Chemical Nomenclature
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Ionic compounds
AKA formula units
Composed of cations and anions
Binary ionic compounds
Composed of two monoatomic ions
Polyatomic ionic compounds
Polyatomic ions act as a group and are held together by covalent bonds
Hydrates
Ionic compounds with water as part of the crystal
Formula ⋅ # H2O
6 ionic compound naming rules
1. Overall charge is 0
2. No prefixes in ionic compounds except naming hydrates
3. Written in the simplest ratios
4. Cation is written first
5. Parenthesis are used only when more than one polyatomic ion are present
6. Use roman numerals only when needed
Binary molecular compounds
Composed of two nonmetals
Represented by molecule particles (includes organic molecules & acids)
Held together by covalent bonds (sharing electrons)
Prefix system used to indicate # of atoms
Formulas identify the number of each atoms present (do not reduce)
Ammonia
NH3
Water
H2O
Hydrogen peroxide
H2O2
Diatomic elements
Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer
Organic molecules
Alkanes and alcohol
Molecules that contain carbon
Use hydrocarbon names (not prefixes)
4
A carbon atom contains __ valence electrons and forms __ covalent bonds with other atoms
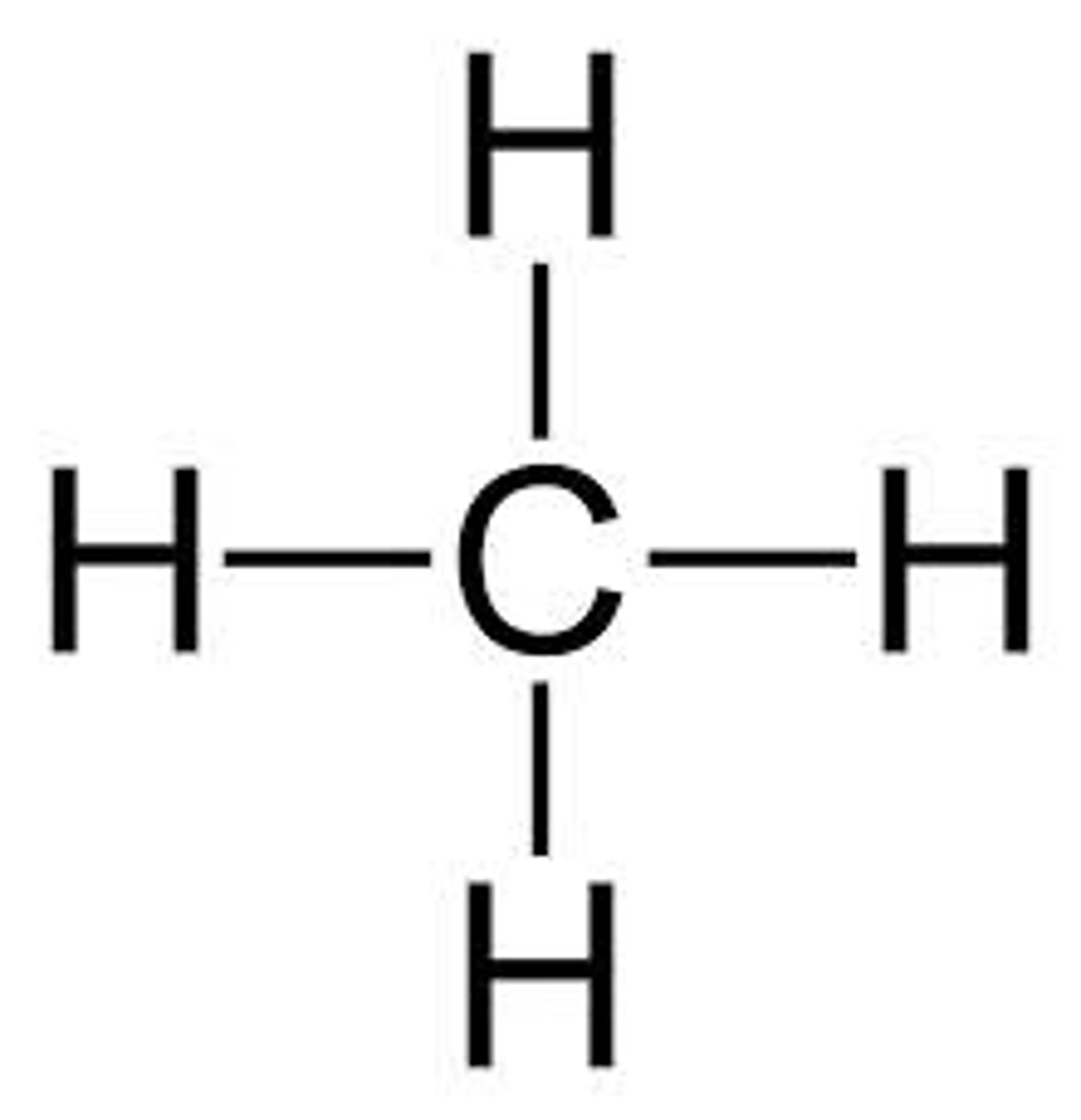
Alkane formula
R-H
C(n)H(2n+2)
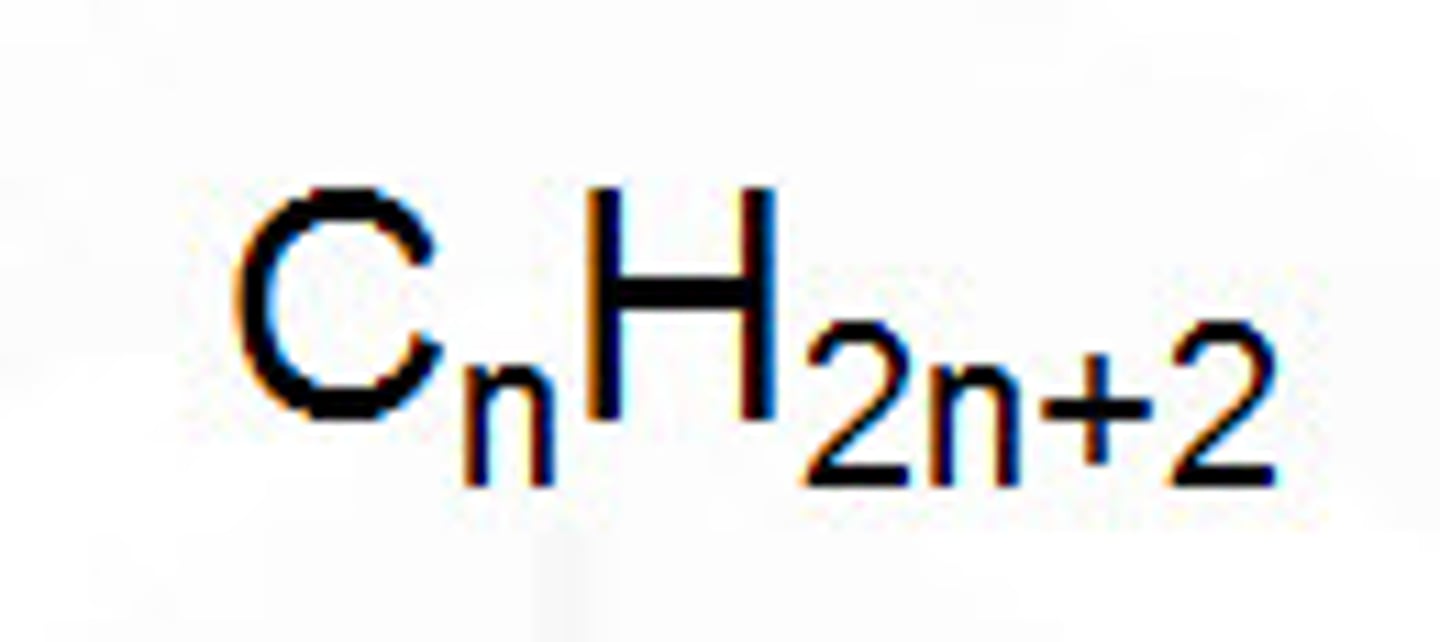
Alcohol formula
R-OH
C(n)H(2n+1)OH
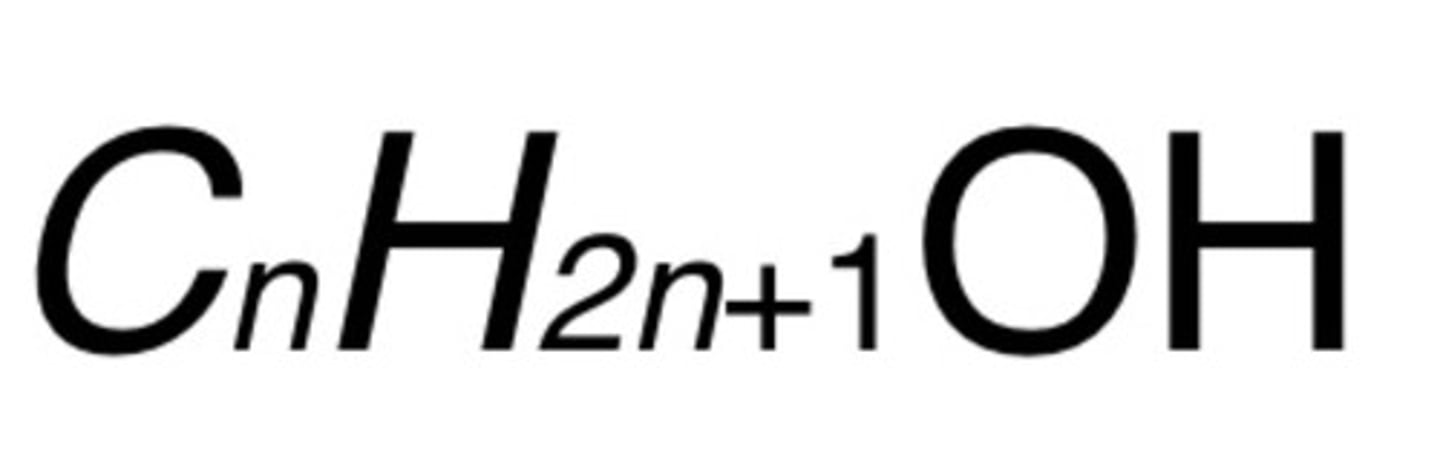
Hydrocarbon names 1-4
Meth, eth, pro, bu
Methane
CH4
Methanol
CH3OH
Acids
Represented by covalent molecule that produces H3O+ in water
Acid naming rules
1. Anion ends in -ide: "Hydro" as prefix and -ic as suffix followed by "acid" (e.g. Hydrochloric acid).
2. Ends in -ite: -ous as suffix followed by "acid" (e.g. Phosphorous acid).
3. Ends in -ate: -ic as suffix followed by "acid" (e.g. Nitric acid).
Mono-
1
Di-
2
Tri-
3
Tetra-
4
Penta-
5
Hexa-
6
Hepta-
7
Octa-
8
Nona-
9
Deca-
10