Gen final y10
1/321
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
322 Terms
what are the 2 types of nucleic acids
deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid
What is the monomer of a nucleic acid
nucleotides
what does the prefix mono mean
one
what does the suffix mer mean
part
what are the 3 parts of a nucleotide
pentose sugar, nitrogen base, and phosphate group
what is the atomic composition and charge of a phosphate group
PO4-3
what is the symbol of a phosphate group
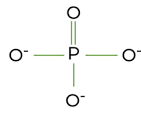
draw the structure of a phosphate group
what class of carbohydrate (sugar) has 5 carbon atoms
pentose sugar
what is the pentose sugar in DNA
deoxyribose
what is the pentose sugar in RNA
ribose
which carbon atom on the pentose sugar allows you to differentiate between deoxyribose and ribose
C2
What is bonded to C2 in deoxyribose
H
what is bonded to C2 in ribose
OH
what are the 2 categories of nitrogen bases
purines and pyrimidines
how many nitrogen rings are found in purines
2
how many nitrogen rings are found in pyrimidines
1
list the purines found in DNA
Adenine and Guanine
list the purines found in RNA
Adenine and Guanine
list the pyrimidines found in DNA
Cytosine and Thiamine
list the pyrimidines found in RNA
Cytosine and Uracil
how many nitrogen bases exist In nature
5
What did Chargaff measure
The amount of nitrogen bases in DNA
What is Chargaff’s rule
amount of A=T and amount of C=G
In a DNA nucleotide, what is bonded to C1
Nitrogen base (A,C,G, or T)
In a DNA nucleotide, what is bonded to C2
H
In a DNA nucleotide, what is bonded to C3
OH
In a DNA nucleotide, what is bonded to C4
C5
In a DNA nucleotide, what is bonded to C5
phosphate group
In a RNA nucleotide, what is bonded to C1
Nitrogen base (A,C,G, or U)
In a RNA nucleotide, what is bonded to C2
OH
In a RNA nucleotide, what is bonded to C3
OH
In a RNA nucleotide, what is bonded to C4
C5
In a RNA nucleotide, what is bonded to C5
phosphate group
Which scientist was the 1st to visualize a DNA molecule
Rosalind Franklin
what is the shape of a DNA molecule
double helix
who was Franklin’s lab partner
maurice wilkens
what type of bond is found between nucleotides of opposite DNA strands
Hydrogen bond (h-bond)
what type of bond is found between nucleotides of the same DNA strand
Phosphodiester bond
what type of bond is a phosphodiester bond
covalent
which 2 scientists determined the molecular structure of a DNA molecule
Watson and crick
What award did Watson, Crick, and Wilkins win
Nobel prize
why didn’t Franklin receive the Nobel prize
she was dead, therefore ineligible
what did Nobel invent
dynamite
what was the first nobel prize
a peace prize
how many hydrogen bonds are located between Adenine and Thymine in a double-stranded DNA molecule
2
how many hydrogen bonds are located between Guanine and Cytosine in a double-stranded DNA/ RNA molecule
3
how many hydrogen bonds are located between Adenine and Uracil in a double-stranded RNA molecule
2
Hydrogen bonds form between ____ molecules
polar
What makes a molecule polar
have a positively charged pole (end) and one negatively charged pole
what causes unequal distribution of electrons between atoms
some atoms attract more electrons than others
Which atoms attract electrons more
N, O, P, S
Which atoms attract electrons less
C, H
Are hydrogen bonds weak or strong
weak
Under what circumstance are hydrogen bonds strong
in large amounts
what does bp stand for
base pair
what are the 2 types of bp in a double stranded DNA molecule
A&T and C&G
do bp involve nucleotides of the same strand or opposite strands
opposite strands
what type of bond is found between the nucleotides of a bp
Hydrogen bond
what type of bond forms when atoms share electrons-
covalent bonds
what type of reaction allows the formation of a phosphodiester bond
condensation rxn
what is another name for a condensation reaction
dehydration synthesis
what is the byproduct of a condensation reaction
H2O
what 2 parts of a nucleotide comprise a nucleoside
nitrogen base and pentose sugar
what is the name of the enzyme that makes DNA
DNA polymerase
what suffix do most enzymes end in
ase
what suffix do most carbohydrates (sugars) end in
ose
what specific bond is made by DNA polymerase
phosphodiester bond
what is the general name for a high energy bond
anhydride bond
what is the specific name for the high energy bond found between phosphate groups
phosphoanhydride bond
what is the symbol for an anhydride bond
~
DNA strands run in opposite directions, this is referred to as
antiparallel
the 2 strands of a DNA molecule are
complimentary and antiparallel
Name the 5 kingdoms
animalia, monera, plant, fungi, protista
name the 4 eukaryotic kingdoms
animalia, plant, fungi, protista
name the prokaryotic kingdom
monera
describe the genetic material in the nucleus of all eukaryotes
DNA, DS, linear
describe the genetic material in the nucleiod of all prokaryotes
DNA, DS, circular
describe the genetic material of viruses
DS or SS, DNA or RNA, linear and circular
which type of organisms have a nucleus (prokaryotes, eukaryotes, or viruses)
eukaryotes
how many cells are in an adult human
100 trillion
how many chromosomes are in MOST human cells
46
genes are located on
chromosomes
how many genes are found in each human cell
21000
how many nucleotides make up the human genome
6 billion
how many bp make u the human genome
3 billion
how many feet of DNA is found in the nucleus of MOST human cells
6 feet
which type of human cell had no nucleus and therefore no DNA
Prokaryotic
which type of human cells have 23 chromosomes and 3 feet of DNA
sperm or egg cells
what is the scientific name of gametes located in females
ova
what is the scientific name of gametes located in males
sperm
Chromo
color
Soma
the non-reproductive part of an organism
Chromosome
a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes
Where in the cell (2) are human chromosomes located
nucleus and mitochondria
Are human chromosomes single stranded or double stranded
double
What is the shape of human nuclear chromosomes
linear
What is the shape of the human mitochondrial chromosome
circular
Chromosomes are made of?
chromatin
Which 2 macromolecules comprise chromatin
DNA and proteins