Memory
Output Data
CPU
Main Memory
Output Data
Basic Computer Architecture