Shadwick POB Exam 4 Chapter Questions - 28,29, 30, 31, 32
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Microbiology is the study of microbes. These include all but which of the following?
A. Archaea
B. Bacteria
C. viruses
D. plants
D
What general feature is necessary to consider an organism a microbe?
A. small enough that a microscope is required to see them
B. heterotrophic
C. sexual reproduction
D. use aerobic respiration for metabolism
A
Miller's laboratory experiments showed that
A. it is possible to form protocells.
B. the primitive gases can react together to produce small organic molecules.
C. atmospheric pressure is required for life to begin.
D. the earth is approximately 4.5 billion years old
B
Which of the following kinds of molecules is thought to have been absent from the primitive reducing atmosphere?
A. water vapor (H2O)
B. methane (CH4)
C. hydrogen (H2)
D. oxygen (O2)
D
Considering the various theories, the energy used in forming organic molecules in the primitive atmosphere could have come from all EXCEPT
A. lightning.
B. ultraviolet radiation.
C. heat from volcanoes.
D. sound.
D
What is the evolutionary relationship among archaea, bacteria, and eukarya?
A. Since archaea are the most primitive, archaean ancestors gave rise to bacteria that in turn gave rise to eukaryotes.
B. All three domains are equally distant from the most primitive common ancestor, a protocell.
C. Archaea and eukarya share nucleic acid similarities, so eukarya split off from archaea.
D. Bacterial ancestors gave rise to both archaea and to eukaryotes as two separate side branches.
C
A new classification by domains separates prokaryotes into
A. Bacteria and Cyanobacteria.
B. photosynthetic bacteria and chemosynthetic bacteria.
C. Archaea and Bacteria.
D. autotrophs and heterotrophs.
C
One bacterial cell passes DNA to a second cell through a sex pilus in the process of
A. transformation.
B. transduction.
C. conjugation.
D. replication.
C
Bacterial cells pick up free pieces of DNA from the medium pieces that were released from dead bacteria in a process called
A. transformation.
B. transduction.
C. conjugation.
D. replication.
A
Which of these is a correct description of a form of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria?
A. Crossing-over occurs between paired chromosomes in meiosis.
B. Conjugation occurs when a cell passes DNA to another cell by means of a sex pilus.
C. Transformation occurs when a bacteriophage carries a bit of DNA from a previous host cell to a new host cell.
D. Transduction occurs when a live bacterium picks up DNA from dead bacteria that have shed it into the environment of the living cell.
B
Which type of genetic exchange occurs among bacteria in which DNA is carried into a bacterial cell by means of a virus?
A. conjugation
B. transformation
C. transduction
D. budding
C
Which statement is true about bacteria?
A. They contain a nucleus.
B. They lack ribosomes.
C. They usually lack a cell wall.
D. They contain a single, circular DNA molecule as the genetic material.
D
Which statement is NOT true about bacteria?
A. They lack mitochondria.
B. They lack a nucleus but contain DNA.
C. They reproduce sexually.
D. They have a single circular chromosome.
C
The capsid of a virus is composed of
A. RNA.
B. protein.
C. DNA.
D. cellulose.
E. lipid
B
Which of the following is NOT true about viruses?
A. The genome may be DNA or RNA.
B. They contain nucleic acid, protein, and mitochondria.
C. They exhibit host specificity.
D. They are obligate intracellular parasites
B
The innermost core of a virus's structure is made up of
A. a membranous envelope.
B. either DNA or RNA.
C. a protein capsid.
D. a protein spore coat.
B
A viral envelope describes
A. the outer layer of some viruses composed of the host's plasma membrane
B. viral DNA.
C. a prion.
D. a protein capsid.
A
Which of these is the most accurate description of a virus?
A. a noncellular living organism
B. one of the smallest bacteria known
C. a cell at the boundary between living and nonliving things
D. chemical complexes of RNA or DNA protected by protein
D
Which of the following is considered to be acellular?
A. bacteria
B. fungi
C. algae
D. protozoans
E. viruses
E
The life cycle stage of an animal virus during which a mature capsid forms around copies of the viral RNA genome is
A. budding.
B. biosynthesis.
C. uncoating.
D. assembly.
D
Which stage of viral reproduction takes place when the spikes of the virus bind to a specific receptor molecule on the surface of a host cell?
A. attachment stage
B. penetration stage
C. biosynthesis stage
D. release stage
A
When an enveloped animal virus enters a cell during the entry stage,
A. the next thing it does is assemble a new virus.
B. the envelope is removed after the virus is inside the cell's nucleus.
C. the protein capsid is removed through uncoating to expose the viral genome.
D. it immediately integrates its nucleic acid genome into the host chromosomes.
C
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), or "mad cow disease," is caused by a(n)
A. archeon.
B. bacterium.
C. cyanobacterium.
D. prion.
E. virus.
D
Some human diseases appear to be due to protein agents that may convert other normal proteins in the cell to also become these agents. This new disease protein agent is called a(n)
A. prion.
B. cyanobacterium.
C. phage.
D. retrovirus.
A
Who invented the term "virus"?
A. Louis Pasteur
B. Anton van Leeuwenhoek
C. Stanley Miller
D. Harold Urey
A
Cyanobacteria
A. do photosynthesis similar to green plants.
B. are heterotrophs.
C. have a nucleus and chloroplast.
D. split hydrogen sulfide
A
The process of bacterial reproduction is referred to as
A. binary fission.
B. budding.
C. mitosis.
D. meiosis.
A
The first membranes that formed before full cells were likely made of
A. fatty acids.
B. phospholipids.
C. proteins.
D. RNA
A
Which type of archaean is likely to be found in the intestines of animals?
A. Methanogen.
B. Halophile.
C. Thermacidophile.
A
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
A. improved microscope lenses to allow him to see tiny organisms he called animalcules.
B. invented the idea of spontaneous generation.
C. did experiments to refute the concept of spontaneous generation.
D. tested theories about how organic molecules could form without the presence of life.
A
Louis Pasteur
A. improved microscope lenses to allow him to see tiny organisms he called animalcules.
B. invented the idea of spontaneous generation.
C. did experiments to refute the concept of spontaneous generation.
D. tested theories about how organic molecules could form without the presence of life.
C
Single-celled eukaryotes are
A. Protists.
B. Archaea.
C. land plants.
D. animals.
A
Which features set most of the members of protista apart from the rest of the kingdoms?
A. unicellular and microscopic
B. multicellular and microscopic
C. photosynthetic and unicellular
D. None of the answer choices is correct.
A
The ____ algae are thought to be closely related to the first plants because they share most of the characteristics of plants.
A. brown
B. red
C. green
D. pink
C
Members of which genus of algae are found in ponds and have chloroplasts that are arranged in a spiral?
A. Spirogyra
B. Euglena
C. Chlamydomonas
D. Volvox
A
Which is an example of an alga?
A. amoebae
B. slime molds
C. diatoms
D. ciliates
C
Which protist is NOT correctly linked to the type of movement it shows?
A. amoeboids-pseudopodia
B. ciliates-cilia
C. Euglena-pseudopod
D. Paramecium-cilia
C
Which of the following organisms move about by means of pseudopodia?
A. trypanosome
B. Amoeba proteus
C. Chlamydomonas
D. Paramecium caudatum
B
The kingdom ____ are characterized by having filaments called hyphae that are used to absorb nutrients.
A. Archaea
B. Protista
C. Fungi
D. Animalia
E. Plantae
C
Molds (except slime and water molds) and mushrooms belong to the kingdom
A. Protists.
B. Fungi.
C. Plantae.
D. Animalia.
B
An organism that will feed on dead plants, animals, and microbes are called
A. autotrophic.
B. heterotrophic.
C. saprotrophs.
D. parasitic.
C
____ are organisms that break down dead organic matter in order to absorb the nutrient molecules.
A. Eukaryotes
B. Parasites
C. Saprotrophs
D. Heterotrophs
C
____ are mostly saprotrophic decomposers that assist in recycling of nutrients in ecosystems.
A. Algae
B. Fungi
C. Protozoans
D. Ciliates
B
In what way are fungi like heterotrophic bacteria?
A. They both produce gametes.
B. They are both heterotrophic and play an important role in ecosystems.
C. They both have cell walls of the same material.
D. They are both photosynthetic and thus are producers.
E. They are both eukaryotic.
B
At one time, biologists thought that fungi were merely forms of plants that had lost their chlorophyll and had returned to saprotrophy to gain food. Why is this no longer considered a solid theory?
A. Fungal cell walls contain chitin rather than cellulose.
B. Fungi attack and engulf food for internal digestion.
C. Fungi have flagella at some stage, providing mobility that plants never have.
D. Plants are multicellular and fungi are unicellular or multinucleated noncellular plasmodia.
E. Plants store glycogen, while fungi store starch.
A
Fungi are NOT photosynthetic because they lack
A. xylem.
B. cell walls.
C. chloroplasts.
D. cell membrane.
C
A chain of asexual spores produced by a sac fungus is called
A. a mycelium.
B. a conidia.
C. an ascospore.
D. a basidiospore.
B
The mycelium is a mesh of filaments, each of which is called
A. a conidium.
B. an ascospore.
C. a basidiospore.
D. a hypha
D
When the cap of an average gilled mushroom is cut off and shaken, a cloud of powdery material is released. The material released are
A. mycelia.
B. sporangia.
C. hyphae.
D. spores.
E. seeds
D
Amoebae
A. have pseudopodia.
B. have a nucleus
C. are heterotrophic.
D. all of the above are true.
E. Only A and C are true.
D
Diatoms
A. are unicellular algae with glassy cell walls.
B. have pseudopodia.
C. are excavates.
D. all of the above are true.
E. Only A and B are true.
A
Euglena
A. is an excavate.
B. is an chromalveolate.
C. has an eyespot.
D. all of the above are true.
E. Only A and C are true
E
Lichens
A. are a symbiotic relationship between an alga and fungus.
B. thrive in areas of high pollution.
C. cause the flavors in blue cheese.
D. are important in making bread
A
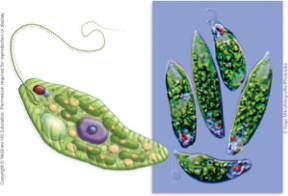
The organism represented in the above image
A. is an excavate.
B. is in the genus Euglena.
C. is a flagellate.
D. is a chromalveolate.
E. is in the genus Amoeba.
F. makes pseudopodia.
A,B,C
Which of the following statements is NOT true about alternation of generations life cycle?
A. Meiosis produces spores that are haploid.
B. Spores develop into the gametophyte generation.
C. The gametophyte produces eggs and sperm.
D. When the sperm fertilizes the egg, a zygote results that develops into the sporophyte.
E. The sporophyte generation produces gametes by mitosis in structures called sporangia
E
Which sequence is correct in the life cycle of alternation of generations?
A. gametophyte → gametes → spores → sporophyte
B. gametophyte → gametes → zygote → spores → sporophyte
C. gametophyte → spores → gametes → zygote → sporophyte
D. gametophyte → gametes → zygote → sporophyte → spores
D
A major evolutionary trend among plants is
A. a reduction in the size of the gametophyte and an increase in the size of the sporophyte.
B. a reduction in the size of the sporophyte and an increase in the size of the gametophyte.
C. an increase in the size of both the sporophyte and the gametophyte.
D. a decrease in the size of both the sporophyte and the gametophyte.
A
Which of the following is NOT a significant event in the evolution of plants?
A. protection of the embryo
B. evolution of vascular tissue
C. evolution of the seed
D. evolution of the flower
E. evolution of the blastula
E
In the moss life cycle, the ______ generation is dominant.
A. haploid gametophyte
B. diploid gametophyte
C. diploid sporophyte
D. diploid antheridium
A
Which life cycle phase is diploid in moss?
A. sporophyte generation
B. gametophyte generation
C. gametes
D. spores
A
Haploid spores are produced in the ___ of a moss.
A. antheridia
B. archegonia
C. sporangium
D. anther
C
Which of the following is a nonvascular plant that has the longest evolutionary history on land?
A. ferns
B. bristlecone pine tree
C. moss
D. redwood tree
C
Which of the following is NOT characteristic of a fern?
A. Ferns are quite small since they lack vascular tissue
B. Fern sporophyte is the dominant generation in the fern life cycle.
C. Fern sporophyte leaves first appear in a curled-up form termed a fiddlehead.
D. Fern sporophyte is vascular.
A
In the life cycle of a fern, the zygote
A. becomes the sporophyte generation.
B. becomes the gametophyte generation.
C. undergoes meiosis.
D. is haploid
A
In the fern life cycle, the ______ generation is dominant.
A. haploid gametophyte
B. diploid gametophyte
C. haploid sporophyte
D. diploid sporophyte
D
Which statement is NOT true about ferns?
A. The sporophyte stage lacks vascular tissue.
B. Antheridia and archegonia develop on the prothallus of the gametophyte stage.
C. Fertilization requires moisture for the sperm to swim to the egg within the archegonia.
D. The sporophyte stage is the dominant generation.
A
The reproductive parts of an angiosperm are the
A. petals and sepals.
B. petals and stamen.
C. sepals and stamen.
D. sepals and carpel.
E. carpel and stamen.
E
During pollination in angiosperms, pollen grains will stick to the enlarged knob in the center of the flower called the
A. stigma.
B. style.
C. ovary.
D. ovule.
E. anther.
A
Ovules are contained within the
A. ovary.
B. stigma.
C. anther.
D. filament.
E. style.
A
The stigma, style, and ovary are located in a
A. carpel.
B. sepal.
C. receptacle.
D. petal.
E. stamen.
A
The site of formation of pollen grains is in the
A. carpel.
B. sepal.
C. receptacle.
D. petal.
E. stamen.
E
Botanically, a seed is a structure developed from a(n)
A. style.
B. ovule.
C. stigma.
D. anther.
E. sepal
B
A plant that makes seeds but not flowers would be
A. a pine tee.
B. a grass.
C. a moss.
D. a fern.
A
Put these in the order in which they occurred over evolutionary time.
1. Evolution of the Seed
2. Evolution of the Embryo
3. Evolution of the Flower
4. Evolution of Vascular Tissue
2, 4, 1, 3
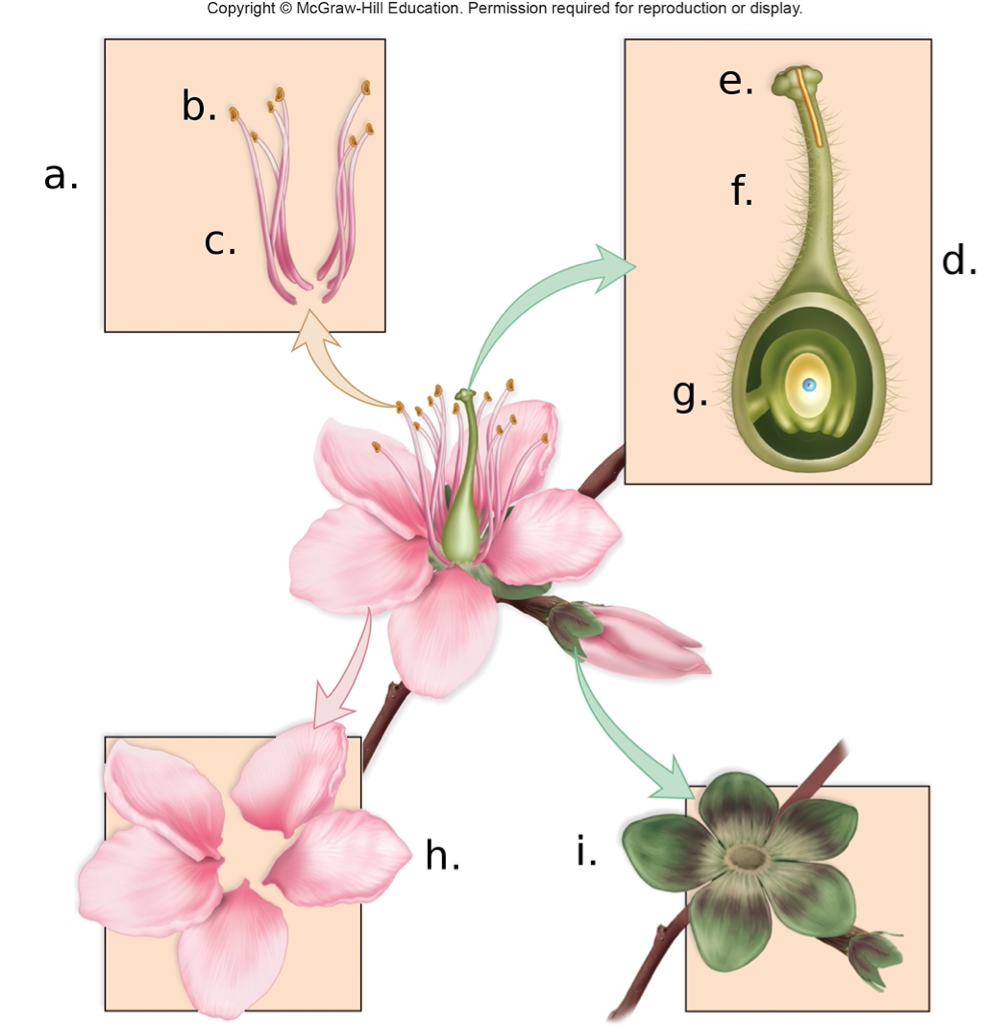
In the above image the ovary is labeled
A. g
B. c
C. e
D. a
A
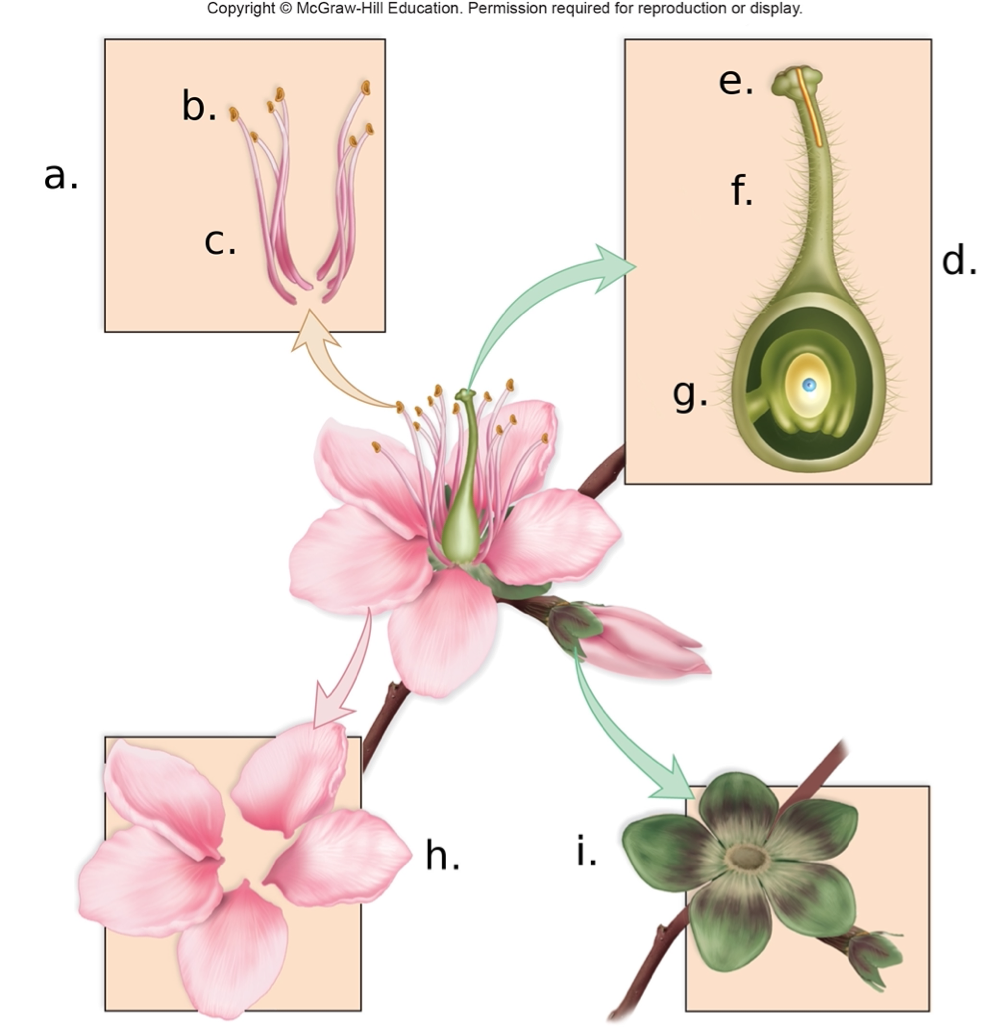
In the above image the stigma is labeled
A. g
B. c
C. e
D. a
C
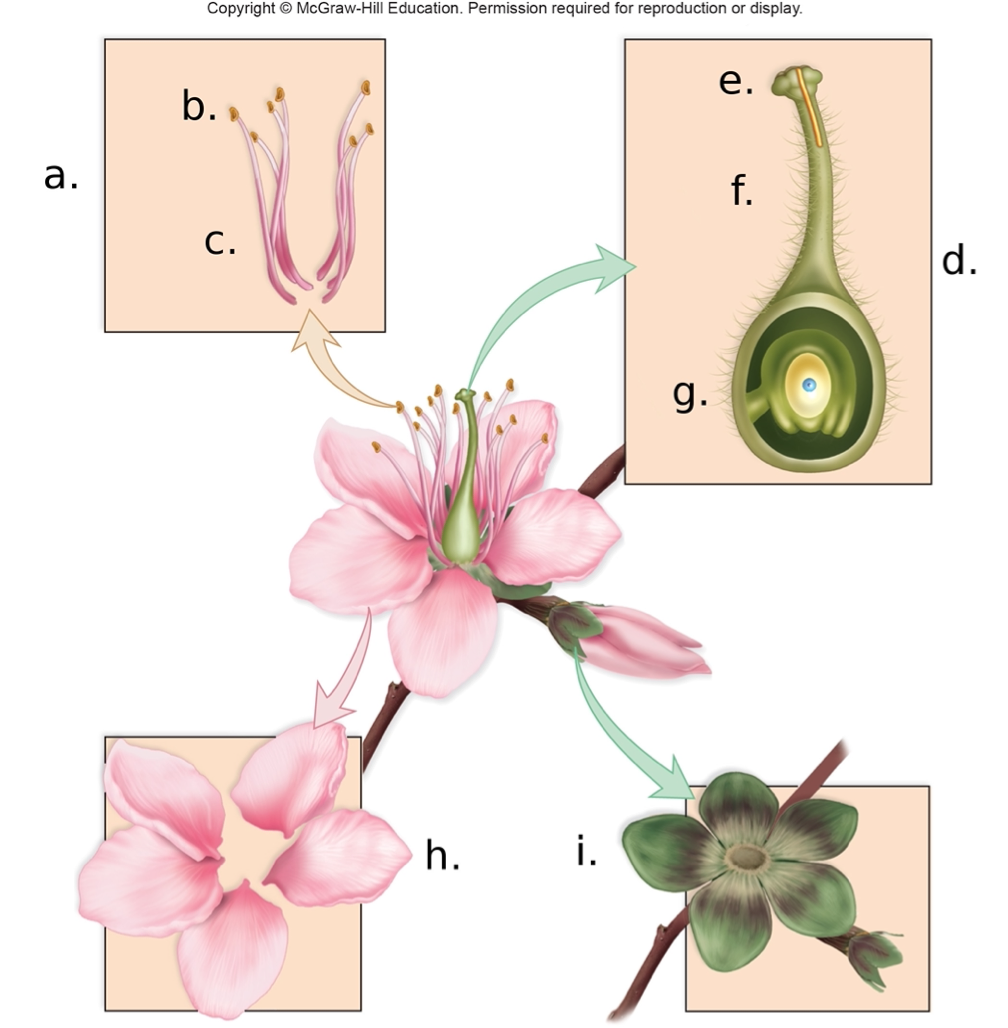
In the above image the carpel is labeled
A. d
B. c
C. e
D. a
A
Animals that have no particular symmetry exhibit
A. asymmetry.
B. radial symmetry.
C. bilateral symmetry.
D. trilateral symmetry.
A
Which type of animal symmetry produces mirror images of each other no matter how the animal is sliced longitudinally?
A. radial symmetry
B. asymmetrical symmetry
C. bilateral symmetry
D. asymmetrical symmetry and bilateral symmetry
A
The term deuterostome refers to
A. having a spiny skin.
B. having three germ layers.
C. possessing a notochord.
D. the second embryonic opening becoming the mouth
D
Which difference distinguishes protostomes from deuterostomes?
A. One has a nervous system, and one doesn't.
B. Their embryonic development is different.
C. One has cephalization and one doesn't.
D. One has a notochord and one doesn't.
B
Which of the following is NOT true about protostomes?
A. They form a true coelom.
B. The first opening during embryonic development becomes the anus.
C. They will become mollusks, annelids, and arthropods.
D. They are more advanced than acoelomates, but not as advanced as deuterostomes.
B
Which of the following statements about sponges is NOT correct?
A. Sponges have no nerve fibers.
B. Sponges have no fully developed muscle fibers.
C. Amoeboid cells capture food particles from the water.
D. Sponges may reproduce asexually by budding or by regeneration from a small piece.
C
Why are real bath sponges so soft?
A. The silica is washed away and the calcium carbonate remains.
B. The spongin spicules are washed away and the silky silica remains.
C. The harder silica or calcium spicules are absent and the softer spongin remains.
D. The silica and spicules are washed away and the spongin treated with softening chemicals.
C
A recent study of the marine hawksbill turtle's stomach contents revealed that sponges constitute a major portion of their diet. Sponge beds are generally protected from predators by the sponge's calcium and silica crystals, but these were found in quantity in the turtles' digestive systems. These structures that protect the sponges from most predators, but not turtles, are
A. amoebocytes.
B. the osculum.
C. spicules.
D. spongin.
C
Which of the following organisms exhibit radial symmetry as adults?
A. flatworms
B. cnidarians
C. roundworms
D. clams
B
Which of the following statements is NOT correct about cnidaria?
A. The adult body is bilaterally symmetrical.
B. There are two tissue layers: an outer epidermis and inner gastrodermis.
C. Stinging cells contain a threadlike nematocyst released to capture prey.
D. A jellylike mesoglea contains cells that form a nerve net throughout the body.
A
The stinging cells or nematocysts are characteristic of
A. sponges.
B. cnidarians.
C. flatworms.
D. roundworms.
B
The molluscs look so different, and yet we can tell they are related because they all
A. are segmented.
B. have an external skeleton.
C. have a mantle, visceral mass, and a foot.
D. have shells.
C
Which of the following is NOT characteristic of earthworms?
A. segmentation
B. hermaphroditic
C. paired nephridia in each segment
D. dorsal solid nerve cord
D
Earthworms are
A. annelids.
B. molluscs.
C. platyhelminthes.
D. arthropods.
A
Which type of organism is characterized by having jointed appendages, ability to molt, and three sets of fused segments?
A. molluscs
B. arthropods
C. annelids
D. chordates
B
The largest animal group, both in number of species and number of individuals, is the
A. annelids.
B. crustacea.
C. insects.
D. reptiles.
C
It is NOT correct to say that arthropods have
A. a variety of respiratory organs.
B. a well-developed nervous system.
C. jointed appendages and a segmented body.
D. a tough exoskeleton that grows by expansion.
D
A major characteristic of the arthropods is the presence of
A. flame cells.
B. radial symmetry.
C. a soft exoskeleton.
D. jointed appendages.
D
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of echinoderms?
A. locomotion by muscles
B. endoskeleton of spiny, calcium-rich plates
C. larva is bilaterally symmetrical
D. both sexual and asexual reproduction
A
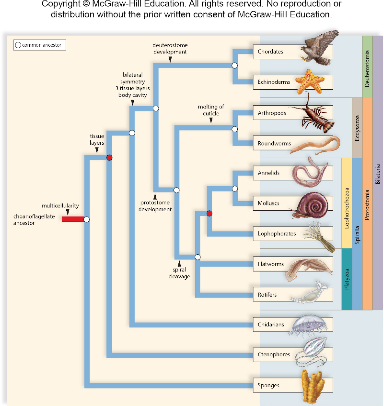
This is a question with multiple correct answers
Look at the phylogenetic tree above. Which of the following organisms are in the Bilateria?
A. snails
B. earthworms
C. sea stars
D. butterflies
E. sponges
F. cnidarians
G. corals
H. hydra
A, B, C, D
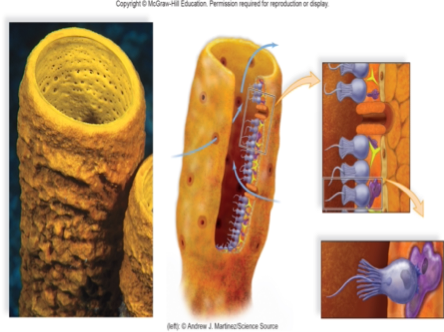
This is a question with multiple correct answers
Which of the following apply to the sponge in the image?
A. no true tissues
B. animal
C. skeleton with spicules or protein spongin
D. asymmetrical
E. cnidarian
F. fungus
G. radial symmetry
H. cnidocytes
A, B, C, D
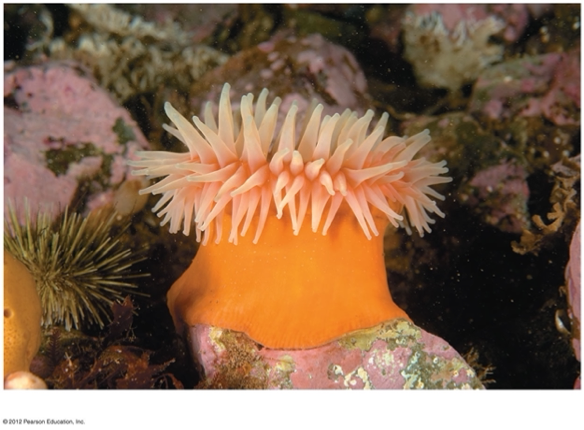

This is a question with multiple correct answers
Which of the following apply to the anemone in the image?
A. medusa
B. polyp
C. arthropod
D. bilateral symmetry
E. cnidarian
F. fungus
G. radial symmetry
H. cnidocytes
B, E, G, H

This is a question with multiple correct answers
Which of the following apply to the slug and snail in the image?
A. mantle
B. gastropod
C. arthropod
D. bilateral symmetry
E. cnidarian
F. cnidocyte
G. radial symmetry
H. mollusc
A, B, D, H