Psych Exam 2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
genetic variation
genetic differences that contribute to a species’ adaptation to its environment
chromosomes
long strips of DNA
DNA
helix shaped molecule made up of nucleotide base pairs
gene
control/partially control visible characteristics (gives thing)
allele
specific version of a gene (gives variation)
theory of evolution
natural selection
genotype
trait you carry
phenotype
trait you physically have
polygenic
controlled by more than one gene
mutation
permanent change in a gene
range of reaction
genes set the boundaries of how we operation, environment interacts with genes to determine where we fall
genetic environment correlation
genes influence our environment and environment influences the expression of our genes (famous soccer players and their kids)
epigenetics
how the same genotype can be express differently and lead to different phenotypes
nervous system
composed of glial cells and neurons
glial cells (glia)
supportive role to neurones
transports, mediates and provides insulation
neurons
information processors that are essential to the nervous system’s central building blocks
semipermeable membrane
allows smaller molecules and molecules without a charge to pass through
soma
cell body
nucleus located here
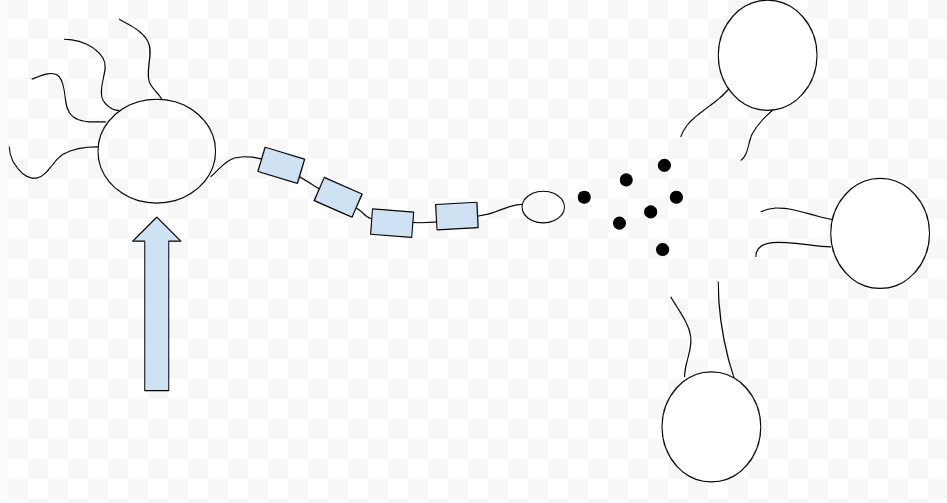
dendrites
branching extensions
input sites for signals
signals go to axon
detect
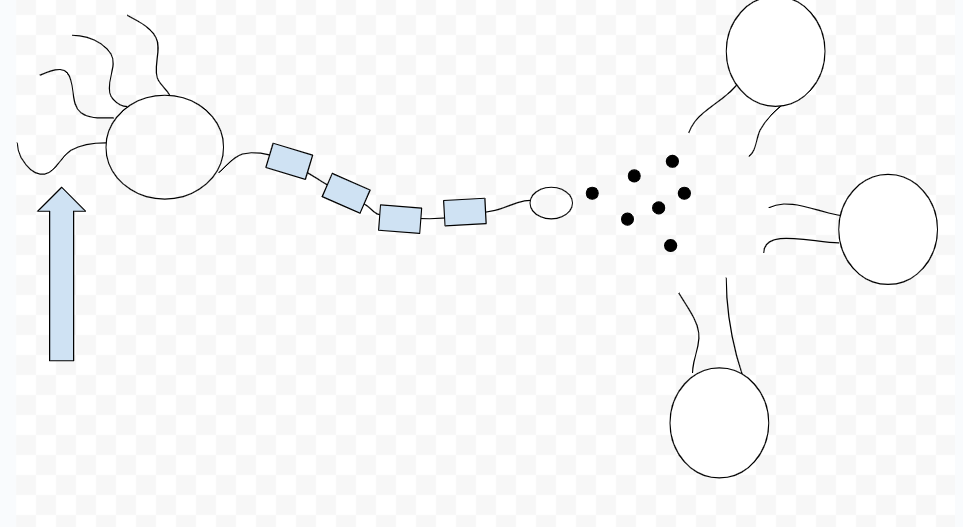
axon
away
myelin sheath
coats axon and acts as insulator
improves efficiency of axon
increases speed of signals and action potential
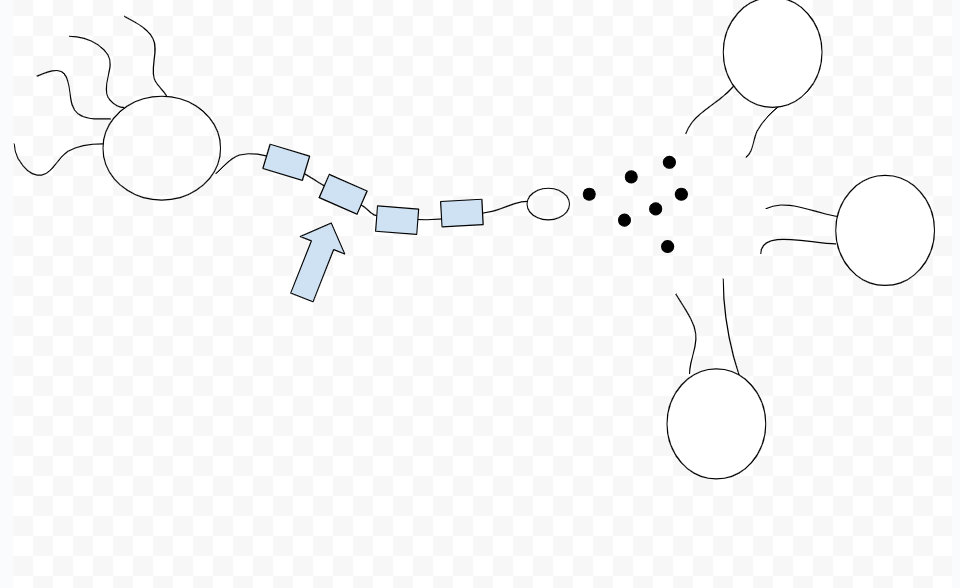
nodes of ranvier
spaces between myelin sheath
terminal button
contains synaptic vesicles which house neurotransmitterss
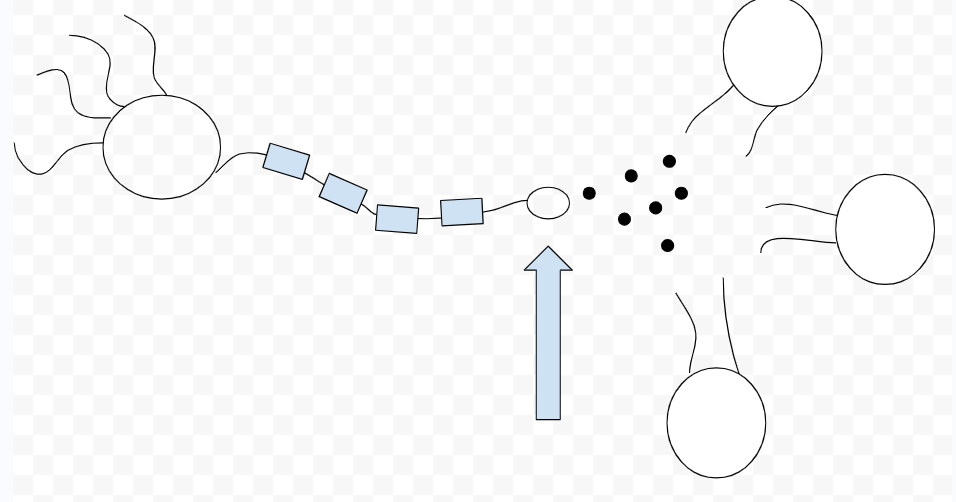
synaptic cleft
very small space between two neurons
where neuron communication occursr
receptors
proteins on cell surface where neurotransmitters attach
relationship between neurotransmitters and receptors
will only bind if they fit
lock and key
membrane potential
signal goes through one of two fluids depending on charge
resting potential
always in state of readiness
negative charge
high sodium concentration
action potential
electrical signal that moves cell body down to axon terminal
positive charge
threshold of excitation
neuron becomes active
action potential begins
all or none
incoming signal is either sufficient or insufficient
agonist
mimic
bind to receptor sites
antagonist
block
bind to receptor sites
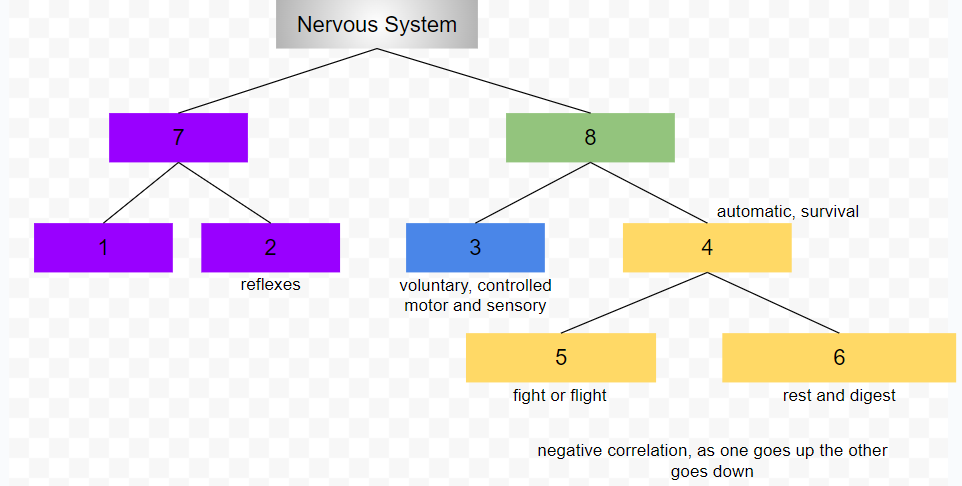
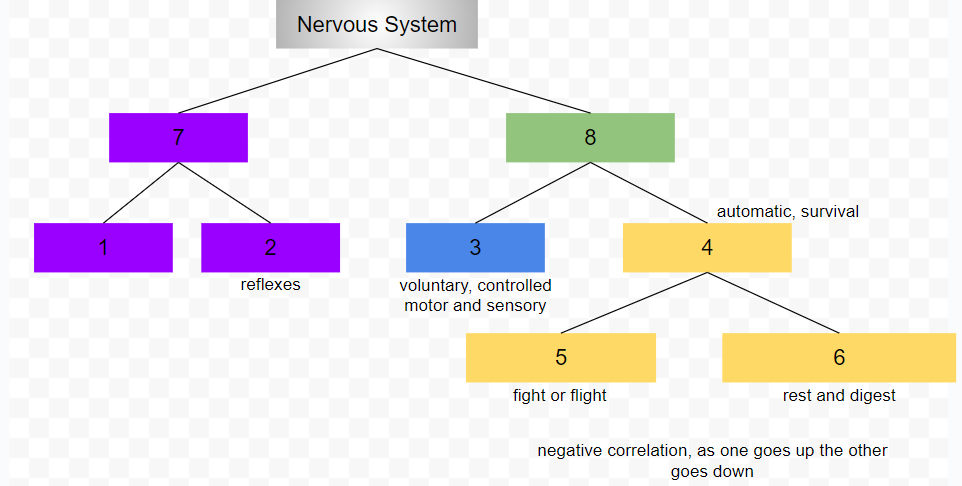
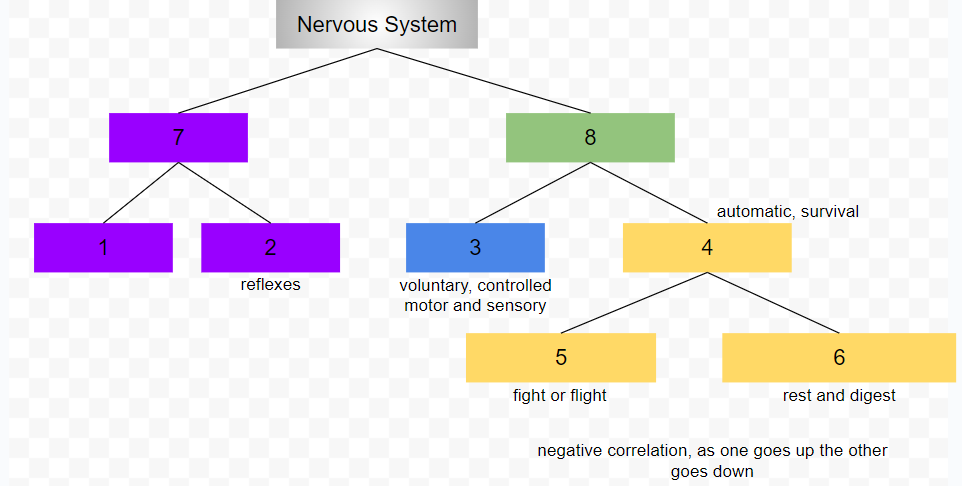
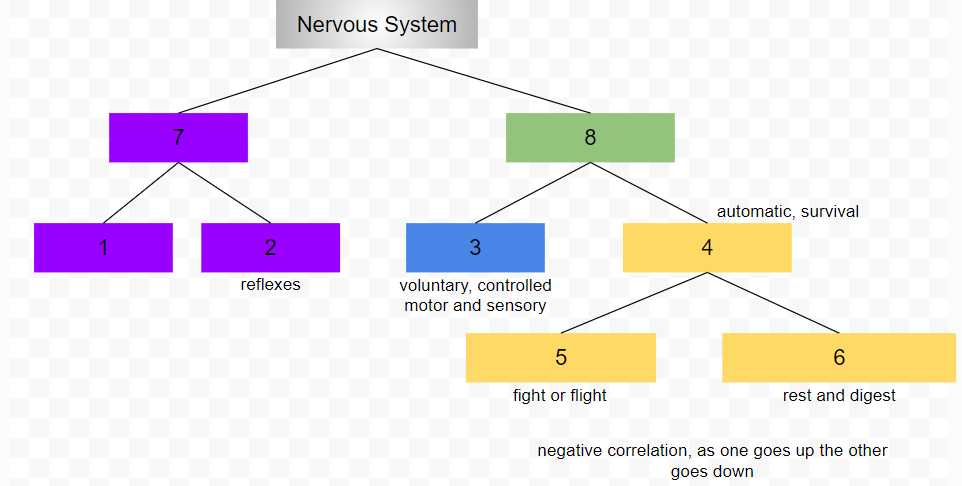
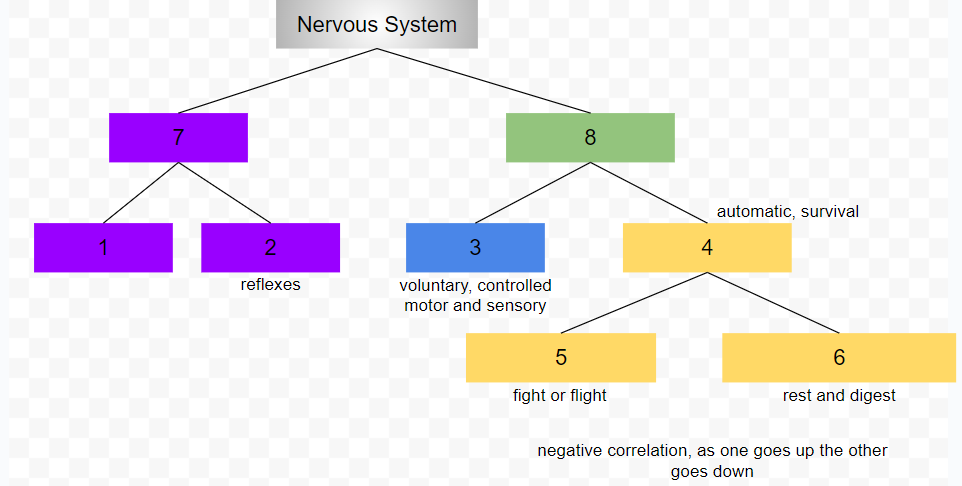
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
connects CNS to rest of the body
thick bundle of axons that carry messages back and forth
somatic nervous system
conscious, voluntary and controlled activities
motor and sensory neurons
motor neurons
carry information from CNS
efferent
sensory neurons
carry information to CNS
afferent
autonomic nervous system
controls internal organs and glands outside of voluntary control
automatic, survival
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
1
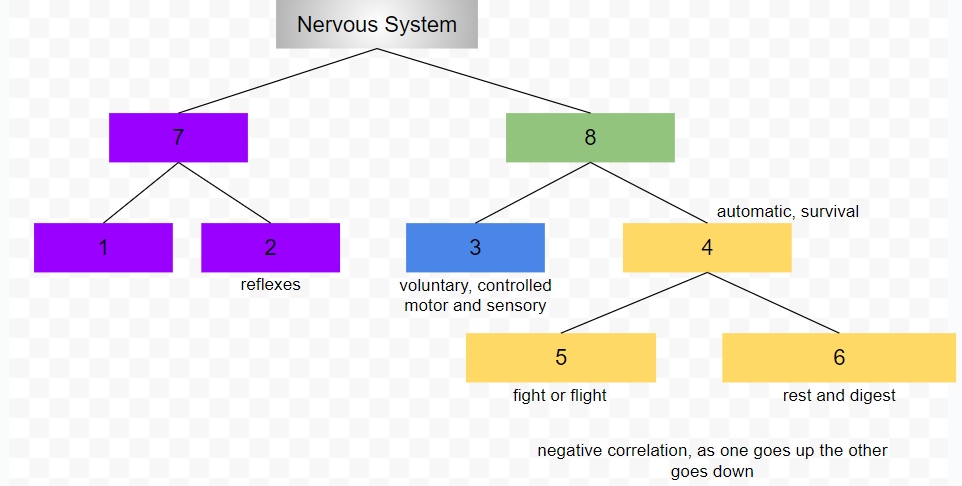
2
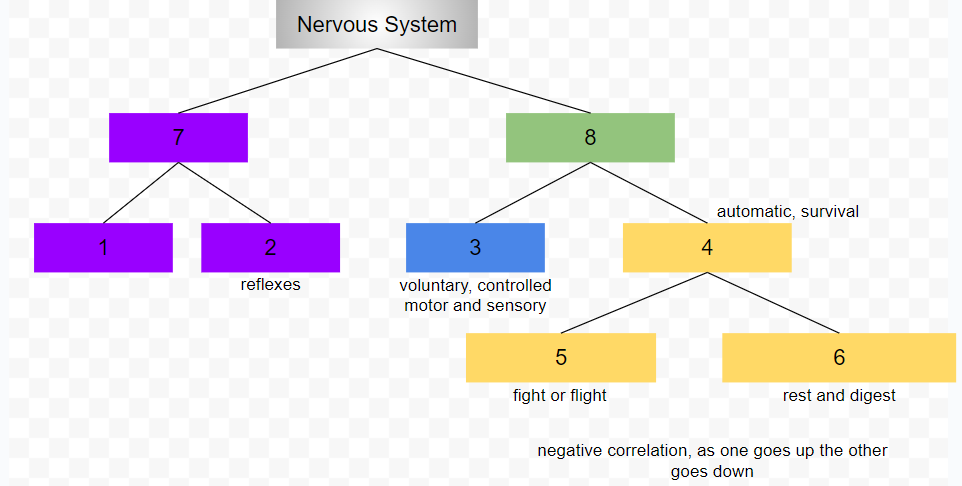
3
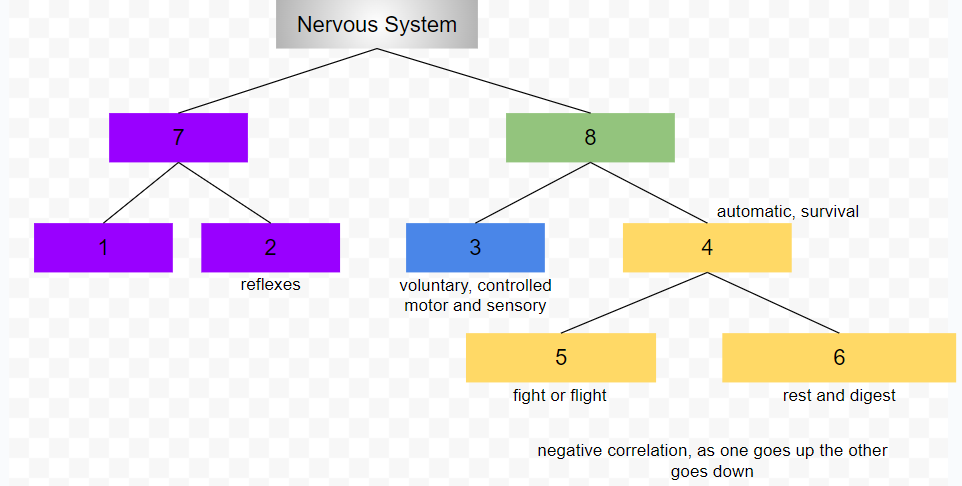
4
5
6
7
8
homeostasis
state of balance where biological conditions are maintained
neuroplaticity
how the nervous system can change and adapt
example: getting into an accident and having to learn how to speak again
cerebral cortex
surface of the brain
consciousness, thought, emotion, reasoning, language, memory
gryi (gyrus)
folds and bumps on the surface of the brain
sulci (sulcus)
grooves on the surface of the brain
longitudinal fissure
deep groove that separates the brain into right and left
lateralization
specialization of function
evidence of this in each hemisphere
right side of body
left brain controls
left side of body
right brain controls
forebrain
two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex
largest part of the brain
includes thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland and limbic system
frontal lobe
forward part of brain
reasoning, motor control, emotion, language
motor cortex, prefrontal cortex, broca’s area
motor cortex
motor control
frontal lobe
prefrontal cortex
reasoning and emotion
frontal lobe
processing and retaining information
broca’s area
language
frontal lobe
parietal lobe
immediately behind frontal lobe
processing information from body’s senses
somatosensory cortex
somatosensory cortex
processes information from senses
parietal lobe
temporal lobe
sides of the head (temples)
hearing, memory, some language
auditory cortex and wernicke’s area
auditory cortex
hearing
temporal lobe
wernicke’s area
memory and some language
temporal lobe
occipital lobe
back of the brain
primary visual cortex
thalamus
all senses (not smell) go here before the rest of the brain
forebrain
limbic system
processes emotion and memory, includes smell
forebrain
hippocampus
learning and memory
forebrain
gives memory meaning
transfers to long term
amygdala
ties emotion into memories
forebrain
regulates emotion
hypothalamus
regulates homeostatic processes
forebrain
releases and inhibits hormones from pituitary gland
midbrain
deep within brain
hindbrain
back of the head
acetylocholine
muscle action and memory nuerotransmitter
beta-endorphin
pain and pleasure neurotransmitter
dopamine
mood, sleep and learning neurotransmitter
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GAMA)
brain function and sleep neurotransmitter
glutamate
memory and learning neurotransmitter
norepinephrine
heart, intestines and alertness neurotransmitter
serotonin
mood and sleep neurotransmitter
reticular formation
regulates sleep/wake cycle, arousal, alterness and motor activity
located in midbrain but extends to forebrain and hindbrain
substantia nigra
produce neurotransmitter dopamine
midbrain
“black substance”
ventral tegmental area (VTA)
produce neurotransmitter dopamine
midbrain
cerebellum
receives from muscles, tendons, joints and structures
hindbrain
allows you to create memories if your hippocampus was damaged
medulla
automatic processes
hindbrain
pons
connects to rest of the brain
hindbrain
CT scan
structure
tumors and atrophy
MRI
structure
moves h atoms and uses a magnet
PET scan
activity
glucose blood flow
EEG
activity
electrical activity
fMRI
structure and activity
blood flow, oxygen levels, uses magnet
pituitary gland
at the base of the brain
works with hypothalamus
master gland
growth hormone
thyroid gland
regulates growth, metabolism and appetite
disorders are treatable with medication
thyroxine and triiodothyronine
adrenal glands
above kidneys
involved in stress response
epinephrine and norepinephrine
pancrease
internal organ with hormones that regulate blood sugar
involved in diabetes
insulin and glucagon
gonads (ovaries and testes)
sexual hormone for reproduction
motivation and behavior
pineal gland
melatonin
regulate sleep