Acid-Base Equilbria
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Bronsted-Lowry Base
Proton acceptors
Bronsted-Lowry acid
Proton donors
What are acid-base reactions?
The transfer of a proton from an acid to a base
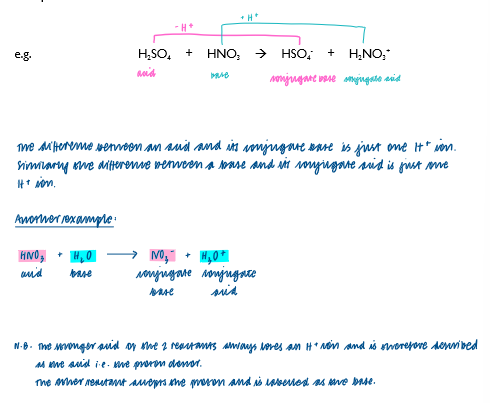
Identify Bronsted-Lowry conjugate acid-base pairs
Define pH
pH= -log10 [H+]
How can you calculate pH from hydrogen ion concentration?

How to calculate the concentration of hydrogen ions, in mol dm^-3, in a solution from its pH

Difference between a weak acid and a strong acid
A strong acid fully dissociates in water.
A weak acid only partially dissociates in water.
How to calculate the pH of a strong acid

How to deduce the expression for the acid dissociation constant, Ka, for a weak acid and carry out relevant equations.

How to calculate the pH of a weak acid

What assumptions are made when calculating the pH of a weak acid
[H+]=[A-], here we’re ignoring any H+ ions from the dissociation of water but as the [H+] from the dissociation of water is very small this will not affect the calculated pH
[HA]equilibrium = [HA]start, this ignores the fact that some of the acid (HA) molecules will have dissociated into ions but as the dissociation is small this is a reasonable assumption to make
Define the ionic product of water, Kw
Kw=[H+(aq)][OH-(aq)]
At room temp, Kw= 1.00 × 10-14
![<p>K<sub>w</sub>=[H<sup>+</sup>(aq)][OH<sup>-</sup>(aq)]</p><p>At room temp, Kw= 1.00 × 10<sup>-14</sup></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d4038785-5c24-420a-b9b6-4c70a8161934.png)
Calculate the pH of a strong base from its concentration, using Kw

Define the terms pKa and pKw
pKa= -log10Ka
pKw= -log10Kw
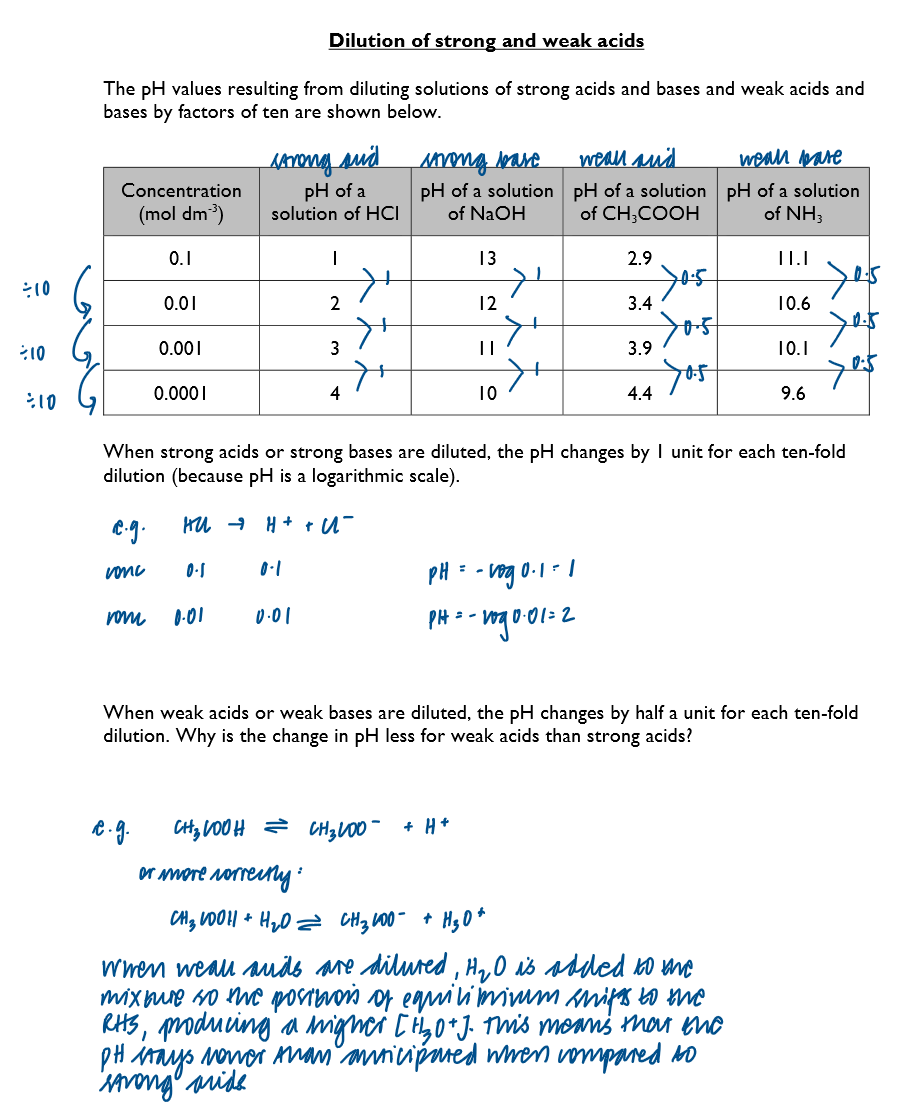
Compare the pH of a strong acid and weak acid after dilution 10, 100 and 1000 times
Measuring the pH of a variety of substances e.g. equimolar solutions of strong and weak acids, strong and weak bases, and salts

Calculate Ka for a weak acid from experimental data given the pH of a solution containing a known mass of acid
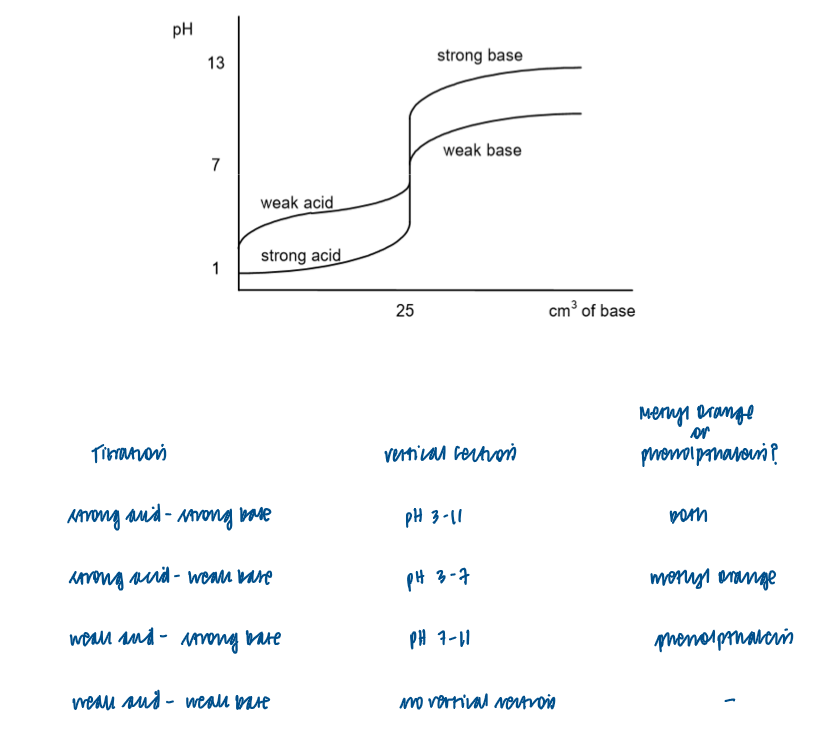
Draw and interpret titration curves using all combinations of strong and weak monobasic acids and bases
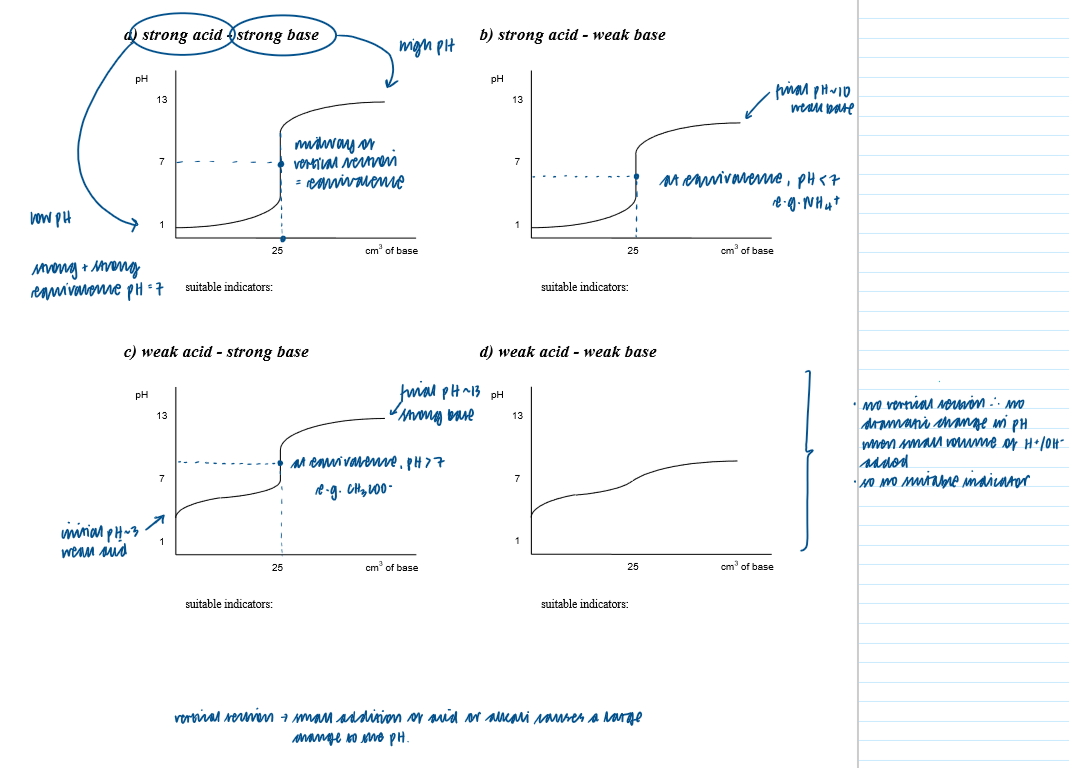
Select a suitable indicator, using a titration curve and appropriate data
Indicators are weak acids. The formula of an indicator is written as HIn. The important property of an indicator is that its colour in acidic solution must be distinctly different to its colour in alkaline solution.

What is meant by the term ‘buffer solution’ ?
Resists a change in pH when a small amount of acid or base is added.
Action of an acidic buffer solution
Consists of weak acid and the salt of a weak acid.
In an acidic buffer solution there has to be a high concentration of both weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid.
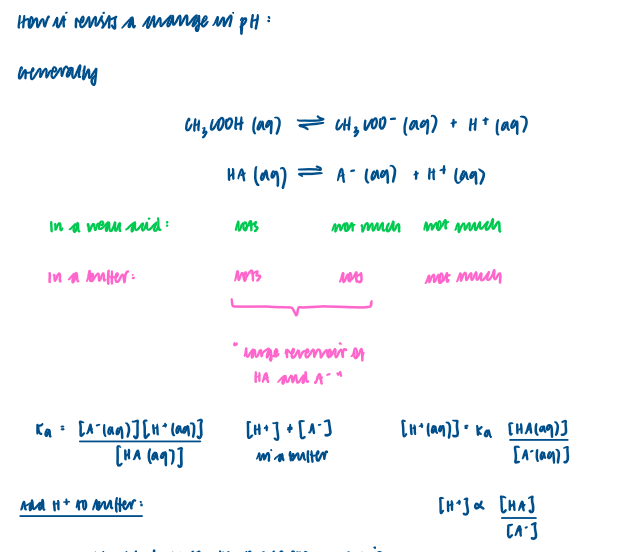
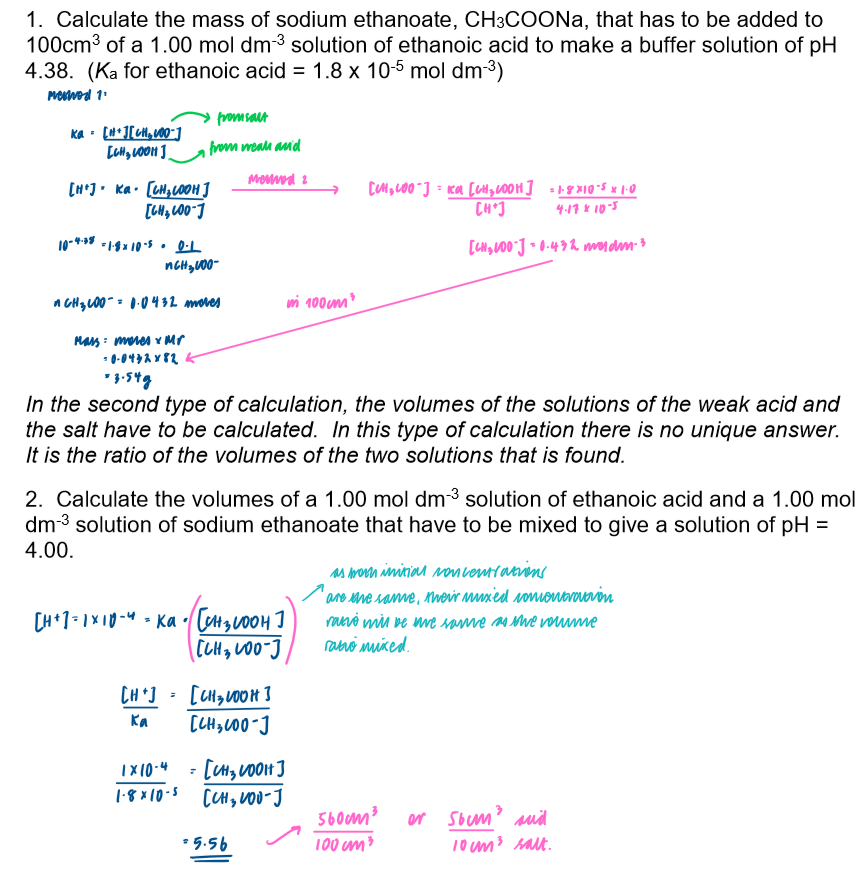
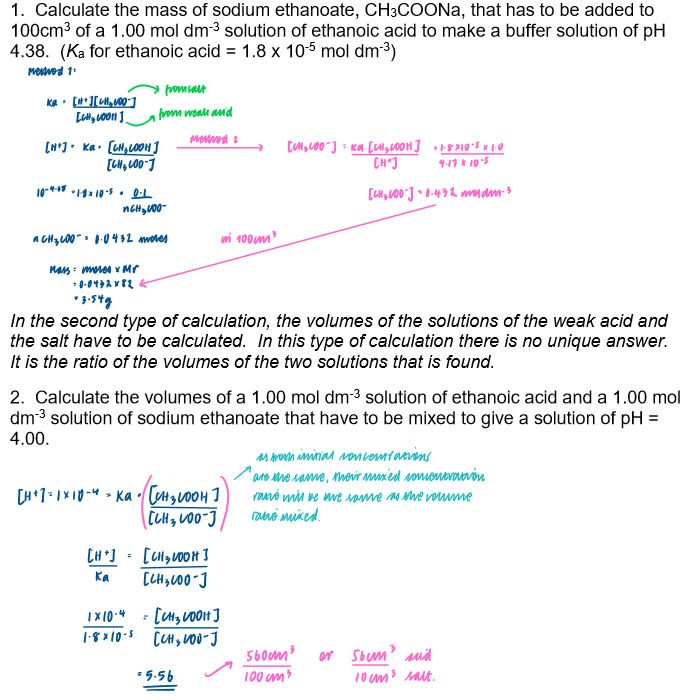
Calculate the pH of a buffer solution given appropriate data - 1

Calculate the concentrations of solutions required to prepare a buffer solution of a given pH
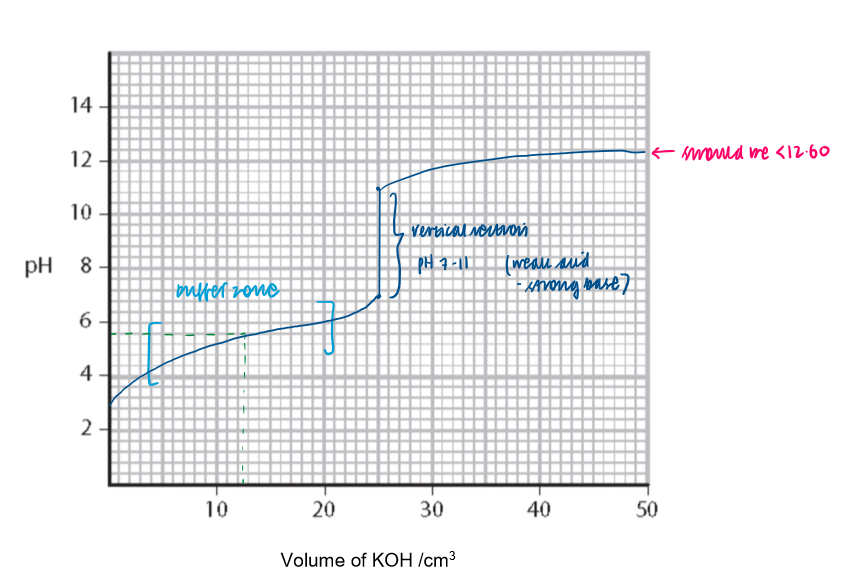
How to use a titration curve to demonstrate buffer action
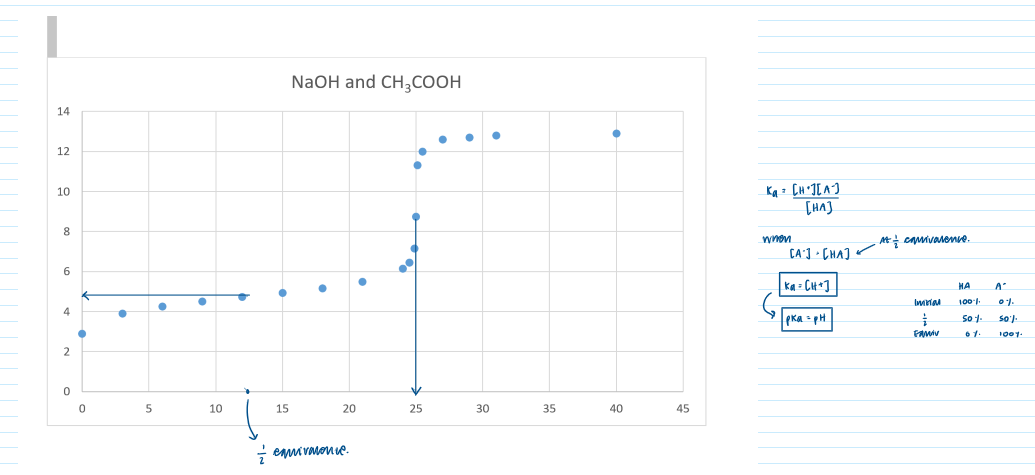
How to use a titration curve the determine Ka from the pH at the point where half the acid is neutralised
Why is there a difference in enthalpy changes of neutralisation values for strong and weak acids?
The enthalpy change of neutralisation = enthalpy change when an acid and alkali react together to form one mole of water.
When strong acids and bases react together they will produce very similar enthalpies of neutralisation. This is because the solutions completely dissociate, so the same, simple acid-base reactions occur between H+ and OH- ions to produce water in each case. The other dissociated ions present are simply spectator ions and do not affect the reaction.
However, in reactions of weak acids and bases, the ions only slightly dissociate so other enthalpy changes also occur within the solution. As a result, the enthalpies of neutralisation can vary quite a lot.

The role of carbonic acid molecules and hydrogencarbonate ions in controlling the pH of blood
The pH of blood is normally about 7.40. If the pH changes by 0.5 it can lead to unconsciousness and death.
The hydrogencarbonate buffer system is perhaps the most important as it is the only one that is coupled to the respiratory system.

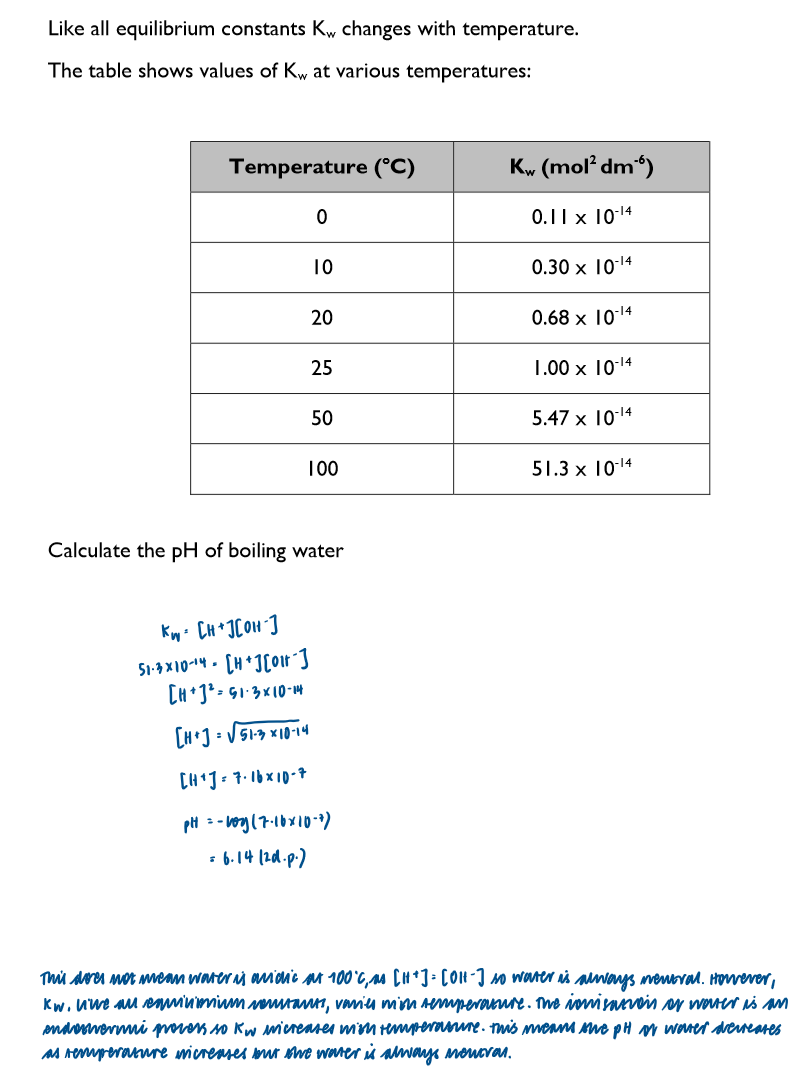
pH of boiling water:
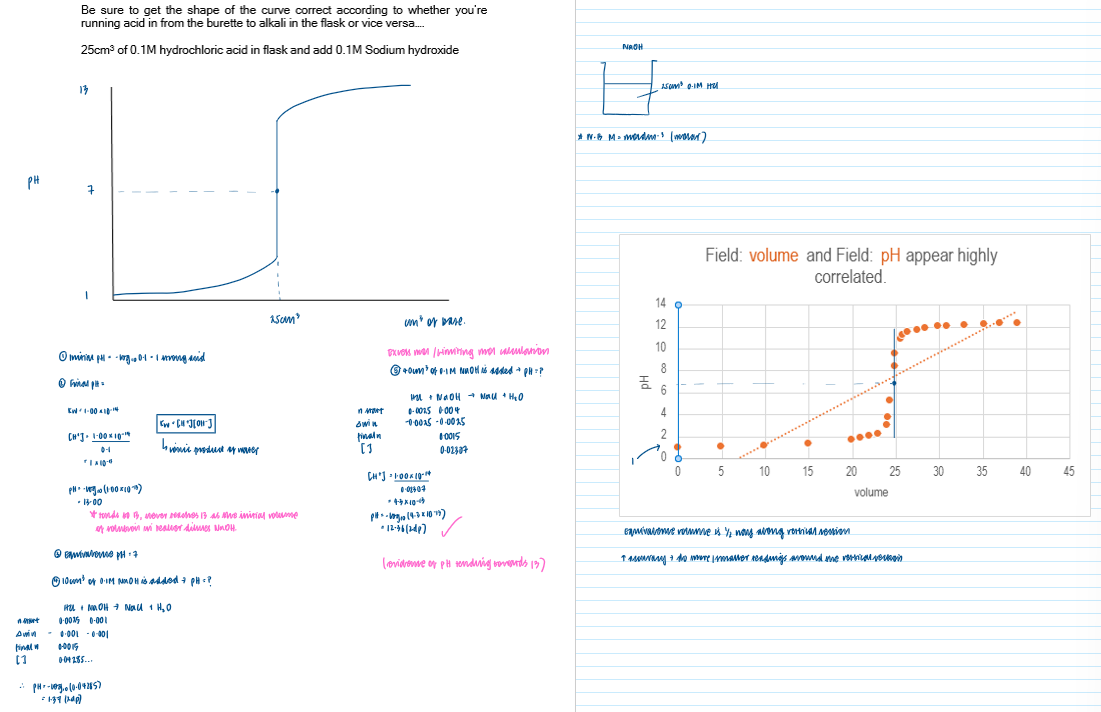
Titration curve - strong acid + strong base
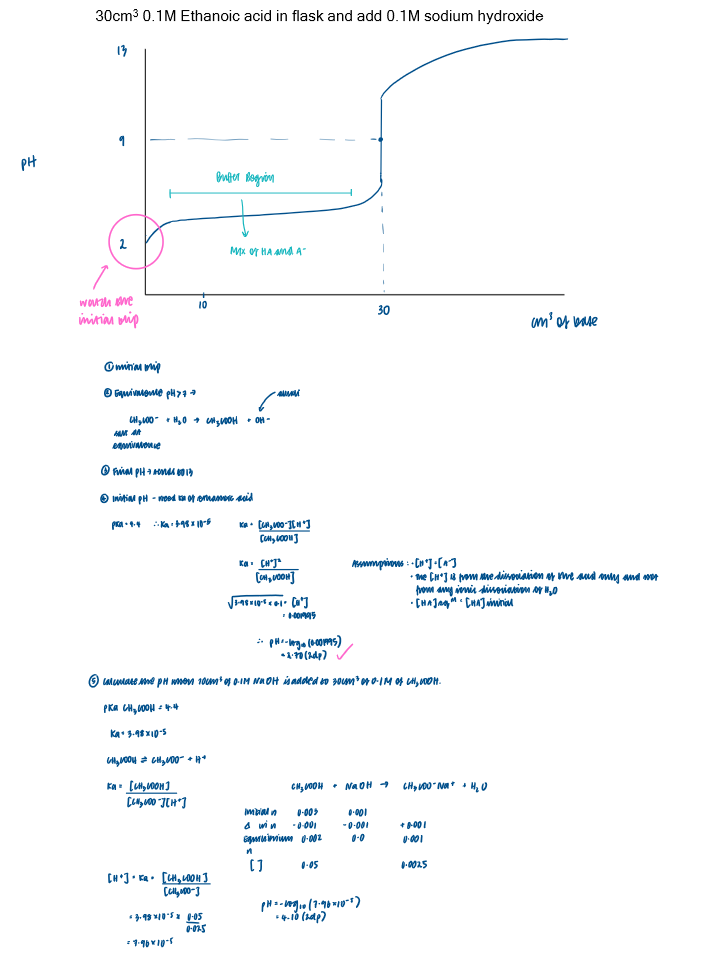
Titration curve - strong base and weak acid
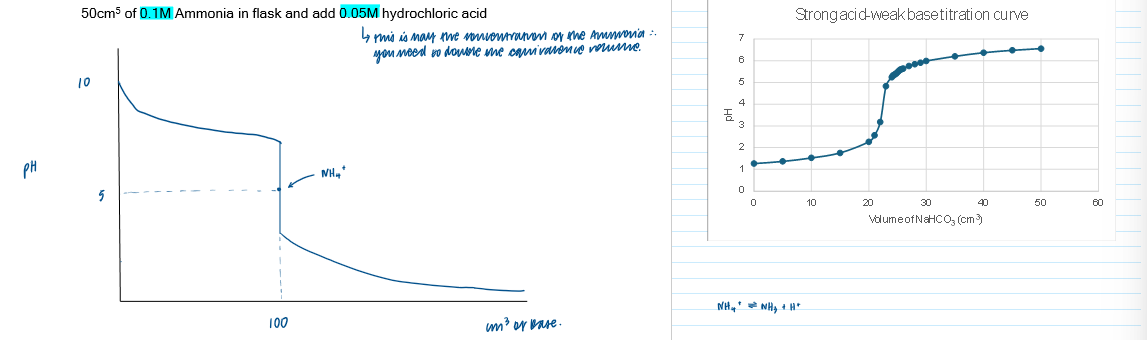
Titration curve - strong acid + weak base [
Titration curve - weak acid + weak base
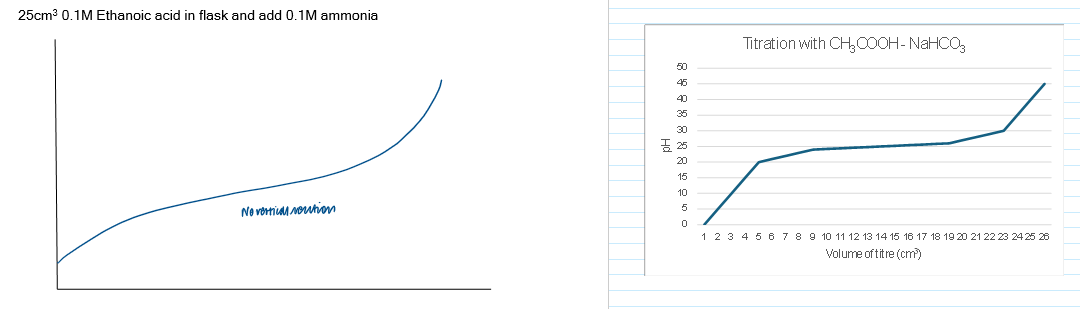
Methyl orange or phenolpthalein?
Adding H+ to an acidic buffer solution
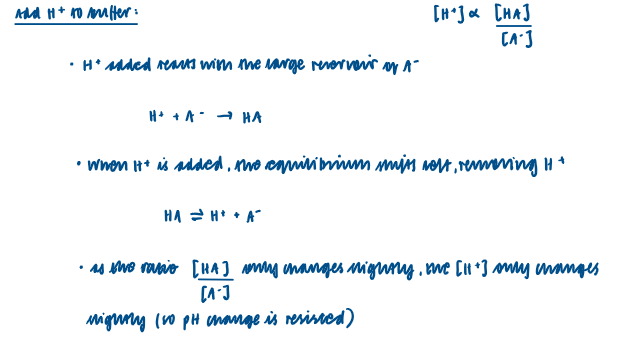
Adding OH- to an acidic buffer solution

Calculate the pH of a buffer solution given appropriate data - 2

Calculate the pH of a buffer solution given appropriate data - 3

Calculate the pH of a buffer solution given appropriate data - 4

Enthalpy of neutralisation calculations

Buffer system in blood questions:
