Visual Dysfunction in Neurological Rehabilitation
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Initial processing of visual-spatial information is processed in the…
right hemisphere
Detail of visual-spatial information is processed in the…
left hemisphere
Function of frontal lobe relating to vision
Voluntary eye movements
Function of parietal lobe related to vision
Distinguishing size, shape, and color; spatial perception, visual perception
Unilateral parietal lobe dysfunction
sensory deficits, motor deficits, visual disorders, contralateral neglect, constructional and dressing apraxia
Dominant parietal lobe dysfunction
language disorders, gertsmann syndrome, apraxia
Non-dominant parietal lobe dysfunction
hemispatial neglect, sensory and visual inattention, constructional and dressing apraxia
Bilateral parietal lobe dysfunction
visuospatial, balint syndromq
Function of occipital lobe
visual reception, synthesis and integration visual info, perception visuospatial relationships
Damage to occipital lobes
visual impairment, blurring or blind spots, visual hallucinations, difficulty reading and writing
visual impairments
visual acuity and accommodation
visual fields
oculomotor
vergence
visual acuity and accomodation deficits
blurred vision, visual fatigue, poor concentration
Visual field deficits
homonymous hemianopia
Oculomotor deficits
excessive head movement, poor attention, slow tracking, skipping when reading, may complain of headaches
vergence deficits
difficulty focusing, depth perception, spatial judgment, eye hand coordination
strabismus
esotropia, exotropia, hyperopia, hypopia, double vision, decreased coordination
functional scanning
omitting words or letters, exaggerated head movement, losing place, using finger to follow
color perception deficits
faded colors, difficulty distinguishing colors
stereopsis
difficulty depth perceptions, spatial judgement, and 3D
Warren’s Visual hierarchy
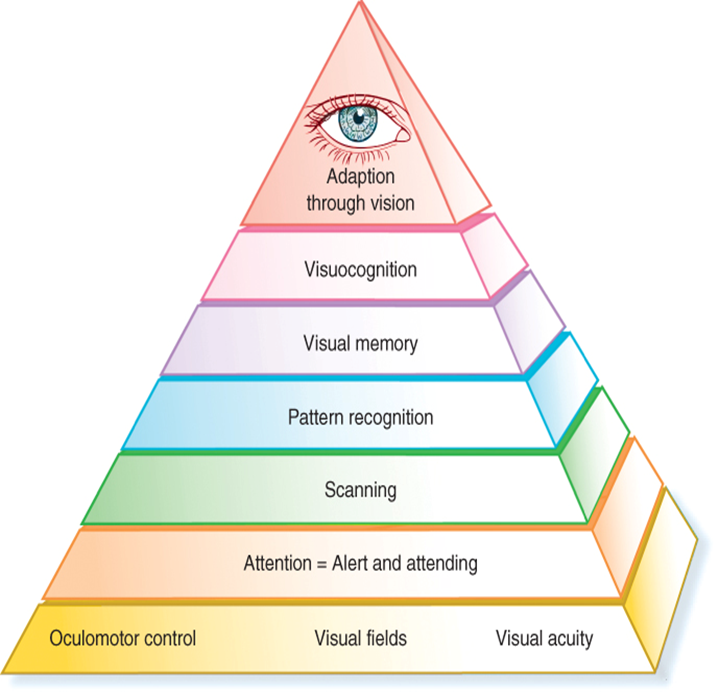
Vision and cognition are interconnected
What are three base levels of Warren’s Hierarchy?
Oculomotor, visual fields, visual acuity
What are some visual screening assessments and tools?
Observatiom, visual pursuit, reading screen, visual search strategies, design copy, confrontation field testing, line bisection, BiVABA
Brain Injury Visual Assessment Battery for Adults
Focused on functional visual components: visual acuity, oculomotor function, visual fields, contrast sensitivity, and visual inattention
Form constancy
the ability to recognize and label an object even when they are viewed from a different angle or position
Screening procedure for form constancy
client situated in well-lit area
lay kitchen utensils on counter
client identifies utensils on display
OT observes for spatial neglect, perseveration, poor scanning patterns, and comprehension
Impact of deficits in form constancy
difficulties with reading, writing, navigating, and locating items within personal environments
Figure ground perception
ability to distinguish a foreground figure from the background
screening procedures for figure ground perception
client locates specific coins from coin array
locate school items in pencil box
identify road signs along busy streetscape
observe for poor acuity, spatial neglect, preservation, poor scanning patterns, agnosia, and comprehension
Figure ground perception impact on daily functioning
difficulties identifying objects from busy or similar backgrounds
visual closure
ability to visualize a complete whole when provided with fragmented pictures or incomplete information
Screening procedures for visual closure
•Client completes a partially drawn picture, or identifies whole image from a partially drawn form |
•Correctly identifies 10 common objects from array of 30 overlapping items |
•Write/draw image on dry erase board – client identifies word or image |
Impact of visual closure deficits
Those with decreased visual closure encounter difficulties with learning tasks, handwriting, home management, etc.
When items are partially occluded within the visual field, accurate identification of objects is difficult.
Visual organization
property of visual perception form discrimination
Screening procedures for visual organization
Using technology, primary goal is quick screen for possible mid-level visual perceptual deficits
Visual organization deficits impact on daily function
Decreased visual organization creates difficulties in making sense of the extrapersonal and intrapersonal visual environments.
Deficits create increased difficulties with figure ground perception and visuoconstructional skills.
Spatial orientation
ability to appreciate the location of objects as related to each other and to oneself.
Screening procedures for spatial orientation
•Provide client with card with cross markings |
•Client reproduces crosses on blank card—accurately as possible |
•OT provides feedback noting disparities |
•Client completes with additional cards and crosses |
•Score measured in cm of discrepancy between model & client reproduction |
Spatial orientation deficits impact on daily function
Visual-spatial deficits create functional difficulties in general awareness of oneself and of objects in the interpersonal and extrapersonal environments
This presents as difficulties with basic self-care
Depth perception
visual perception using binocular cues and disparity with monocular cues (e.g., shading).
Screening procedures for depth perception
Two screens detect deficits in stereopsis—Lang Stereo Test I and the Titmus Test.
Depth perception deficits impact on daily function
Assessing depth perception through binocular or monocular cues—imperative for safety.
Low depth perception is frustrating (e.g., dressing and hygiene)
Compensations for depth perception
Environmental contextual cues, interpreting visual illusions and monocular cues
Intervention for oculomotor deficits - diplopia
Patching one eye or partial visual occlusion, prism glasses, vision therapy/eye exercises
Interventions for acuity
Increase illumination, increase contrast, decrease background pattern, decrease clutter and organize the environment, increase size
What is the incidence of hemianopsia with a stroke?
30% of clients
Interventions for scanning
Rotation activities, scanning while static, scanning while mobile, scanning newspaper ads, sorting items, specific reading, writing, and mathematical calculations training
Compensations for scanning
Visual scanning training
paper-and pencil tasks, computer activities
vision coach training
Unilateral inattention
decreased awareness of the body and spatial environment on the side contralateral to the brain lesion
Screening procedures for unilateral inattention
Commonly used screens in practice are the Bell’s Test, Clock Drawing Test, Single Letter Cancellation Test & others
Impact of unilateral inattention deficits
Impact difficulties range from reading to missing information while driving or walking in parking lot
Visual inattention
occurs with right hemisphere damage, does not have awareness of deficit, disorganized scanning patterns
Visual field
common with PCA lesions, retains awareness
Interventions for unilateral inattention
prisms, attention training, scrolling text, audiovisual stimulation, video feedback training, learning new scanning patterns, and lighthouse scanning to affected side
Effective intervention principles
1) Remove or minimize sensory deficits of foundational skills
2) Provide education to increase awareness of deficits
3) Incorporate consistent training to remediate and develop compensation strategies
What are some general strategies for interventions?
Discuss the purpose and results of activity w/ client
behavior modifications → “do this, not that”
use functional tasks
use individuals’ routine and habits
practice activities in appropriate environment
vanishing cues
graded assistance
Adapt task or adaptive equipment strategies
turn written work sideways and read up and down
use anchoring technique
position objects and people on affected side to necessitate client turning
use of prism glasses shift image
What can an OT do if they have client’s who do not response to strategies or recover?
Environmental adaptation such as placing food in preferred visual field, using colored cues.
Visuospatial
process needed to identify, integrate, and analyze space, visual forms, structure, and spatial relations in more than one dimension
temporal lobe
interprets visual meaning and object recognition
parietal lobe
spatial navigation
prefrontal lobe
visual perception and decision making, assists in processing information and allow adaptation to the environment
brainstem
responsible for pupillary responses and reflexes working in conjunction with the cerebellum for control of eye movements and coordination of the entire visual system
visuo-spatial impairments
stereopsis
spatial relations
right/left discrimination
topographic orientation
figure ground discrimination
Symptoms of visuospatial deficits
confusion related to space and objects
difficulty reaching accurately for objects
difficulty determining what body mechanics to use to transfer
feeing unsafe
familiar objects now being unfamiliar
difficulty finding everyday objects
difficulty with mobility
Intervention for spatial positioning/relations
increase client’s awareness of impairment
compensation strategies
provide models for language
practice following right/left directions using body and environmental space
Interventions for figure ground discrimination
teach awareness of deficit
teach organization skills
slow down to identify all details of object
use contrasts between foreground objects and background
task practice
Interventions for topographical disorientation
mazes simple to complex
colored dots to mark the route
with mastery, take away cues
Interventions agnosia
increase awareness, compensation to use alternative intact senses to recognize objects