plant cells and tissues
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
botany, dr. kohnen
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
continuous growth
indeterminate growth
perpetual embryogenesis
plant undergo this with meristematic cells
meristematic cells
cells divide, one remains meristematic and one differentiates

three basic cell types
parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma (categorized based on cell walls)
parenchyma
thin cell walls
remain alive at maturity
metabolically active
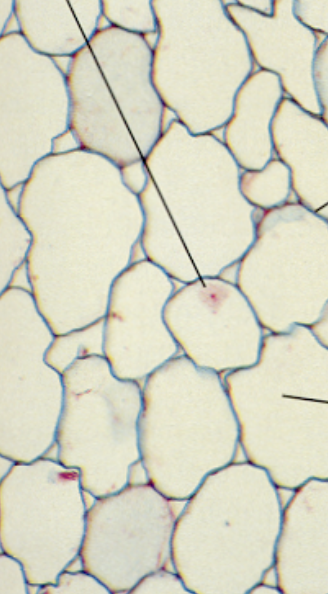
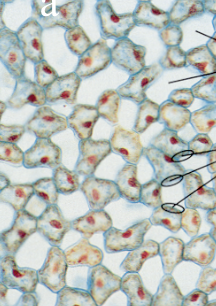
three types: chlorenchyma, glandular cells, and transfer cells
chlorenchyma
photosynthetic
glandular cells
produce resin (ex. pine sap)
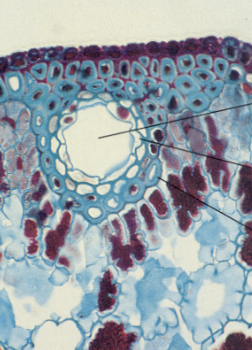
transfer cells
contoured cell walls to increase surface area
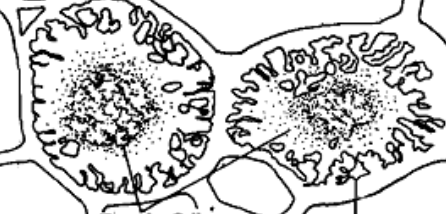
collenchyma
thickened wall cells
elongaded
vines
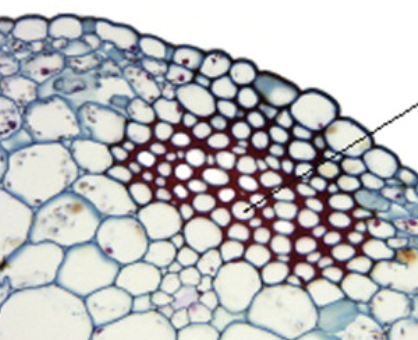
sclerenchyma
thick cell walls (lignified)
often die at maturity
found in mature tissues
mechanical and conducting
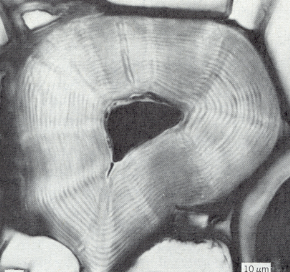
mechanical sclerenchyma
fibers (slight flexibility while being sturdy)
sclerids
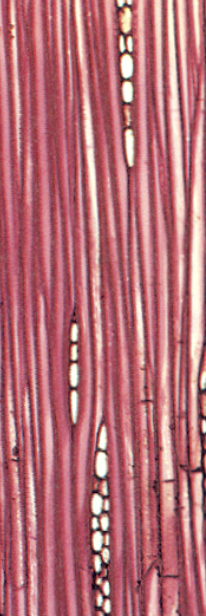
conducting sclerenchyma
conduct water
tracheids and vessel elements
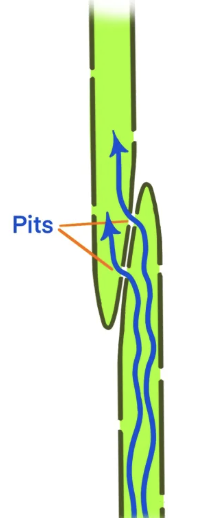
tracheids
gymnosperms
pit membrane = middle lamella
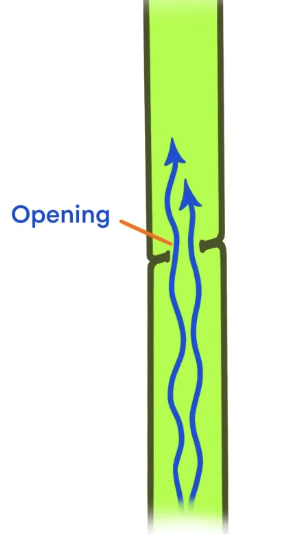
vessel elements
angiosperms
perforation plate
water can move through smoothly
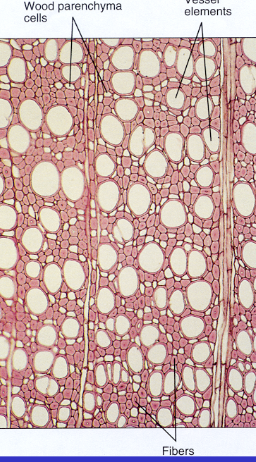
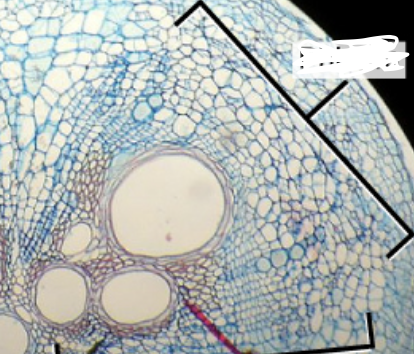
xylem
conducts water, includes trachear elements and fibers
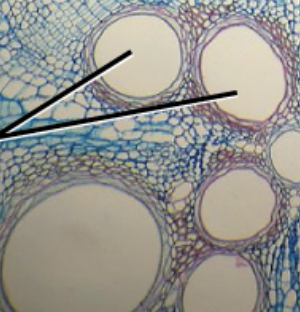
phloem
translocate photosynthate (product of photosynthesis - sugar)
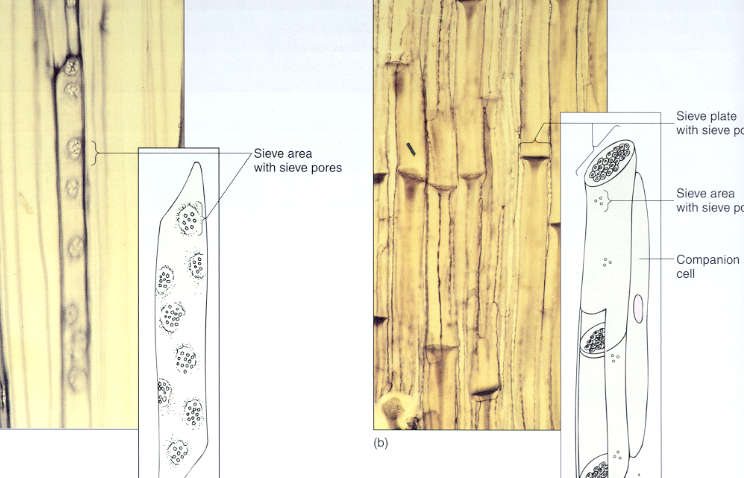
composed of sieve tube elements (STE’s)
STE
sieve tube elements
sieve cells = gymnosperms (naked seed)
sieve tube elements - angiosperms (covered seed)
live in close association to companion cells that assist them
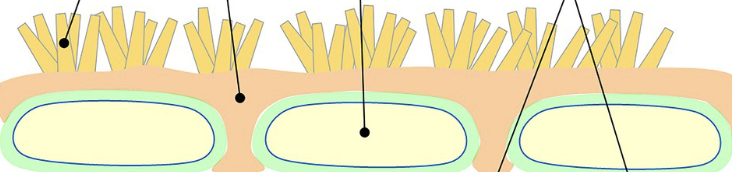
dermal tissues
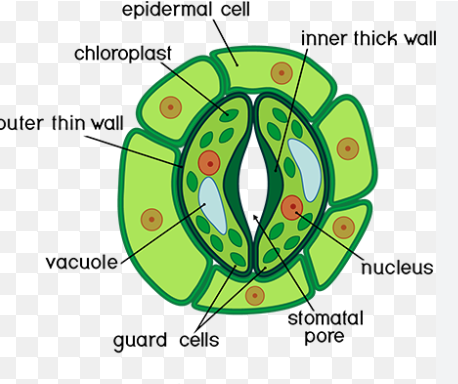
epidermis
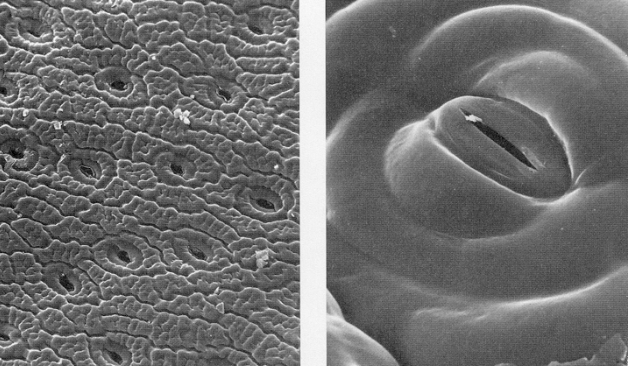
guard cells
trichromes
epidermis structure
cuticle
guard cells
control size of pore, allowing gas exchange
trichromes
hair-like structures
deter herbivores
guard cell pores
needed for transpiration