NS 1600 Classes 2-18 and Research Papers
1/324
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
325 Terms
What is Public Health?
Organized community effort aimed at the prevention of disease and the promotion of health
What report defined the three core functions of public health?
The Future of Public Health, published in 1988 by the Institute of Medicine
What are the three core functions of public health?
Assessment, Policy Development, and Assurance
What is Assessment in public health?
The diagnostic function, in which a public health agency collects, assembles, analyzes, and makes available information on the health of the population
What is Policy Development in public health?
The use of scientific knowledge to develop a strategic approach to improving the community's health
What is Assurance in public health?
Assuring that the services needed for the protection of public health in the community are available and accessible to everyone, including environmental, educational, and basic medical services
How many Essential Public Health Services are there?
Ten Essential Public Health Services
What are the two Assessment services in the Ten Essential Public Health Services?
1) Monitor health status to identify community health problems,
2) Diagnose and investigate health problems and health hazards in the community
What are the three Policy Development services in the Ten Essential Public Health Services?
3) Inform, educate, and empower people about health issues,
4) Mobilize community partnerships to identify and solve health problems,
5) Develop policies and plans that support individual and community health efforts
What are the four Assurance services in the Ten Essential Public Health Services?
6) Enforce laws and regulations that protect health and ensure safety,
7) Link people to needed personal health services and assure provision of health care when otherwise unavailable,
8) Assure a competent public health and personal healthcare workforce,
9) Evaluate effectiveness, accessibility, and quality of personal and population-based health services
What is the 10th Essential Public Health Service and what function does it serve?
10) Research for new insights and innovative solutions to health problems (serves all functions)
Differences between Public Health and Medicine?
Public Health focuses on population health while Medicine focuses on individual health
Public Health emphasizes disease prevention while Medicine emphasizes disease treatment
Public Health interventions may involve medical care, but also environment, social and behavioral factors; Medicine interventions primarily involve medical care
What are the five sciences of public health?
Epidemiology
Statistics
Biomedical sciences
Environmental health sciences
Social and behavioral sciences
What is Epidemiology?
The study of populations to seek the causes of health and disease
What is Statistics in public health?
A way of gathering and analyzing data to extract information, seek causation, and calculate probabilities
What is Biomedical Science?
The study of the biological basis of human health and disease, including genetics, immunology, infectious diseases, chronic diseases, and molecular approaches to treatment
What is Environmental Health?
Those aspects of human health, diseases, and injury that are determined or influenced by factors in the environment
What is Social and Behavioral Science in public health?
How human behavior, social structures, and cultural norms influence health outcomes and designing interventions to improve population health; used to predict, prevent, and manage diseases in individuals and populations
What is Primary Prevention?
Intervening before the onset of disease
example: legislation and enforcement to ban or control the use of hazardous products (e.g. asbestos) or to mandate safe and healthy practices (e.g. use of seatbelts and bike helmets)
What is Secondary Prevention?
Screening to identify a disease at early onset
example: daily, low-dose aspirins and/or diet and exercise programs to prevent further heart attacks or strokes
What is Tertiary Prevention?
Managing a disease, including treatment and rehabilitation
example: cardiac or stroke rehabilitation programs, chronic disease management
What economic considerations are involved in public health interventions?
Who pays and who gains (i.e. loss of jobs, increase in price of products, increase in taxes, deciding if interventions are worth the cost)
What is Paternalism?
Restriction of people's individual freedom with the aim of protecting their health and safety
e.g. mandatory seatbelt laws
What is Libertarianism?
A belief system that holds that an individual's rights can only be restricted in order to prevent harm to others
e.g. supporting the legalization of drugs
What is the Tragedy of the Commons?
A situation where individuals acting independently in their own self-interest deplete or spoil shared resources, even when it's clear that it's not in anyone's long-term interest
Solutions to the tragedy of the commons include government regulation, privatization of resources, and community-based management
What is Justice in public health ethics?
Fairness in the distribution of benefits and burdens in society
What is Fairness in public health?
Equal and equitable treatment of individuals and groups, ensuring that resources and opportunities are distributed justly
What are examples of moral and religious opposition in public health?
Sex education in schools, needle exchange programs, physician assisted suicides, etc.
What is the standard structure of a scientific paper?
Title and authors, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, References
(pretty much a lab report but w/ Methods section instead of Experimental section)
What 6 things should you identify in an Abstract?
Objectives/Hypothesis/Research question
Research gap
Study design
Methods
Results
Conclusion
To examine
(1) whether the SHHC intervention improved social network members' (SNMs') weight, exercise, and diet and
(2) whether SNMs' weight and behavioral changes were modified by their relationship closeness and/or spatial closeness with trial participants
The number or proportion of existing cases, events, or conditions in a population at a specific time
Prevalence = (# of people in a population with given condition) / (Total # of people in population)
What is incidence?
The number of new cases that develop in a population during a defined time period
Incidence = (# of new cases occurring) / (# of people at risk) during a time period
What is the denominator for incidence?
People who did not have the disease at baseline and were at risk
What is the numerator for incidence?
New cases at follow-up
What three factors affect prevalence changes over time?
Incidence
The number of people cured
The number of people that die
What are disease determinants?
Factors that are associated with the development of a disease
i.e. pathogens (bacteria and viruses)
behavior (diet and physical activity)
genetics
social and structural determinants (policies, racism, socioeconomic position)
Any characteristic that may explain or predict the presence or absence of a study outcome; can be positive or negative
The relationship between two or more events or variables; events are said to be associated when they occur more frequently together than one would expect by chance. Does NOT imply causation.
What is a risk factor?
A characteristic, behavior, or exposure that increases the likelihood of developing a disease or experiencing a negative outcome
What is a confounder?
A variable that affects both the exposure and the outcome, making it hard to tell if the exposure really caused the outcome.
Can be handled during study design by using randomization, restriction, or matching to control for variables that might distort the true relationship between exposure and outcome.
Identify behaviors that influence a public health problem
Use the COM-B model to identify potential barriers to achieving desired behavior changes
Use the Behavior Change Wheel to identify intervention functions to address barriers
Identify determinants of a behavior
Create a causal model of the problem with detailed components
Select intervention methods to match targets
Inform evaluation
Identify active ingredients needed for change
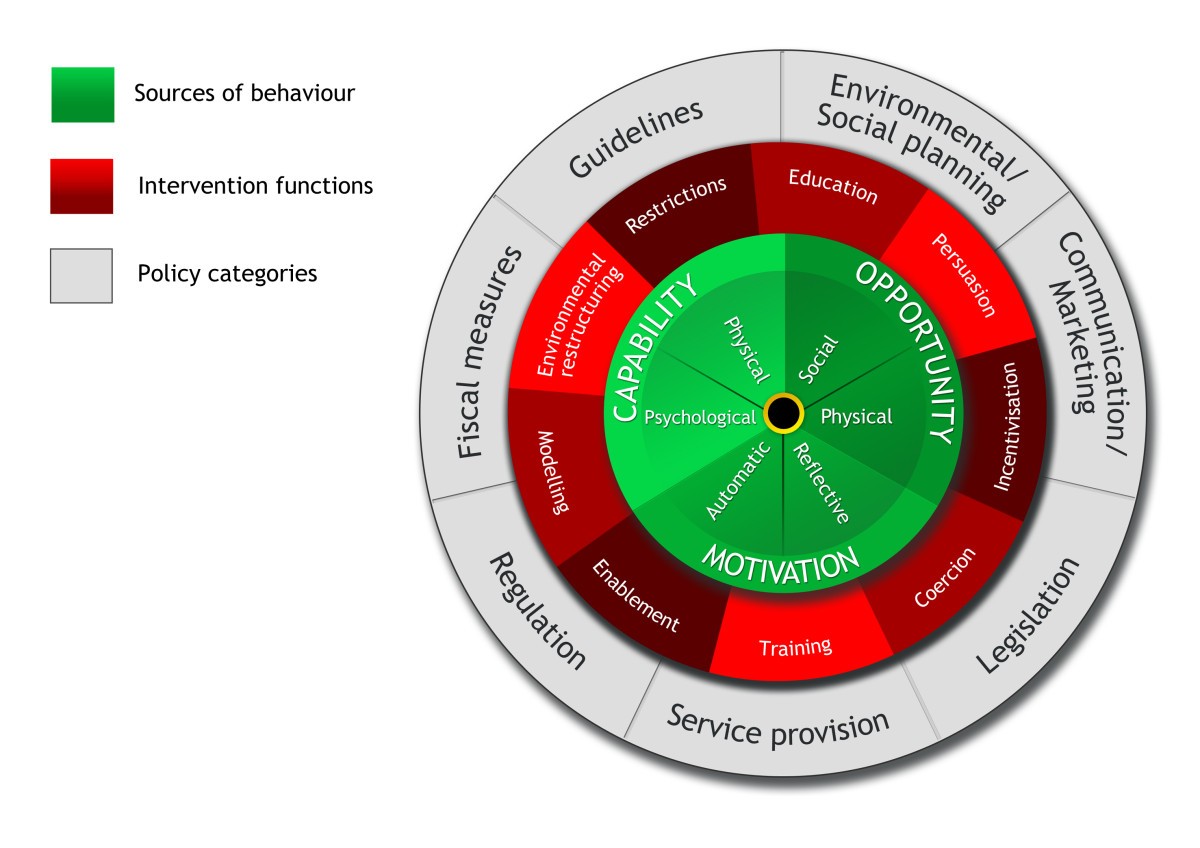
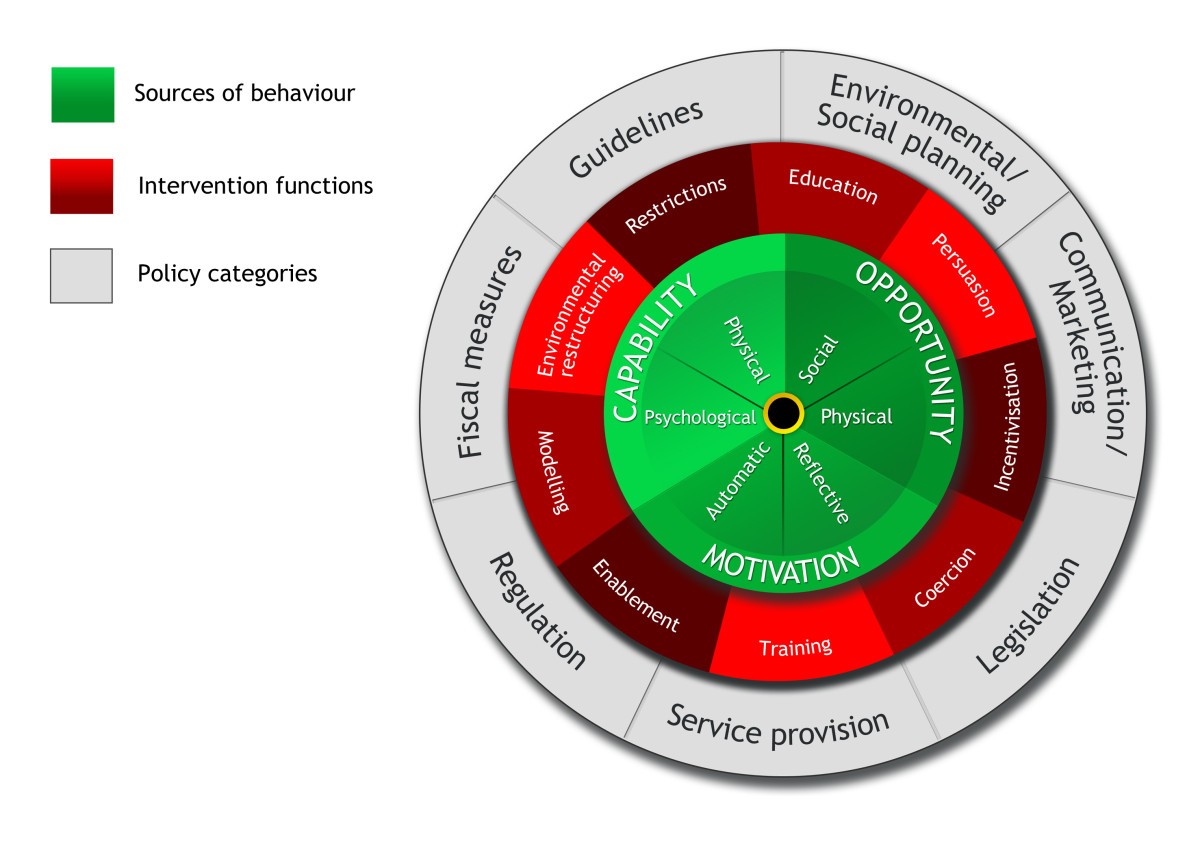

What is Capability in COM-B?
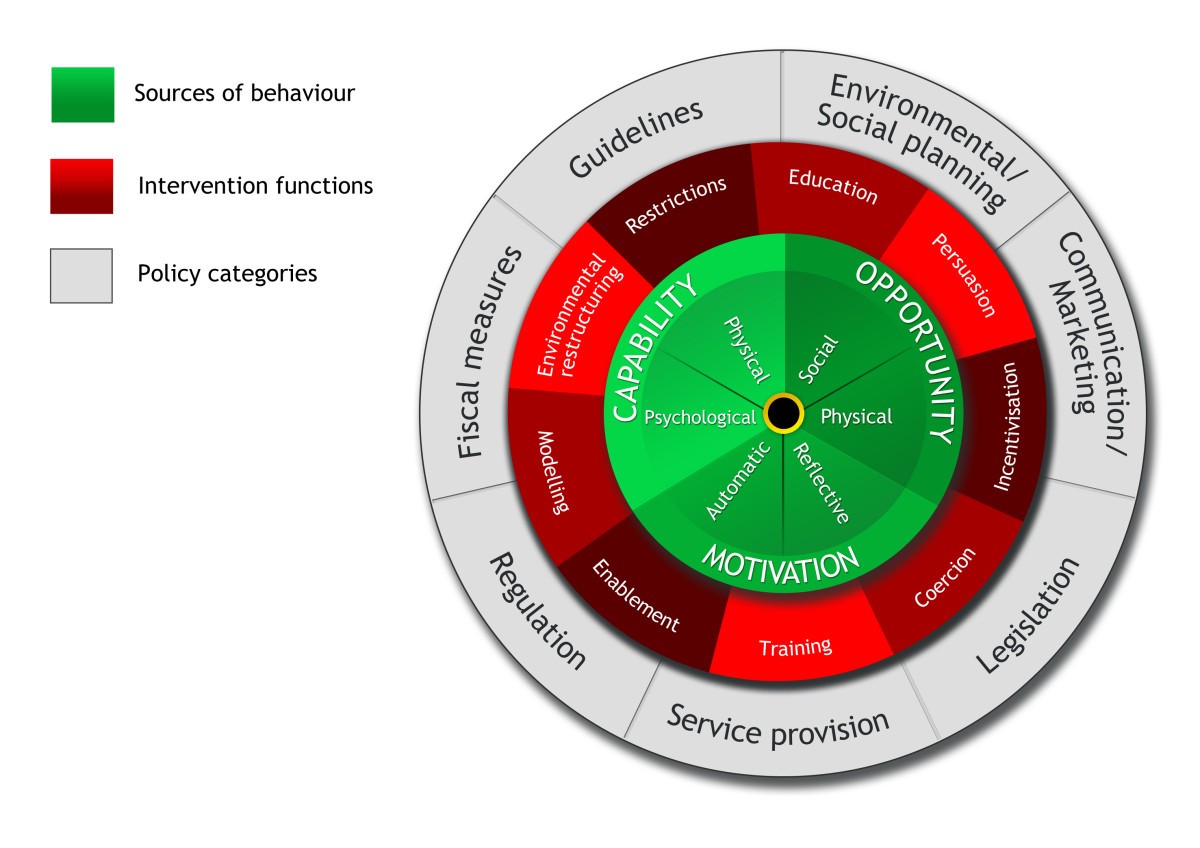
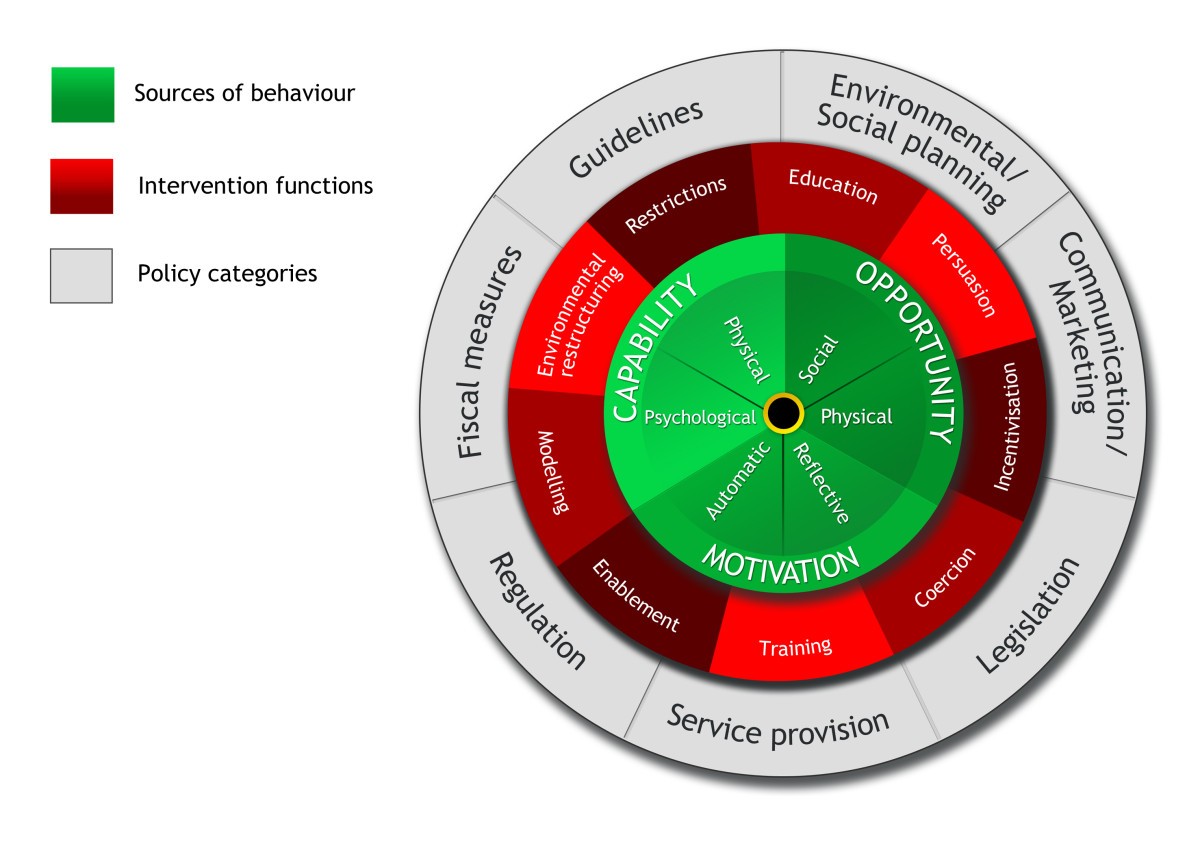
What is Opportunity in COM-B?
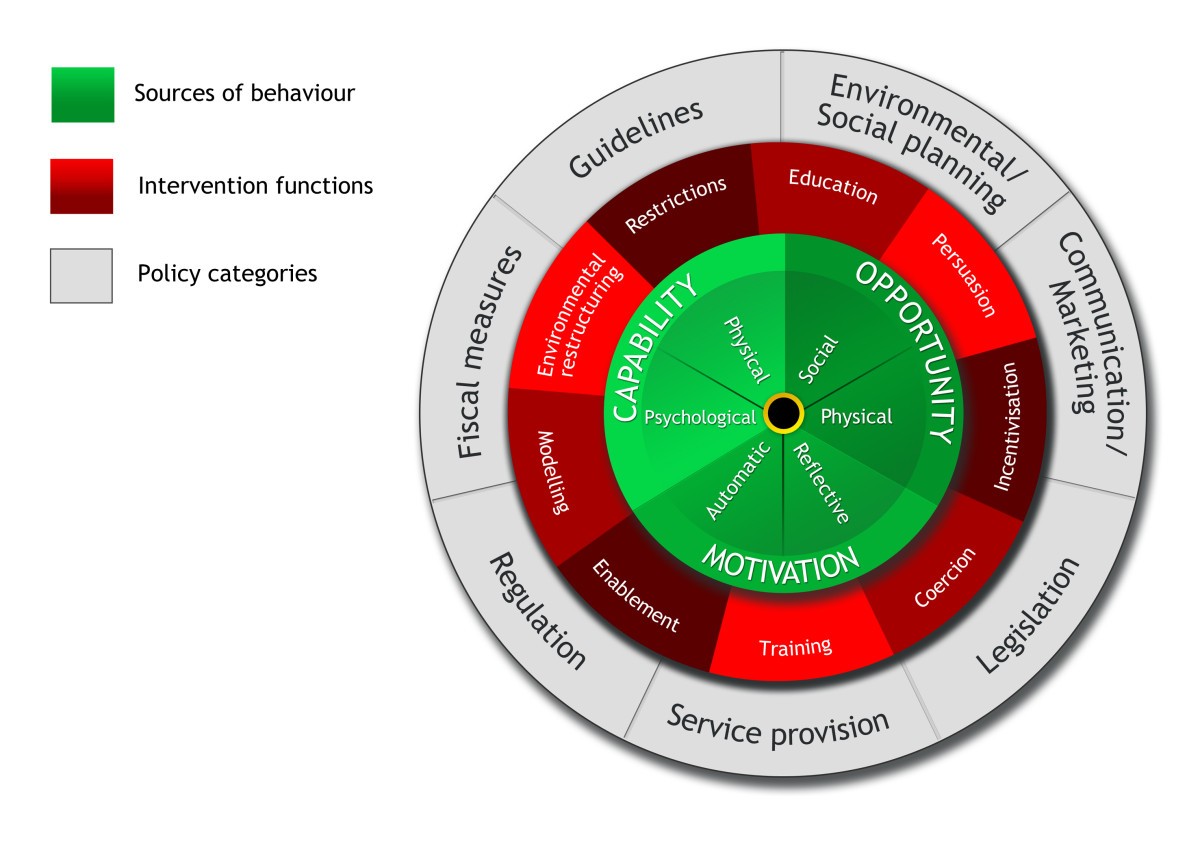
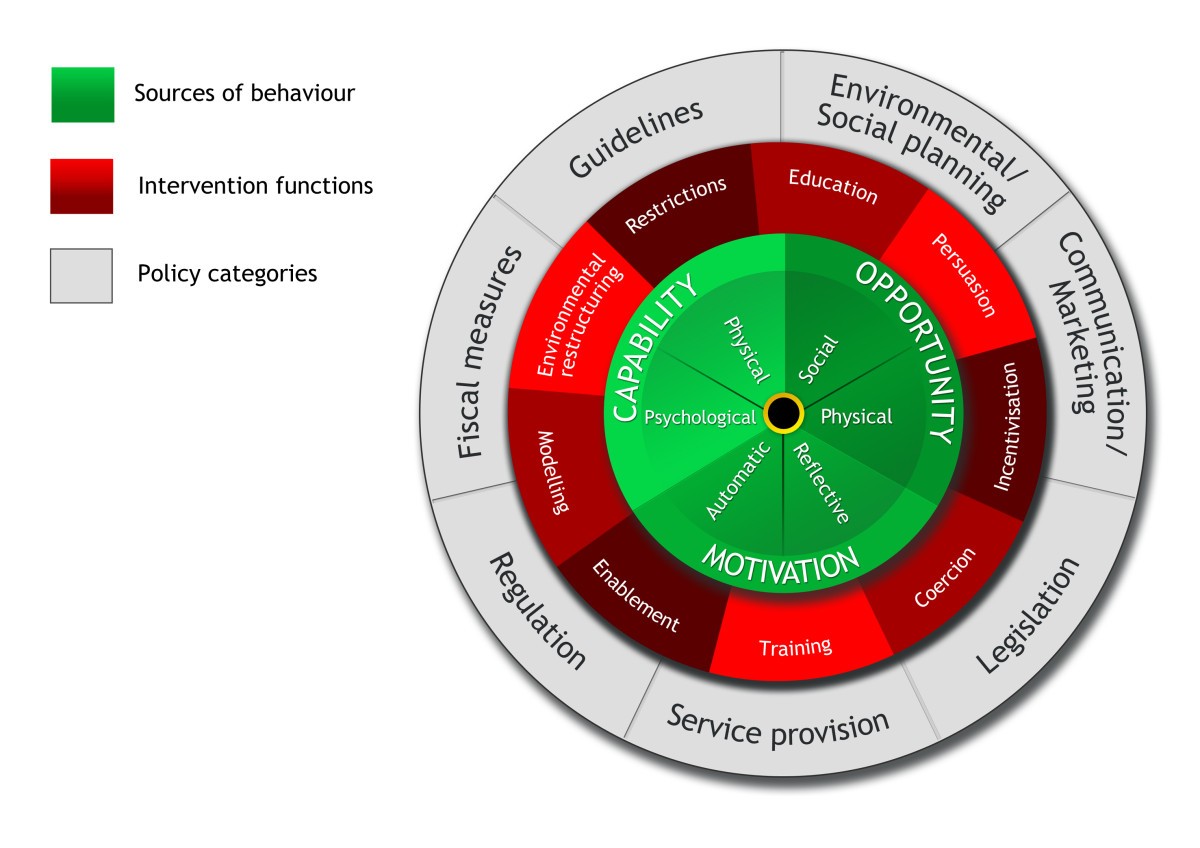
What is Motivation in COM-B?
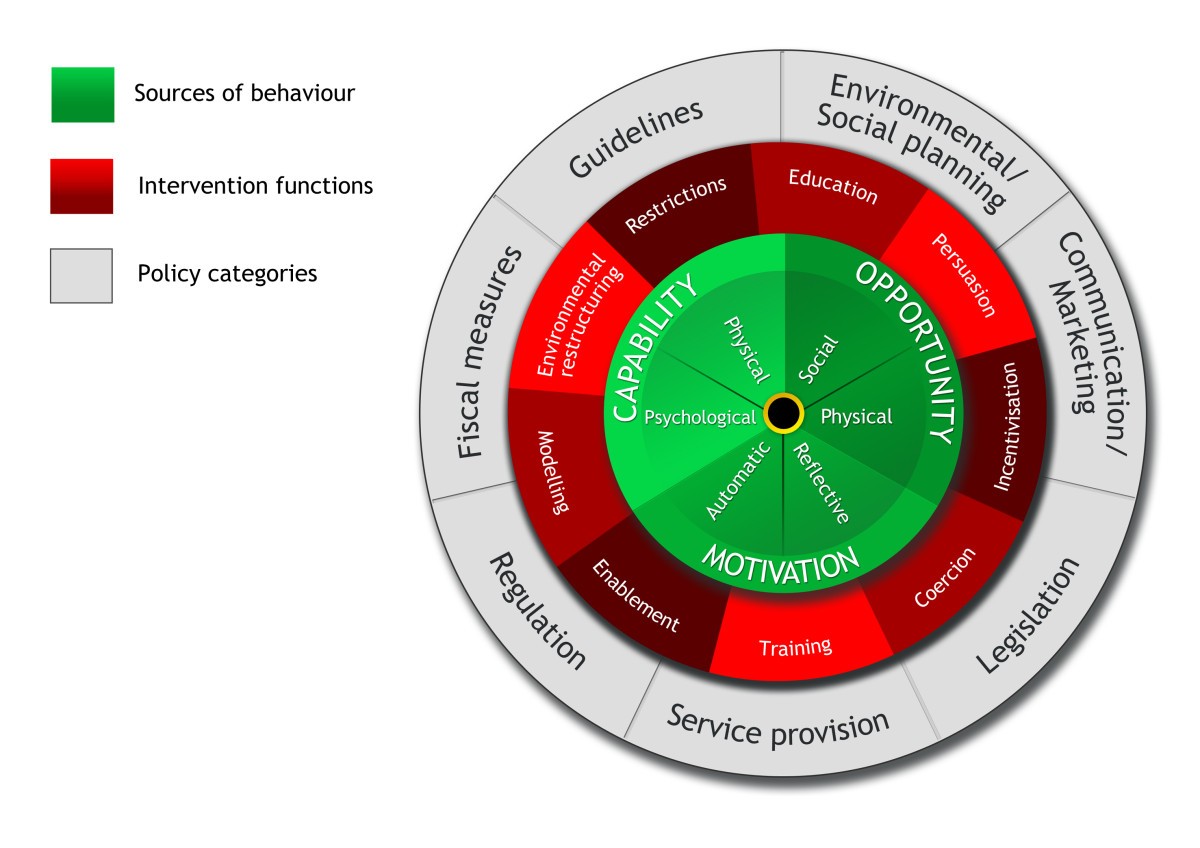
To help you understand the behavior as you develop targeted interventions; provides a general model of the drivers of behavior; can serve as a framework theory
What are the 9 intervention functions?
Education, Persuasion, Incentivization, Coercion, Training, Restriction, Environmental restructuring, Modeling, Enablement
acronym: EPICTREME
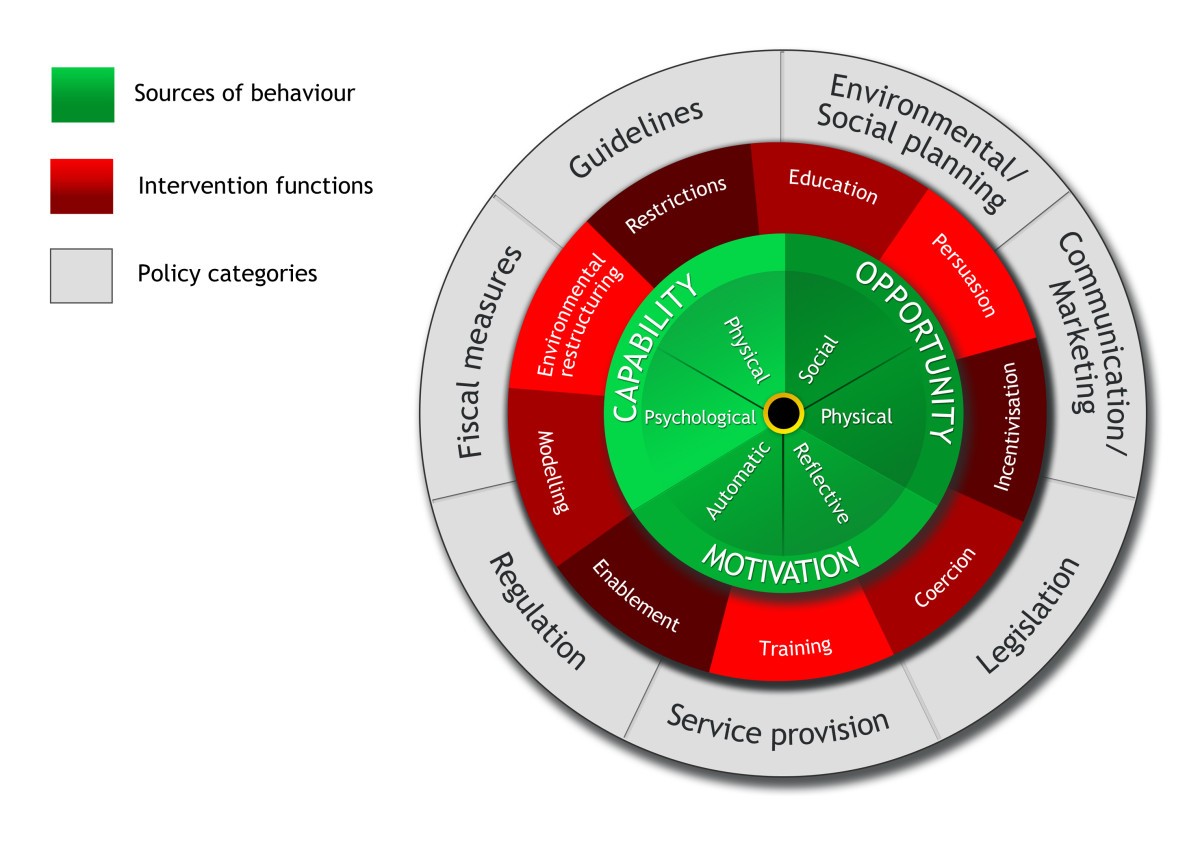
What is Environmental Restructuring as an intervention function?
(the lower the score the better)
unacceptable (4 points)
unpromising but worth considering (3 points)
promising (2 points)
very promising (1 point)