Chemistry -- Organic ALL
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
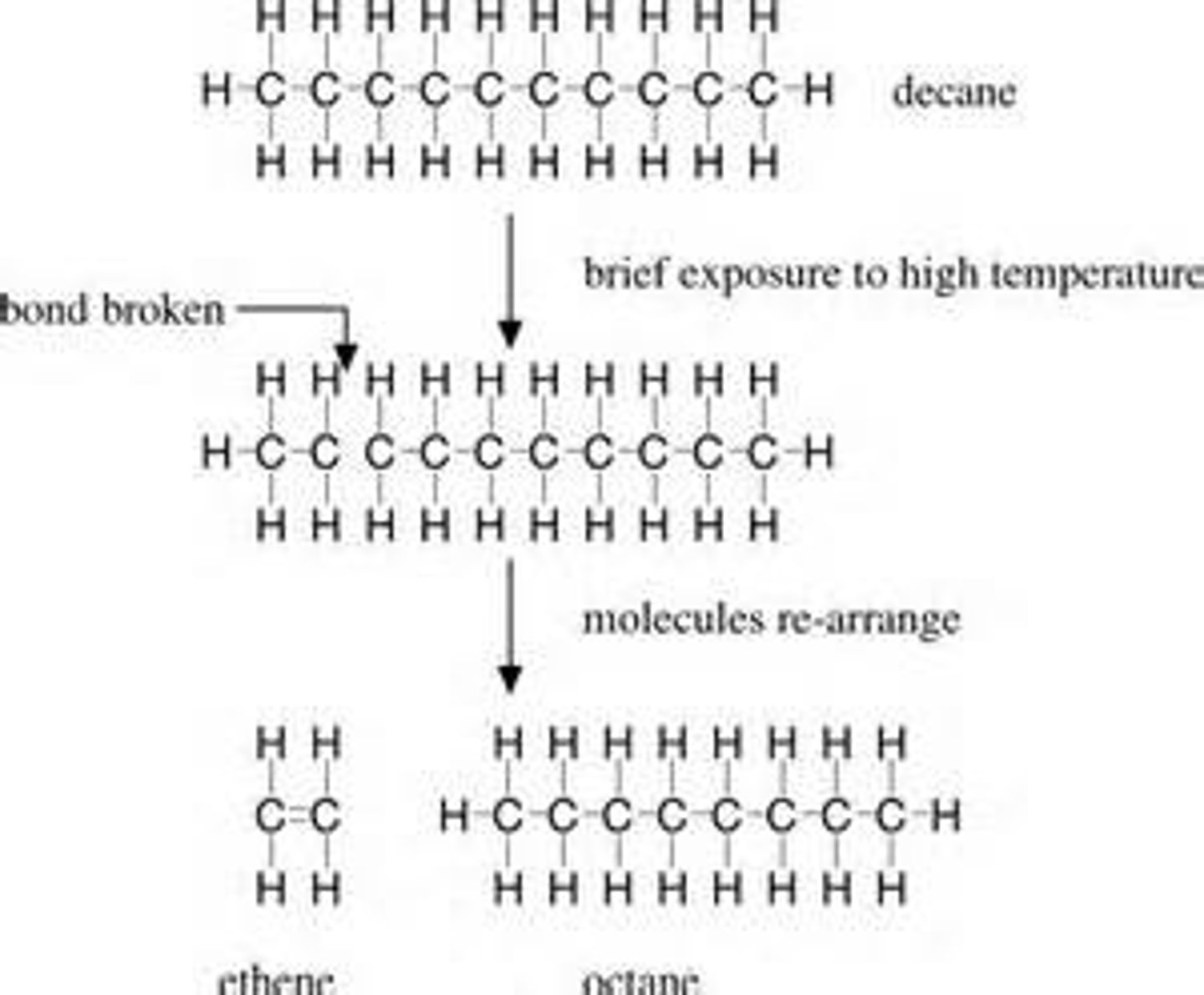
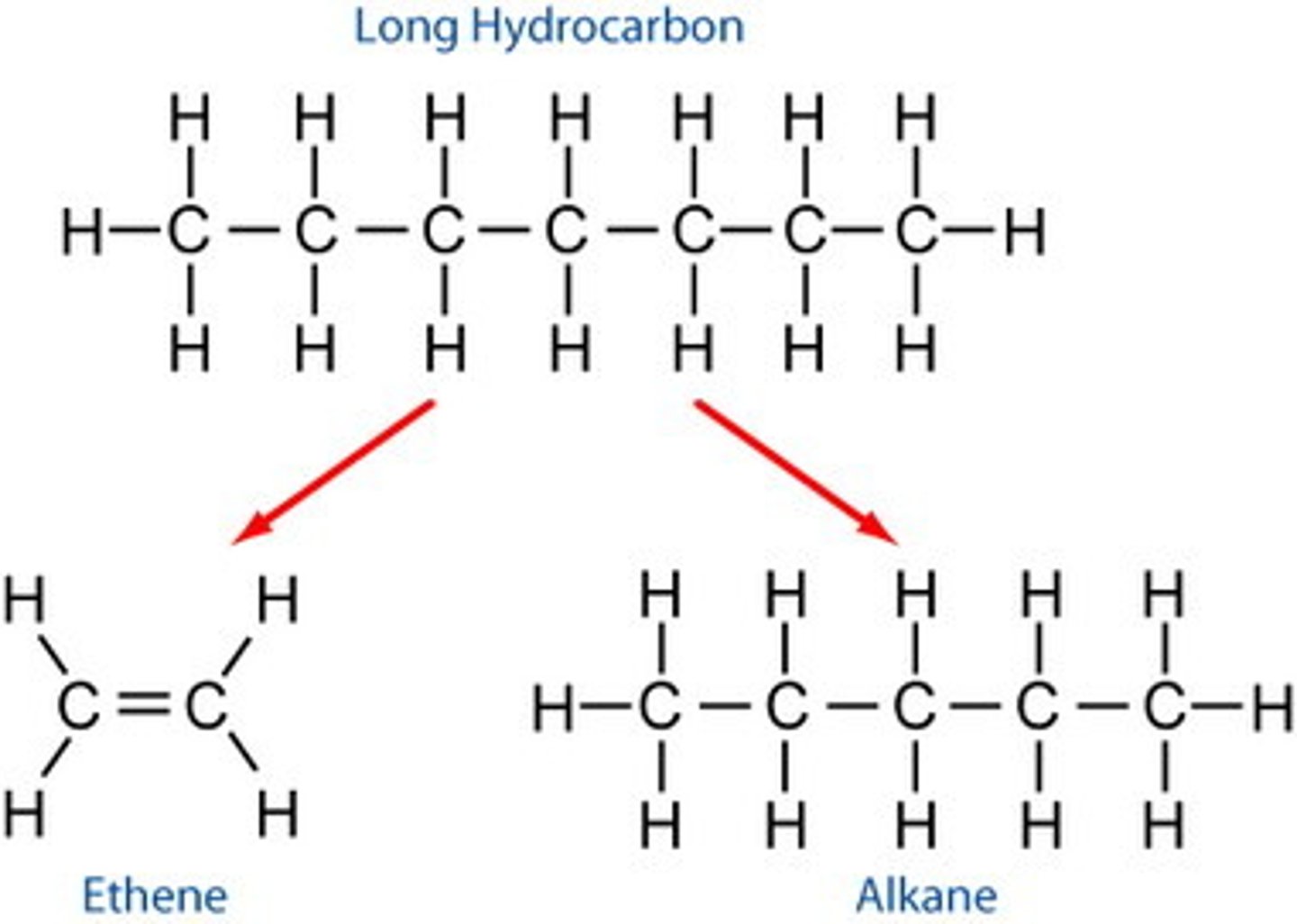
Cracking of hydrocarbons
Breaking apart long hydrocarbons into shorter more useful hydrocarbons
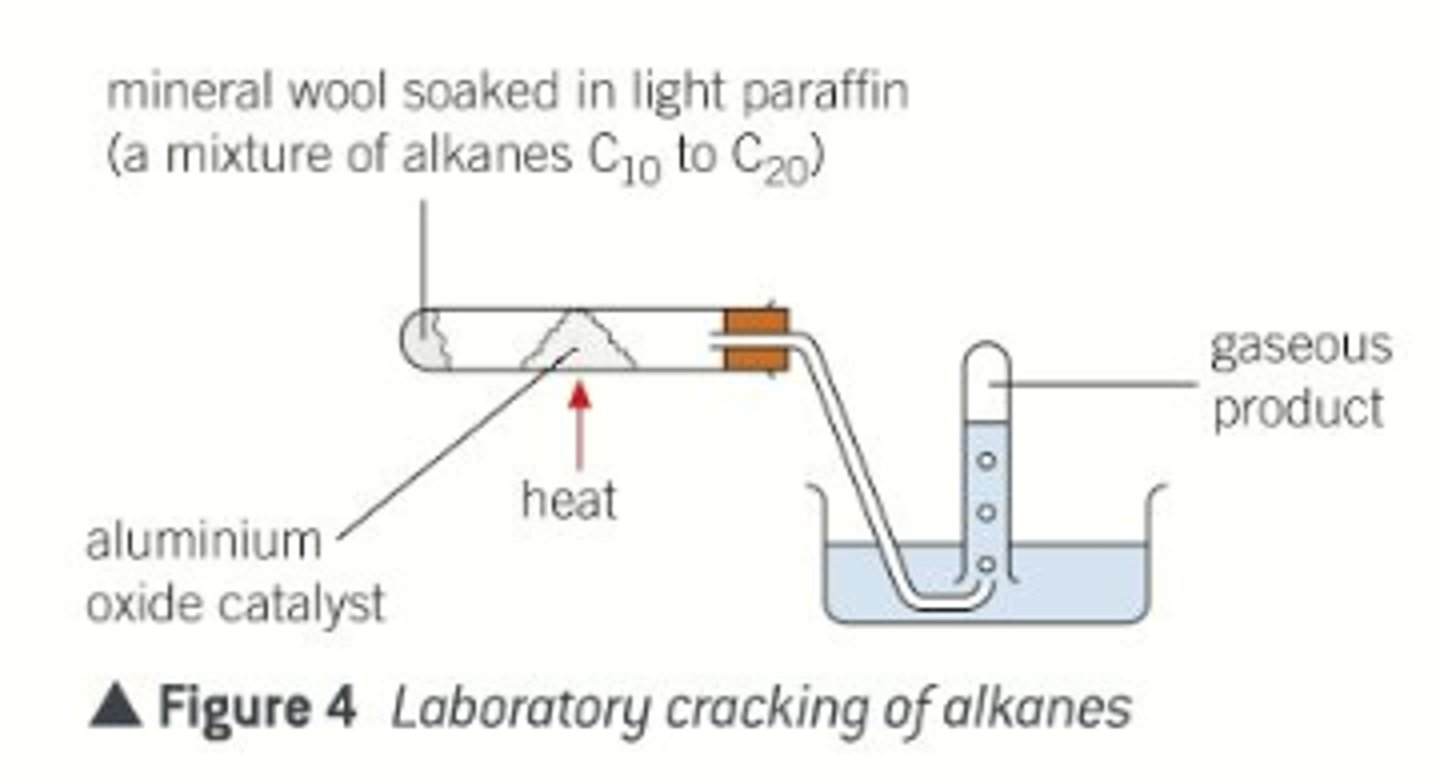
Catalytic cracking
Vaporise hydrocarbon and pass gas over a hot powered aluminium oxide catalyst
Steam cracking
Vaporise hydrocarbon, mix with steam, heat to a very high temperature
Reactant in cracking
Long alkane molecules
Products of cracking
Shorter chain alkanes and alkenes
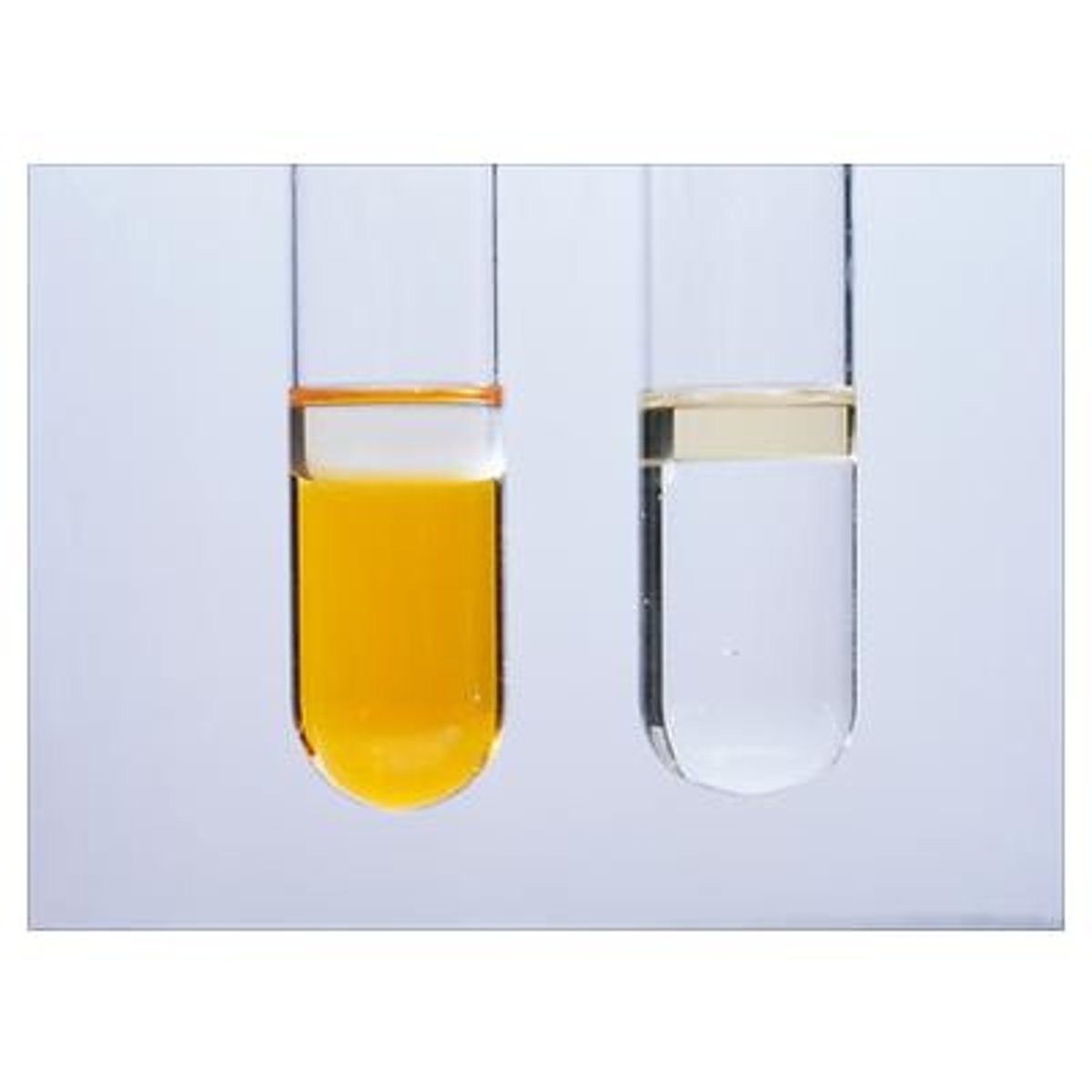
Test for alkenes
Turn bromine water orange to colourless

Long alkanes are not useful
As they are not very flammable
Shorter chain alkanes are more useful
As they are more flammable
Uses of alkenes
Making polymers and making other chemicals
Reactivity of alkenes
More reactive than alkanes
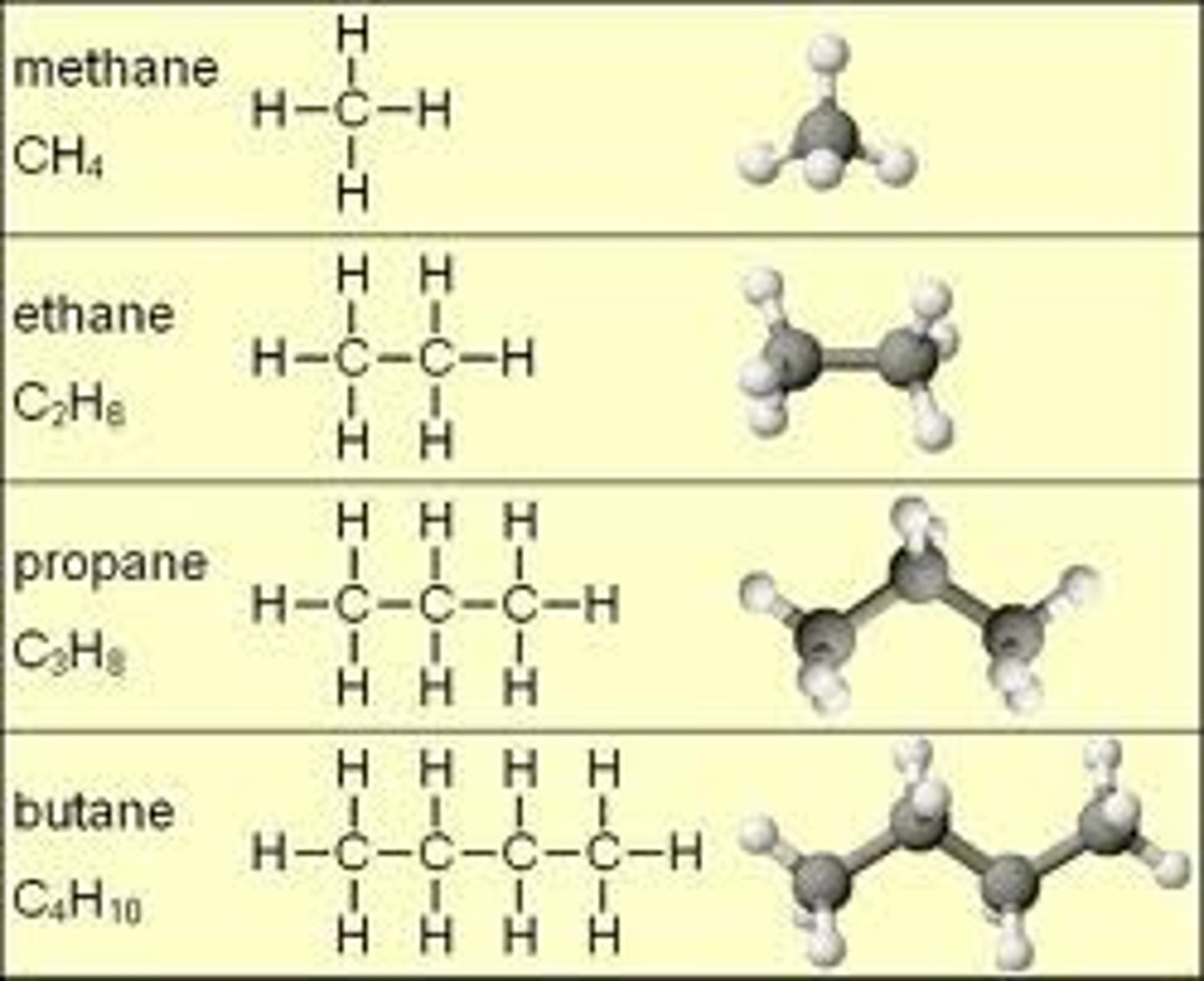
Ethene
C2H4
propene
C3H6
Butene
C4H8
Homologous series
A series of organic compounds with the same functional group but with each successive compound differing by CH2
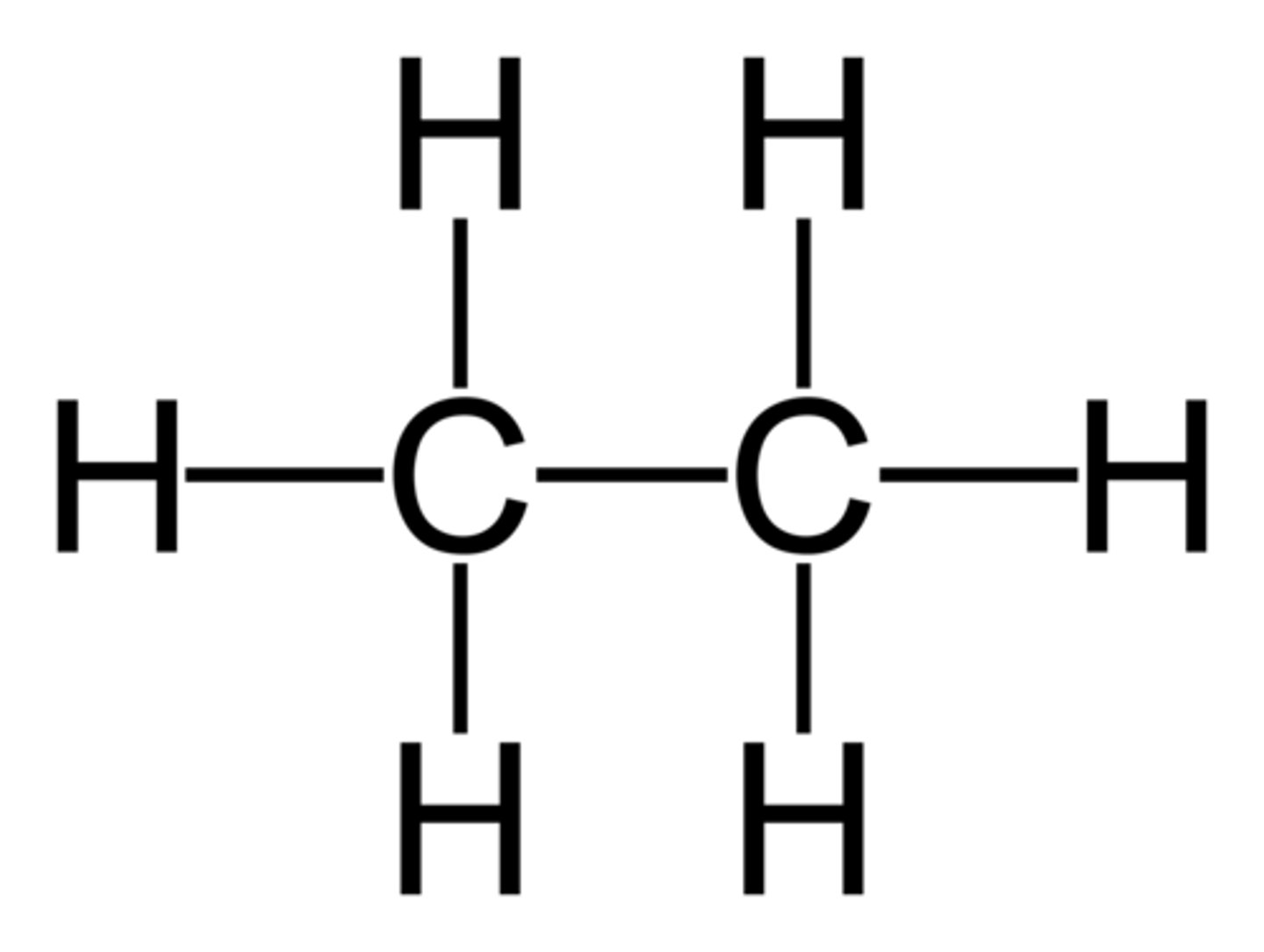
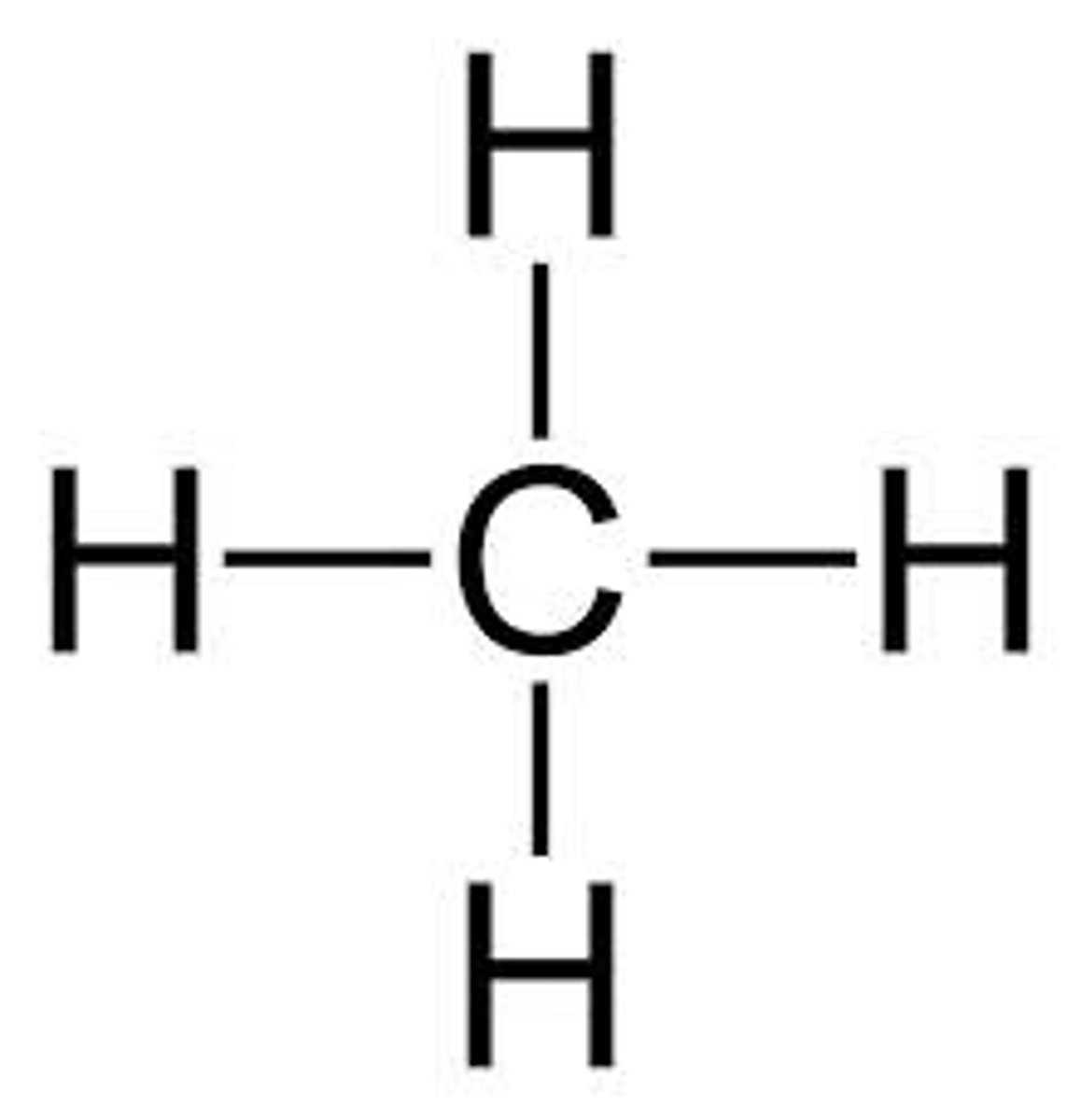
Alkane
a hydrocarbon containing only single covalent bonds
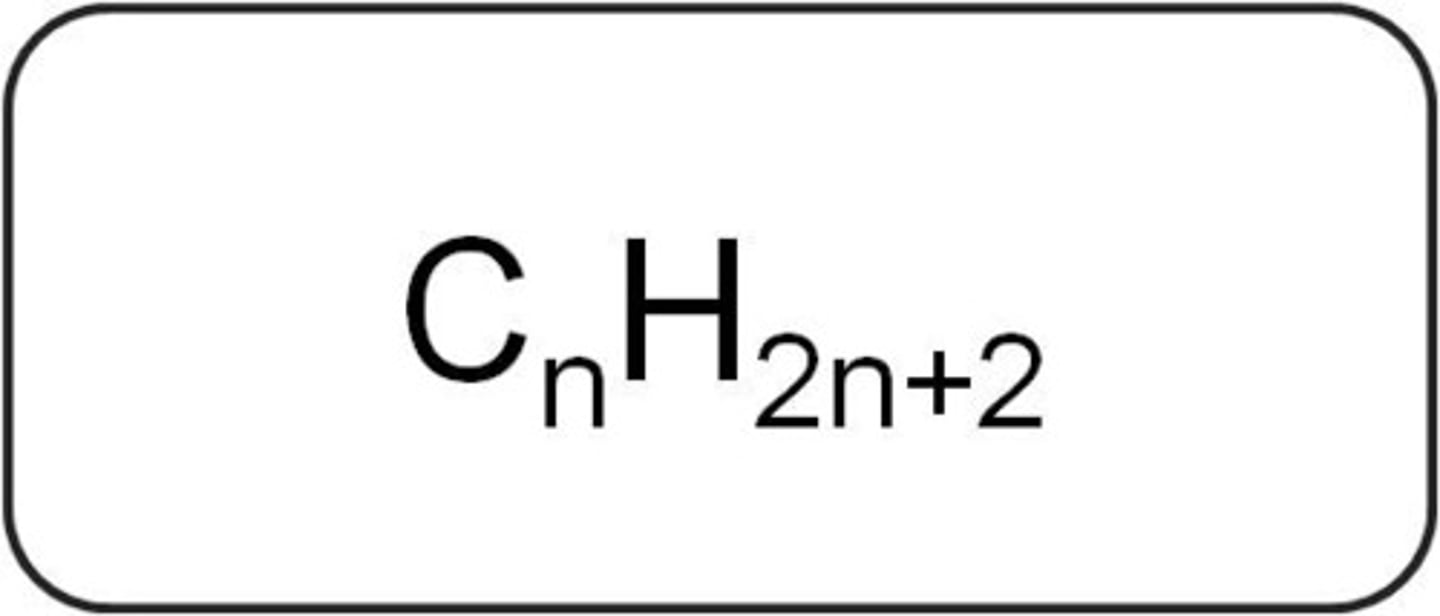
General formula of alkanes
CnH2n+2
Alkene
A hydrocarbon that contains a double bond.
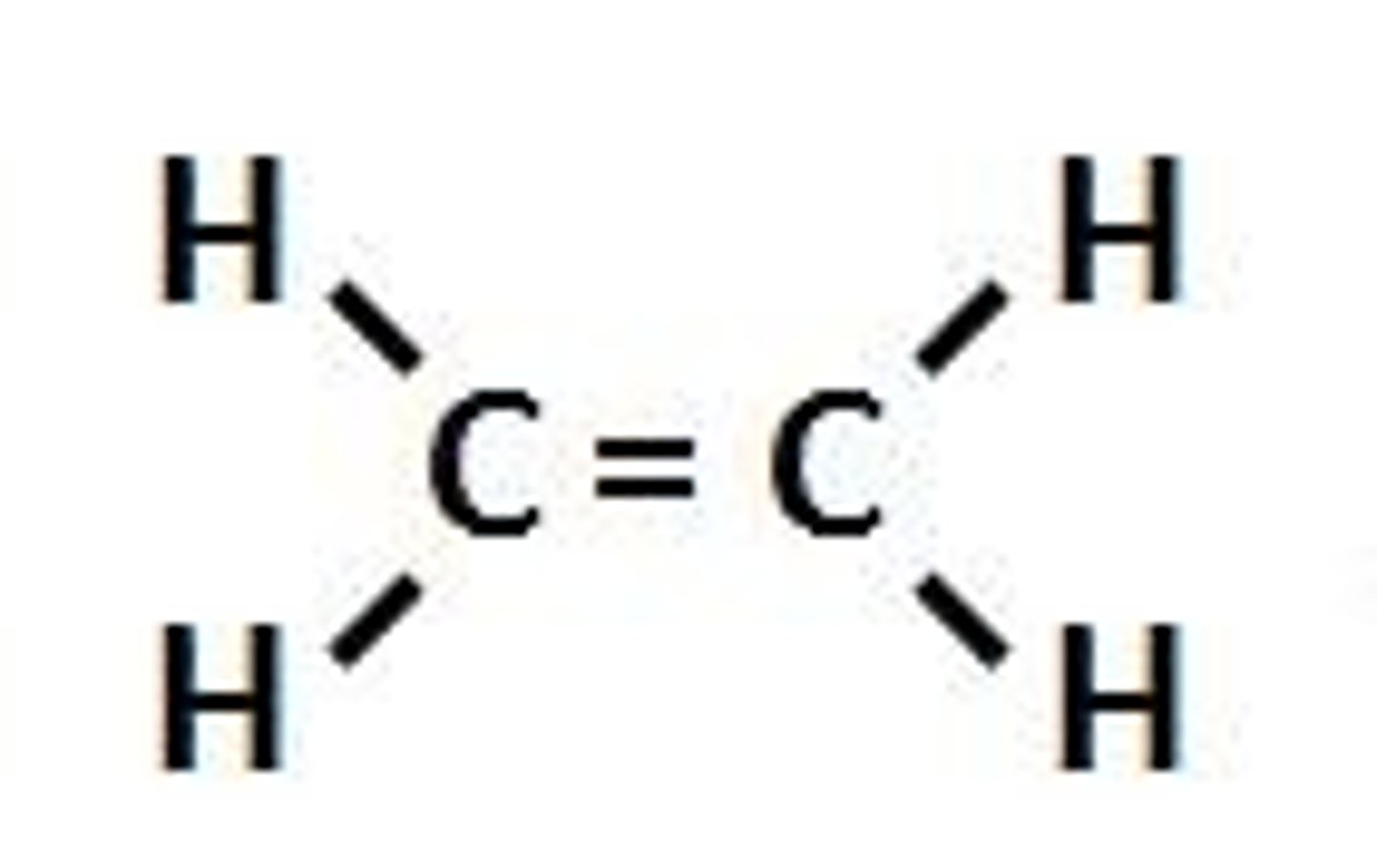
double covalent bond
a bond in which two atoms share two pairs of electrons
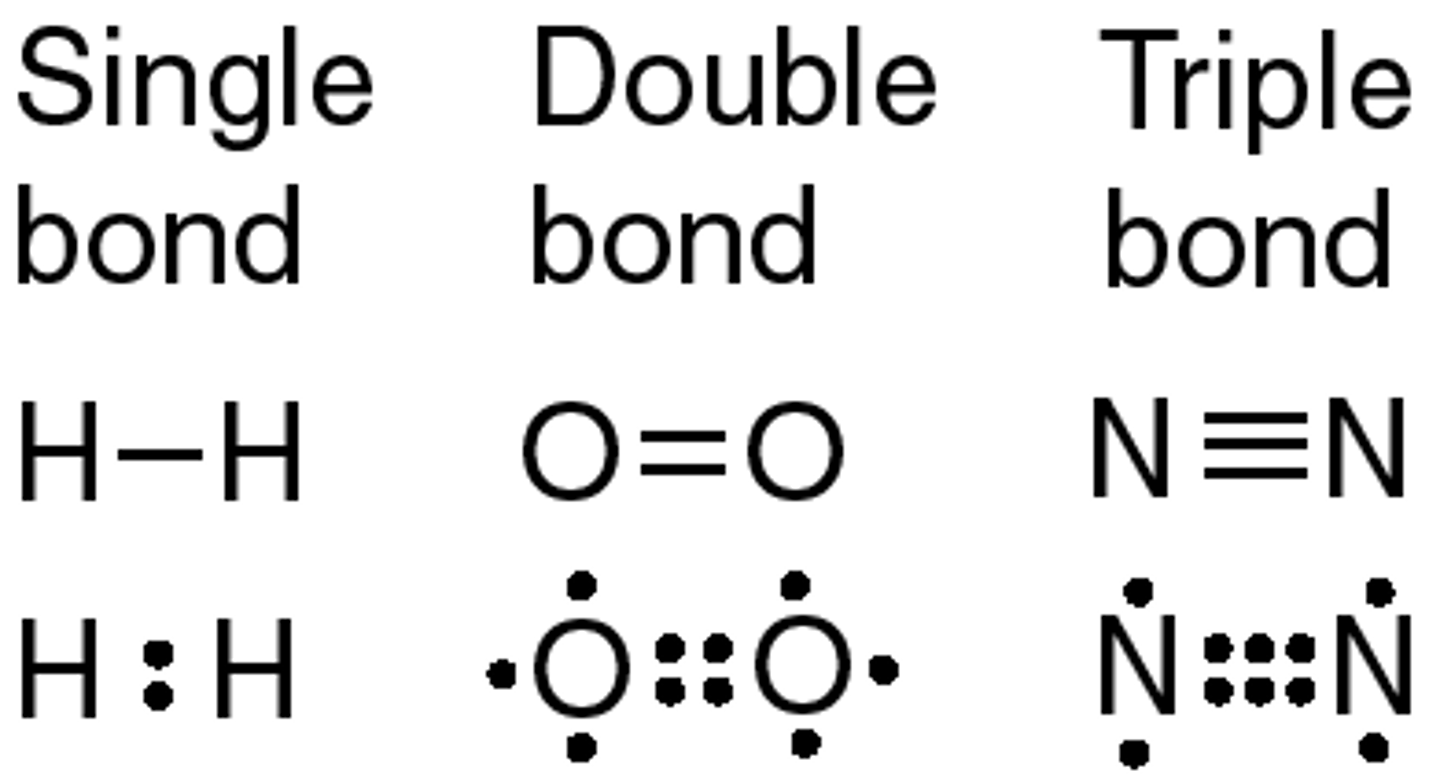
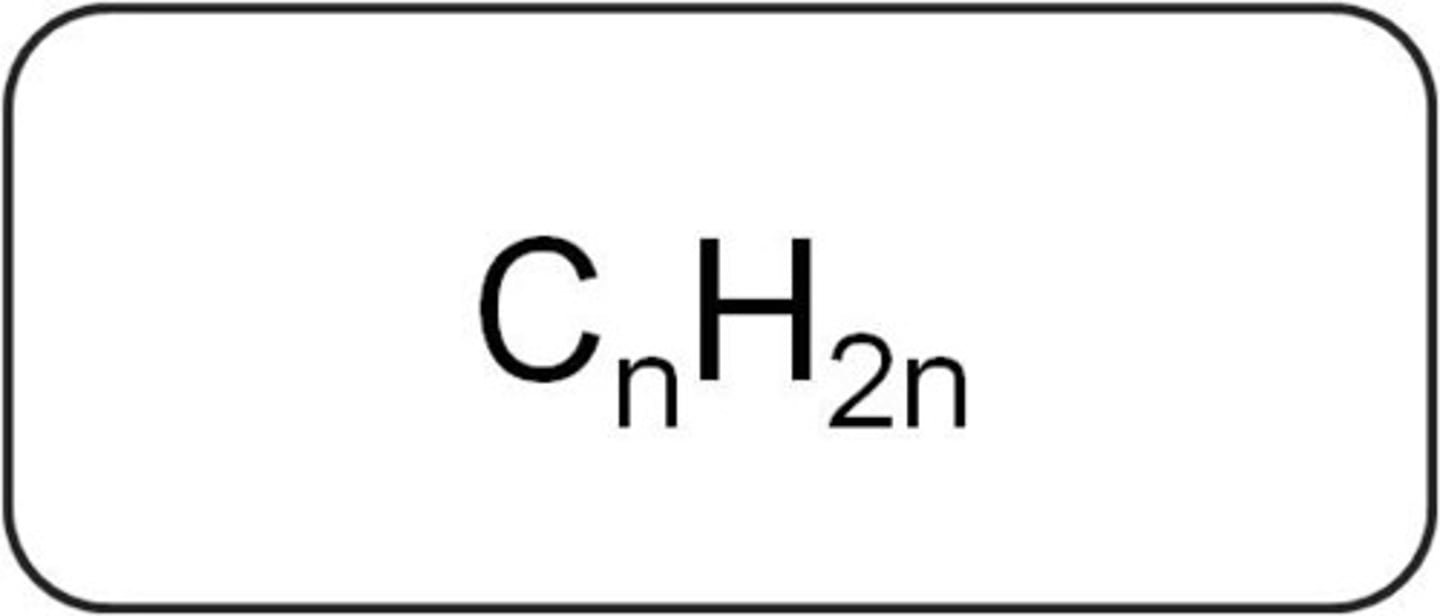
General formula of alkenes
CnH2n
Alkenes suffix
-ene
Alkanes suffix
-ane
Meth- prefix
1 carbon
Eth- prefix
2 carbons
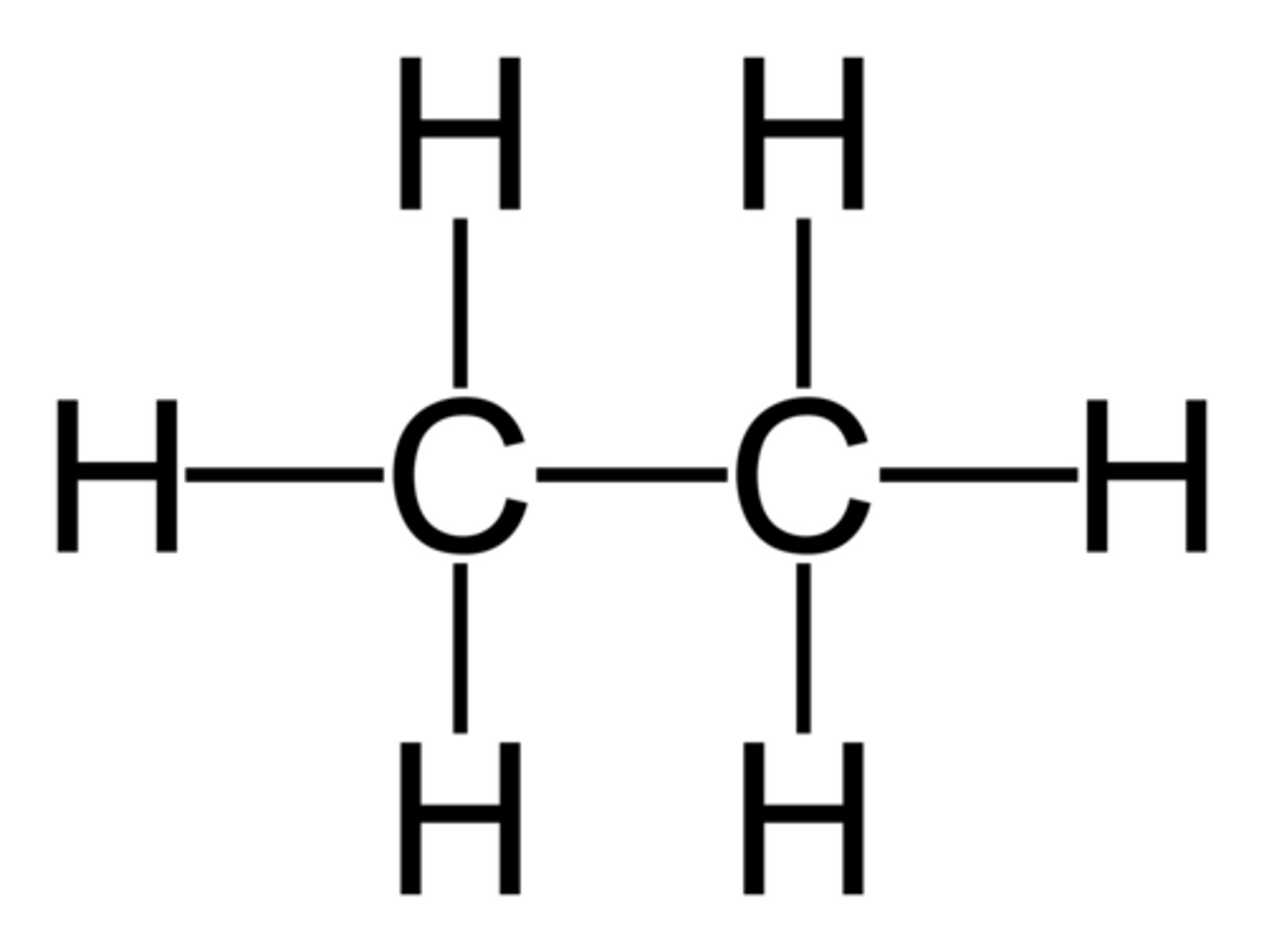
Prop- prefix
3 carbons
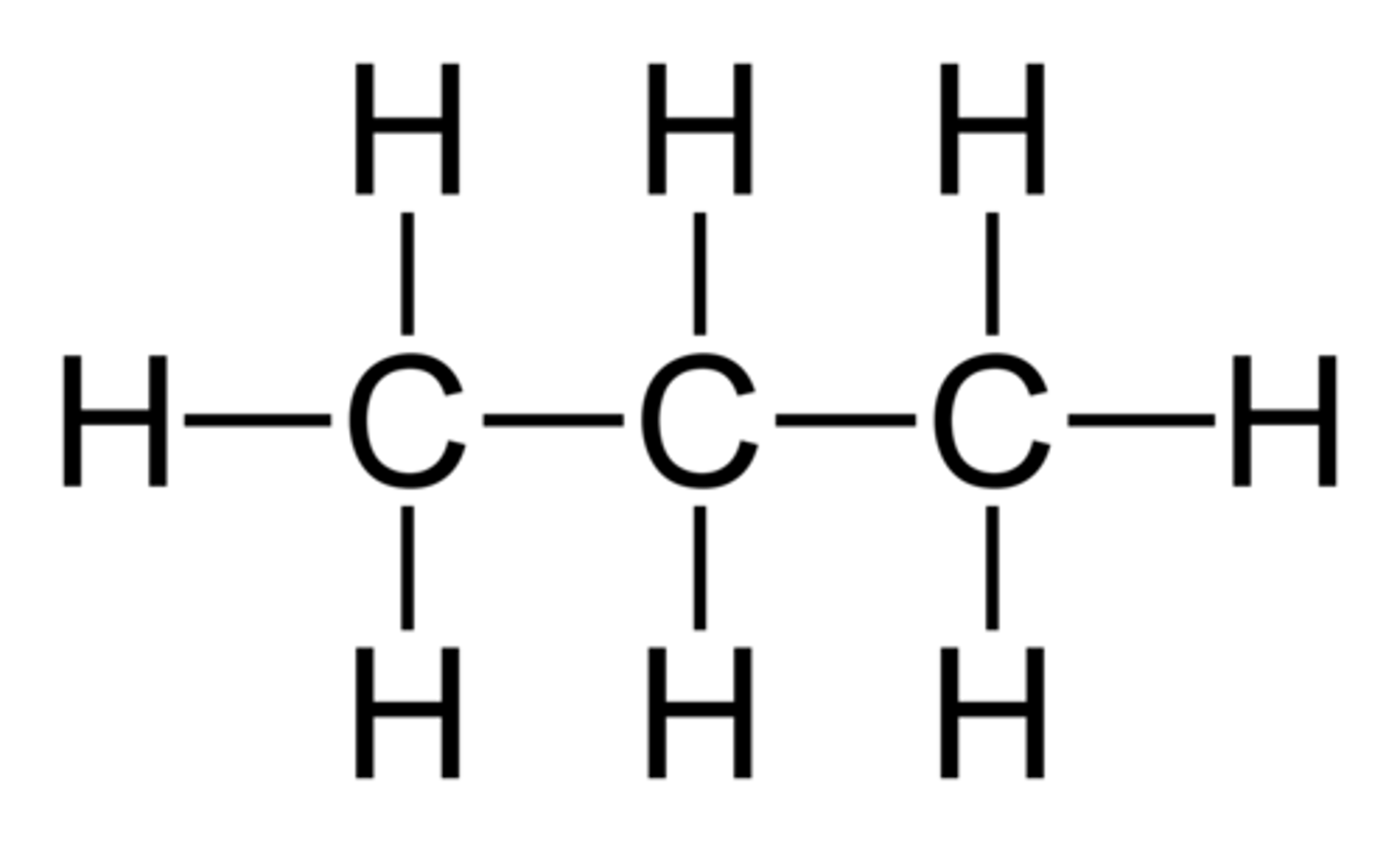
But- prefix
4 carbons
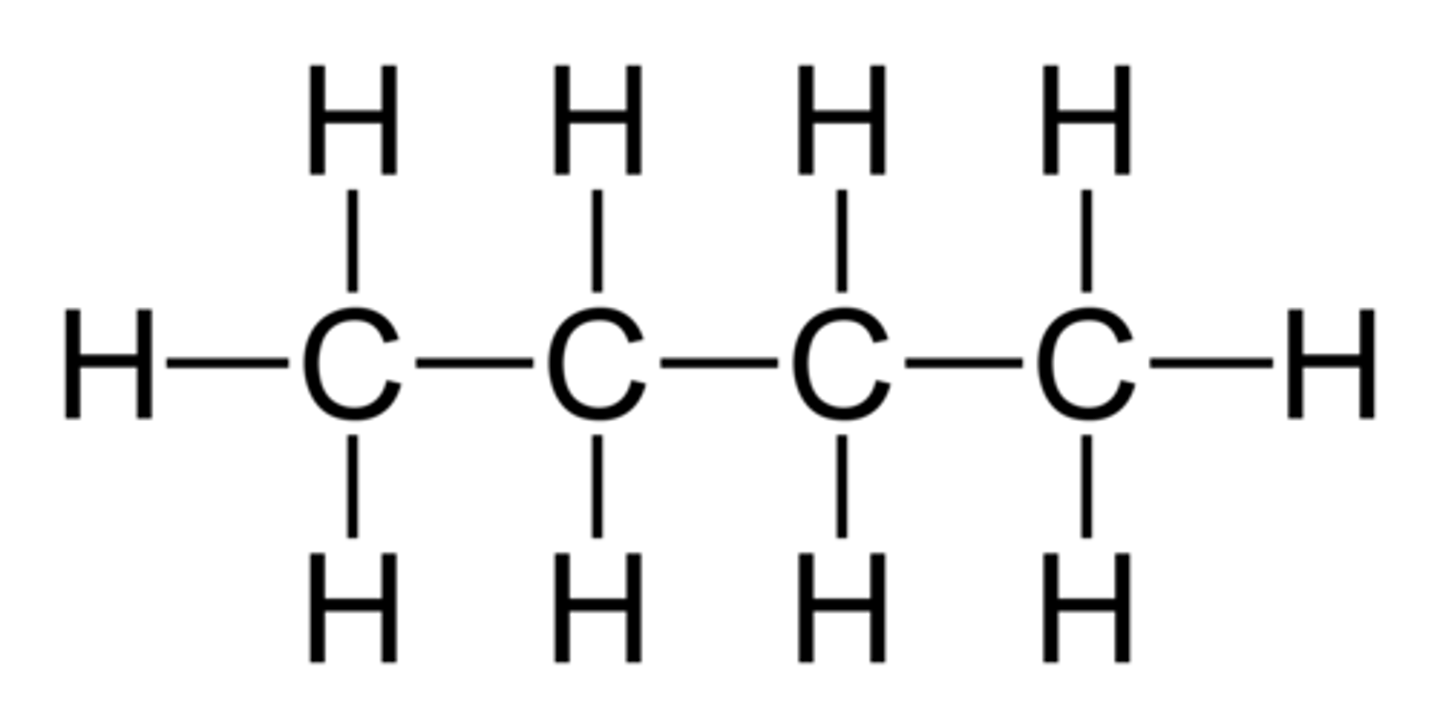
Molecular formula
A chemical formula that shows the number and kinds of atoms in a molecule, but not the arrangement of the atoms.
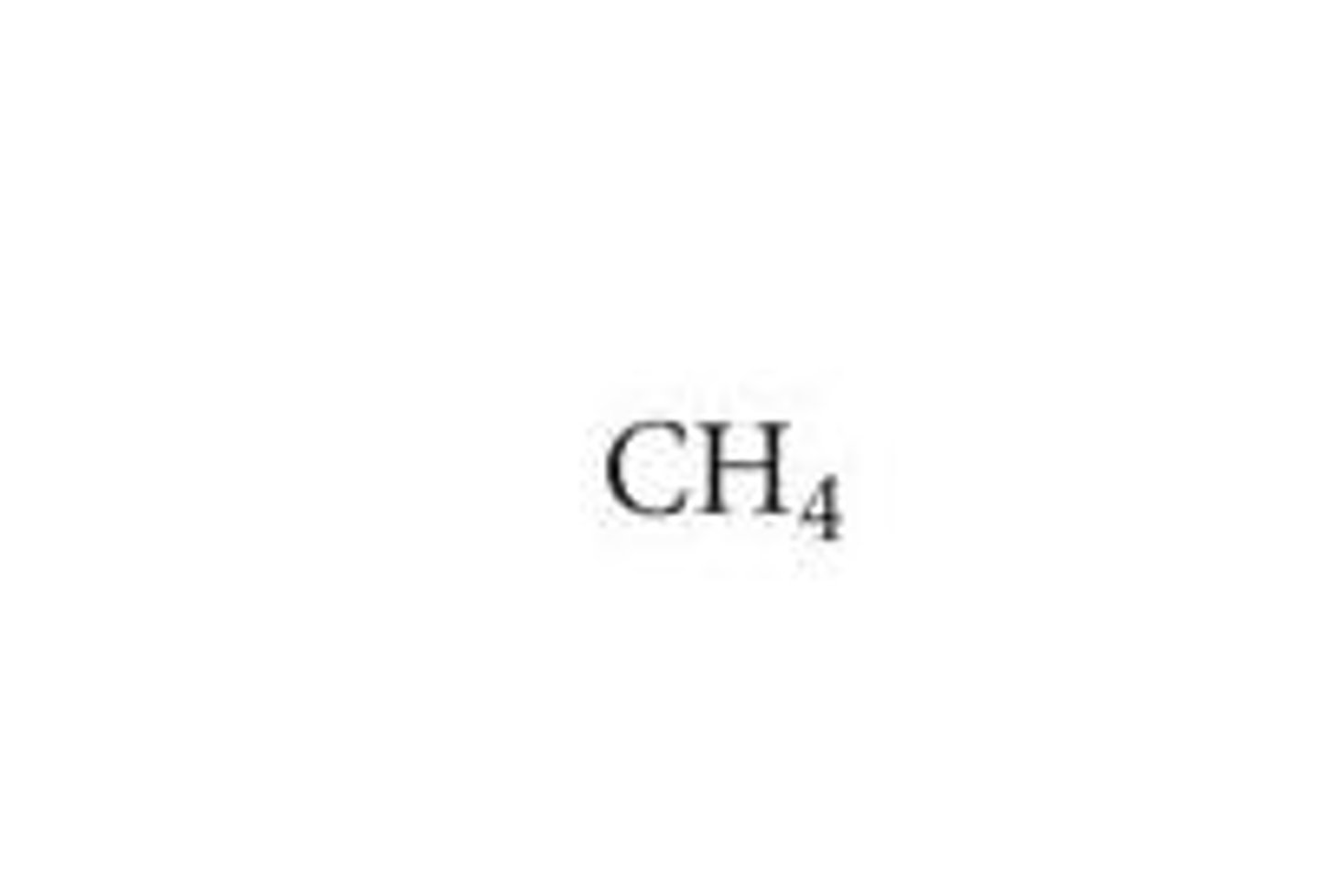
Display formula
Shows all of the atoms in the molecule and their arrangements
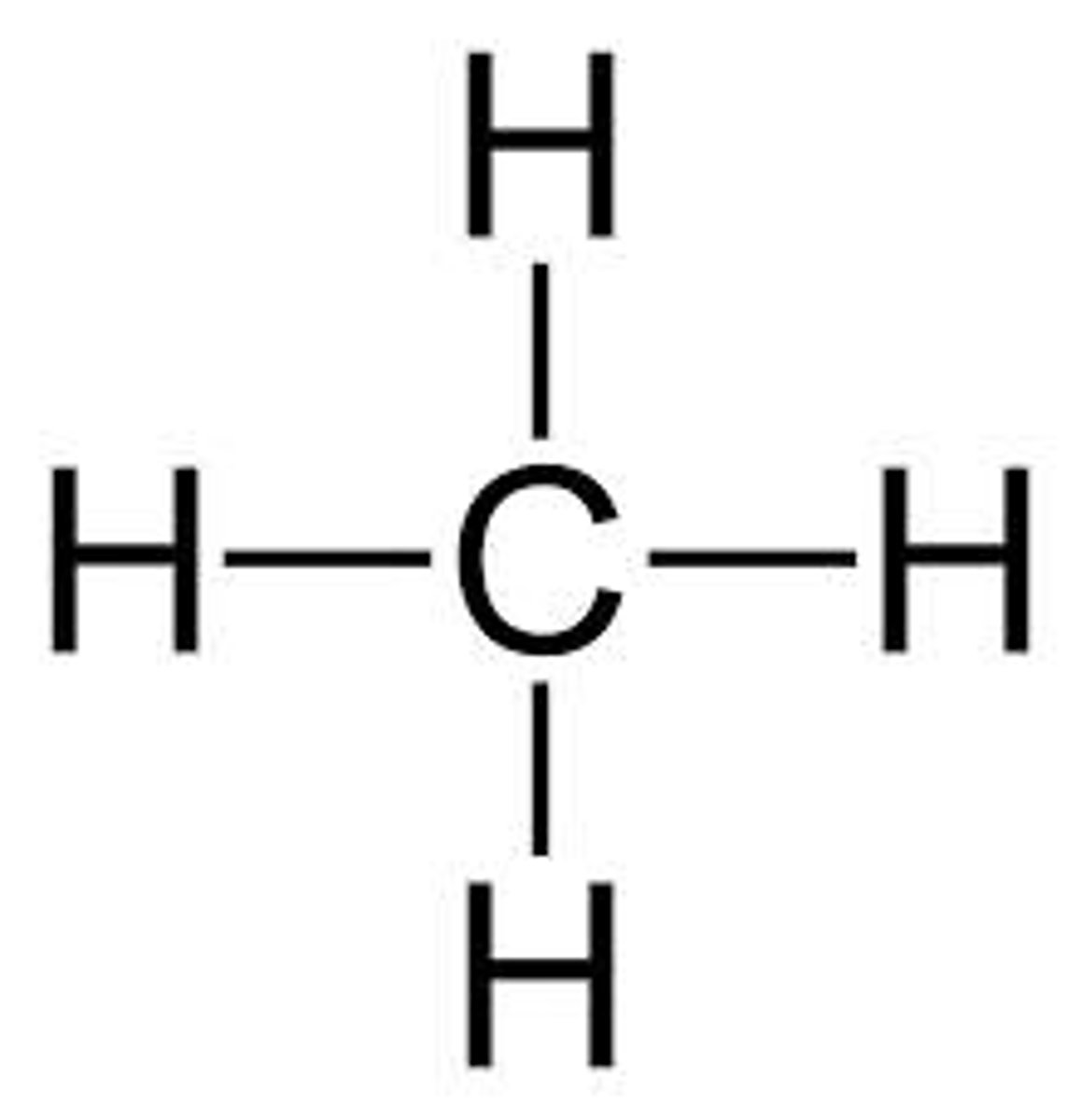
saturated hydrocarbon
A hydrocarbon in which all the bonds between carbon atoms are single bonds
Hydrocarbons - Trend in boiling point
The longer the hydrocarbon, the higher its boiling point
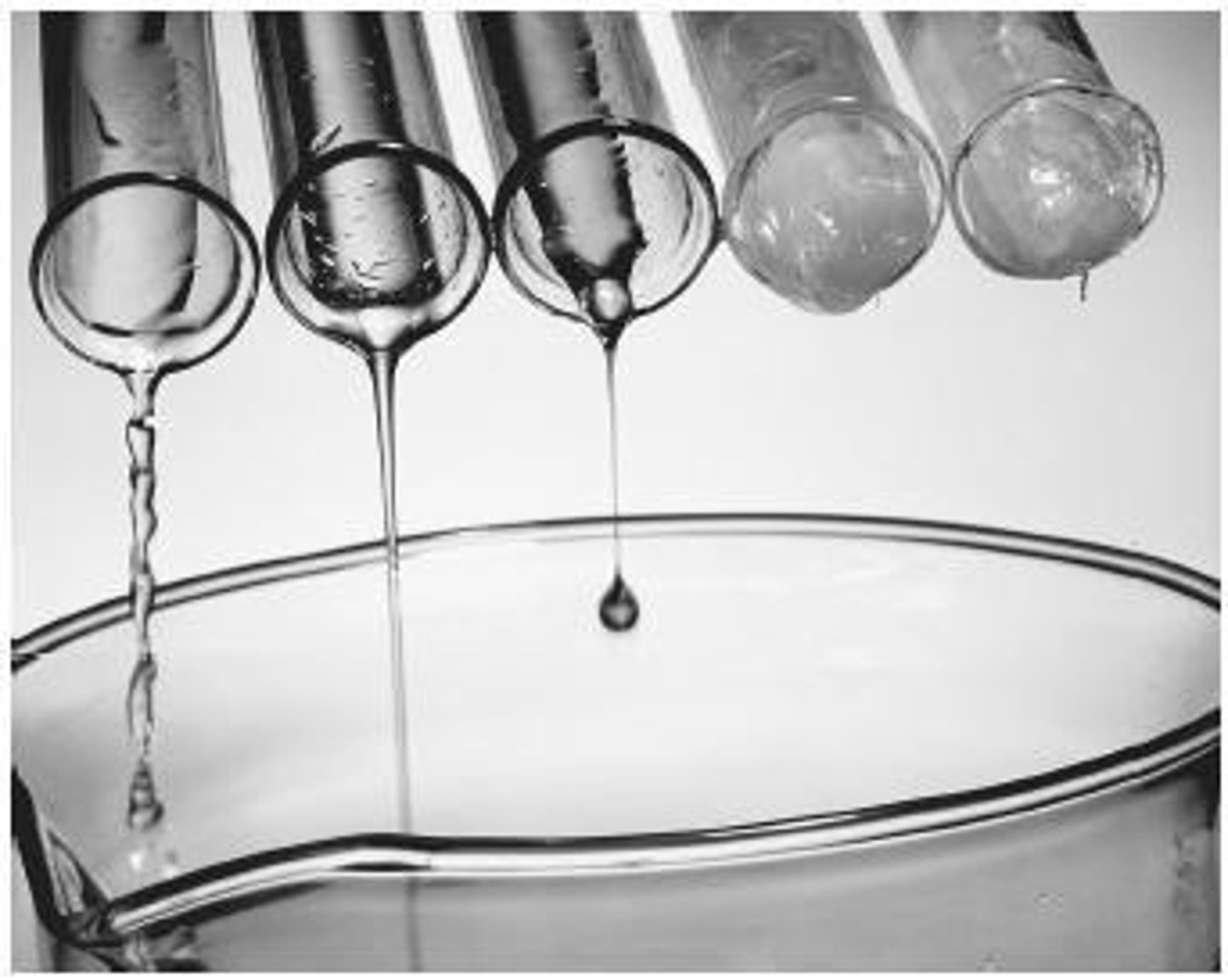
Hydrocarbons - Trend in viscosity
The longer the hydrocarbon, the more viscous it is

Hydrocarbons - Trend in flammability
The shorter the hydrocarbon, the more flammable it is

Complete combustion
A combustion reaction in the presence of plenty of oxygen, producing carbon dioxide and water

Incomplete combustion
Combustion with insufficient oxygen, producing water, carbon particulates and carbon monoxide.

Crude oil
A finite fossil fuel made from buried plankton which has decomposed under mud for millions of years

Crude oil isn't useful because
It is a mixture of lots of hydrocarbons of a huge range of lengths
Composition of crude oil
Mainly hydrocarbons, with a few impurities such as sulfur
Hydrocarbon
A substance which is only made of hydrogen and carbon
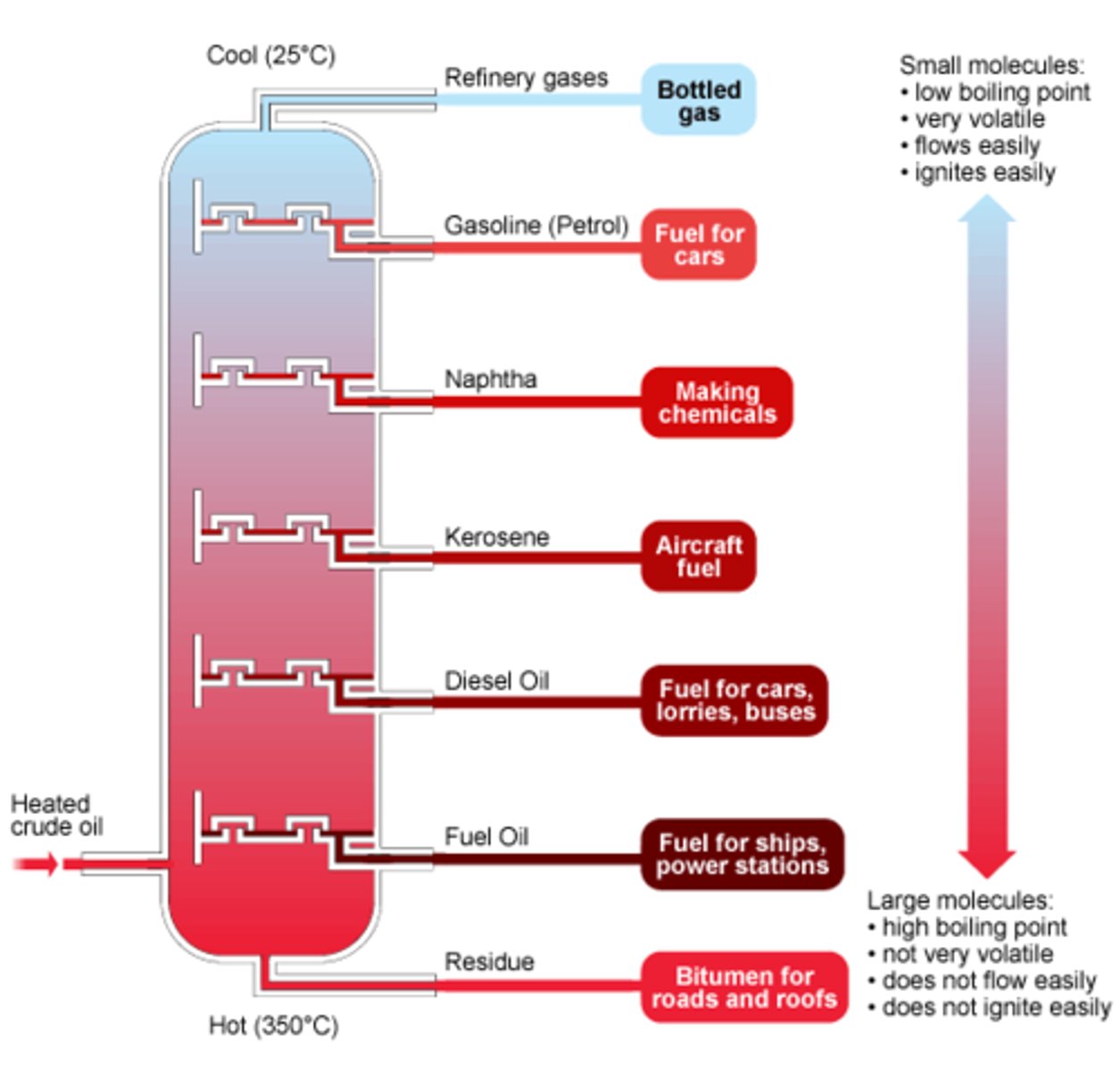
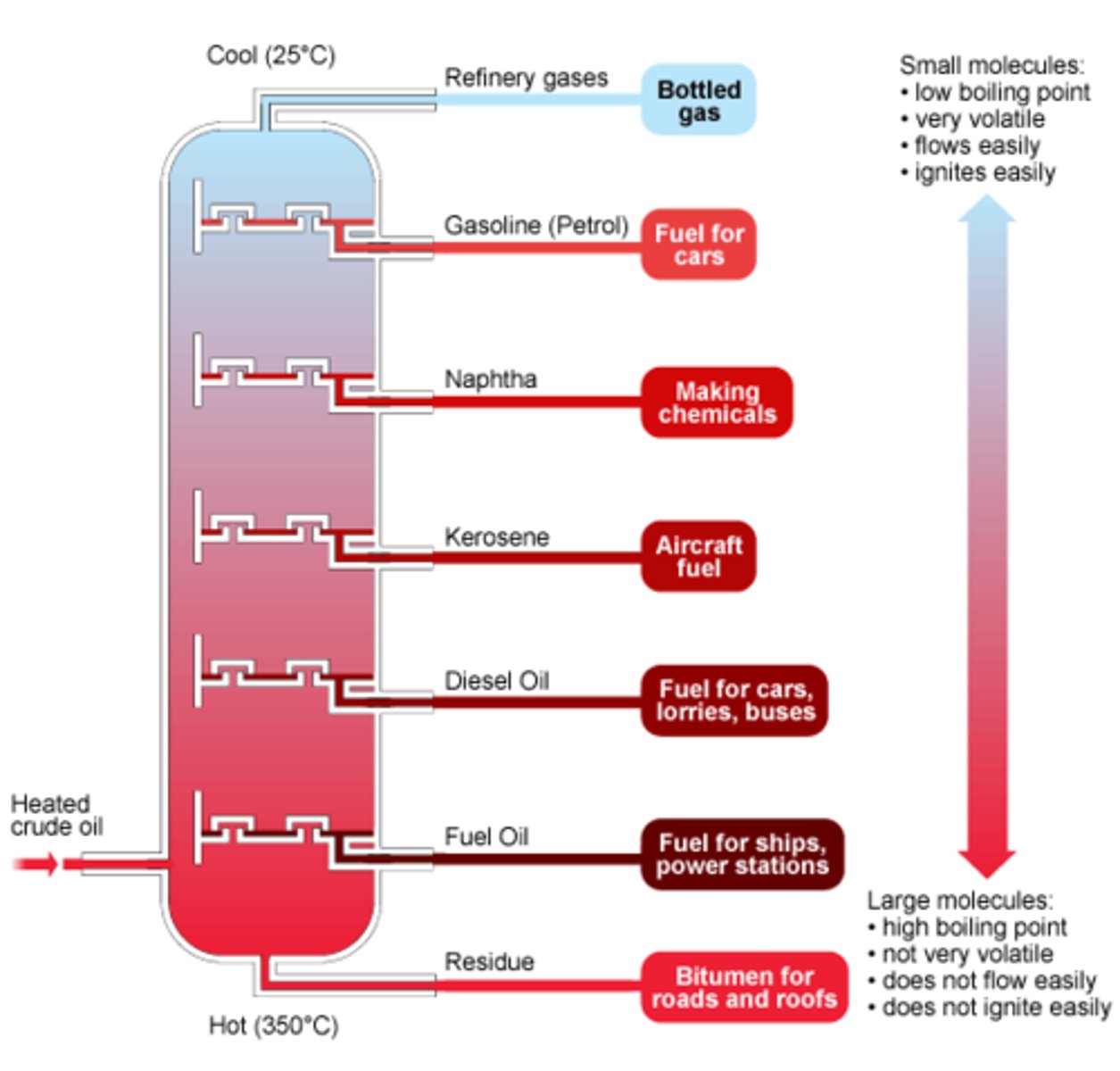
Fractional distillation of crude oil
The separation of crude oil into fractions
Hydrocarbon fraction
A group of hydrocarbons with similar boiling points and numbers of carbon atoms
Fuel
A material that releases energy when it burns

Common hydrocarbon fractions
Petrol, diesel oil, kerosene, fuel oil, LPG
Petrol
A liquid fuel used in cars

Diesel
A liquid fuel used in large cars and trucks

Kerosene
A liquid fuel used in jet engines (planes)

Fuel oil
A liquid fuel for ships and power stations

LPG
a gas fuel used in cooking
Products made from crude oil
solvents, lubricants, polymers, detergents

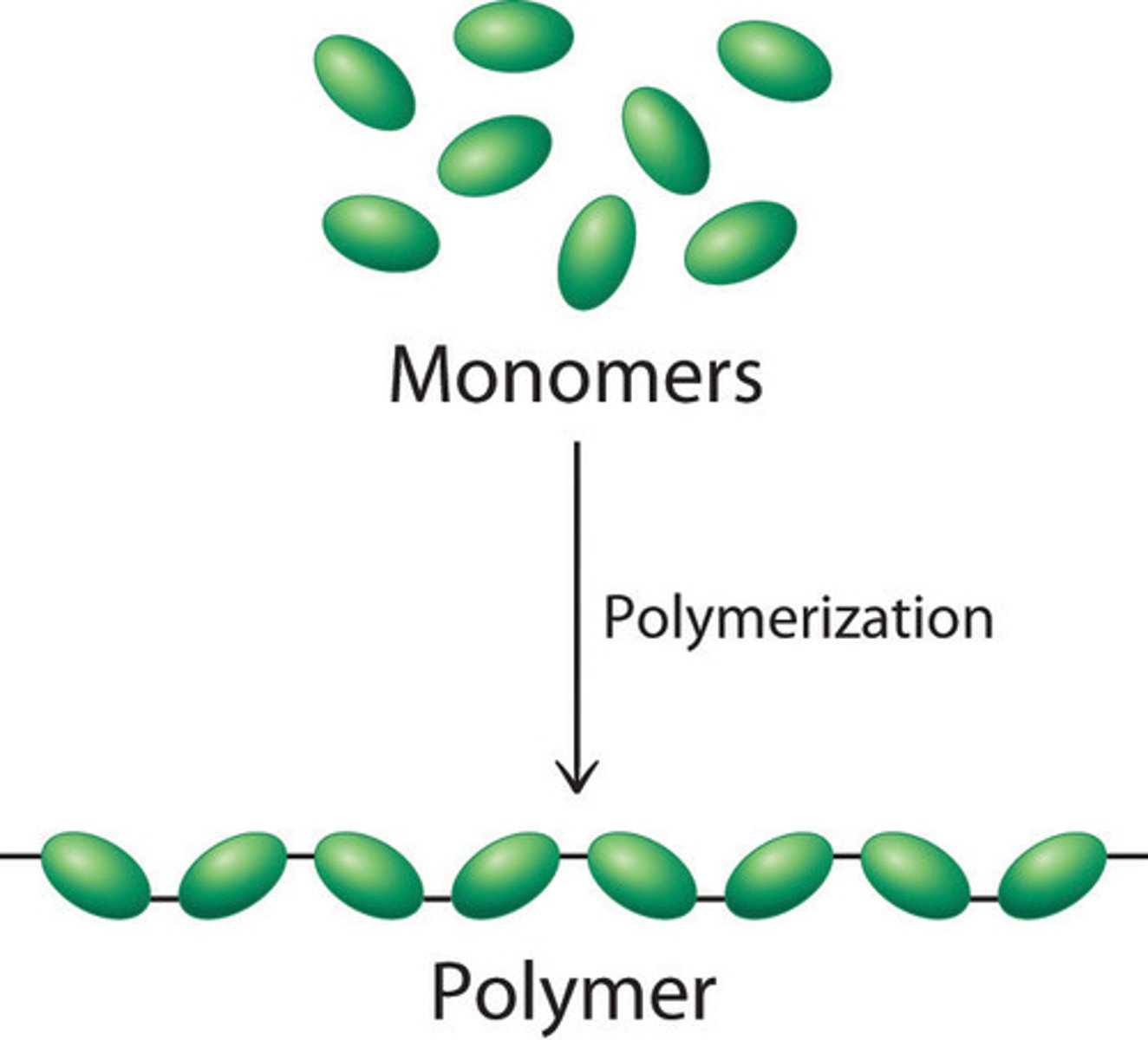
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
Evaporation
The change of state from a liquid to a gas

Condensation
The change of state from a gas to a liquid

1st step of fractional distillation in crude oil
Crude oil is heated and vapourised
Fractionating column
The vertical column, used in fractional distillation which is hottest at the bottom and cools towards the top
Hydrocarbon chain length
Number of carbon atoms in a hydrocarbon molecule
Shortest chains in fractional distillation
Are found at the top of the fractionating column
Longest chains in fractional distillation
Are found at the bottom of the fractionating column
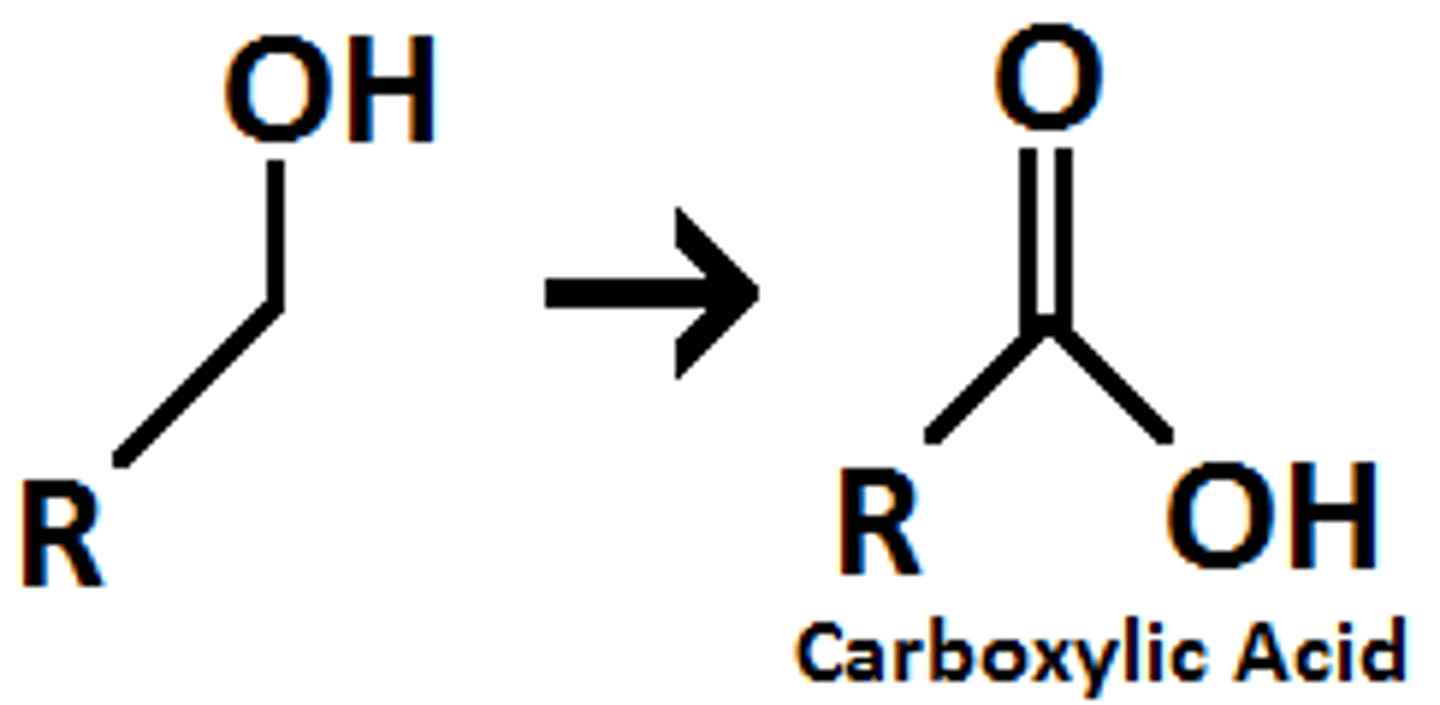
Carboxylic acid
organic compounds that are weak acids
Functional group of carboxylic acids
-COOH
suffix of carboxylic acid
-anoic acid
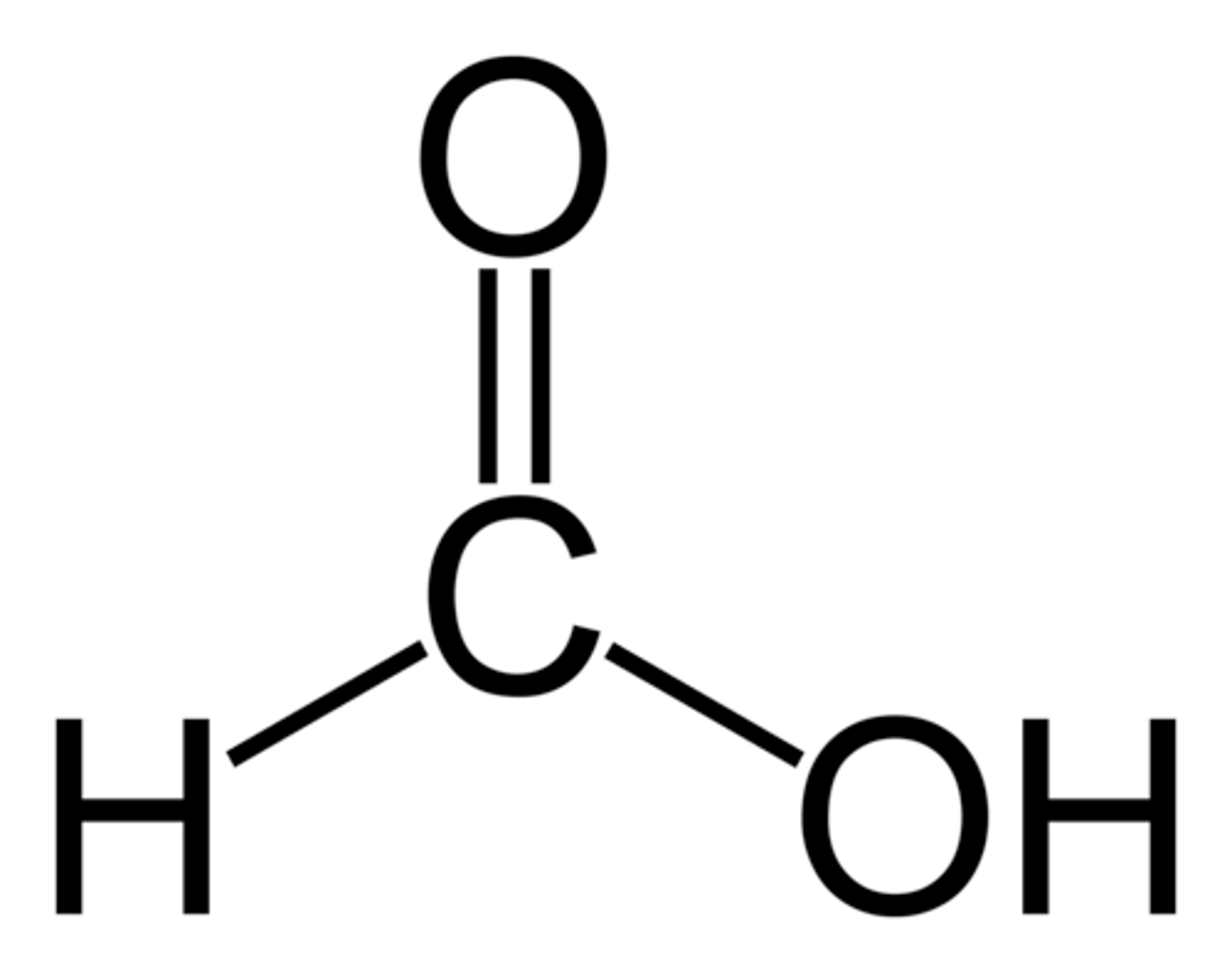
Methanoic acid
CHOOH
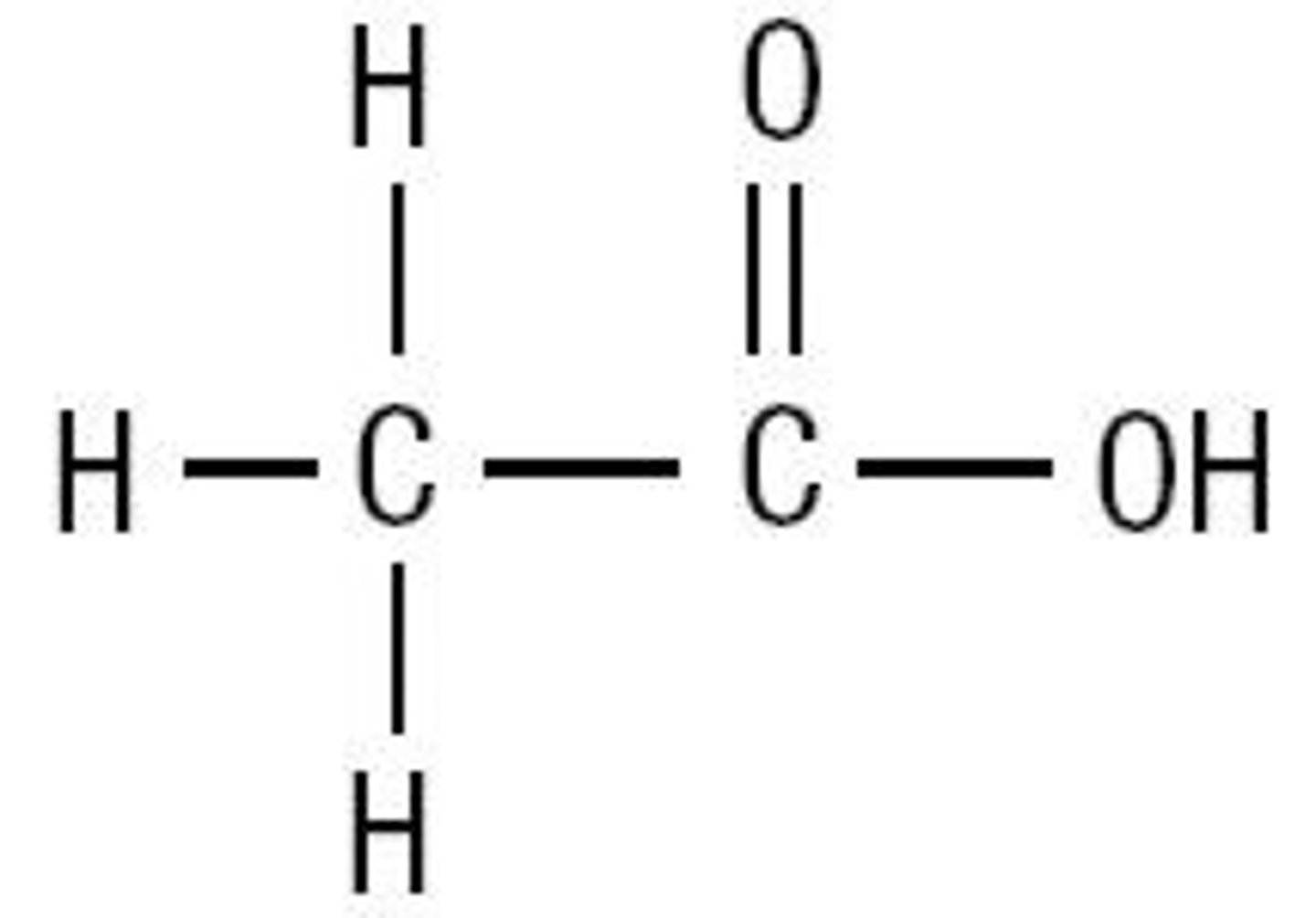
Ethanoic acid
CH3COOH
Propanoic acid
CH3CH2COOH
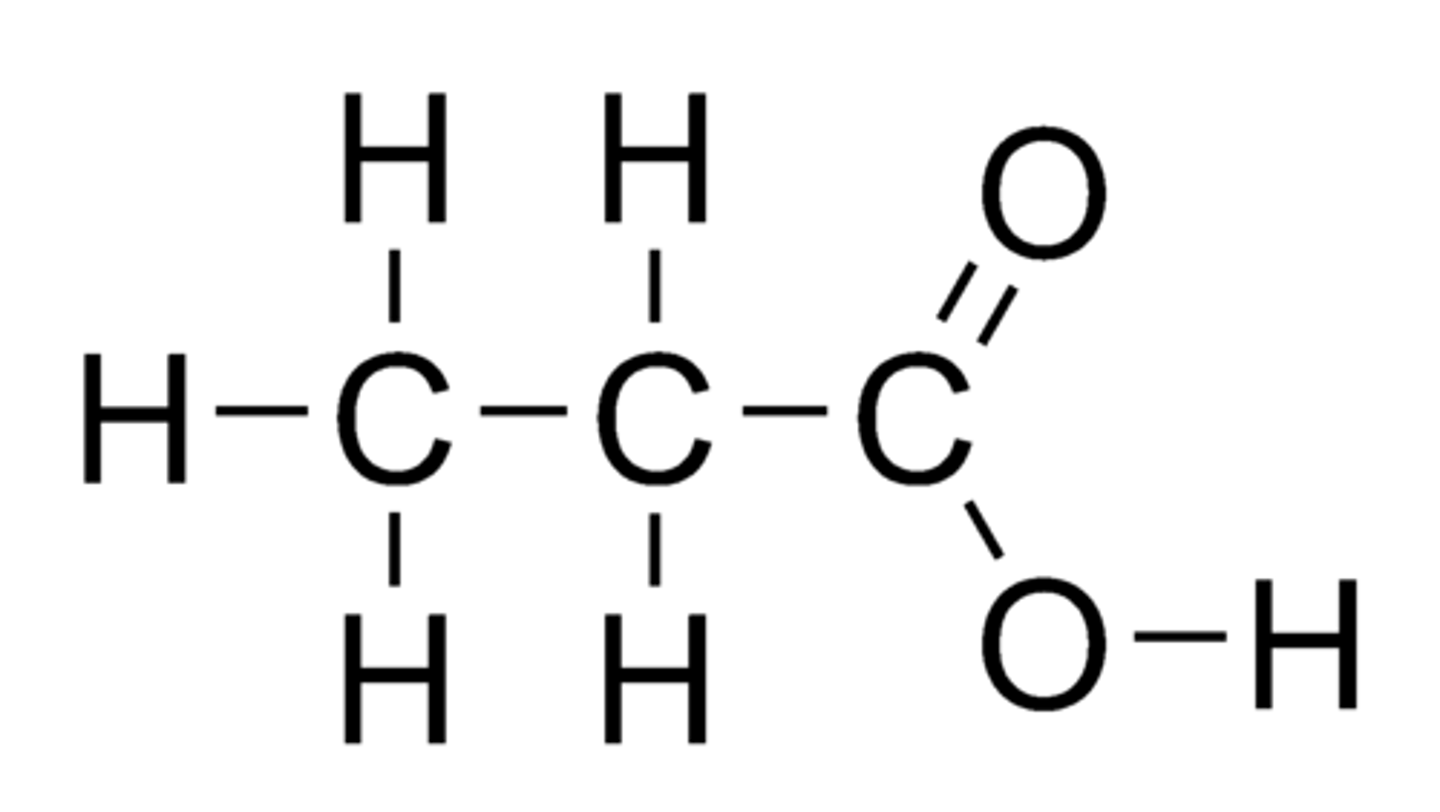
Butanoic acid (display)
CH3CH2CH2COOH
Ethanoic acid + sodium carbonate -->
Sodium ethanoate + water + carbon dioxide
Solubility of carboxylic acids
soluble in water
pH of carboxylic acids
Less than 7
Observations of reactions
Same as those for strong acids, but with slower reactions
Carboxylic acid + alcohol -->
Ester + water
Esters
Fragrant organic compounds with -COOC- groups
Functional group of esters
-COOC-
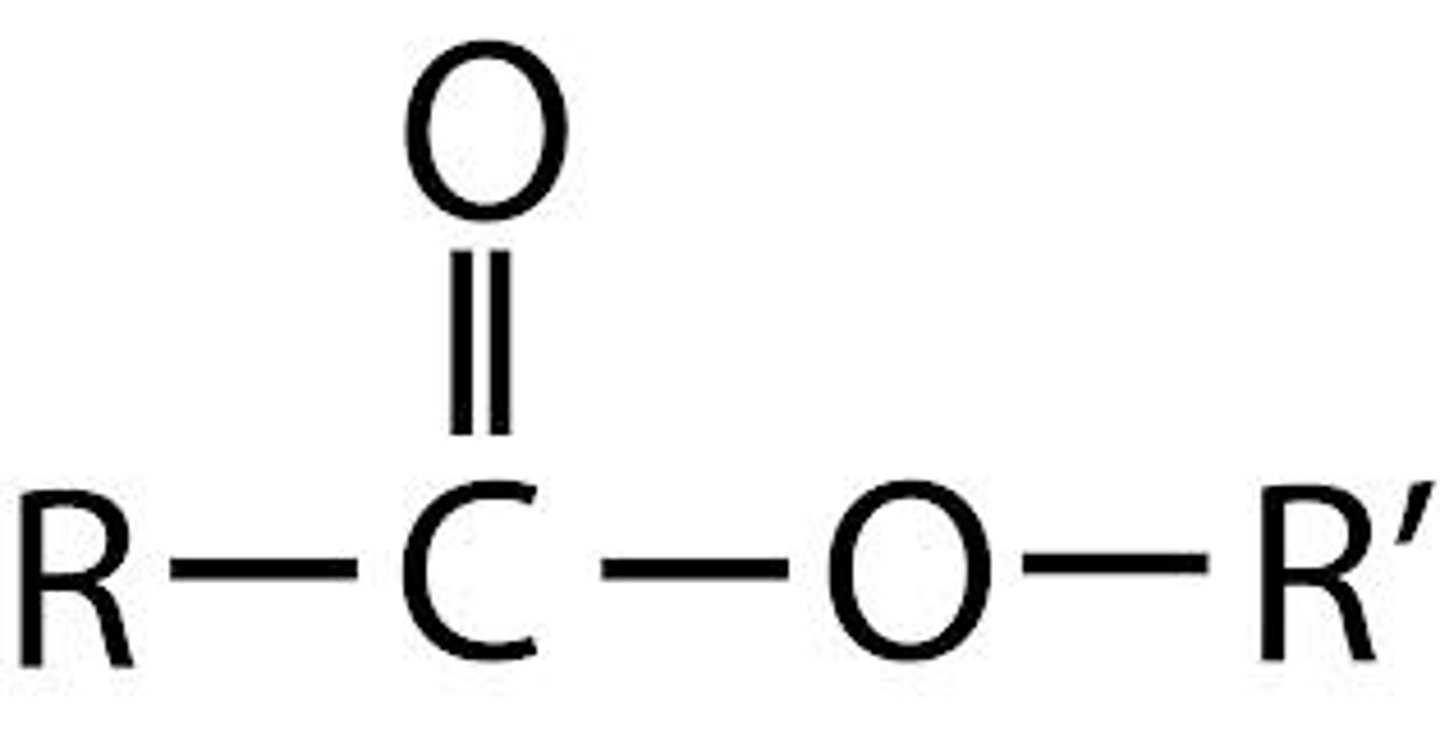
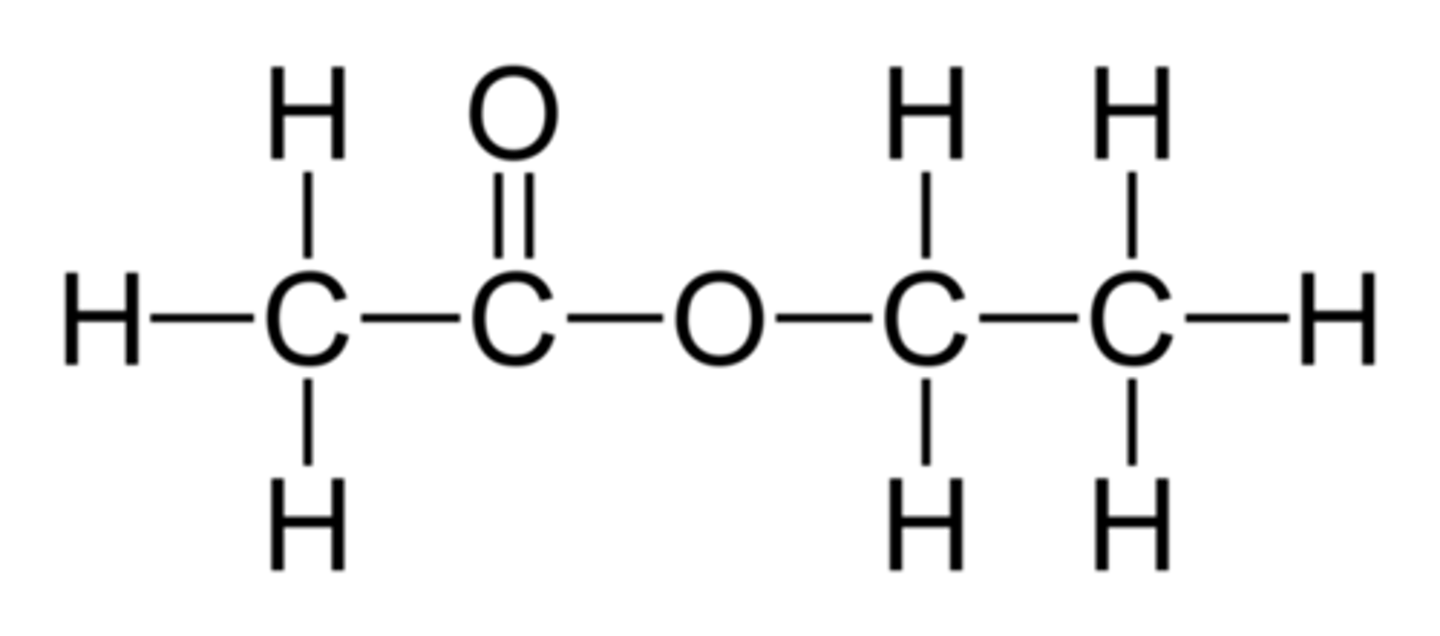
ethyl ethanoate
CH3COOC2H5
Uses of esters
Solvents, perfumes and flavourings

Alcohols
Organic compounds containing OH group
Functional group alcohol
-OH
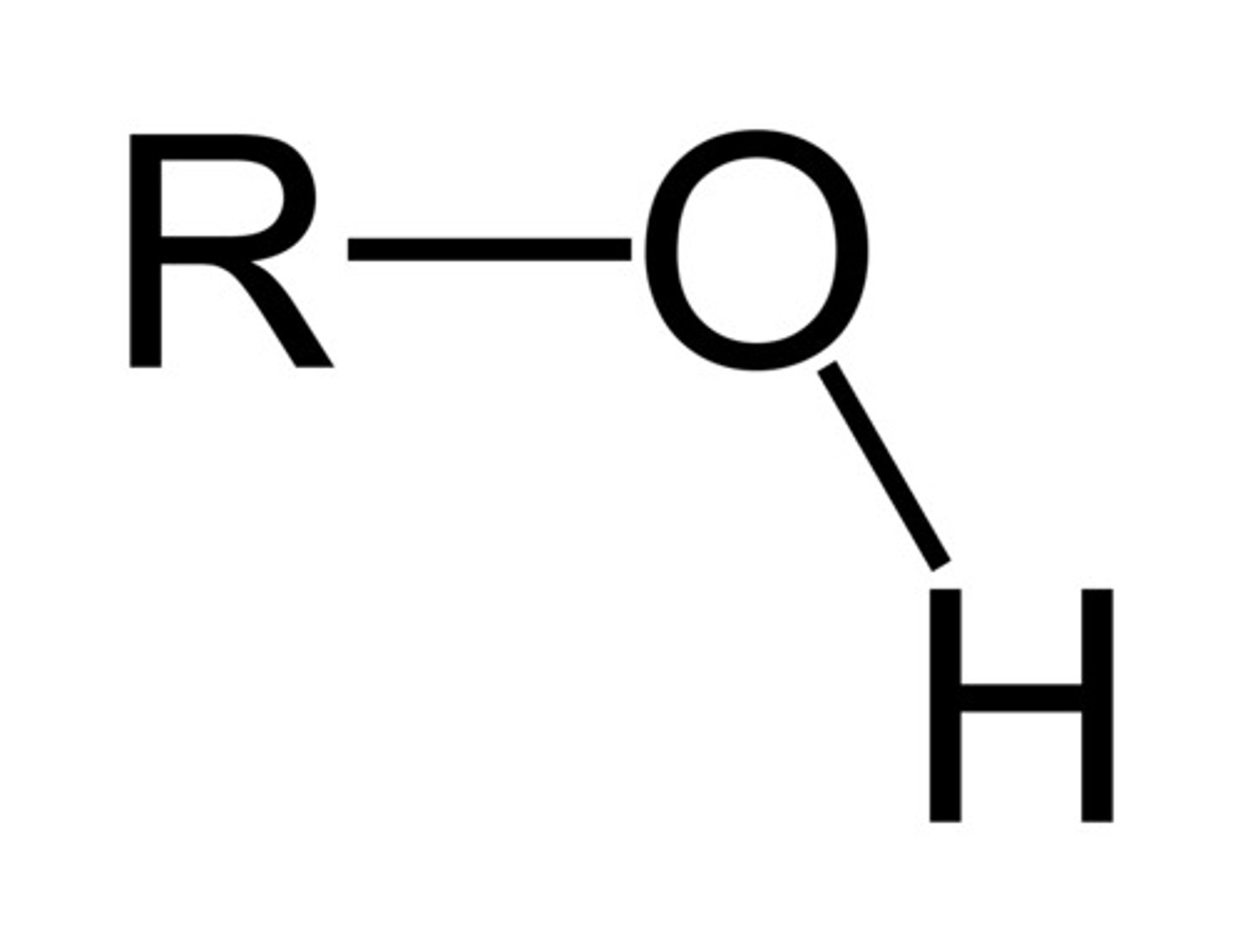
Suffix for alcohol
-anol
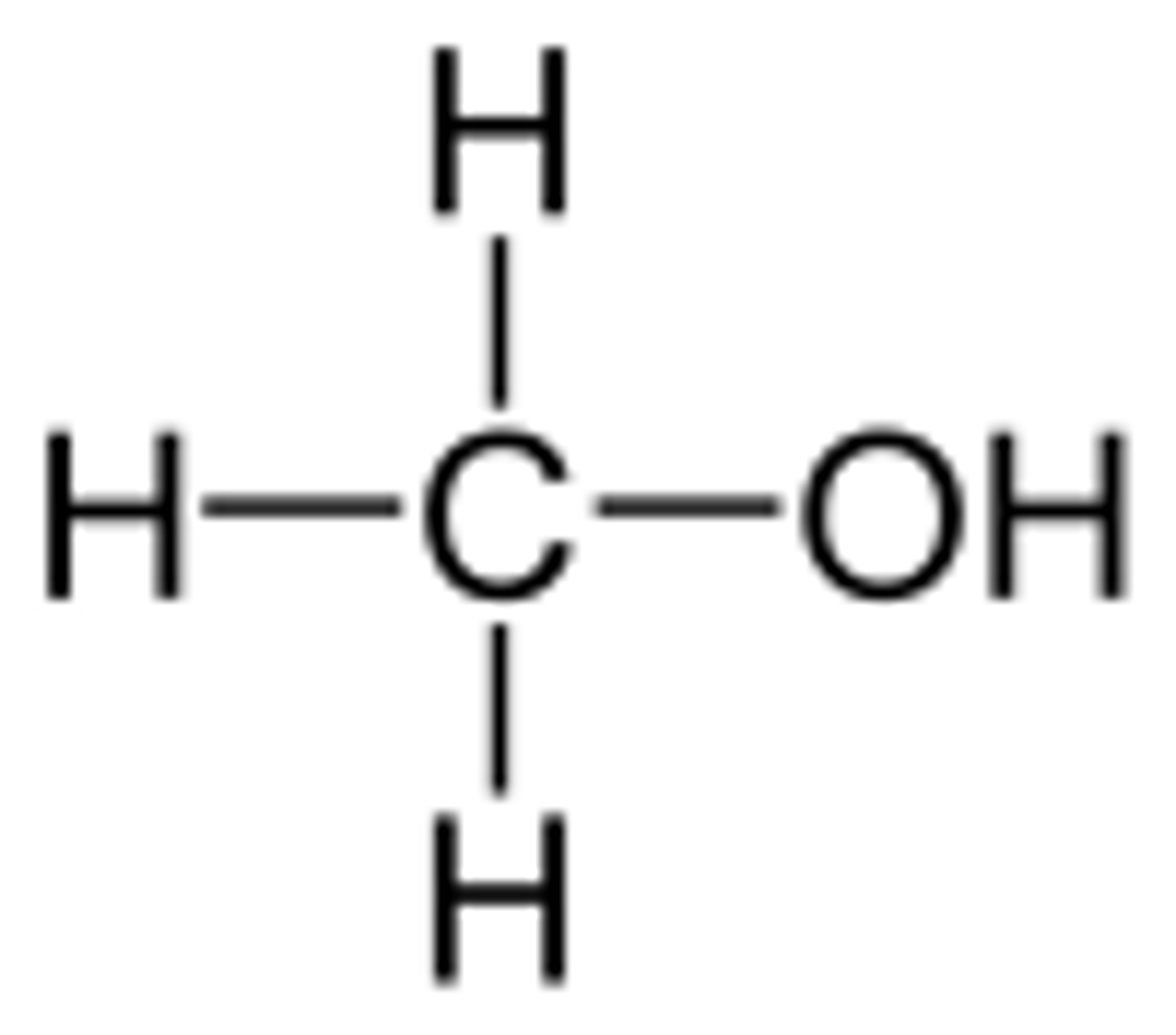
Methanol
CH3OH
Ethanol
C2H5OH
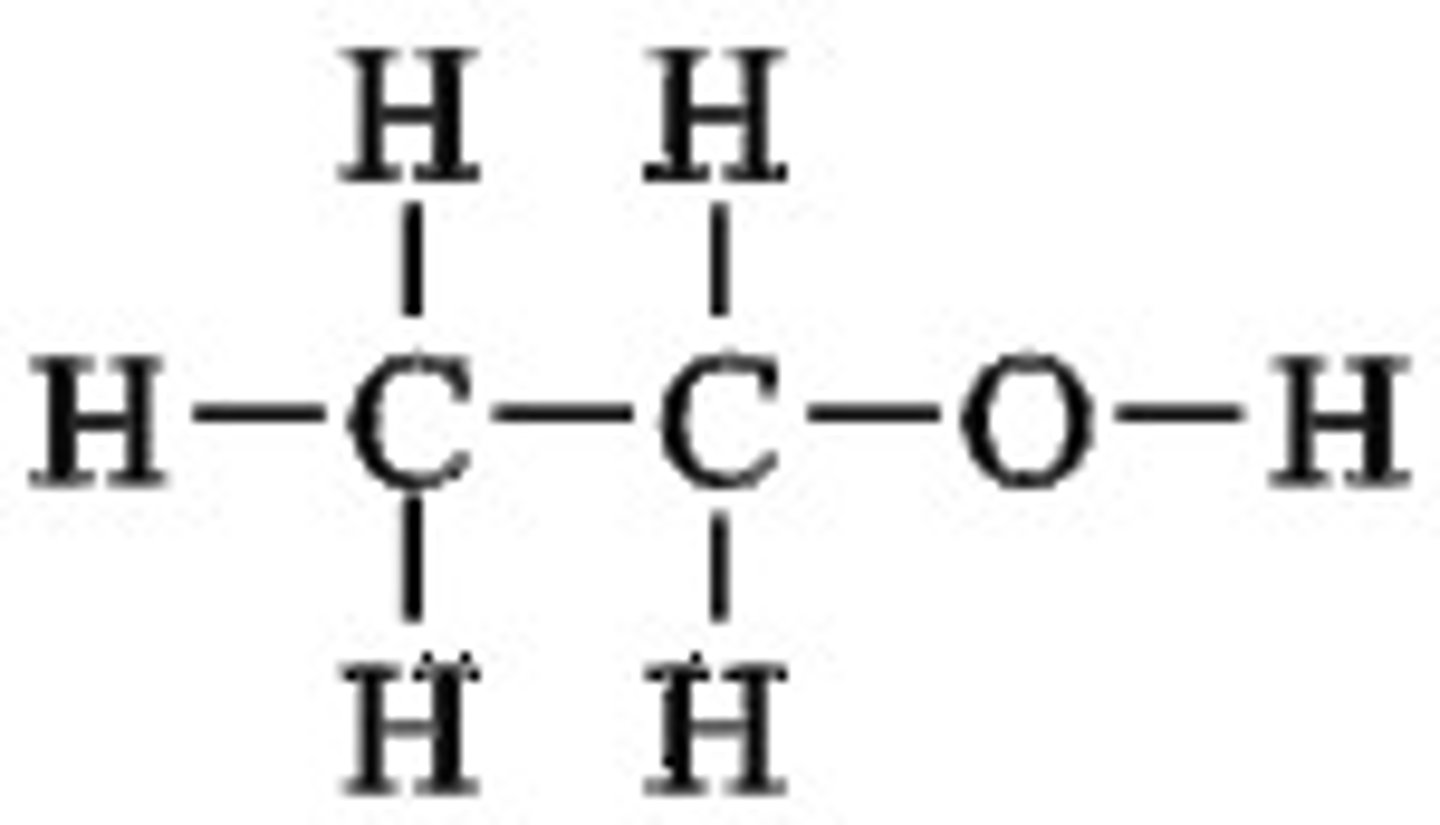
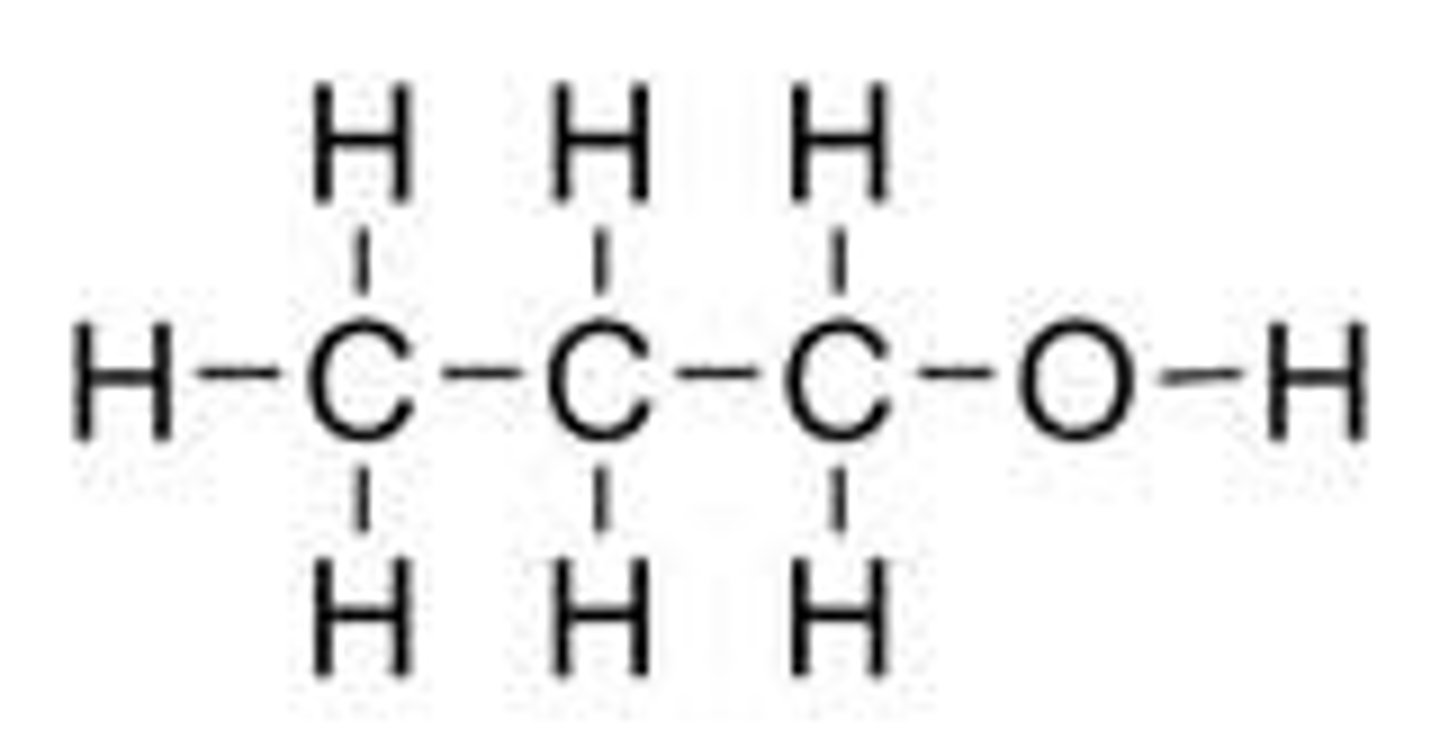
Propanol
C3H7OH
Butanol
C4H9OH
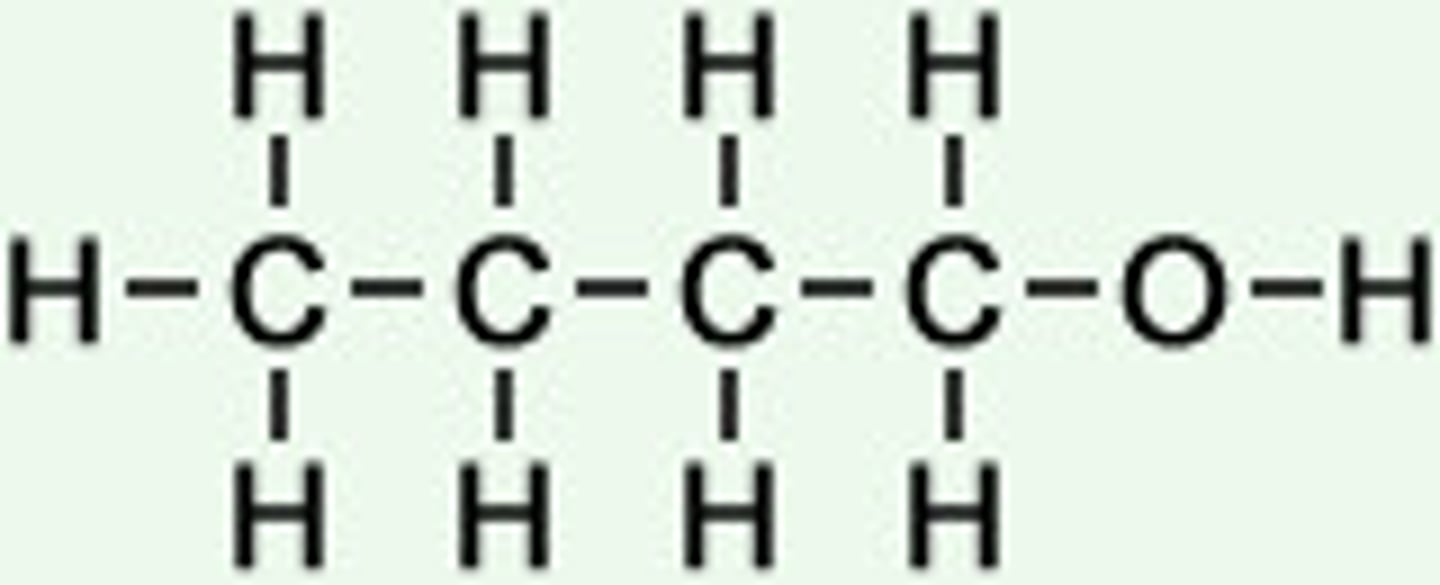
Combustion of alcohols
Burn completely in oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water

Alcohol + Sodium -->
Sodium alkoxide + hydrogen
Sodium + ethanol -->
Sodium ethoxide + hydrogen
Alcohols in water
Short chain alcohols dissolve easily in water
Oxidation of alcohols
Forms a carboxylic acid
Oxidising agents for alcohols
Potassium dichromate, bacterial enzymes

2 ways to produce ethanol
fermentation, hydration of ethene
Conditions of fermentation of glucose
yeast, glucose, warm temperature
Advantages of producing ethanol by fermentation
Uses renewable resources
Disadvantages of producing ethanol by fermentation
Labour intensive batch process
Advantages of hydration of ethene
Continuous process, 100% atom economy
Disadvantages of hydration of ethene
Uses finite resources
Uses of alchols
Solvents, fuels, drinks

Plastics
Synthetic polymers that can be molded or shaped

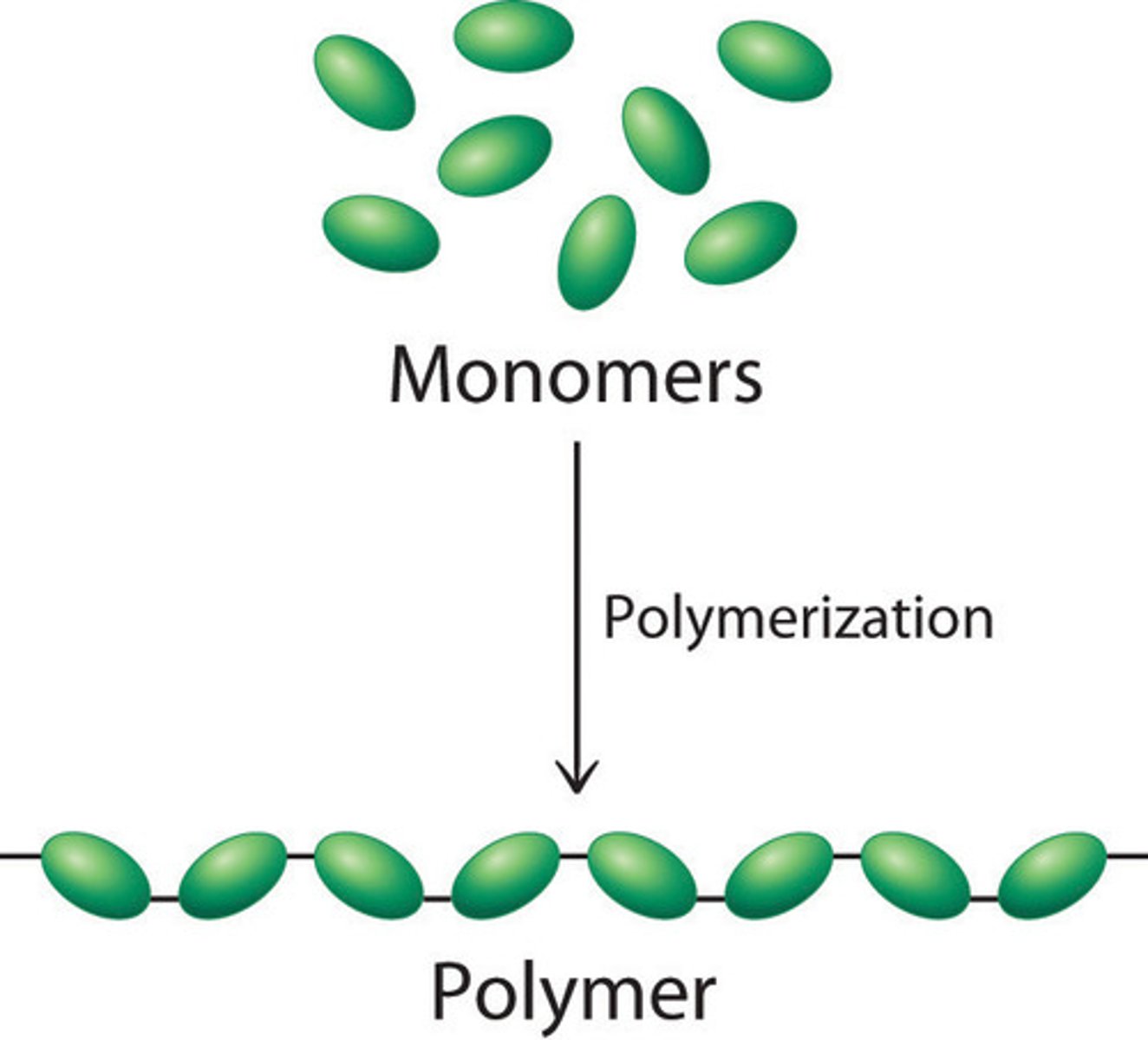
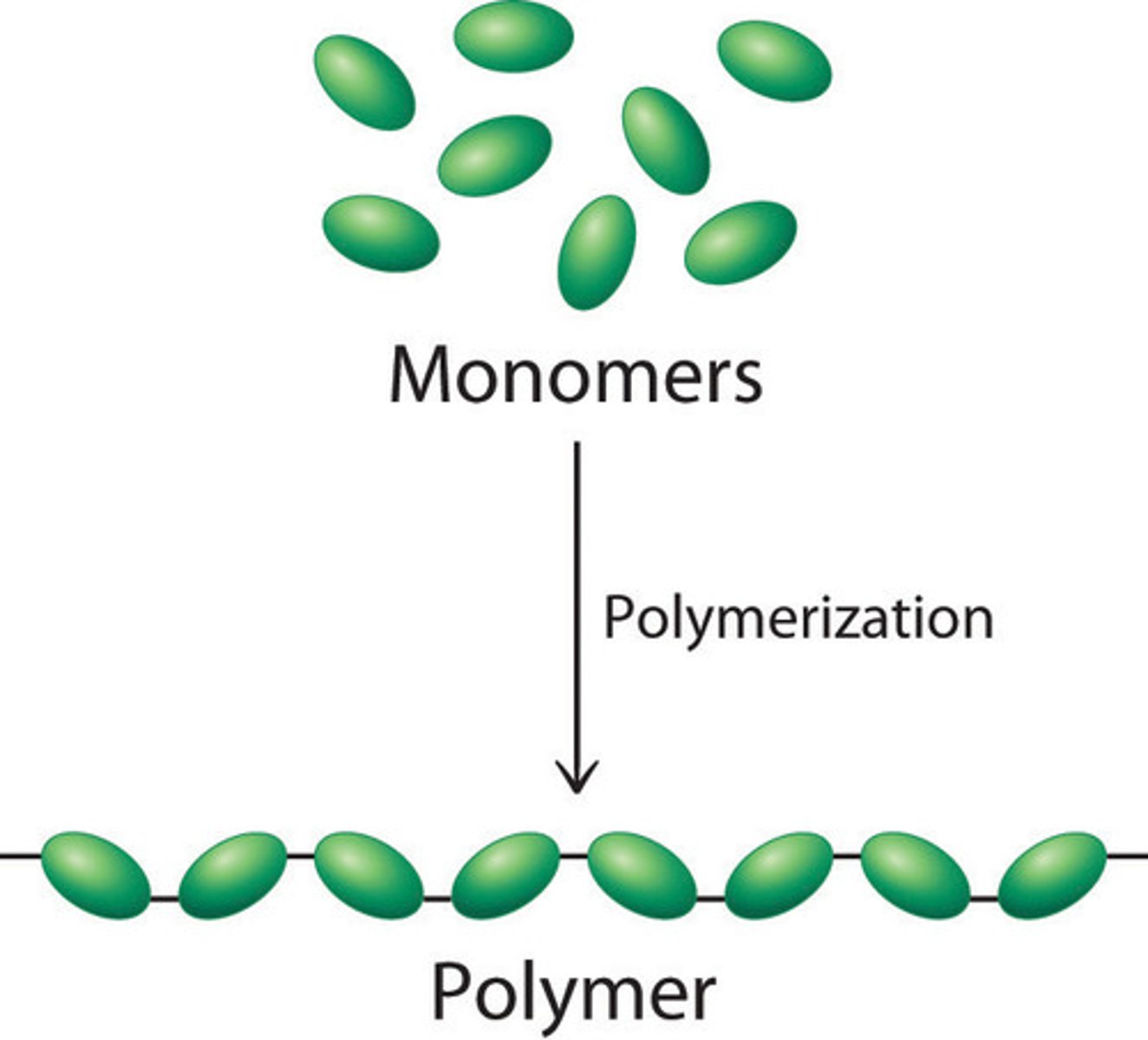
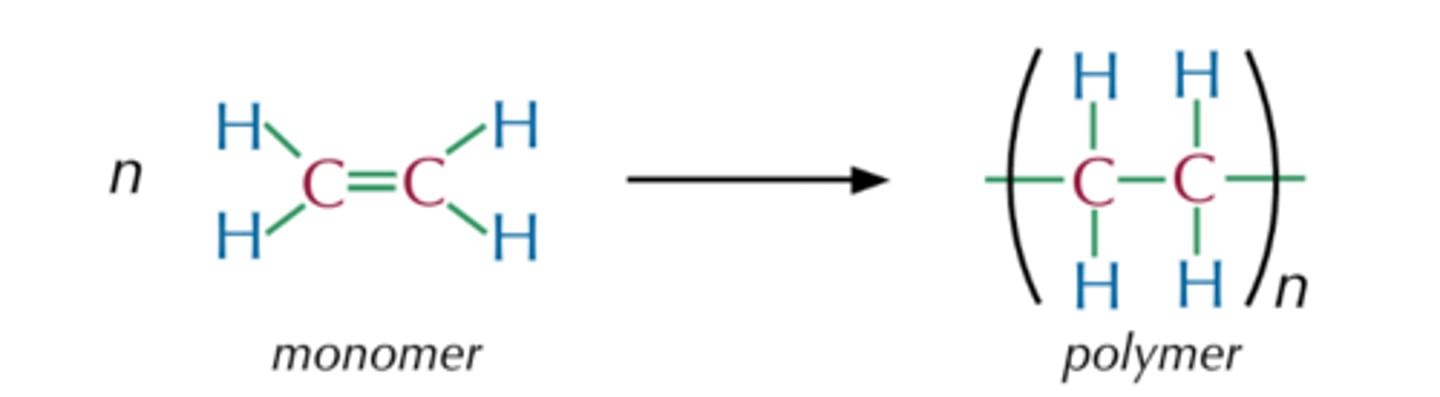
Polymers
Long molecules made by joining lots of monomers
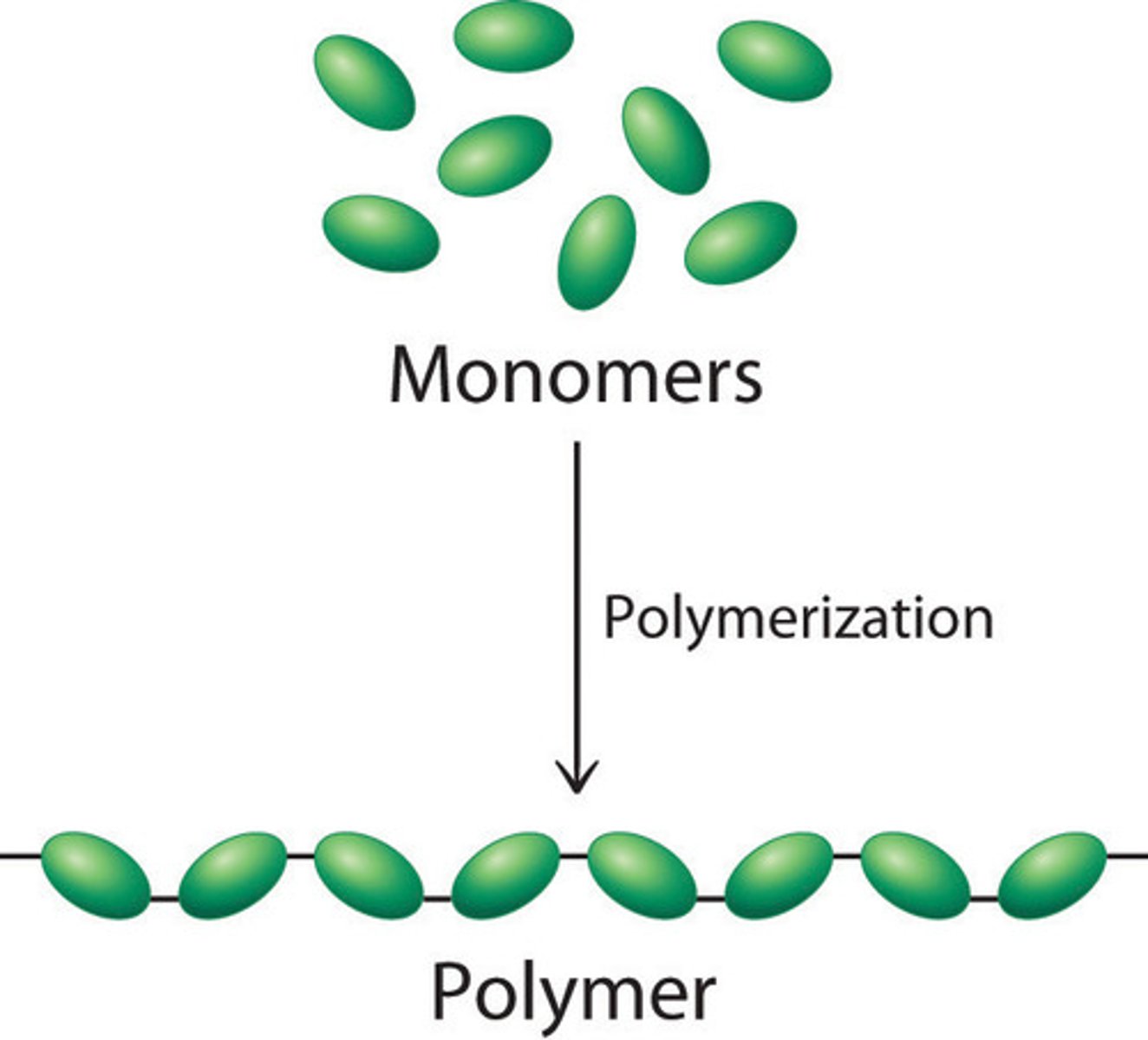
Monomers
A small molecule that can join together with other small molecules to form polymers
Addition polymers
Alkenes (monomers) join up and the double bond is removed
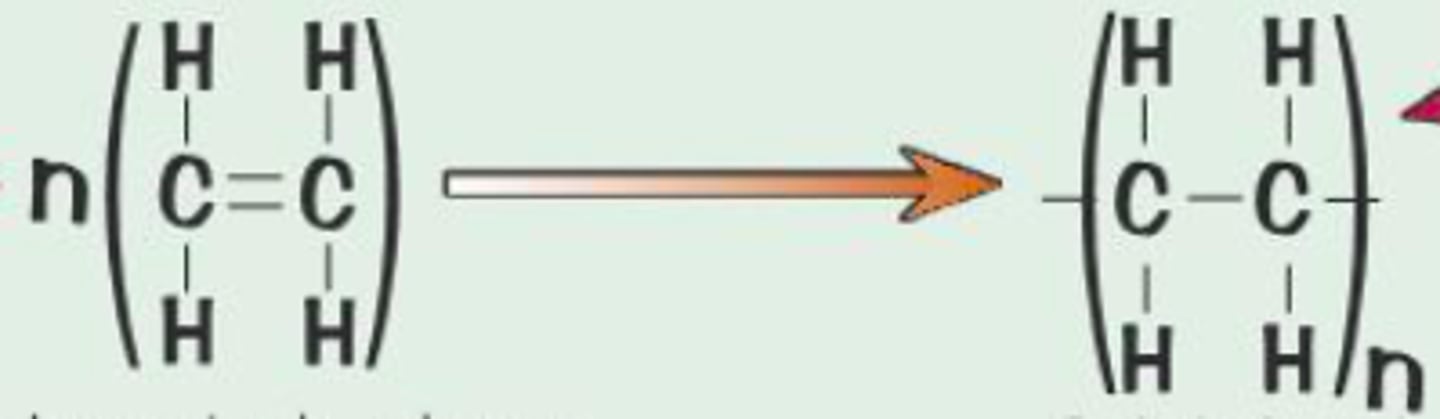
Naming polymers
Poly(monomer)
Polymer made from ethene
Poly(ethene)
Condensation polymers
Polymers containing different functional groups form a long chain and a small molecule (usually water)
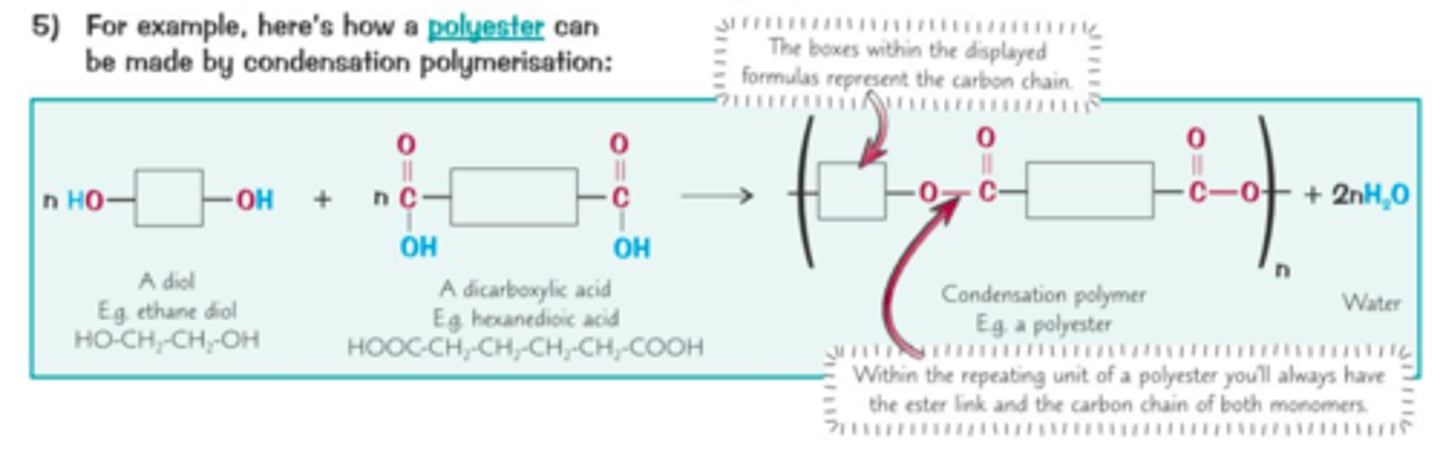
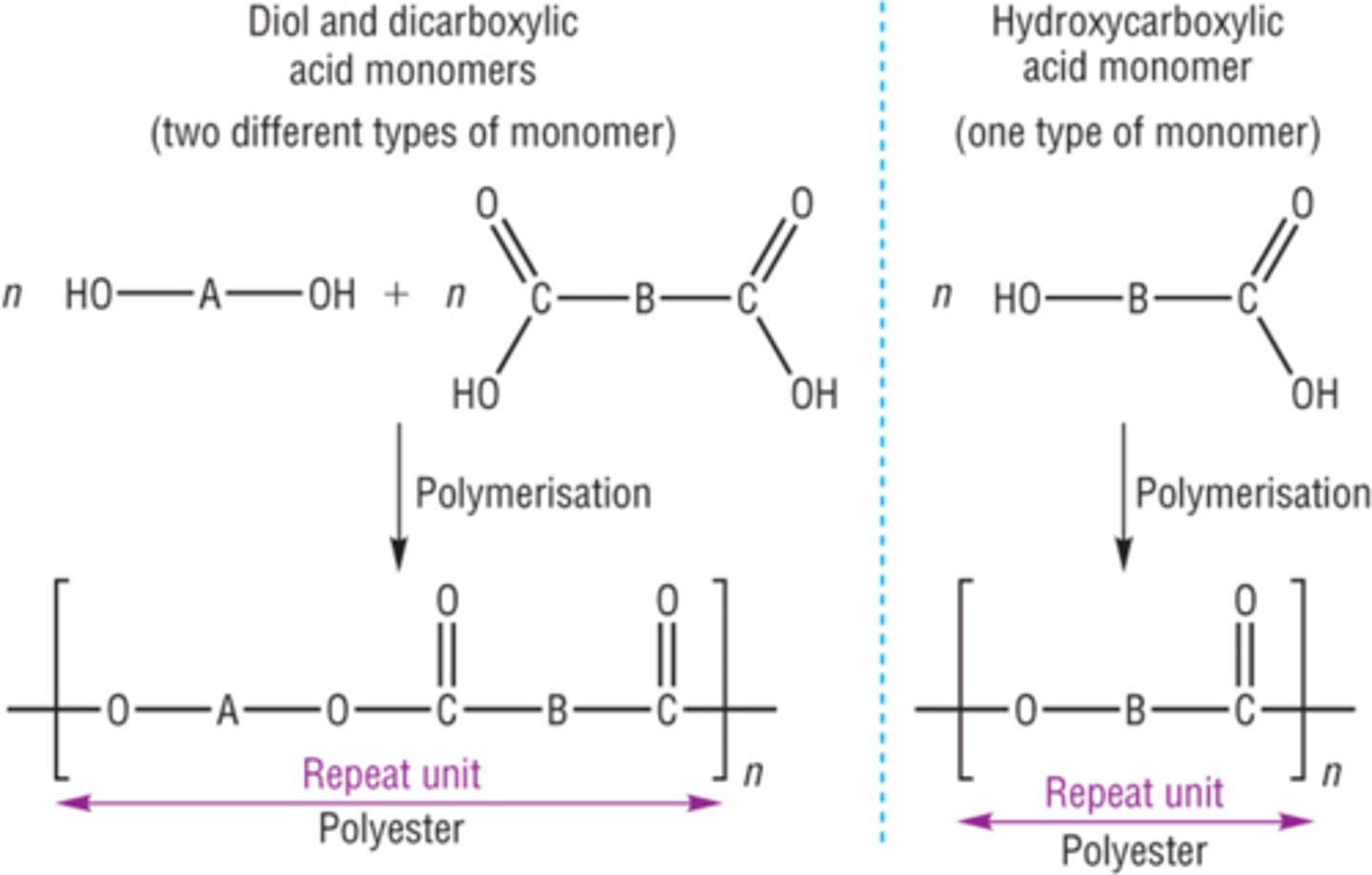
Polyester
A synthetic polymer linked by ester groups

Monomers for polyester
Diol, dicarboxylic acid