Organic Chemistry Test 1
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Carbon wants to make __ bonds?
4
Formal charge
Valence-sticks-dots
formal charge: oxygen with 1 single bond
-1
Formal charge: nitrogen with 4 bonds
+1
Octet rule exemptions
Be, B and anything n=3 or below can have more than an octet
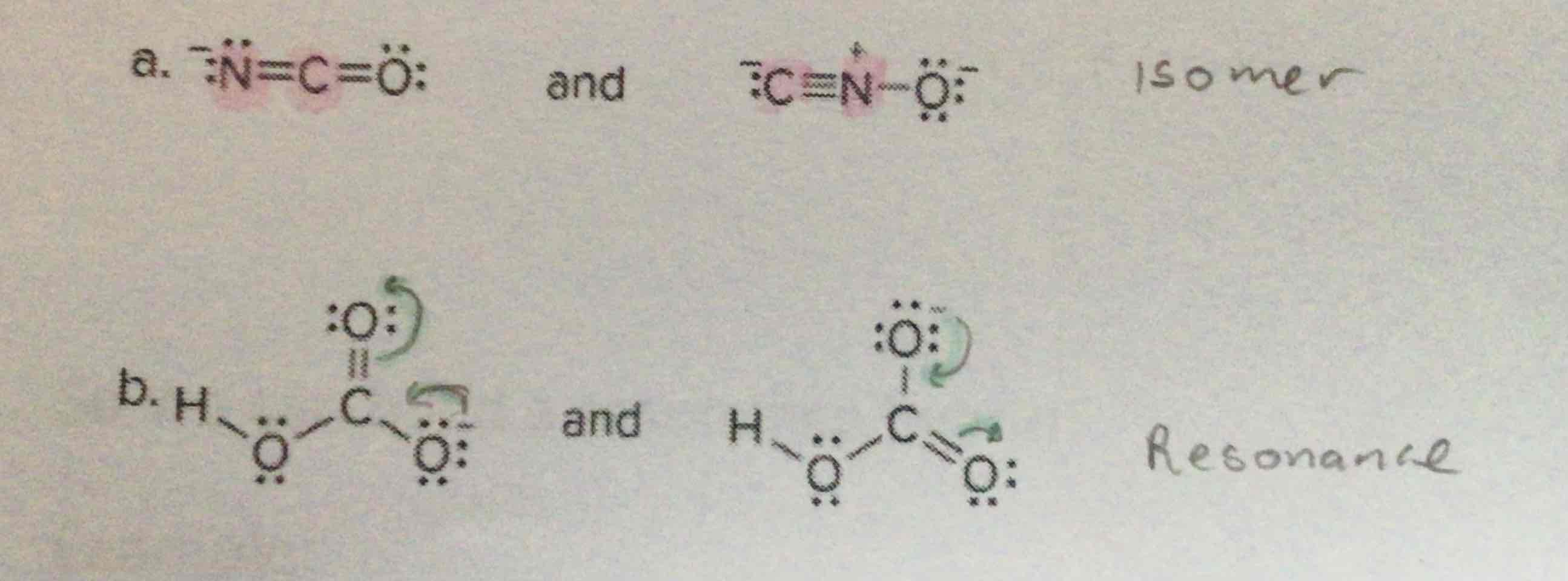
Resonance vs Isomers
Isomers have atoms in different places
Resonance has charges in different places-electrons move around
Chain length: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,20,30
Meth,eth,prop,but,pent,hex,hept,oct,non,dec,undec,Dedec,icosane,triacontane
Hybridization shortcut
Write, spppddddd and the number of electron groups
Single bonded carbons, double bonded carbons, triple bonded carbons hybridization
Sp3, sp2, sp
Bonds are strong when the length ain’t long
S-character shows how strong a bond is based on hybridization, sp is the strongest followed by sp2, sp3 and so on
Most electronegative elements
Can Not Clean Out Fridge, carbon nitrogen chlorine oxygen fluorine (in that order)
Acid strength pKas H-cl
-7
PKa Ch3CO2-H
Carboxylic acid, 4.8
PKa HO-H
15.7
CH3CH2O-H
16
PKas HC-triple bond-CH
25
Pkas H-H
35
PKas H2N-H
38
PKas CH2-double bond-CH2
44
PKas CH3-H
50
Low PKa=
=stronger acid
4 factors affect the acidity of HA
element effects
Inductive effects
Resonance effects
Hybridization effects
Common Lewis acids
BF3 and AlCl3
Lewis acids are called ___ and Lewis bases are called __
Electrophiles, nucleophiles
Alkane
Sigma bond
Alkene
Sigma + pi
Alkyne
Sigma + 2pi
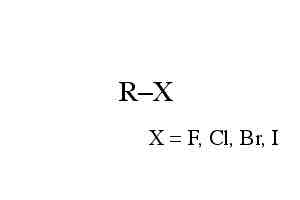
Ex. CH3-Br
Alkyl Halide, r group with an x where x= a halogen (F,cl ,br,I)
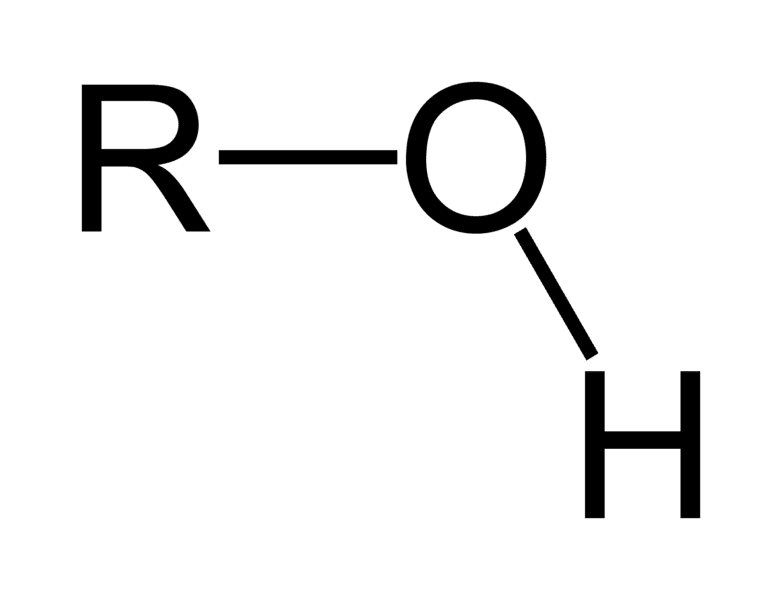
ex. CH3-OH
Alcohol

Ex. CH3-O-CH3
Ether ( looks like a pregnant lady don’t it?)
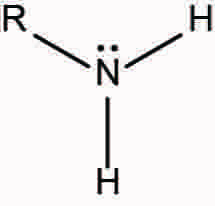
Ex. CH3-NH2
Amine! My beloved <3. Basically if you see a nitrogen and only single bonds
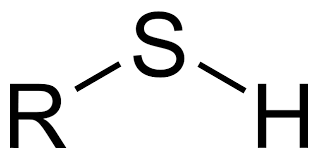
Ex. CH3-S-H
Thiol, basically if you see a sulfur and its bonded to a hydrogen
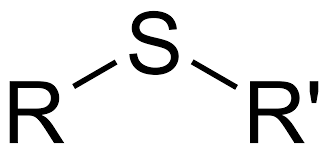
Ex. CH3-S-CH3
Sulfide, sulfur bonded to r groups ( and not a direct hydrogen)
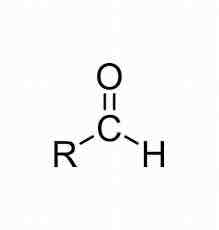
Ex. CH3CHO
Aldehyde, kinda like a ketone but with a hydrogen or a carboxylic acid but without oxygen
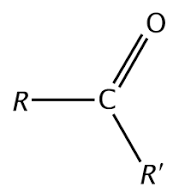
Ex. (CH3)2CO
Ketone, looks like a key!
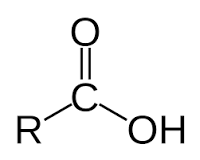
Ex. CH3CO2H
Carboxylic acid, like a ketone with an additional alcohol group (OH)
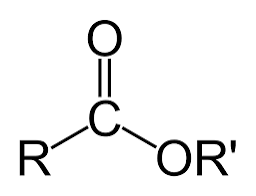
Ex. CH3CO2CH3
Ester
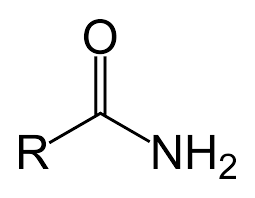
Ex. CH3CONH2
Amide, it’s like an amine but with a ketone (fun fact: amides can result from a reaction between an amine and a carboxylic acid, that’s why they’re a mix!)
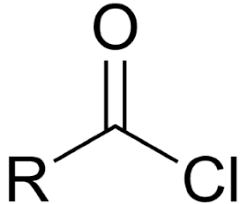
Ex. CH3COCl
Acid chloride