biological molecules
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Monomers are joined to form polymers by which reaction?
Condensation Reaction
what is a monomer?
smaller units from which larger molecules are made
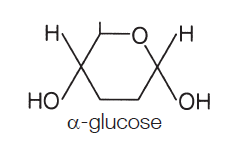
What does alpha glucose look like?
hexagonal structure, 6 carbons, (C6H1206) OH at the bottom.
what does beta glucose look like?
hexagonal structure, 6 carbons (C6H1206) OH at the top
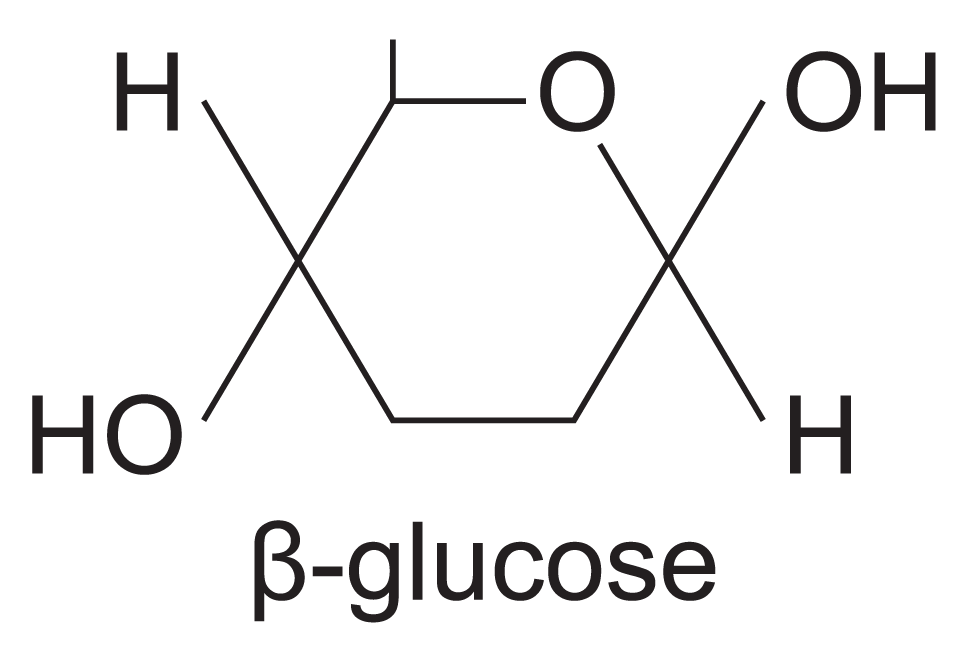
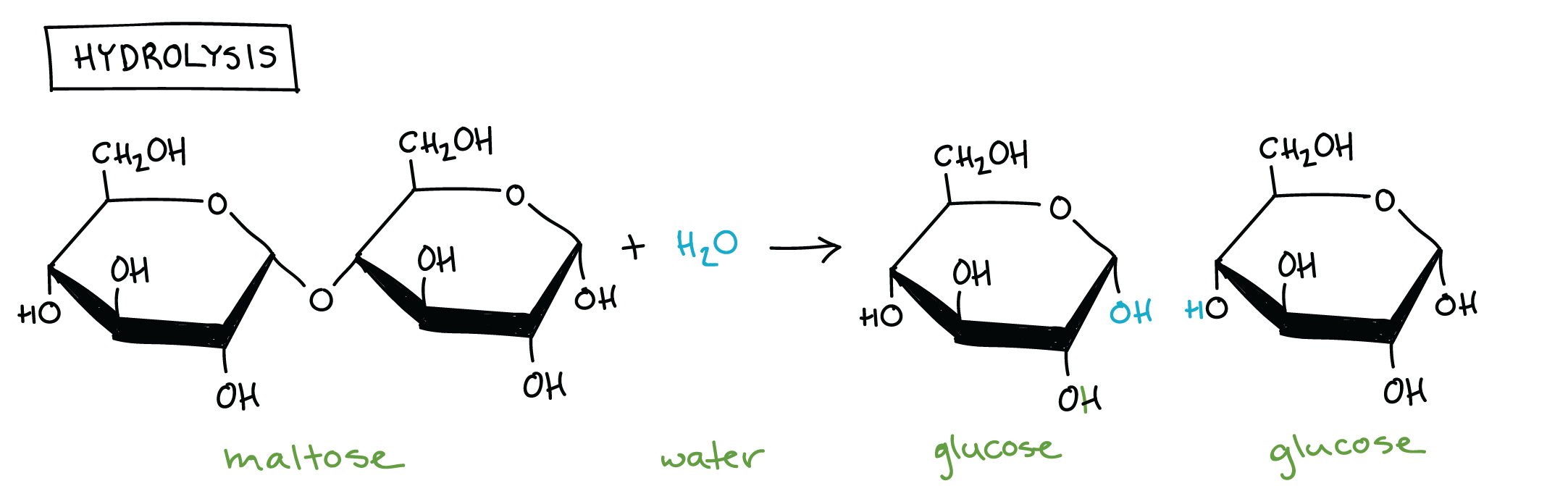
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
a reaction in which a bond is broken by the addition of a water molecule
Which disaccharide is formed from glucose and glucose?
Maltose
Draw the reaction for hydrolysis of maltose
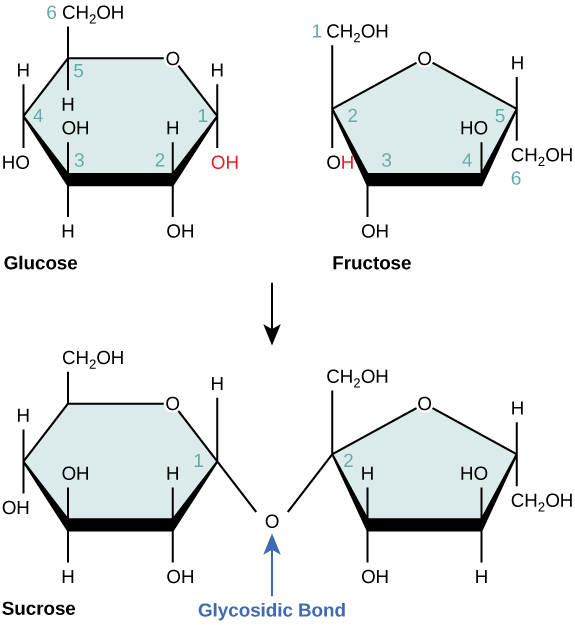
Draw the condensation of the two monosaccharides glucose and fructose
Is sucrose a reducing sugar?
no, sucrose is a nonreducing sugar
What is the test for reducing sugars?
Benedict's test
Which monosaccharides make up sucrose?
glucose and fructose
Name the three elements contained in carbohydrates
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
What colour would Benedict's reagent turn when added to sucrose?
Blue
Explain why Benedict's reagent turns red when heated with a reducing sugar.
Sugar donates electrons that reduce blue copper (II) sulfate to orange copper (I) oxide
Describe a chemical test that would enable you to show that glucose syrup contained reducing sugar.
Add benedict's reagent AND heat by placing in water bath. Turns from blue to Green= very low Yellow=low Orange=medium and Brick red=high
A condensation reaction between two monosaccharides forms what bond?
glycosidic bond
what monomer makes up starch and glycogen?
alpha glucose
What monomer makes up cellulose?
beta glucose
Which polysaccharides contain 1-4 glycosidic bonds?
Cellulose, Starch and Glycogen
What other glycosidic bonds do starch and glycogen have?
1-6
What is the test for starch?
Add iodine and it changes from yellow to blue/black if starch is present
What is the structure of glycogen?
Highly branched
What is the structure of cellulose?
long unbranched straight chains that run parallel
What is the structure of Starch?
branched, helical and compact
Give two ways starch is suited to its role as an energy storage molecule
-its insoluble so doesn't affect water potential
-large and insoluble so doesn't diffuse out the cell
-compact so lots can be stored in small spaces
-when hydrolysed forms alpha glucose—> readily used in respiration many ends which can be acted on simultaneously by enzymes meaning glucose molecules are released very rapidly
Where is glycogen found?
animal and bacterial cells
Where is glycogen stored?
granules in the muscles and liver
Give two ways glycogen is suited to its role as an energy storage molecule
-insoluble so doesn't tend to draw water into cells by osmosis
-being insoluble so does not diffuse out of cells
-it is more highly branched than starch and so has more ends that can be acted on simultaneously by enzymes therefore rapidly broken down to form glucose monomers which are used in respiration.
Describe how the monomers in cellulose are arranged to produce a polymer that is good for support.
Has lots of hydrogen bonds which provide collective strength, molecules are grouped to form microfibrils which in turn are grouped to form fibres all of which provides yet more strength.
What do the numbers 1 and 4 refer to in glycosidic bonds?
the carbons
What allows herbivorous mammals to digest starch but not cellulose?
herbivorous mammals produce amylase and maltase but not cellulase or cellobiose, they don't have the enzymes to digest cellulose.
Explain the difference between the structure of the starch molecule and the cellulose
Starch molecules contain alpha glucose with 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds whereas cellulose molecules contain beta glucose with 1-4 glycosidic bonds. The position of the hydrogen and the hydroxyl group on carbon atoms are inverted.
What are the roles of lipids?
-energy source (x2 calories as the same mass of carbs or protein)
-waterproofing (sebum in mammals)
-thermal insulation
-protection for delicate organs
What are triglycerides composed of?
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids that join via 3 condensation reactions
Draw a triglyceride
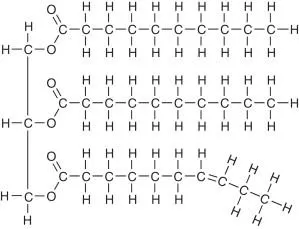
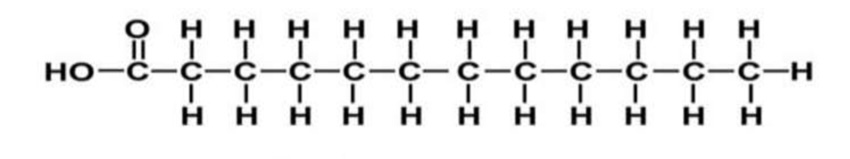
Which fatty acid is shown in this diagram?
Saturated fatty acid
What is the difference between an unsaturated fatty acid and a saturated?
the unsaturated fatty acid contains at least one double carbon-carbon bond
Describe how a phospholipid is different to a triglyceride
Phospholipids contain 2 fatty acids and a phosphate molecule where as triglycerides contain 3 fatty acids and a glycerol molecule.
Give the property of the phosphate head and the tail on the phospholipid
Head=hydrophilic head
Tail-hydrophobic tail
Animal and plant seeds use lipids rather than carbohydrates as a long-term energy store. Suggest and explain one advantage of this.
Provides twice as much energy as carbohydrates of the same mass so is a lighter storage molecule.
Name the test used to identify the presence of lipids
Emulsion test
Describe how you would carry out the emulsion test on a food sample
-Fill a test tube with 2cm cubed of tested sample
-Add around 5cm cubed of ethanol and shake the tube rigorously to dissolve the lipid in the sample
-Add 5cm cubed of water and shake slightly less rigorously
-If it turns cloudy white (an emulsion) lipid is present
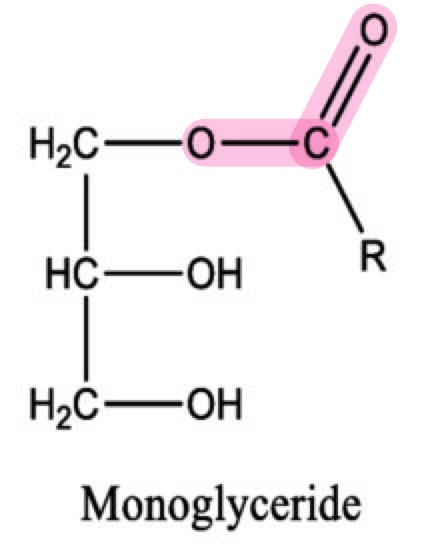
What is the bond that joins a glycerol molecule to a fatty acid?
Ester bond
Explain why triglycerides are not considered to be polymers
because its only one glycerol molecule and a fatty acid whereas polymers are long chains of repeating monomers.
How many different amino acids are found in nature?
20
What are the three groups that make up an amino acids?
Amine group, variable group and carboxylic acid group
Draw the general structure of amino acids
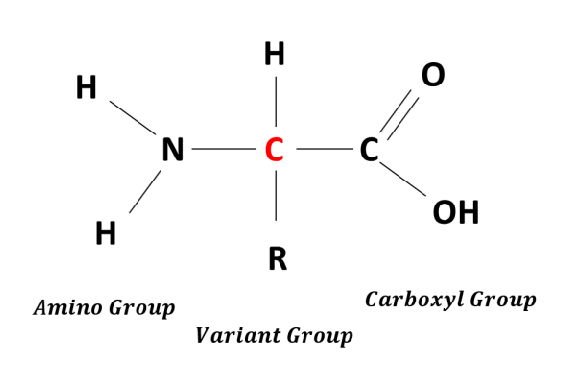
Draw a diagram to represent the formation of a dipeptide (label the reaction and the bond)
peptide bond and condensation reaction
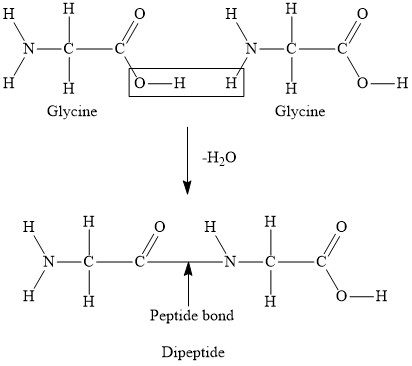
Explain how a change in one amino acid may lead to a change in the function of a protein
-Change in primary structure (sequence of amino acids)
-Leads to a change in secondary structure (alpha helix and beta sheet)
-Leading to a change in tertiary structure due to a different number/position of the ionic, disulphide and hydrogen bonds (as R groups have changed)
-Therefore forming a different protein with a different function
What bonds hold together an alpha helix?
hydrogen bonds
List the features of the following bonds that maintain the tertiary structure of a protein
Hydrogen bonds- numerous of them but easily broken
Ionic bonds- formed between carboxyl and amino acids that aren’t involved in forming peptide bonds, easily broken by pH changes and weaker than disulphide bonds
Disulphide bonds- fairly strong and not easily broken
What is meant by the quaternary structure of a protein?
large proteins often form complex molecules with more than one polypeptide chain containing a number of individual polypeptide chains linked linked in various ways.
Describe fibrous proteins
they have structural functions, form long chains that run parallel, they are very stable molecules e.g. collagen
Whats an example of a globular proteins?
enzymes and haemoglobin
Give one way in which formation of a peptide bond is similar to the formation of a glycosidic bond
both peptide and glycosidic bonds are formed by a condensation reactions
Name one chemical element found in all amino acids but not in monosaccharides
Nitrogen
Describe a biochemical test to find out if a substance contains a protein
-Add small volume of sodium hydroxide
-Add a few drops of Biuret reagent into the test tube
-Agitate the mixture gently will turn from blue to lilac
What is activation energy?
the minimum amount of energy that must be available to reactants for a chemical reaction to occur
What are enzymes?
Biological catalysts i.e. they don’t make biochemical reactions happen but simply speed them up
Name two properties of enzymes
-globular proteins
-can alter rate of reaction without undergoing permanent change
-effective in very small amounts
-most enzyme controlled reactions are reversible
-most enzymes are denatured by high temperatures and extreme pHs
what are three conditions required for typical chemical reaction to occur?
-substrates collide with the enzyme with sufficient kinetic energy to alter arrangement of atoms
-energy of the production (glucose and fructose) must be lower than the substrates
-an initial boost of energy is required to start the reaction-activation energy
Draw a labelled graph showing how enzymes lower activation energy
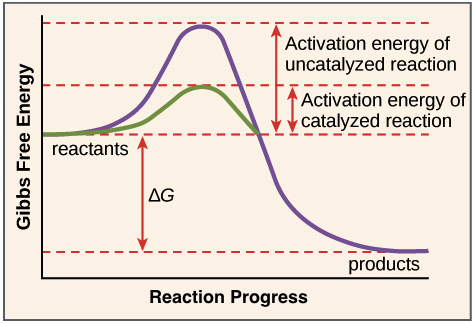
Make brief notes on the structure of enzymes
-substrate situated in enzymes active site
-single polypeptide chain of 50 amino acids
-amino acids not apart of active site
-hydrogen, ionic and disulphide bonds
-6 amino acids that bind to the substrate
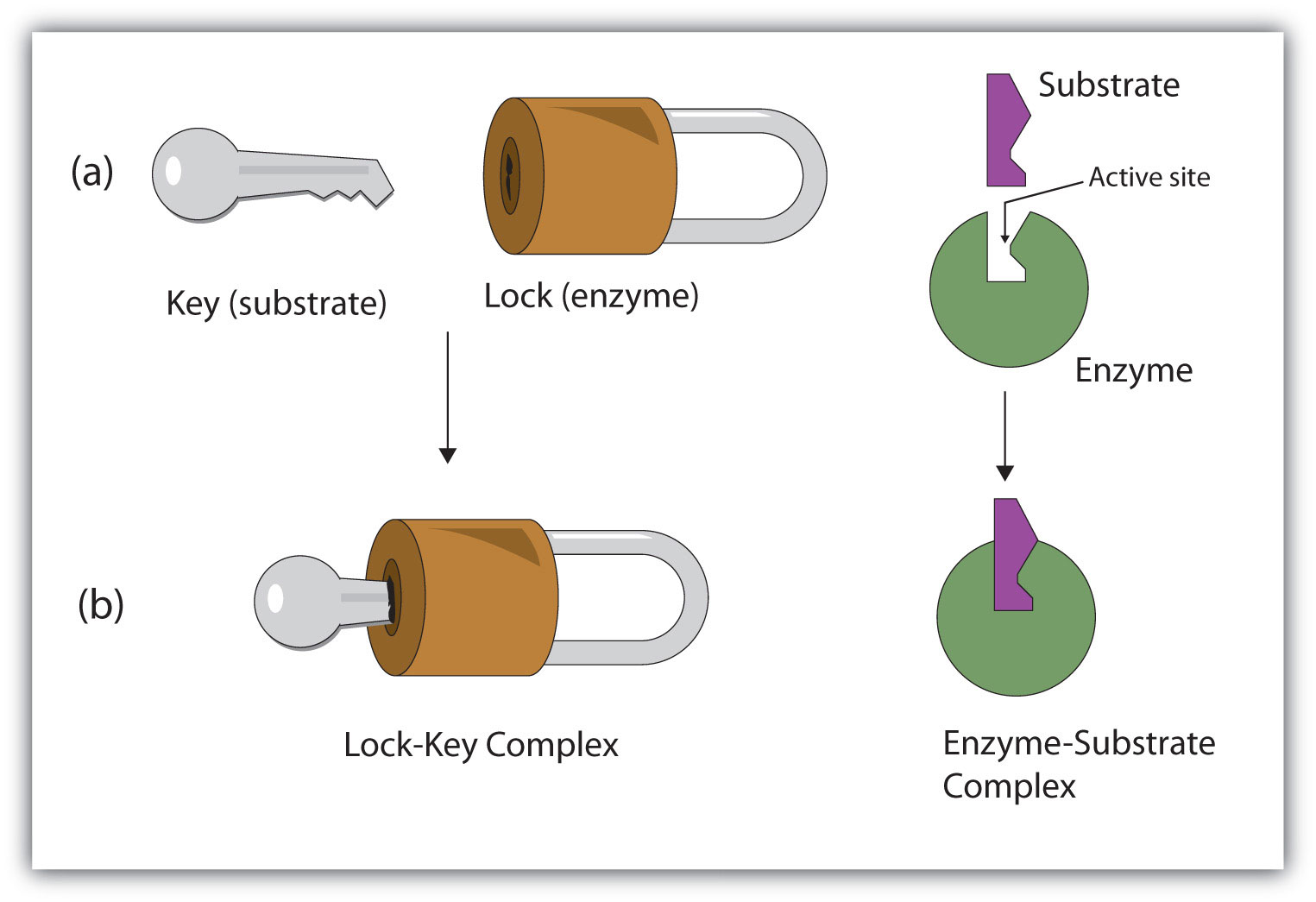
How does the lock and key model work? Draw a diagram
works similarly to a key and how they only fit specific locks, the substrate only fits the active of one particular enzyme
What is the induced fit model? Draw a diagram
The active site forms around substrate as the active site and substrate bind. It has a specific shape but can mould itself around the substrate.
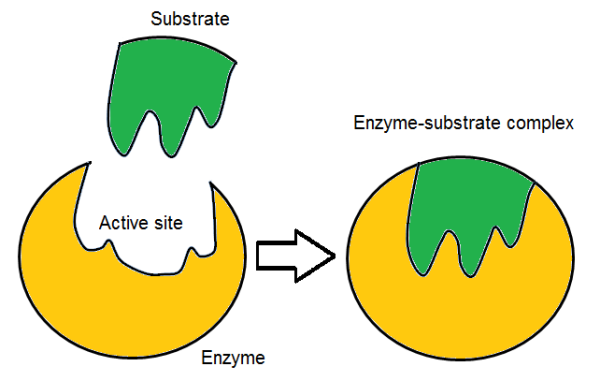
Why is the induced fit model more widely accepted?
It helps us explain how enzymes reduce activation energy and shows the enzyme is flexible
How does the induced fit model explain how activation energy is lowered?
It shows how bonds are weakened and distorted
Why might changing certain amino acids that are part of the active site prevent the enzyme from functioning?
Because it’ll change the active site and it will no longer be complementary to the substrate. this means that it the substrate can no longer bind and wont form the enzyme-substrate complex.
Explain why enzymes are highly effective in tiny quantities
they don’t get used up so the same enzyme can speed up lots of reactions over and over again so not much is needed
For an enzyme to work it must…
-have an active site that is complementary to the substrate
-the active site has to come into physical contact with the substrate
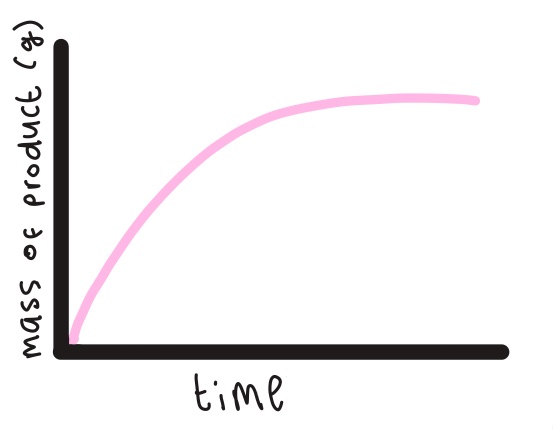
Explain the shape of the graph (the rate of formation of product molecule)
The more time goes on the more substrate is hydrolysed therefore more product is produced. the line doesn't continue to rise because eventually the substrate molecules begin to run out.
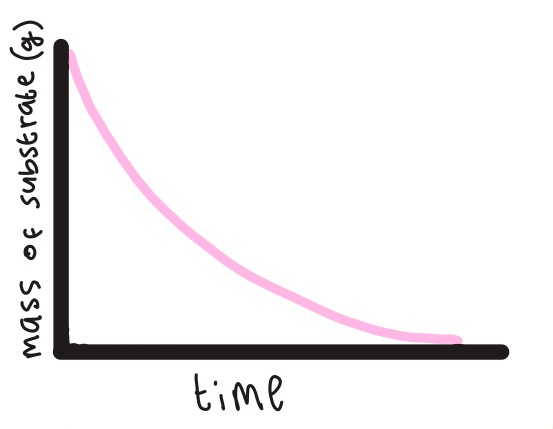
Explain the shape of this graph (the rate of the disappearance of substrate molecules)
It decreases because the substrate is being hydrolysed into products. It levels out once all the substrate is used up.
Describe the effects of increasing temperature on the rate of reaction
As the temperature increases the rate of reaction increases until an optimum temperature is reached. At this point the rate of reaction rapidly decreases as temperature increases.
Explain the changes that occur to the enzyme until optimum temperature was reached.
As temperature increases rate starts to increase. This is because the enzymes have more kinetic energy making them move faster and have more collisions. This means that more enzymes and substrates are colliding forming more enzyme substrate complexes.
Generally, temperatures in excess of 45 degrees C cause enzymes to denature. Explain why this happens.
Because the enzymes have too much kinetic energy and the vibrations are too strong for the hydrogen, ionic and disulphide bonds that hold the enzyme together. The bonds break causing the active site to change the shape and denature. Therefore the active site is no longer complementary to the substrate and it cannot form the enzyme-substrate complex.
Changes in the pH affect the action of an enzyme in 2 ways. Explain these two ways
-Depending on how significant the change in pH is it may break the hydrogen and ionic bonds that maintain the enzymes tertiary structure. Therefore changing the active site making it no longer complementary and unable to form enzyme-substrate complexes.
-A change in pH alters the changes on the amino acids that make up the active site of the enzyme. As a result the substrate is no longer complementary to the active site and the enzyme substrate can no longer form.
How does increasing the enzyme concentration affect rate of reaction? Explain why
The rate of reaction is increases as enzyme concentration increases. More enzyme active sites, so more to collide with substrates. Therefore more enzyme-substrate complexes are formed.
However on a graph the line would level off as there is a limiting factor. There is not enough substrates to form enzyme-substrate complexes with the growing amount of active sites.
What are enzyme inhibitors?
Molecules that have an altering effect on the active site of an enzyme. The reduce the activity of an enzyme and therefore the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction.
What is the difference between a competitive and non-competitive inhibitor?
Competitive
-fit directly into active site. -they are competing with substrate for active site so is similar in shape to substrate
Non-Competitive
-attach to a site other than the active site -their shape doesn’t have to be similar to substrate or active site
Describe what would happen to the rate of reaction. If you increased the concentration of a competitive inhibitor? Explain your answer.
The rate of reaction would decrease because competitive inhibitors have a similar shape to the substrate meaning they can bind to the active site. If there are more competitive inhibitors there will be less active sites for the substrates to bind to. Therefore less enzyme-substrate complexes will be formed.
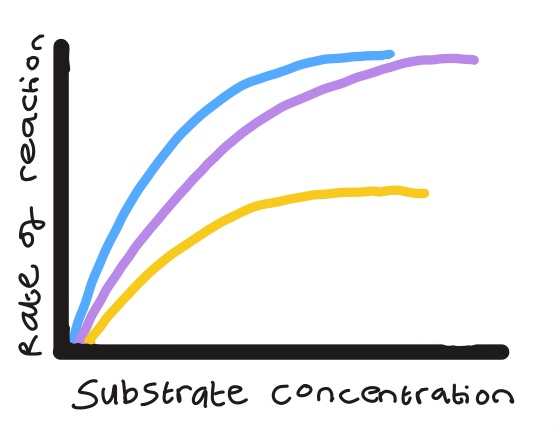
Competitive and non-competitive inhibitors affect ROR in different ways. What does each line on the graph represent?
Blue- No inhibitor present
Purple- Fixed quantity of competitive inhibitors
Yellow- Fixed quantity of non-competitive inhibitors