B8 - photosynthesis
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
photosynthesis definition
photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction in which energy is transferred from the environment to chloroplasts by light.
process of photosynthesis
energy is transferred from the environment to the chloroplast by light - endothermic reaction
used to convert carbon dioxide n water into glucose
oxygen is also released as by product
leaves adaptations
a large surface area to maximise photosynthesis
a thin n flat shape to increase the absorption of sunlight
stomata for gas exchange
a waxy cuticle to prevent water loss
some leaves have spines/ hairs for protection against herbivores/ reduce water loss
word equation for photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water ----→ oxygen + glucose
how does light affect photosynthesis?
the intensity of the light available to the plant will depend on the amount of energy that it has to carry out photosynthesis
the more light a plant receives, the faster the rate of photosynthesis
how does temperature affect photosynthesis?
the temp of the environment affects how much kinetic energy all particles have – so temp affects the speed at which carbon dioxide n water moves through a plant
the lower the temp, the less kinetic energy particles have, resulting in fewer collisions occurring
increasing temp increases the kinetic energy of particles, increasing the chance of collisions between reactants n enzymes, results in the formation of products
at higher temps, enzymes that control the processes of photosynthesis can be denatured - reduces the overall rate
how does carbon dioxide concentration affect photosynthesis?
the more carbon dioxide that is present, the faster the reaction can occur
how does chlorophyll levels affect photosynthesis?
the number of chloroplasts will affect the rate of photosynthesis
the more chloroplasts a plant has, the faster the rate of photosynthesis
the amount of chlorophyll can be affected by:
diseases (such as tobacco mosaic virus)
lack of nutrients (such as magnesium)
loss of leaves (fewer leaves means fewer chloroplasts)
light intensity equation - inverse square law
light intensity = 1/ density^2
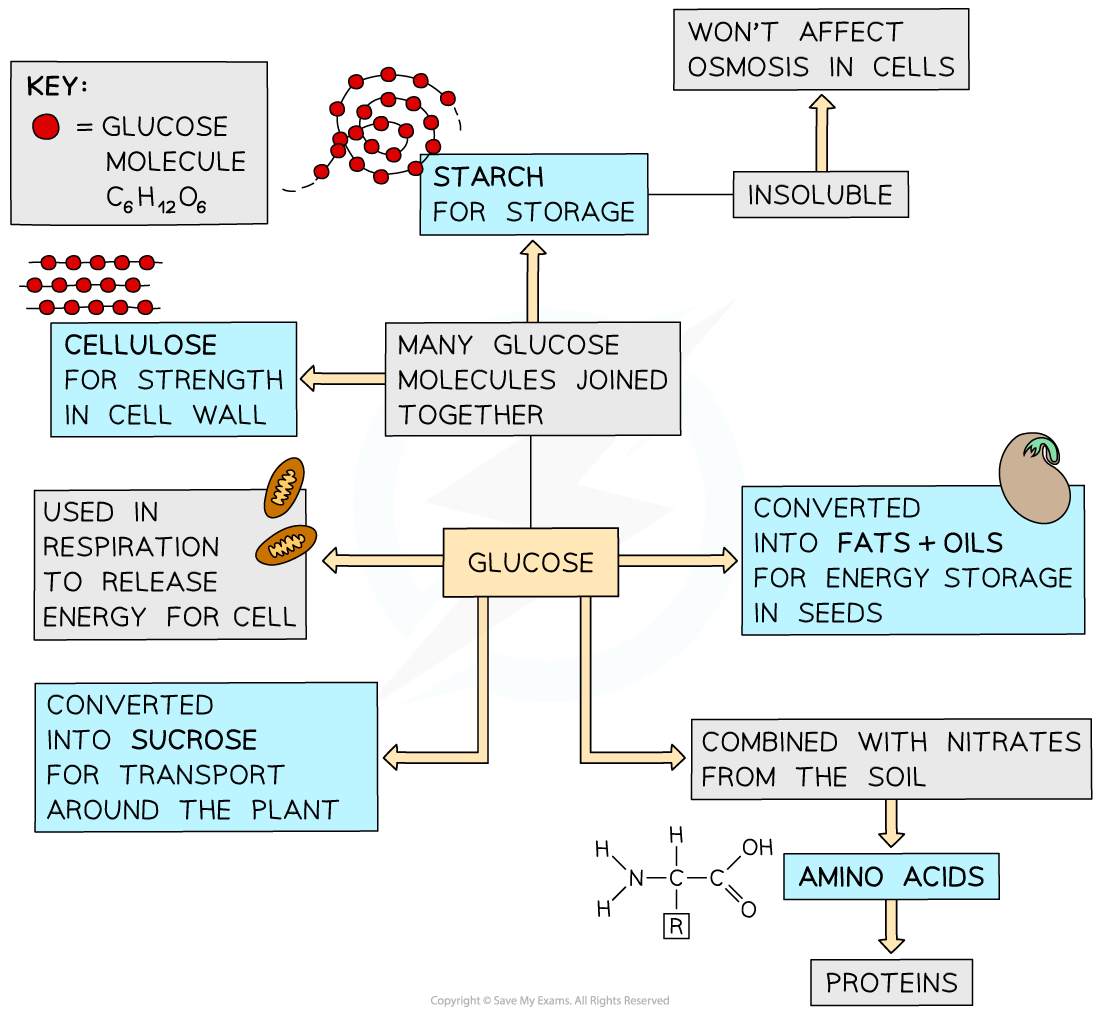
uses of glucose in plants
used for respiration (both aerobic n anaerobic)
converted into insoluble starch for storage in the stems, leaves n roots
used to produce fat/ oil for storage
used to produce cellulose, strengthens the cell wall
combined with nitrate ions absorbed from soil to produce amino acids for protein synthesis
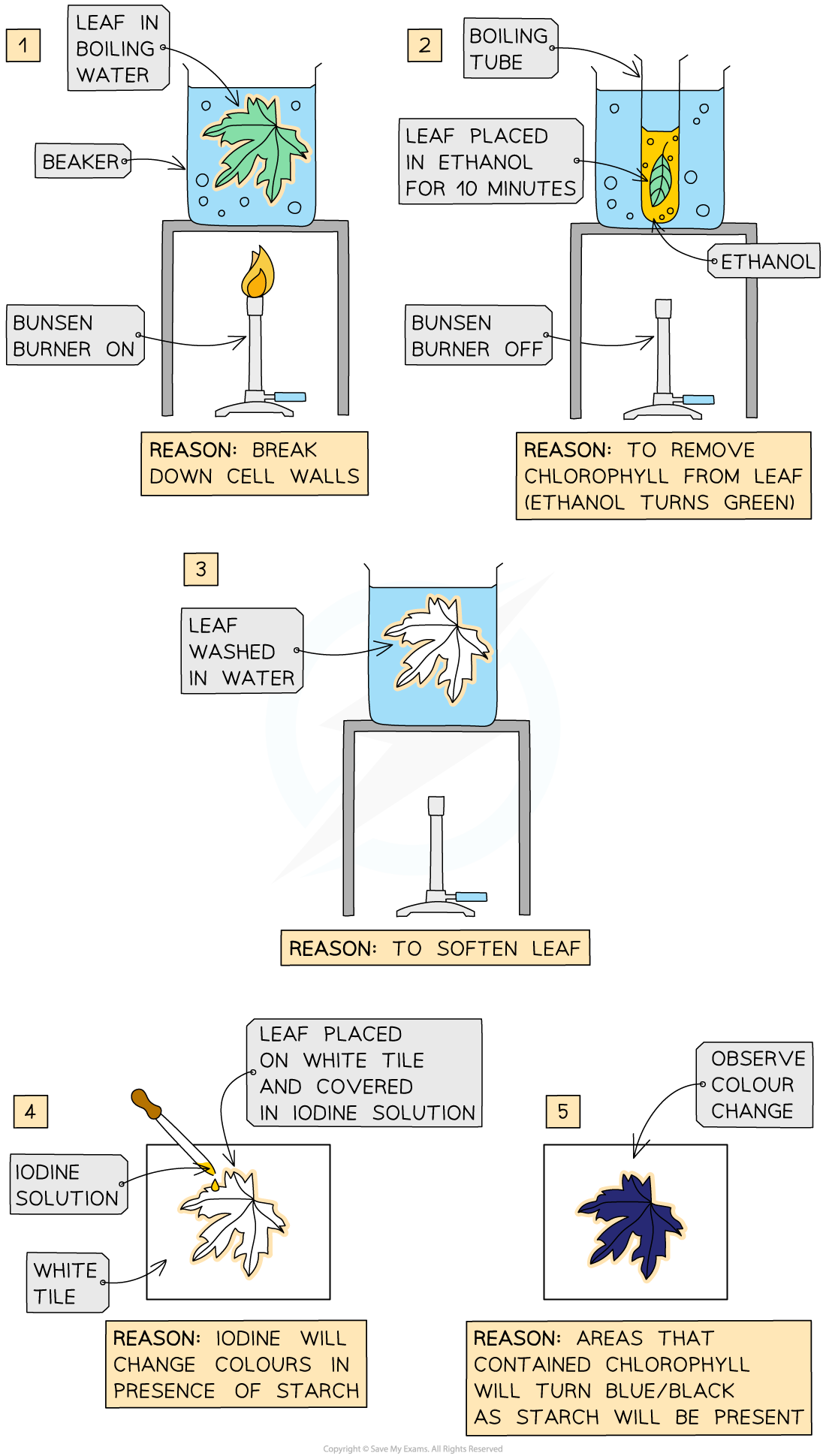
testing for starch - practical
what are greenhouses n their functions?
the environment is more controlled
the air is warmer
greenhouses can be use to overcome limiting factors.
allows the plants to grow faster as they are making more food
what are hydroponics n their functions?
hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using nutrient-rich water instead
the functions of hydroponics include faster growth rates, higher yields, n more efficient use of resources such as water n space
also allows for greater control over the growing environment, including temperature, pH levels, n nutrient levels
what are polytunnels n their functions?
polytunnels are structures made of polyethene that are used in agriculture to create a controlled environment for plants.
they are designed to protect crops from harsh weather conditions, pests, n diseases.
polytunnels also help to extend the growing season by providing a warmer environment for plants to grow in.
the polyethene material allows sunlight to pass through, which helps to promote photosynthesis
polytunnels can be used to regulate the amount of water n nutrients that plants receive, which can improve crop yields.