Psychological approaches to depression
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is the core feature of depressive disorders in DSM‑5‑TR?
They are marked by unipolar depression (persistent low mood without mania).
Name 6 depressive disorders included in DSM‑5‑TR.
Major depressive disorder
Persistent depressive disorder
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder
Postpartum depression
Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder
Medication‑induced depressive disorder
Depressive disorder due to another medical condition
What disorder includes both mania and depression?
Bipolar disorder
What are the emotional symptoms of MDD?
Sadness, emotional numbing, anxiety, anger, agitation.
What are the cognitive symptoms of MDD?
Negative self‑view, guilt, self‑blame, hopelessness about the future.
What are the motivational symptoms of MDD?
Trouble starting tasks, inertia, difficulty making decisions.
What are the somatic(physical) symptoms of MDD?
Appetite loss, sleep disturbance, fatigue, loss of libido, hypochondriasis.
What is the time requirement for diagnosing MDD?
At least 5 symptoms nearly every day for 2 weeks, including depressed mood and/or loss of pleasure.
What is the difference between single episode and recurrent MDD?
Recurrent episodes have periods of remission longer than 2 months
What is persistent depressive disorder?
Milder but chronic depression lasting ≥ 2 years in adults or 1 year in children, without remission longer than 2 months.
Name 2 of the required symptoms of PDD (must have at least 2).
Appetite changes, sleep changes, low energy, low self‑esteem, poor concentration, hopelessness.
Name biological or medical risk factors for depression.
Chronic medical conditions (e.g. diabetes), gender (female), older age, recent childbirth.
What is the aetiology of behavioural approach
learned helplessness: failure to learn that actions can change outcomes because past attempts were unsuccessful (Seligman & Maier, 1976 study: non depressed volunteers stopped trying to make noise when previous attempts was unsuccessful
Perceived uncontrollability of aversive stimuli that produces learned helplessness
Reduced rewards: Loss of social rewards → withdrawal → further loss of rewards → downward spiral.
What behavioural treatments are used for depression?
Operant conditioning: testing out controllability
Classical conditioning: learning new non‑depressive associations
not normally used on own - in combination with other things
What is the cognitive refocus of learned helplessness?
Depression is caused by expectations that negative events will occur and cannot be controlled.
What are the three depressive attributions? (cognitive approach)
Internal (some inherent personal failing)
Stable (the negative thing will persist over time)
Global (will persist over different situations)
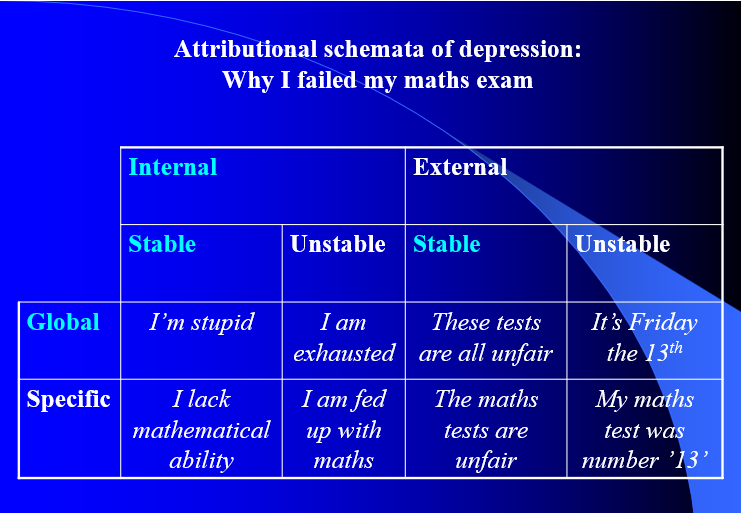
What is the negative cognitive triad?
Negative views of self, world, and future.
rooted in childhood
What are schemata in cognitive models?
Rigid, unspoken assumptions formed in childhood and triggered by stress.
What does CBT aim to do?
Correct dysfunctional thoughts and test beliefs through behavioural exercises.
however: It assumes negative thoughts cause depression, but this may not be true without longitudinal evidence.
What is the classical vs modern psychodynamic explanation for depression?
Classic: Depression results from ego defences against internal conflicts (Freud).
Modern: Depression comes from repressed negative feelings and relational difficulties
What does traditional psychoanalysis aim to do?
Uncover childhood roots, explore ambivalence, and address unconscious conflict using free association, dreams, and analysis of resistance/transference.
How is modern psychodynamic therapy different?
Focuses more on present relationships and how depression operates within them.