Paranasal Sinus and Nasal Cavity
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Review Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
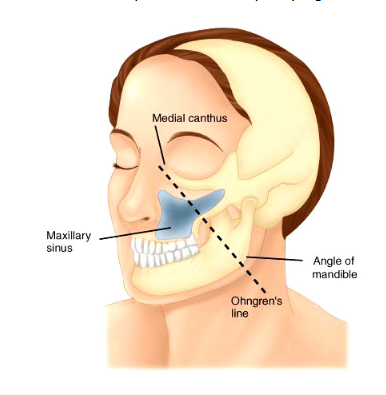
Ohngren’s Line
Extends from medial canthus to the mandibular angle
Theoretical line used divide the maxillary antrum into anteroinferior and posterosuperior portion
Postero/suprastructure - poor prognosis with early extension
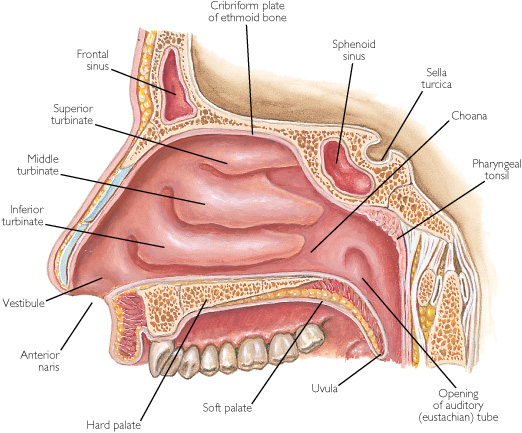
Paranasal Sinus Borders
Superior - orbital floor
Medial - thin walls of the nasal fossa
Posterior - pterygoid area (orbital apex and paranasopharyngeal area)
Inferior - hard palate and superior alveolar ridge
Treatment management of the nasal vestibule is:
Radiation therapy
Surgery is limited to small lesions and optimal locations
Radiation therapy treatment to the nasal cavity is prescribed ______ Gy for radiation alone or a postoperative dose of _______Gy.
74-79 Gy
60-68 Gy
Risk factors for paranasal sinus cancer:
Chromium, Asbestos, Nickel
Glues, formeldahyde, etc
Dusts from woods, textiles, leathers
Viral
HPV
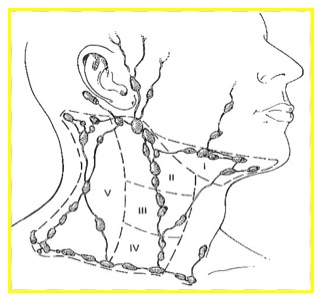
Most common lymph nodes involved in paranasal and nasal treatment areas:
Submandibular and Jugulodigastric (Levels I-II)
Treatment modalities for paranasal cancer:
Surgery
Radiation
Chemotherapy
Most common histology for cancer of the paranasal sinus:
Squamous cell carcinoma
Epidemiology of paranasal sinus:
Age 50-60
Higher incidence in Japan and South Africa
More common in men than women
very rare - <1% of all malignancies
Paranasal sinus signs and symptoms
Frequent nosebleeds
decreases sense of smell
one-sided nasal obstruction
pain above/below the eyes
enlarged neck lymph nodes
T/F: Tumors of the paranasal sinus exhibit signs and symptoms at the initial onset of the disease.
False - symptoms arise when extension beyond the outside sinus walls occurs and is considered “silent” until then
What are the 4 paranasal sinuses?
Frontal
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Maxillary
Approximately ____% of paranasal sinus cases present with nodal disease and _______% will develop nodal disease during the disease course.
10%
25-35%
What 3 anatomical parts comprise the nasal cavity?
Vestibule (open airway)
Septum (cartilage)
Turbinates (Conchae)
What is the purpose of a bite block in paranasal and nasal cavity irradiation?
Avoid bolus effect and moist desquamation at the commissure of the lips
Displace tongue inferiorly from the treatment field