Gene Expression Regulation in Bacteria and Eukaryotes: Operons, Transcription Factors, and Chromatin Modifications
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is the role of a repressor in gene regulation?
A repressor blocks gene transcription when it is bound to DNA.
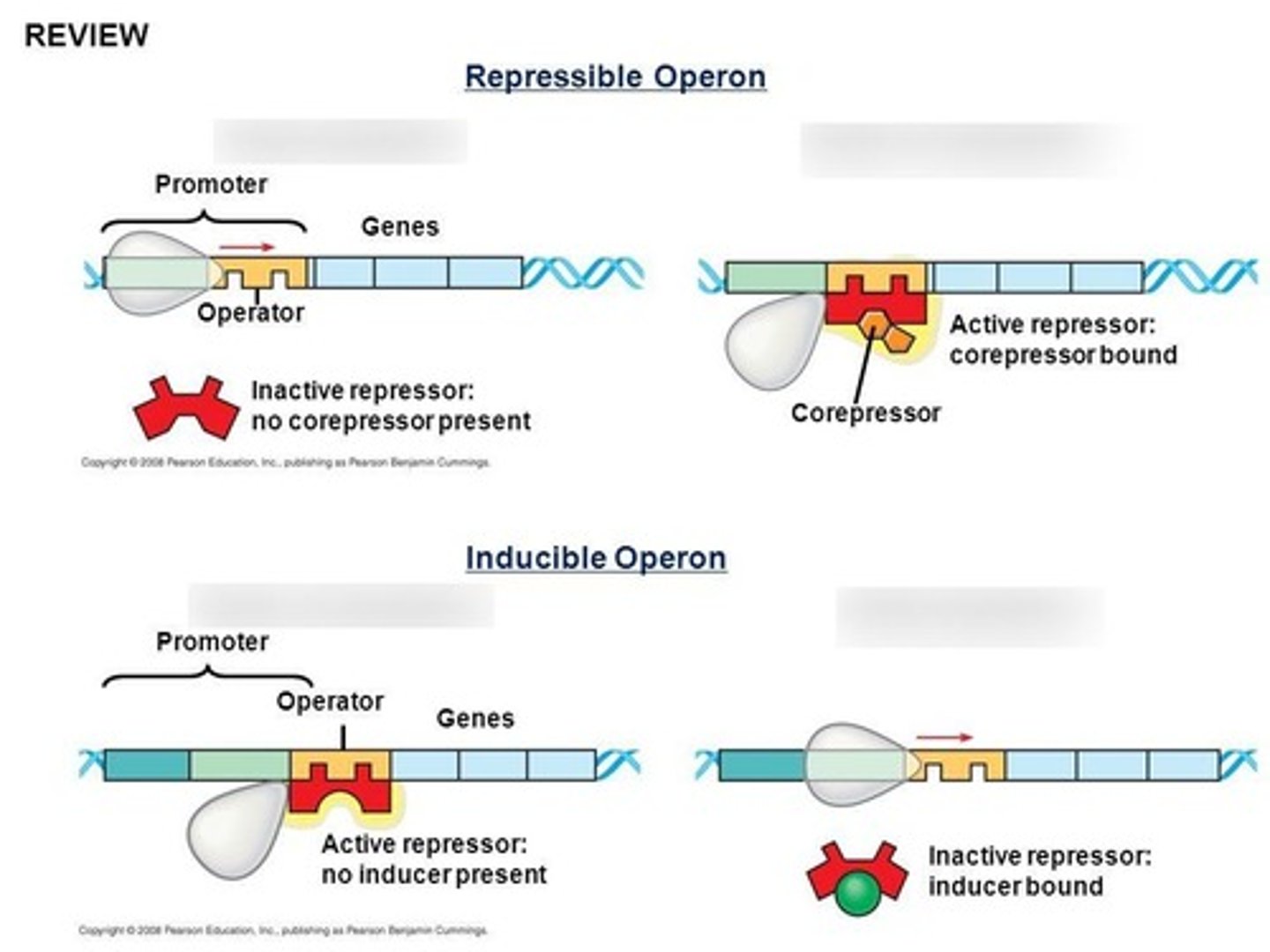
What is a repressible operon?
A repressible operon is usually on; binding of a repressor to the operator shuts off transcription.
What is the trp operon in E. coli?
The trp operon is a repressible operon that is ON by default and controls the synthesis of tryptophan.
Under what condition is the trp operon turned off?
The trp operon is turned off when tryptophan is present, activating the repressor to bind to the operator.
What is a corepressor?
A corepressor is a molecule that cooperates with a repressor protein to switch an operon off.
What is an inducible operon?
An inducible operon is usually off; an inducer inactivates the repressor to turn the operon on.
What is the lac operon in E. coli?
The lac operon contains genes that code for enzymes used in the breakdown of lactose and is controlled by a repressor.
How does lactose affect the lac operon?
When lactose is present, it acts as an inducer, inactivating the repressor and turning the lac operon on.
What is negative gene regulation?
Negative gene regulation involves a repressor that blocks gene transcription when bound to DNA.
What is positive gene regulation?
Positive gene regulation involves an activator that promotes gene transcription when bound to DNA.
What role does catabolite activator protein (CAP) play in the lac operon?
CAP promotes the transcription of the lac operon when glucose is scarce and cAMP levels are high.
What happens to lac operon transcription when glucose is present?
When glucose is present, cAMP levels are low, resulting in little lac mRNA being synthesized.
What is differential gene expression?
Differential gene expression is the expression of different genes that allows cells to carry out specific functions.
How do transcription factors influence gene expression?
Different cells have different transcription factors that determine which genes are expressed.
What is the significance of gene expression regulation in multicellular organisms?
Gene expression regulation is essential for cell specialization in multicellular organisms.
What is the function of the operator in an operon?
The operator is a DNA segment that acts as a regulatory switch controlling the binding of a repressor.
What is the default state of the trp repressor?
The trp repressor is inactive in its default state and does not bind to the operator.
What happens when tryptophan is absent in E. coli?
When tryptophan is absent, the repressor is inactive, and the trp operon remains on.
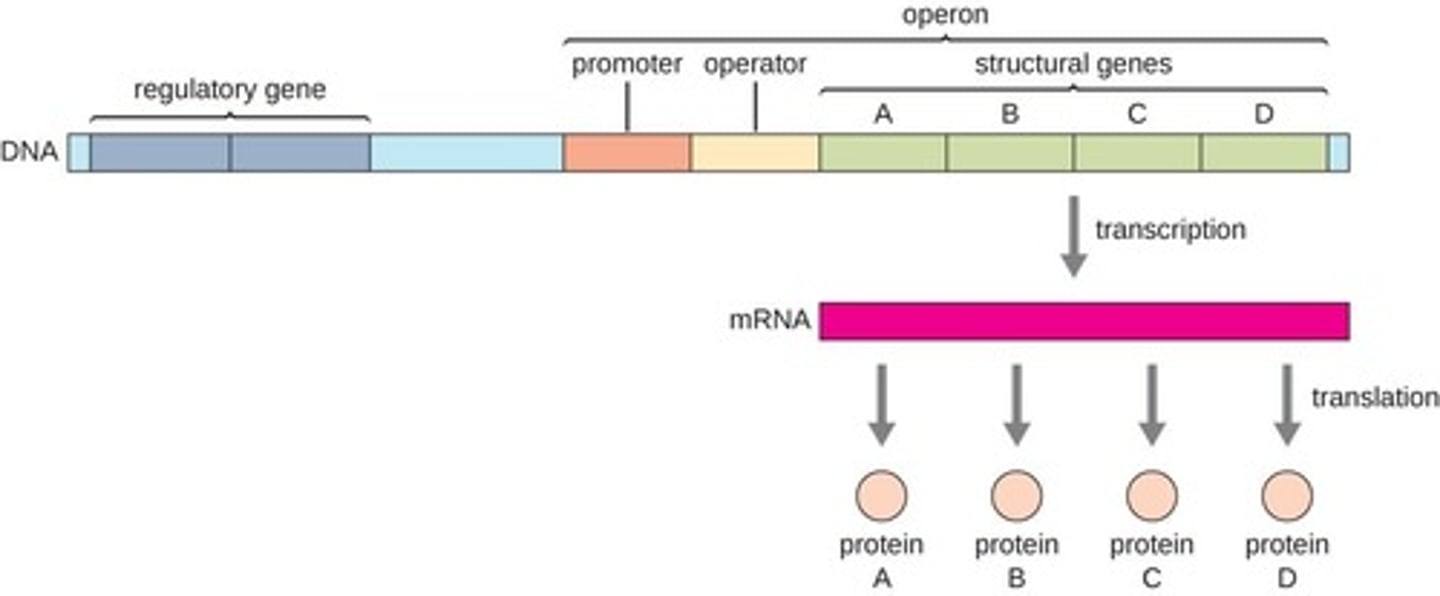
What are the components of an operon?
An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and the genes they control.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in gene expression?
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter to initiate transcription of the genes in the operon.
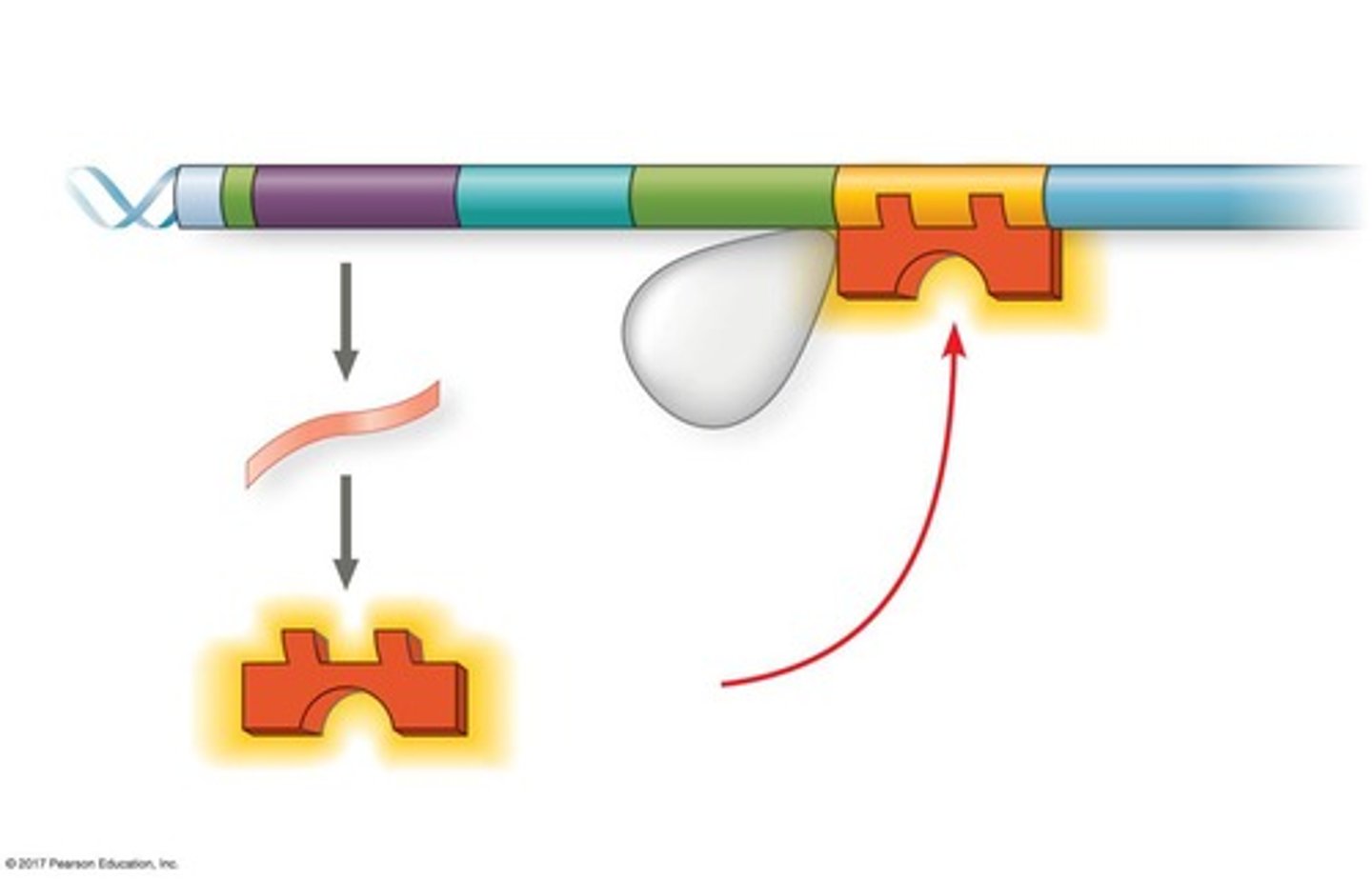
What is the relationship between transcription factors and gene products?
Transcription factors regulate the expression of genes, leading to the production of specific gene products.
What is the significance of the lacZ gene in the lac operon?
The lacZ gene codes for β-Galactosidase, an enzyme that breaks down lactose.
What is the function of allolactose in the lac operon?
Allolactose acts as an inducer that inactivates the lac repressor, allowing transcription to occur.
What is the first stage of eukaryotic gene expression regulation?
Chromatin modification
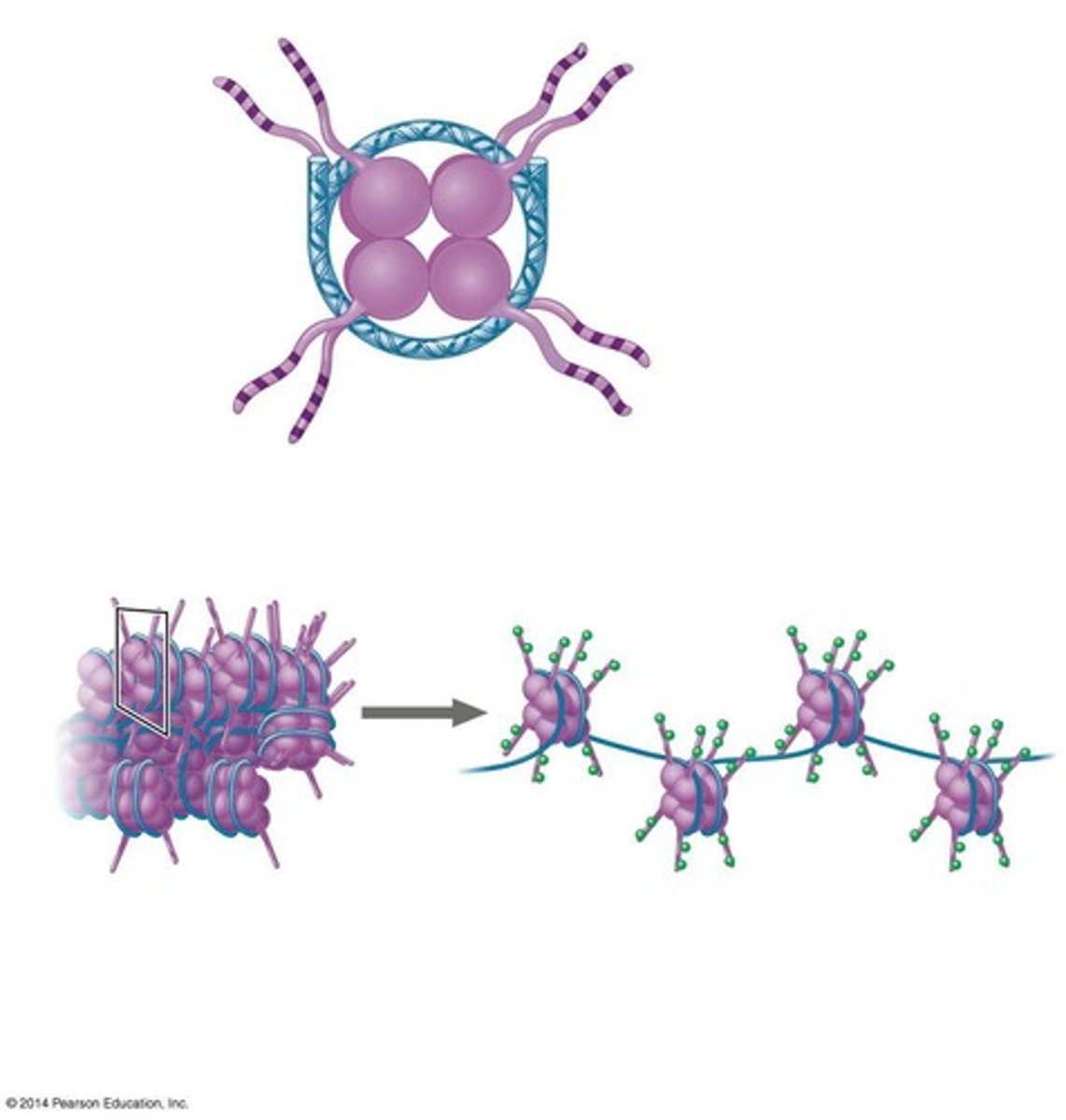
What are the two main types of chromatin modifications?
Histone modification and DNA methylation
How does histone acetylation affect chromatin structure?
It opens up chromatin, allowing for transcription.
What is the effect of DNA methylation on chromatin?
It closes chromatin, inhibiting transcription.
What are euchromatin and heterochromatin?
Euchromatin is 'open' and allows transcription; heterochromatin is 'closed' and prevents transcription.
What is epigenetic inheritance?
Inheritance of traits not involving changes in the DNA sequence itself.
Give an example of epigenetic inheritance.
Children born to mothers who experienced the Dutch Hunger Winter have long-term effects due to changes in methylation.
What role do transcriptional activators play in gene expression?
They bind to enhancers and stimulate transcription.
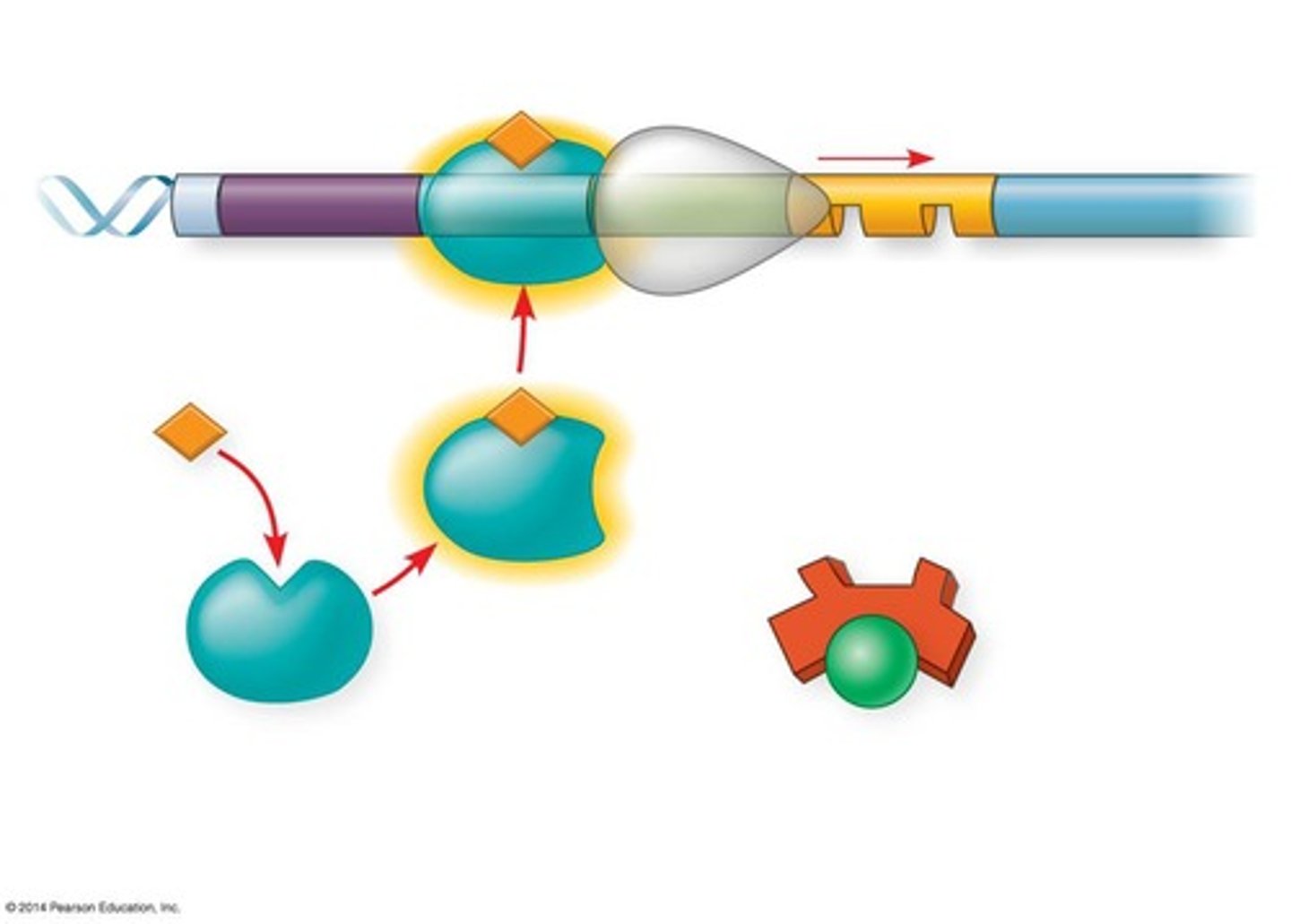
What is the function of transcriptional repressors?
They bind to silencers and inhibit transcription.
What are control elements in gene regulation?
Short DNA sequences that serve as binding sites for transcription factors.
What is required for RNA polymerase to initiate transcription?
General transcription factors.
What is alternative RNA splicing?
A process that allows for the production of multiple proteins from a single gene by splicing different combinations of exons.
What is the primary RNA transcript?
The initial RNA molecule synthesized from a DNA template before processing.
What happens to mRNA after it is transported to the cytoplasm?
It undergoes translation to produce polypeptides.
What is the role of the 5' cap and poly-A tail in mRNA?
They protect mRNA from degradation and assist in translation initiation.
What is the significance of the promoter in gene expression?
It is the region where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
What is combinatorial control of gene activation?
The integration of multiple signals from transcription factors to regulate gene expression.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene regulation?
Eukaryotic genes are controlled individually with their own promoters and control elements, unlike prokaryotic operons.
What is the role of RNA polymerase II?
It synthesizes RNA from a DNA template during transcription.
How do activators and repressors influence chromatin structure?
They can promote or silence transcription by altering chromatin accessibility.
What is the function of the transcription initiation complex?
It assembles at the promoter to facilitate the start of transcription.
What is the purpose of the termination region in transcription?
It signals the end of transcription.
What is the significance of the 3' UTR in mRNA?
It plays a role in the regulation of translation and mRNA stability.
What is the role of DNA-bending proteins in transcription?
They help bring distant enhancers and promoters into proximity to facilitate transcription.
What is the relationship between gene expression and cell type?
Gene expression is regulated to ensure that specific genes are activated in the appropriate cell types.
What is the role of mediator proteins in transcription?
They facilitate the interaction between transcription factors and RNA polymerase.