Chapter 20: Electric Current, Resistance, and Ohm's Law
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
AC Current
current that fluctuates sinusoidally with time, expressed as I = I0 sin 2πft, where I is the current at time t, I0 is the peak current, and f is the frequency in hertz
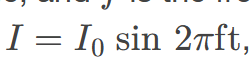
AC voltage
voltage that fluctuates sinusoidally with time, expressed as V = V0 sin 2πft, where V is the voltage at time t, V0 is the peak voltage, and f is the frequency in hertz
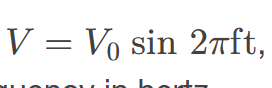
Alternating Current
(AC) the flow of electric charge that periodically reverses direction
Ampere
(amp) the SI unit for current; 1 A = 1 C/s
Bioelectricity
electrical effects in and created by biological systems
Direct Current
(DC) the flow of electric charge in only one direction
Drift velocity
the average velocity at which free charges flow in response to an electric field
Electric Current
the rate at which charge flows, I = ΔQ/Δt
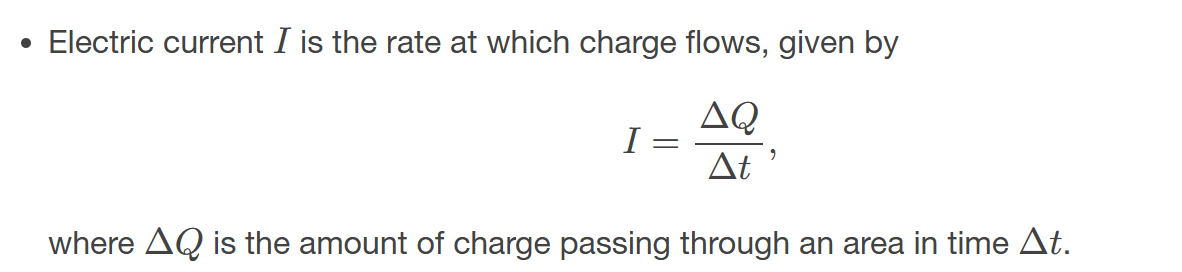
Electric Power
the rate at which electrical energy is supplied by a source or dissipated by a device; it is the product of current times voltage
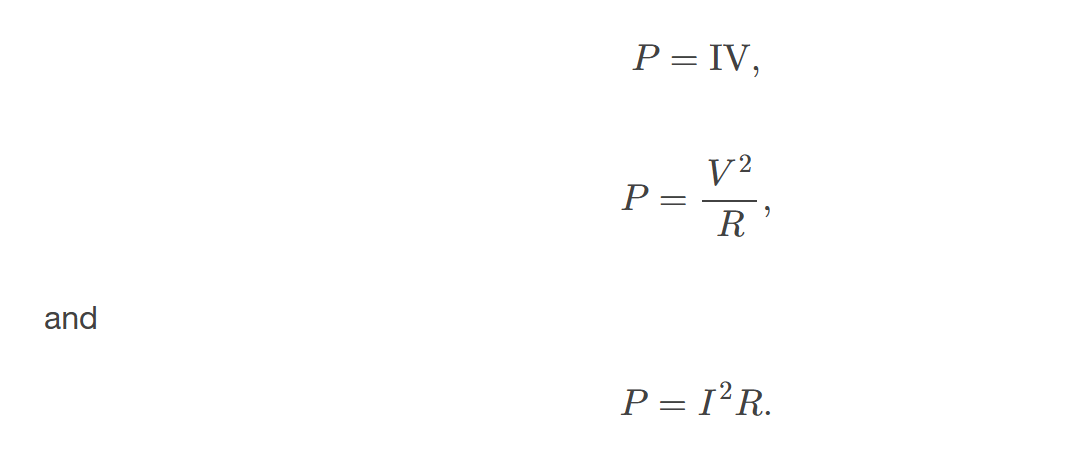
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
usually abbreviated ECG, a record of voltages created by depolarization and repolarization, especially in the heart
microshock sensitive
a condition in which a person’s skin resistance is bypassed, possibly by a medical procedure, rendering the person vulnerable to electrical shock at currents about 1/1000 the normally required level
nerve conduction
the transport of electrical signals by nerve cells
ohm
the unit of resistance, given by 1Ω = 1 V/A
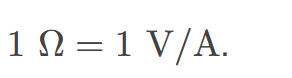
Ohm’s Law
an empirical relation stating that the current I is proportional to the potential difference V, ∝ V; it is often written as I = V/R, where R is the resistance
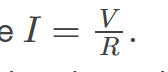
Ohmic
a type of a material for which Ohm's law is valid
Resistance
the electric property that impedes current; for ohmic materials, it is the ratio of voltage to current, R = V/I
Resistivity
an intrinsic property of a material, independent of its shape or size, directly proportional to the resistance, denoted by ρ
rms current
the root mean square of the current, 𝐼rms=𝐼0/√2 , where I0 is the peak current, in an AC system
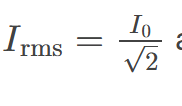
rms voltage
the root mean square of the voltage, 𝑉rms=𝑉0/√2 , where V0 is the peak voltage, in an AC system
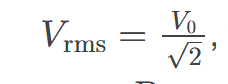
semipermeable
property of a membrane that allows only certain types of ions to cross it
shock hazard
when electric current passes through a person
short circuit
also known as a “short,” a low-resistance path between terminals of a voltage source
simple circuit
a circuit with a single voltage source and a single resistor
temperature coefficient of resistivity
an empirical quantity, denoted by α, which describes the change in resistance or resistivity of a material with temperature
thermal hazard
a hazard in which electric current causes undesired thermal effects
Ampere (A)
SI unit for current equal to one coulomb per second.
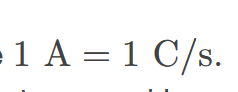
Relationship of Current to Drift Velocity
the proportionality between the electric current flowing through a conductor and the drift velocity of charge carriers, indicating how the movement of these carriers contributes to the current
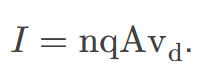
a voltage or IR drop across a resistor,
resulting in a decrease in current flow through the circuit.
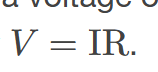
The resistance 𝑅 of a cylinder
is defined as the ratio of voltage to current flowing through it, reflecting how much it opposes the flow of electric current.
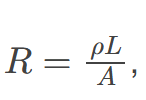
Temperature Affecting Resistivity
describes how the resistivity of a material typically increases with temperature, impacting its ability to conduct electricity.
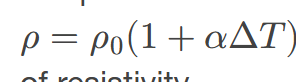
The energy used by a device with a power 𝑃 over a time 𝑡
is known as electrical energy, calculated as the product of power and time, expressed in joules.
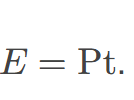
Average AC Power
is the measure of the effective power consumption in an alternating current (AC) circuit, calculated by averaging the instantaneous power over one complete cycle.
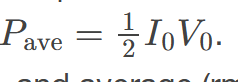
Ohm’s law for AC
relates AC voltage (V) and AC current (I) to impedance (Z) in alternating current circuits, given by V = IZ.
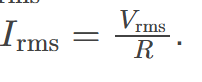
Expressions for the average power of an AC circuit
𝑃ave=𝐼rms𝑉rms, 𝑃ave=𝑉2rms𝑅, and 𝑃ave=𝐼2rms𝑅, analogous to the expressions for DC circuits.