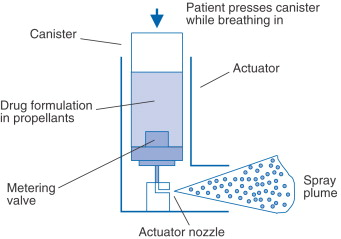
P2 PMDIs: pressurised metered dose inhalers
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is PMDI
compact pressurised aerosol dispenser
most common
25ug-5mg
advantage of pmdi
Large dose range
several hundred accurately metered measured doses
•Many doses
•Compact
•Consistent delivery
•Relatively cheap
•Sealed canister protects drug
•Lower capital costs for market entry
disadvantage pmdi
•Patient co-ordination and force required to actuate
•“Cold Freon Effect”
•Tail off at the end of a can
•Force of aerosol spray
•Varying deposition pattern in airways
•Minimum IP protection for pharmaceutical industry
Propellant
Gas compressed to 300-500 kPa
Converts to liquid
Liquid rapidly boils to form a gas
Leaving behind an aerosol of drug particles
Made from hydrofluroalkanes used to be CFC as they destroy ozone layer
Metering valve
At rest
Start of actuation
Dose release

How is the spray formed

Ligaments shear
Particles released are slightly too large but they evaporate decreasing their size
Actuator
it is the component in any machine that enables movement.
Describe the types of drug particles used in pMDIs

If drug is insoluble like solid particles suspended in solution= suspension
The more soluble the drug the more drug in each droplet = larger particle size
Add another non-volatile (non-evaporating) liquid e.g. glycerine when the particle is too small
Advantages/ Disadvantages of suspension formulation
Deliver high powder doses
Disadvantages:
Requires milling or micro ionised
Requires drug to be insoluble other leads to changes in particle size going to other parts of the body
Requires drug to be freely dispersed
Homogeneity + physical stability as particles disperse = shake vigorously
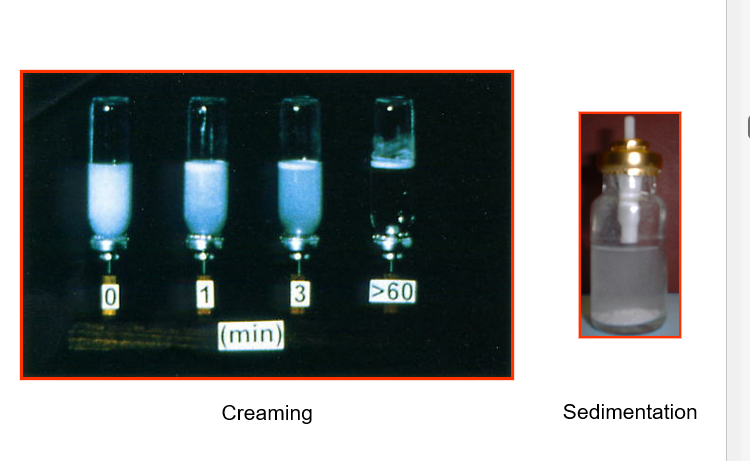
List and define 5 types of physical instability
•Rapid Flocculation - Loose Agglomerates (Interparticulate Forces)
•Bulk Separation - Creaming or Sedimentation (Density, Particle Size). Creaming = rise to the top. Sedimentation= sink to the bottom. Drug at the top is not delivered
•Irreversible Aggregation - Ostwald Ripening, Crystal Growth and Caking (Solubility)
•Crystal Structure Instability - Polymorphic interconversion (different crystal structure)
•Adhesion to the canister – inside surface often coated, e.g. PTFE
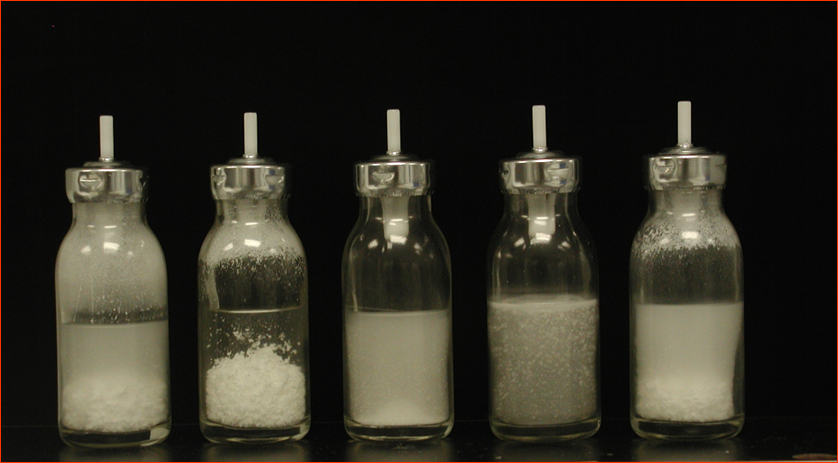
Flocculation
Clumping/ aggregation of particles that don’t break when shaken
So important to shake to remove clumps and create uniform suspension

What is the purpose of excipients
Enhance physical stability of a drug
Allows dispersing + redispersion + homogenous distribution
Prevents segregation
Examples: Oleic acid, Magnesium Stearate, PEG
Solution based formulation
Only used if solubility and stability is adequate as it can lead to chemical reactions may lead to crystallisation during shelf life
MORE DRUG DISSOLVED = HIGHER DOSE OUT
Requires co-solvent e.g. ethanol

Solution disadvantages
•Co-solvent can cause corrosion of aluminium canister
•Drugs can be relatively unstable.
•Co-solvent lowers the internal propellant pressure, thus, atomisation is less effective.
•Modification of drug chemical structure
How to test pMDI formulation
•Sedimentation rates
•Particle size changes
•Microscopy
•Dose uniformity measurements
•Ultimate test – uniformity in the aerosol dose
•Need a consistent dose
•Particle size distribution must be consistent
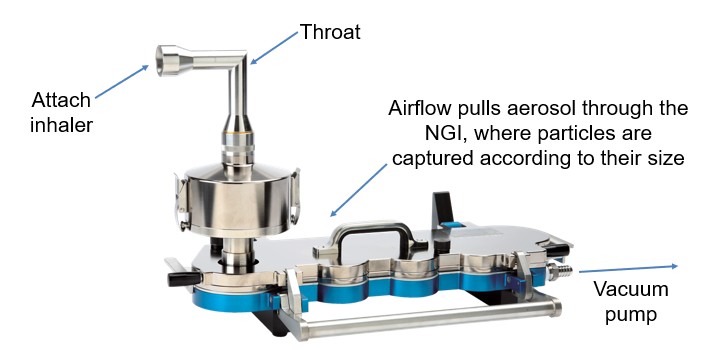
How do we measure particle size in aerosol dose
Use an impactor
Spray inhaler
Into throat mimetic
particles into collecting pan with different hole sizes
smaller and smaller particles collected
Divides aerosol cloud into 8 different compartments
Wash the pans, dissolve into solvent and can measure concentration and dose distributed into lungs
ensures same particle size distribution over time/ shelf-life and over each compartment = same performance
PMDI technique
•Shake before use.
•Breath out as far as comfortably possible away from the inhaler
•Place inhaler in mouth, inhale slowly while simultaneously pressing the canister.
•Continue to inhale slowly until lungs full
•Hold breath for around 10 seconds
•Only 20-25% of patients perform these
essential instructions.
•More can follow DPI instructions.

List some patient problems with PMDIs
Incorrect use e.g. not removing cap, don’t shake, forget to inhale, don’t hold breath, don’t exhale slowly
Actuation at start inhalation leads to poorly controlled asthma
Comorbidities e.g. arthritis find it difficult to press
Examples of training devices
In-check dial
Vitalograph AIM
Dose counters