AP Psych Unit 1 - Biological Perspectives
1/169
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Psych bio (Excluding sleep and sensations since I was too lazy to add those, but I will soon)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
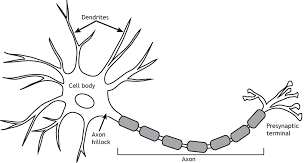
Neuron
The building blocks of the nervous system
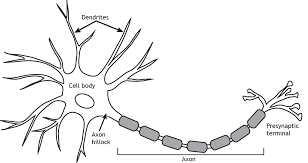
SOMA/Cell Body
The body of the cell that encompasses the nucleus
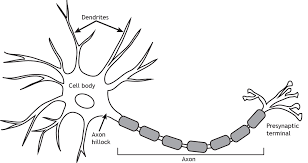
Dendrites
Branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses towards the cell body
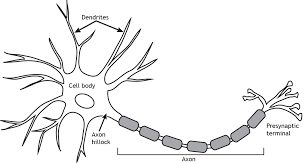
Axon
The part of a neuron in which messages travel through
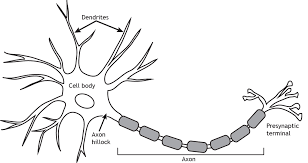
Myelin Sheath
A fatty substance found in some neurons which protects and insulates the axon. Speeds up the rate at which messages travel
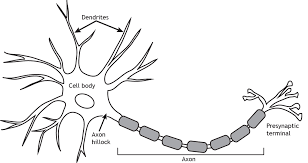
Axon Terminal
Located at the end of the neuron. Terminal buttons protrude from it to send on messages
Action Potential
A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon (In more scientific terms, a rapid sequence of changes in the voltage across a membrane)
Reuptake
A neurotransmitter’s re-absorption after it has been released into the synapse by the sending neuron
Refractory Period
A period of inactivity after a neuron has fired
All-or-None Response
A neuron’s reaction of either firing or not firing- there is no in between
Synaptic Gap/Synapse
The space between dendrites and terminal buttons. Neurotransmitters jump across this gap
Sensory Neurons/Afferent Neurons
Neurons that carry messages from the senses to the brain for processing
Motor Neurons/Efferent Neurons
Neurons that carry messages from the brain to the body for reaction to stimuli
Interneurons
Neurons located in the brain and spinal cord. Communicate between sensory input and motor output by taking messages and sending them elsewhere
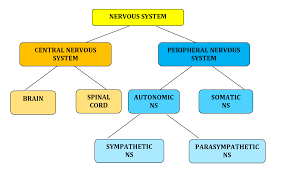
Central Nervous System (CNS)
One of the two main division of the nervous system. Consists of the brain and spinal cord (all of the nerves housed within bone) and transmits information from the rest of the body to the brain
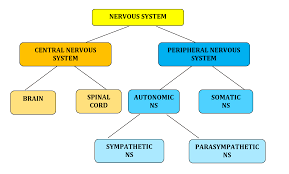
Peripheral Nervous System
One of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Consists of the nervous system outside of the brain and spinal cord (all of the nerves not encased in bone). Can be broken down further into the Autonomic and Somatic Nervous Systems
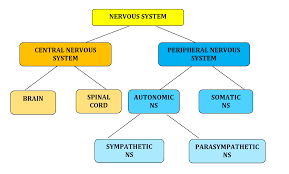
Somatic Nervous System
Also called the skeletal nervous system. It is a part of the PNS and controls voluntary muscle movements
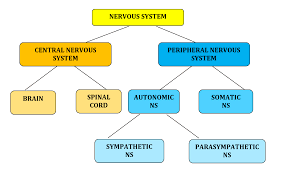
Autonomic Nervous System
Part of the PNS that controls involuntary, automatic functions of the body such as our heart, lungs, and internal organs. This nervous system can be further broken down into the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
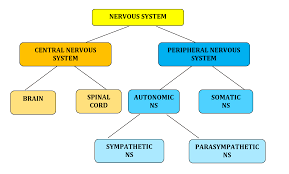
Sympathetic Nervous System
The division of the ANS that mobilizes our body to respond to stress. It carries messages to the control systems that direct our body’s response to stress (fight-or-flight). When stress is perceived it accelerates some functions (HR, BP, breathing) but slows others (digestion)
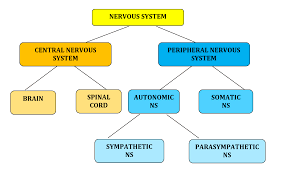
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The division of the ANS that calms the body after a perceived danger. It carries messages to the stress response system that cause many body activities to slow down and return the body to homeostasis (rest-and-digest)
Neurotransmitter
A chemical messenger fired by neurons
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Neurotransmitter linked to muscle movement, learning, and memory (Excitatory)
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter linked with learning, emotion, pleasure & reward, motor movement, and alertness (Excitatory)
Seratonin
Neurotransmitter linked with mood stabilization, hunger, sleep, and arousal (Inhibitory)
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter linked with alertness and arousal (Excitatory)
GABA
Neurotransmitter linked with sleepiness (Inhibitory)
Glutamate
Neurotransmitter linked with memory and all cognitive functions (Excitatory)
Endorphines
Neurotransmitter linked with being a natural pain killer (Inhibitory)
Substance P
Neurotransmitter linked with pain perception and immune response (Excitatory)
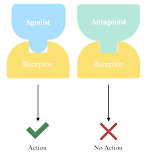
Agonist
A substance that mimics a neurotransmitters and binds to a receptor site, stimulating a response
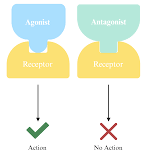
Antagonist
A substance that occupies space in receptor sites and prevents neurotransmitters/agonists from causing reactions
Depressants
Psychoactive drugs that slow down the ANS. They can also cause slow reactions/judgments, and cause a sense of euphoria
Examples: Alcohol, barbiturates, tranquilizers
Opiates/Opioids
Psychoactive drugs that act as agonists for endorphins. This makes them powerful painkillers and mood elevators, and they also cause drowsiness and euphoria. They are some of the most physically addictive drugs
Examples: Morphine, heroin, methadone, codeine, fentanyl
Stimulants
Psychoactive drugs that speed up body processes, including ANS functions like heart and respiration rates. They also cause a sense of euphoria, more powerful ones may cause a person to feel self-confident and invincible
Examples: Caffeine, cocaine, amphetamines, nicotine
Hallucinogens/Psychedelics
Psychoactive drugs that cause changes in perceptions of reality. They cause sensory hallucinations, loss of identity, vivid fantasies, and are know for persistence (can last in the body for weeks)
Example: Marijuana, LSD, peyote, mushrooms, psilocybin
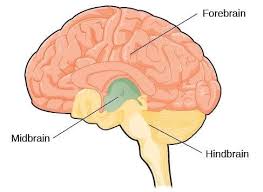
Hindbrain
The oldest part of the brain that takes care of basic biological functions that keep us alive. Consists of structures located on top of the spinal cord
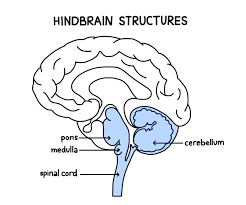
Medulla
Part of the hindbrain. It is located above the spinal cord and is involved in basic autonomic functions like heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. Also involved in reflexes like sneezing, swallowing, and vomiting

Pons
Part of the hindbrain, located above the medulla and toward the front. Acts as a bridge that connects the brainstem with the cerebellum. Involved in sleep function, facial expressions, and coordinating movement
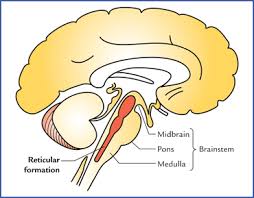
Reticular Formation/Reticular Activating System
Considered either part of the hind- or midbrain depending on the source. It is a bundle of nerves that runs through the medulla and pons. It is involved in general body arousal, alertness, and the ability to focus our attention. If it does not functions, we fall into a deep coma
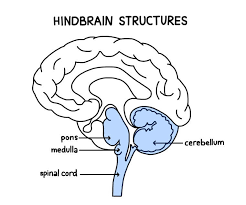
Cerebellum
Part of the hindbrain, located on the bottom rear of the brain. Involved in habitual muscle movements (like tracking targets w/ your eyes), coordinated sequences of movements, balance and equilibrium, and implicit memories
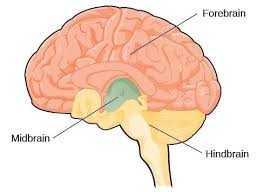
Midbrain
The border between the older and newer parts of the brain coordinates simple muscle movements with sensory information
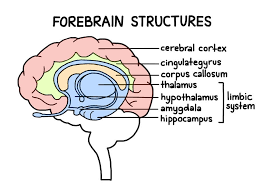
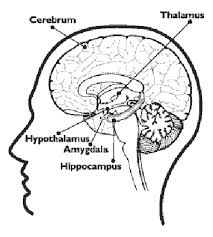
Hypothalamus
Part of the forebrain and limbic system. Involved in the three F’s: Fight-or-flight (regulates sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems), Feeding (initiates hunger/thirst), and Fornication (sexual arousal/motivation). Controls our biological rhythms and endocrine system
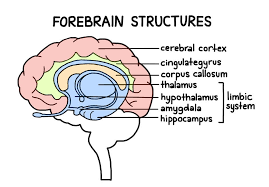
Thalamus
Part of the forebrain and limbic system located on top of the brain stem. Responsible for receiving sensory signals (except smell) and sending them to the appropriate areas
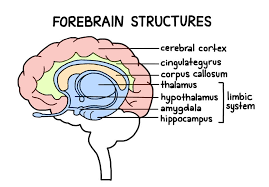
Amygdala
Part of the forebrain and limbic system. Involved in the three A’s: Anger, Aggression, and Afraid (fear). Involved in experiences of emotion/ingraining highly emotional memories
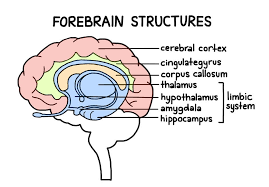
Hippocampus
Part of the forebrain and limbic system. Involved in processing and retrieving declarative and spatial memories, but memory isn’t stored here. It converts short-term memories to long-term
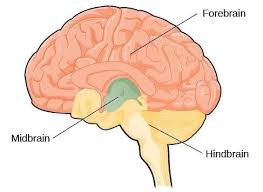
Forebrain
The newest part of the brain (also the largest). It controls what we think of as thought and reason, and the size of it is what makes humans human
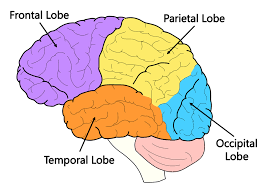
Frontal Lobes
The lobes located in the top front part of the brain, behind the eyes. It is responsible for a wide range of functions, including speaking, muscle movement, and judeg
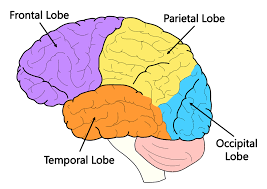
Parietal Lobes
The lobes located behind the frontal lobe on the top of the brain. They receive sensory input for touch/pain/pressure and body position
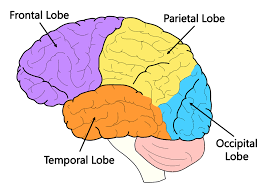
Temporal Lobes
The lobes located just behind the ears. They are responsible for auditory processing and language comprehension
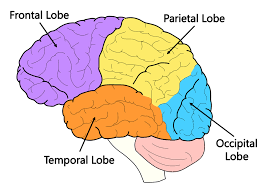
Occipital Lobes
The lobes located at the very back of our brain. They are responsible for interpreting messages from our eyes in our visual cortex
Corpus Callosum
The band of neural fibers that connects both brain hemispheres and carries messages between them
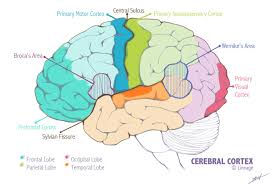
Motor Cortex
A cortex located at the back of the frontal lobe. This part of the cerebral cortex sends signals to our muscles, controlling our voluntary movements. The top of the body is controlled by the neurons at the bottom of this cortex and vice versa
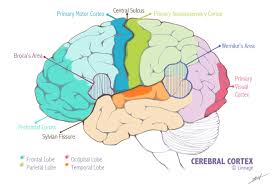
Somatosensory Cortex
A cortex located at the front of the parietal lobe, right behind the motor cortex. It receives incoming touch sensations from the rest of our body. The top of the cortex receives sensation from the bottom of our body, and vice versa
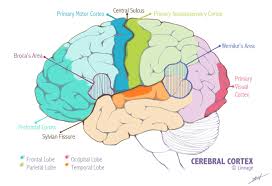
Auditory Cortex
A cortex located in the temporal lobe that is responsible for processing auditory information
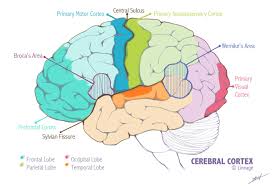
Visual Cortex
A cortex located in the occipital lobe that is responsible for processing visual information from the eyes
Association Areas
Parts of the cerebral cortex that are not associated with receiving sensory input or controlling muscle movement, but instead involved in complex mental functions like learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking.
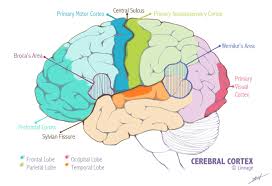
Prefrontal Cortex
An association area located in the front of the frontal lobe. It is responsible for directing thought processes, predicting consequences, pursuing goals, maintaining emotional control, and engaging in abstract thought
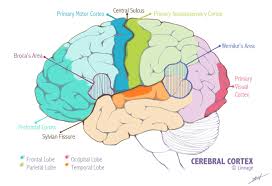
Broca’s area
An association area located in the frontal lobe. It is responsible for controlling the muscles involved in producing speech
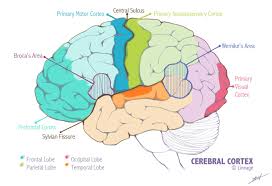
Wernicke’s Area
An association area located in the temporal lobe of the brain. It is involved with linguistic processing via both written and spoken speech
Genetic Predisposition
The increased chance of developing a specific trait or condition due to our genetic code
Neurons
Individual nerve cells that make up our entire nervous system
Neural Transmission
The process by which neurons communicate with each other/send messages
Resting Potential
A neuron’s resting state where it has an overall slightly negative charge
Threshold
The critical level of electrical stimulation or depolarization that a neuron must reach in order to initiate an action potential. This is essentially the point where a neuron "fires" and transmits an electrical signal
Depolarization
Another name for the process of neuron firing. Named so because the resting potential of the cell (negatively charged) becomes depolarized when positive ions rush in
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters that excite the next cell into firing
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters that inhibit the next cell from firing
Alzheimer’s Disease
A disease that is linked with a lack of Acetylcholine (ACh)
Myasthenia gravis
A condition that causes muscle weakness that causes the body to attack ACh receptors
Reflex Arcs
Reflexes that do not travel all the way to the brain (normally just to the spinal cord) before reactions occur
E.g. when the spot right under your knee is hit, this sensory info is processed by the spine, which tells your leg to move. Then the info reaches your brain, and you realize your leg has moved
Endocrine System
A system of glands that secrete hormones that affect many different biological processes in our bodies. The complex system is controlled by the hypothalamus
Hormones
Chemical messengers secreted by the endocrine system that travel through the bloodstream to affect distant organs and tissues, regulating bodily functions like growth, metabolism, and stress response
Adrenaline
A hormone that is activated during the fight-or-flight response in stressful situations that speeds up bodily processes
Leptin
A hormone involved in weight regulation. It suppresses hunger (may make food appear as less appetizing)
Ghrelin
A hormone involved in motivating eating/increasing hunger (may make food appear as more appetizing)
Melatonin
A hormone that triggers sleep and wakefulness responses in the brain
Oxytocin
A hormone involved in promoting good feelings such as trust and bonding
Lesioning
Removing or destroying part of the brain. Not used in experiments for obvious reasons, just as surgery for serious conditions (E.g. removing a brain tumor). When it occurs, researchers are able to monitor any behavior changes afterwards as a way to infer the function of that part of the brain
A famous example is the frontal lobotomy
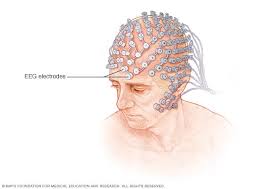
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
A test that detects brain waves. Researchers can examine the different types of brain waves produced during different states of consciousness to generalize about brain function. This type of test is commonly used in sleep research
Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT or CT Scan)
This imaging procedure is a type of sophisticated X-ray. It uses several X-ray cameras that rotate around the brain and combines the images into a three-dimensional picture. It can only show the structure of the brain, not functions or activity
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
An imaging technique that uses magnetic fields to measure the density and location of brain material. Gives information only about the structure of the brain, not the function
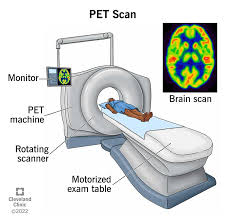
Positron Emission Tomography (PET Scan)
An imaging technique that lets researchers see what areas of the brain are most active during certain tasks. It measures how much of a certain chemical (E.g. glucose) parts of the brain are using- high levels of activity are indicated by warm colors, and low levels by cool
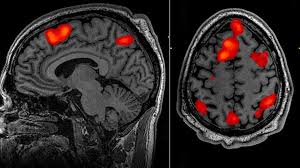
Functional MRI (fMRI)
A brain imaging technique that combines elements of the MRI and PET scans. It can both show details of brain structure and measure brain activity by detecting changes about blood flow in the brain
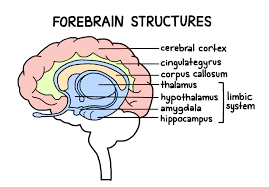
Cerebral Cortex
A gray, wrinkly, and thin layer of densely packed neurons that covers the rest of the brain
Limbic System
The name for the thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus, and amygdala grouped together. This grouping was created because all parts are involved in emotion and memory
Contralateral Hemispheric Organization
The idea that each side of the brain controls the opposite side of the body (The left hemisphere gets sensory messages and controls the motor functions of the right half of the body and vice versa)
Hemispheric Specialization/Brain Lateralization
The specialization of the brain's two hemispheres for different cognitive functions. The fact that typically, the left hemisphere is more active during logic tasks and the right during creative tasks
Split-Brain Procedure/Corpus Callosotomy
A procedure pioneered by neuropsychologists Roger Sperry and Michael Gazzaniga. It is an operation that involves severing the corpus callosum, and it is used to treat severe epilepsy
Aphasia
A language disorder that affects a person's ability to communicate/speak. Can result from damage to Wernicke’s Area
Phantom Limb Syndrome
A condition where a person loses a part of their body but still perceives sensations from that lost limb. This is because their somatosensory cortex still has the body part “mapped”
Priming
A phenomenon in which exposure to one stimulus influences how a person responds to a subsequent, related stimulus
Blind Sight
A phenomenon where some people who report being blind can still accurately describe the path of a moving object or grasp objects they cannot see. One level of their consciousness isn’t getting any visual information, while another is able to “see”
Psychoactive Drugs
Chemicals that change the chemistry of the brain (and the rest of the body) and induce an altered state of consciousness
Blood-Brain Barrier
A semipermeable membrane that separates the brain’s blood vessels from the brain tissue to protect the brain from harmful substances in the blood. The molecules that make up psychoactive drugs are small enough to pass through this barrier
Reuptake Inhibitor
A class of drugs that prevent the re-absorption of neurotransmitters back into the nerve cells that released them. This creates an abundance of the neurotransmitter in the synapse
Tolerance
A physiological change that produces a need for more of the same drug in order to achieve the same effect
Withdrawal
The physical and mental symptoms that occur after stopping or reducing intake of a substance such as drugs or alcohol, which the body has become dependent on
Circadian Rhythm
Our internal clock, controlling our temperature, wakefulness, metabolic processes, and thought processes in 24-hour cycles
NREM Stage 1
The lightest stage of sleep, right after you doze off. You experience slow breathing and irregular brain waves in this stage, along with (possibly) hallucinations and hypnagogic sensations. In this stage, it is very easy to wake up
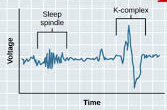
NREM Stage 2
The sleep stage characterized by deeper sleep than NREM Stage 1, but still quite light. You are now clearly asleep, but can still be woken up. Sleep spindles show up on EEGs, and we are in this stage most of the night